Hyperhidrosis is increased sweating.
Normally, our body secretes 400–600 ml of sweat per day. In the heat, during physical activity, visiting a sauna, drinking hot drinks, or experiencing stress, this volume increases significantly. After the action of the provoking factors ceases, the sweat glands turn off and the person stops sweating. This is a natural physiological process. But disturbances in it lead to the fact that the palms, face, and armpits become wet for no apparent reason. People with hyperhidrosis sweat even when not physically active. For example, when sitting under air conditioning or swimming in a pool.
Causes of hyperhidrosis
Normally, every person in hot weather, when playing sports, physical activity or at high body temperature, sweating increases. At the reflex level, excessive sweating is caused by worries, stress, pain, ingestion of hot, spicy food, and alcoholic drinks. Hyperhidrosis is caused by tight synthetic clothing, shoes, and staying in stuffy, damp rooms. Sweating for the reasons listed above is physiological. This is a normal protective reaction of the body against overheating.
With pathological hyperhidrosis, the reasons are completely different. It is caused by neuroendocrine disorders and does not depend on temperature exposure. Occurs in 3% of adults. It can be local and generalized, primary and secondary.
In the local form, sweating increases only in certain areas. For example, on the face, armpits, hands or feet. Hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet is most common because these areas of the body have more sweat glands than any other. Generalized hyperhidrosis affects the entire body.
Depending on the cause, primary and secondary hyperhidrosis are distinguished.
Primary hyperhidrosis
Primary hyperhidrosis is excessive sweating that is not associated with any other disease. It occurs in separate parts of the body symmetrically. Most often, primary hyperhidrosis occurs on the palms, feet, face, head, and armpits. Most people experience excessive sweating in more than one area. If your palms sweat, your feet almost always sweat too.
Primary hyperhidrosis usually begins during adolescence. But it happens from birth or later in childhood. Hyperhidrosis in a small child is caused by insufficiently developed thermoregulation, outdoor games, dryness, heat in the room, and too warm clothes.
In primary hyperhidrosis, episodes of excessive sweating occur at least once a week. They are provoked by emotions, nervous shocks, and physical exertion. Sometimes a person just needs to think about the irritant and sweat starts flowing. For example, palms become wet just from the thought of an upcoming handshake. Sometimes sweating happens for no apparent reason. During night sleep in the primary form, hyperhidrosis stops.
Risk factors for the development of primary hyperhidrosis include genetic predisposition. The disease can be inherited. Then many members of the same family suffer from this condition.
Secondary hyperhidrosis
In the secondary form, excessive sweating occurs throughout the body, often during nighttime sleep. It is caused by overheating, taking certain medications, poisoning, and internal pathologies. The abundance of sweat does not depend on the time of day, but depends only on the activity of the underlying disease.
The cause of secondary hyperhidrosis in women is often hormonal changes during adolescence, pregnancy or menopause. By the age of 45–50, the level of estrogen and progesterone decreases, and in adolescence, on the contrary, it increases. Changes in hormonal levels lead to disruption of thermoregulation. During pregnancy, increased sweating is typical in the first trimester, when the body adapts to the changes occurring in it. The level of some hormones drops sharply, while others increase. An increase in body weight in the second and third trimester also provokes a violation of thermoregulation, especially if the weight gain is significant.
Diseases that cause excessive sweating include:
- Endocrine disorders: hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, acromegaly (excessive production of growth hormone). In diabetes mellitus, hyperhidrosis occurs during moments of hypoglycemia, and cold sweat is released throughout the body. Excessive sweating with acromegaly is caused by enlarged sweat glands and increased metabolism. When the level of thyroid hormones (thyroxine, triiodothyronine) increases, metabolism significantly accelerates. A person feels hot even in cold weather, he is bothered by insomnia, irritability, and general weakness;
- Obesity. Obese people sweat more often and more. As your body increases in size, a lot of heat is generated, and a thick layer of fat prevents normal heat transfer. To somehow cool down, the body secretes more sweat;
- Nervous system disorders. These include pathologies that affect nervous regulation at different levels. These are polyneuropathy, conditions after strokes, Parkinson's disease, vegetative-vascular dystonia. They cause various abnormalities in the body, including disturbances in heat exchange;
- Psycho-emotional disorders. Include attacks of panic attacks, phobias, anxiety, obsessive inexplicable fear of certain objects, activities, situations;
- Infectious diseases. This is ARVI with high temperature, fever, tuberculosis, in which sweating increases at night. Cold sweat combined with fever and chills is characteristic of malaria. With purulent lesions, excessive sweating is also observed;
- Tumors. Sometimes excessive sweating is an early sign of a malignant or benign tumor in the body;
- Inflammatory kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis).
