Onychomycosis, better known in everyday life as nail fungus, is familiar to almost every fifth inhabitant of our planet. People consider this disease shameful and, if it occurs, they are in no hurry to visit a dermatologist. When the nail plate is affected by a fungus, thickening and change in color of the nail are observed. If the disease is advanced, the nail begins to deteriorate. There are many ways to treat nail fungus. Let's figure out why this disease occurs, what are its symptoms and how to cure the fungus using table vinegar.
Why does fungus appear on the nail?
Onychomycosis of the toenails is most common. Of course, first of all, people who have a genetic predisposition to this disease are susceptible to this disease. This disease can also develop in people with impaired vascular tone. For example, people who suffer from heart failure, varicose veins or disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system are at risk.
The fungus spreads almost everywhere. You can get this disease anywhere:
- indoors swimming pool, sauna, bathhouse;
- in the sports complex;
- in public transport;
- on the beach, etc.
The appearance of onychomycosis may be due to the following factors:
- wearing tight shoes;
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- wearing the same shoes for a long time (mostly closed ones);
- using shoes or clothing of people suffering from onychomycosis.
How to recognize the disease?
The success of treatment for onychomycosis depends on how timely the disease was detected. And if a person often visits public places (baths, saunas, swimming pools), regularly gets pedicures in salons, suffers from excessive sweating, and neglects personal hygiene, he is at risk.
Onychomycosis can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- longitudinal scars or whitish round spots appear on the nail plate;
- the nail changes color, and the shade can be either white, black, green or brown;
- a void forms between the nail and the nail bed;
- the nail peels off, crumbles, becomes deformed;
- the nail thickens or, conversely, becomes thinner;
- an unpleasant odor appears;
- pain is felt in the finger with the affected nail.
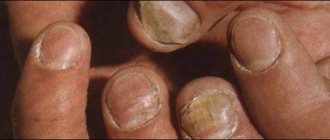
The initial form of onychomycosis is quite difficult to recognize. However, the advanced form is manifested by such signs that are difficult not to notice: nail crumbling, deformation, thickening, discoloration and other symptoms characteristic of fungus.
To confirm the disease, it is necessary to submit a scraping of the nail and the cuticle surrounding the nail plate for analysis. Next, according to laboratory testing, the dermatologist determines how to treat the fungal infection, where one of the methods of therapy may be treating the fungus with vinegar.
How to get rid of nail fungus?
When the first symptoms of nail fungus appear (changes in the structure of the nail and its color), you need to contact your doctor. There are cases when the causative agents of a fungal infection do not manifest themselves for a long time, so the disease occurs in a latent form and there are no symptoms. Treatment of an advanced form of fungus can be significantly delayed.
When conducting an examination, the doctor must take a scraping from the diseased nail and conduct an analysis, as a result of which it will be possible to accurately determine which group of pathogens a particular fungal microorganism belongs to. As practice shows, drug treatment consists of using ointments or taking pharmacological agents orally. For local effects, you can use special ointments, for example:
- Nizoral;
- Clotrimazole;
- Exoderil;
- Lamisil.
If the nail fungus is in an advanced form, then an additional course of pills and treatment procedures are prescribed. For example, every day you can independently take baths prepared from a soda-soap solution:
- Add 1 tbsp to hot water. l. soda and 50 g of soap (preferably laundry soap).
- The affected nail is placed in the container for 25 minutes.
After softening, the deformed layer of the nail plate must be carefully cut off using manicure accessories. Many people who have suffered such a disease leave reviews that they cured nail fungus with the help of table and apple cider vinegar.
Indications for use
Nail fungus
Nail fungus, or onocomycosis, is an infectious pathology, the development of which is provoked by different types of fungus-like microorganisms. Therefore, symptoms may sometimes change. The causative agents of the disease can persist for several years in the environment, and when favorable conditions appear, they begin to actively reproduce. This explains the possibility of human infection through indirect contact, that is, through objects on which epidermal scales with fungal mycelium remain.
The first signs indicating the development of onychomycosis:
- thickening or thinning of nails;
- discoloration of the affected area, and subsequently the appearance of a yellow tint;
- white spots, grooves or blotches on the nails;
- detachment of the nail plate from the bed;
- deformation of the nail, in which it peels off and crumbles.