In addition to the pathologies listed above, secondary hyperhidrosis is caused by:
- side effects of certain medications (antidepressants, opioid analgesics, anxiolytics, insulin drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- alcohol abuse;
- taking drugs;
- poisoning with mushrooms, organophosphorus compounds.
What can cause increased sweating?
- Infectious diseases (such as tuberculosis)
- Disorders of the endocrine system (insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus)
- Disorders of the nervous system (vegetative-vascular dystonia, neurosis)
- Intoxication of the body (alcoholism, drug addiction)
- Poor personal hygiene
- Wearing clothes made of synthetic fabric, shoes made of artificial leather or rubber.
How does it manifest?
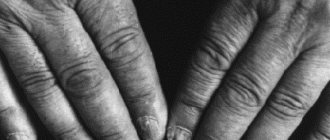
In addition to the obvious symptoms of hyperhidrosis of the arms or legs, there are others. For example, the hands and soles feel cold and sticky to the touch. The skin on them is slightly reddened, the lines and furrows are clear and deep.
In people suffering from excessive sweating, embarrassment, withdrawal, and embarrassment are noticeable from the outside. They are afraid to extend their hand to shake hands, afraid of close physical contact, and have difficulty holding slippery objects.
Increased secretion often leads to irritation, inflammation of the skin, and infection. Common complications of hyperhidrosis on the feet include fungal infections of the skin and nails.
What examination is needed?
If you have excessive sweating, you need a dermatologist, and if you have hyperhidrosis of the feet, you need a podiatrist. To find out the type and causes of hyperhidrosis, the doctor will definitely conduct an examination before treatment. If necessary, he will refer you to a neurologist or other specialized specialists.
Answering the following questions will help you determine the type of hyperhidrosis:
- Does sweating happen for no apparent reason?
- Is it the same on both sides of the body?
- How does it affect quality of life?
- How often do episodes of excessive sweating occur?
- When did the first symptoms appear?
- Do relatives have this problem?
- Do you sweat during night sleep?
Special functional tests have been developed to assess the degree of hyperhidrosis. They are used to determine the amount of sweat secreted, the intensity of sweating, and find the places on the body where it is most pronounced. Most tests have no practical diagnostic value. They are used for scientific research or to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
These methods include:
- calculation of body weight loss over a certain time;
- absorption of sweat from the skin or in special chambers by various absorbers;
- measurement of skin surface resistance, which changes depending on the intensity of sweating;
- provocative tests with the introduction of substances that stimulate or inhibit sweating;
- tests using substances that can change color when combined with sweat (iodine-starch test).
In case of secondary hyperhidrosis, the doctor will ask you in detail about your health status. He will prescribe blood and urine tests, hormonal tests, and measure blood pressure to find the true cause. If you have a chronic illness or are taking any medications, tell your doctor.
Popular questions
1. How much water should you drink if you have hyperhidrosis?
Water will not help reduce sweating of the feet, armpits or palms, but it will help avoid dehydration caused by hyperhidrosis. The required amount of water is determined by a dermatologist-cosmetologist after determining the type of hyperhidrosis.
2. Hyperhidrosis is a symptom of what diseases?
Hyperhidrosis of the armpits may indicate thyroid disease (hyperthyroidism), diabetes, tuberculosis, and gout. Excessive sweating may also indicate menopausal hot flashes, Alert syndrome, or malaria.
3. How does Botox work for hyperhidrosis?
Botox injections for hyperhidrosis can change the functioning of neurotransmitters (substances responsible for transmitting nerve impulses). Botox blocks the nerve that activates the sweat glands. Botulinum therapy allows you to get rid of hyperhidrosis for a period of six months to a year.
0
0
0
Article rating:
5 out of 5 based on 1 rating
Author: Novikova Anna Igorevna
Dermatovenerologist, trichologist, cosmetologist. Highest qualification category. Work experience 23 years.
How to treat hyperhidrosis?
Excessive sweating is not dangerous to health; many people do not take it seriously and tolerate it. But if a disease worsens the quality of life, deprives you of freedom of communication, spoils makeup and clothes, and makes you worry, you need to fight it. Hyperhidrosis in men and women causes irritability, complexes, and psychological disorders. Moreover, people often do not know that there are much more effective options for combating it than antiperspirants. However, many new treatments for hyperhidrosis have now been developed. Research in this direction is continuously ongoing.
Attempts to cope with excessive sweating on your own are often unsuccessful. People look for advice on the Internet, follow them and only get disappointed, because the reasons are different for everyone. Therefore, there are contradictory reviews about the treatment of hyperhidrosis. For help, it is right to go to a doctor, not to the Internet. He will help you find the best solution specifically for your case.
First you need to go to a therapist or family doctor, take general tests, and check your health. This step is necessary to rule out internal systemic diseases as the cause of the problem.
The choice of method to combat excessive sweating depends on the type, cause of the disease, and on what part of the body the excessive sweating occurs. With secondary hyperhidrosis, treatment is aimed at eliminating the root cause or underlying disease. The doctor may prescribe diet, exercise, sedatives, hormonal, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
The following methods help with primary hyperhidrosis.
Antiperspirants
This is the easiest, fastest, inexpensive and painless way to get rid of excessive sweating. Doctors recommend trying it first. Their main drawback is the short duration of the effect; such products will have to be used daily.
How does antiperspirant work?
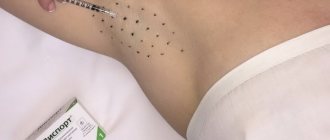
After applying antiperspirant to the skin, the sweat generated under the arms captures and dissolves the antiperspirant particles. They are drawn into the pores of the sweat glands, forming surface plugs. The body senses that the sweat duct is clogged and stops sweat production. The plugs remain for about 24 hours and are then washed off. The action of the antiperspirant is shown schematically in the photo:
Antiperspirants are divided into two groups: conventional and medical. Regular ones are sold in any supermarket. However, they hardly help people suffering from hyperhidrosis. Sweating is so strong that the sweat easily passes through the cork barrier that forms on the surface of the skin.
For hyperhidrosis, medical antiperspirants are used, sold in pharmacies or specialty stores. They act much stronger than usual, as they contain high concentrations of active components - aluminum or zinc salts. For each zone there are special professional remedies for hyperhidrosis. They are produced in the form of sprays, solutions, lotions. In antiperspirants for the palms and feet, the concentration of active ingredients is 2 to 3 times higher than for the armpits.
A dermatologist will help you choose the right antiperspirant for you. It is recommended to start with weaker compounds, and then move on to stronger ones if there is no effect. When using antiperspirants, adverse reactions are possible in the form of irritation and burning of the skin. If they appear, tell your doctor to change the product or adjust the mode of use.
Iontophoresis
Iontophoresis is used mainly to treat hyperhidrosis of the feet and palms. The principle of the method is based on blocking the activity of the sweat glands under the influence of electric current. During the procedure, a person immerses his hands or feet in a container of water to which electrodes are connected. Sometimes soda or medications are added to the water to enhance the effect. A low-voltage electric current is passed through the water. The procedure takes 20 – 40 minutes. To obtain results, 8 to 12 sessions are required (daily or 5 times a week). Then, to maintain the effect, iontophoresis is done once a week or less.
Iontophoresis brings relief to many people suffering from excessive sweating. The disadvantages of the method include the duration of the procedures and the course of treatment. Some experience dryness, redness, skin irritation, and discomfort during the session.
Contraindications include:
- pregnancy;
- the presence of a pacemaker or metal implants in the body;
- heart diseases;
- epilepsy.
Treatment of hyperhidrosis with iontophoresis is also carried out at home. There are devices for independent use. Which one is better to buy, how to use it, how often to carry out procedures, you need to check with the doctor who prescribed the treatment. The device works for many years and is suitable for several family members at the same time.
Microwave therapy on the MiraDry device
The MiraDry device is a device that destroys sweat glands using the heat of microwaves. Microwaves work at a depth of 2 – 5 mm below the surface of the skin, where most of the sweat glands are located. The procedure reduces sweating in people with primary hyperhidrosis and eliminates the unpleasant odor of sweat. The method is relatively new, so far it is used only for the armpit area. In Russia, the first MiraDry devices appeared in 2022. In America, the procedure has been performed since 2011, in European countries - since 2014.
Microwave therapy is carried out under local anesthesia with subcutaneous injections of anesthetics. It takes about an hour. The effect is noticeable immediately and lasts for a long time. On average, in 1 – 2 sessions, sweating is reduced by 80%. If necessary, a second procedure is performed after 3 months.
The disadvantages of the method include high cost and difficult recovery period. For several weeks, redness, severe swelling, numbness, and pain are observed in the area treated with the device. To reduce them, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed for the first 2 to 3 days. Pain and increased sensitivity can persist for up to several months.
Botulinum therapy
Botox injections are widely used not only in cosmetology, but also in medicine to combat hyperhidrosis. When treating hyperhidrosis with Botox (botulinum toxin type A), the neurotoxin temporarily blocks the transmission of nerve impulses to the sweat glands, causing them to stop producing sweat.
The first improvements will be noticeable after 2 – 3 days. During the procedure, sometimes people experience discomfort or slight pain. Injections are performed with a thin needle in the form of a mesh at a distance of 1 – 2 cm from each other. The procedure takes 10–20 minutes, depending on the area of treatment and the experience of the doctor. Immediately after a botulinum therapy session, a person can return to the normal rhythm of life, excluding only visiting the sauna and intense physical training on the first day.
The maximum effect develops 2 weeks after injections and lasts from 6 to 12 months. Sweating is reduced by an average of 85%, which significantly improves the quality of life of people for the duration of the drug. After the Botox wears off, repeat injections are given. Treatment of hyperhidrosis with Dysport, Botox, Xeomin is successfully used for excessive sweating of the armpits, feet, and palms.
Side effects include muscle weakness in the injection area. Most often it is observed when treating the palms. There may be a compensatory increase in sweating in other areas of the body, but this is usually not a major concern.
Medications
Oral medications are prescribed, as a rule, for excessive sweating in large areas of the body, when sweat is intensely produced simultaneously in several areas. And also if previous local treatment with medical antiperspirants, iontophoresis or botulinum therapy is ineffective. Other medications are prescribed for facial hyperhidrosis, if local treatment in this area irritates sensitive, delicate skin.
These drugs primarily include anticholinergics, which are dispensed from pharmacies with a doctor’s prescription. They block the transmission of nerve impulses to the receptors of the sweat glands. When taken over a long period of time, medications cause unpleasant side effects.
These include:
- drowsiness;
- dry mouth;
- visual impairment;
- development of glaucoma;
- nausea, vomiting, constipation;
- rapid heartbeat, etc.
For hyperhidrosis, such drugs are taken in short courses or once before important events, a performance, a holiday, or a visit, which can be spoiled by excessive sweating.
They are prescribed with caution to people over 65 years of age, patients suffering from glaucoma or having problems with the kidneys and urinary system.
In addition to anticholinergic drugs, beta-blockers and drugs from the benzodiazepine group are used for hyperhidrosis. These drugs affect the central nervous system. They have a sedative effect and block the physical manifestations of anxiety. They are suitable for people who experience episodic hyperhidrosis, depending on external factors, experiences, and stress.
Laser therapy
Laser treatment for hyperhidrosis promises to cure the problem permanently, but has limited use. It can only be used for the armpit area. The laser beam, due to its thermal effect, completely destroys the sweat glands; they are no longer restored. It acts purposefully, without affecting surrounding tissues, nerve endings, and muscles.
At the beginning of the procedure, pinpoint micropunctures are made in the skin, through which a flexible tube with a laser emitter is inserted. The sweat glands are affected from the inside. Traces from micropunctures heal quickly without leaving scars.
The high temperature of the laser radiation reduces the risk of infection and bleeding. The procedure is safe, performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia in a doctor's office, and does not require long-term rehabilitation. It takes about an hour. Side effects include swelling, bruising, and numbness. They usually go away on their own within 1 to 2 weeks.
Laser therapy can be combined with other methods. Among the disadvantages is the high price of laser treatment for hyperhidrosis.
Contraindications include:
- pregnancy;
- inflammatory processes;
- bleeding disorders;
- oncological diseases;
- endocrine diseases.
Surgical methods
Surgical interventions are resorted to in extreme cases, if all other methods have proven ineffective. They are used to treat hyperhidrosis of the palms and armpits.
Two methods are used:
- Removal of sweat glands in the problem area by scraping the inner surface of the skin through small incisions;
- Thoracic sympathectomy. The operation consists of cutting, pinching or destroying the nerves that innervate the sweat glands and are responsible for sweating. Used to combat hyperhidrosis of the palms that does not respond to other more gentle treatment options.
Surgical treatment is traumatic and fraught with a number of complications. It is possible that infection may enter the wound surface, the development of compensatory excessive sweating in other parts of the body (chest, back, legs), bleeding, scars, cicatricial changes in the skin. With thoracic sympathectomy, nervous regulation disorders and loss of sensation in the armpit area occur.