Subsequently, redness of the finger, itching, burning and an unpleasant odor appear. If left untreated, the nail completely moves away from its bed.
Onychomycosis primarily develops on the skin between the 3rd and 4th, as well as the 5th and 6th fingers, and then moves to the nails and feet.
Recipe No. 1
Compound:
- 0.5 l 9% table vinegar.
Mode of application:
- You need to take vinegar and heat it slightly.
- Pour the heated vinegar into the bath and dip the affected nail in it. It is imperative that the nails are completely immersed in the liquid.
- Leave it on for about 15 minutes, after which it should not be washed off with running water.
You can apply compresses at night. To do this, just soak your socks in wine vinegar and put them on your feet. Such baths have already been tested by many people who leave only positive reviews. The effectiveness of treatment with vinegar is due to the fact that fungal microorganisms die in an acidic environment.
Treating shoes with vinegar
To cure a fungus, it is not enough to treat only the skin and nails. All shoes worn by the patient should be regularly disinfected. This will prevent re-infection and stop the spread of the disease among others.
Regular table vinegar copes with nail fungus, but will not help disinfect shoes. Regular processing requires a strong composition, so essence is used.
Proper disinfection of shoes:
- If there are insoles, they are removed and soaked in vinegar separately.
- Generously soak a small cotton ball with essence.
- Place the tampon in the toes of the shoes.
- The pair is hermetically sealed in polyethylene.
After 48 hours, the package can be opened, the shoes can be dried and ventilated from the pungent odor. Such measures are disastrous for the fungus, but shoes can also be damaged. Rubber is especially vulnerable to the effects of vinegar vapor. With frequent processing, the sole and heel are the first to suffer.
It is necessary to treat shoes against fungus every day. Stockings, socks, and tights are also washed and disinfected. If possible, replace all old shoes with new ones.
Avoid contact of the skin of your hands with concentrated vinegar. Wear gloves when handling shoes.
Recipe No. 2
After looking at user reviews, we can come to the conclusion that the best effect in the fight against advanced forms of nail fungus is achieved using lotions with apple cider vinegar.
Mode of application:
- You need to mix vinegar and iodine in equal proportions.
- Apply this mixture to all affected areas of the nail plate twice a day.
- The course of treatment lasts until the healthy nail grows completely. This mixture can also be used for preventive purposes.
Side effects and contraindications
Some people are intolerant to vinegar and other components. Therefore, if side effects appear in the form of a small rash, itching and burning, you must stop all procedures and consult a doctor.
Vinegar therapy has certain contraindications:
- children under 10 years of age;
- pregnancy;
- the presence of open wounds and damage to the tissues adjacent to the nail;
- psoriasis;
- eczema.
Women during breastfeeding can use vinegar for treatment, but only in consultation with their doctor.
Recipe No. 3
This recipe is perfect for treating fungal diseases of the nail plate in various forms, including advanced ones.
Compound:
- sea buckthorn, olive or sunflower oil;
- Apple vinegar.
Mode of application:
- Both ingredients are mixed in equal parts and applied using tampons to the affected nail plate.
- The cotton wool soaked in the solution is fixed with a plaster.
- If the fungus has developed on the toenails, then it is advisable to wear socks on top. This compress is done at night.
Modern methods of treating onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is the most common nail disease. It has been established that 50% of cases of changes in the nail plates are associated with a mycotic infection. Epidemiological studies conducted in Russia and foreign countries have revealed a high incidence of onychomycosis, which ranged from 2 to 13% in the general population [1, 2, 3]. The risk of developing onychomycosis is highest in older patients. For example, in people over 70 years of age, the prevalence of onychomycosis of the feet can be 50% or higher [2, 4, 5]. It is believed that this is facilitated by the slow growth of nail plates and disorders of peripheral and main circulation in the elderly [6]. A high frequency of onychomycosis is also detected in patients with immunodeficiency conditions (including AIDS patients) and in patients with diabetes mellitus [6, 7, 8].
Often patients and some doctors perceive onychomycosis as an exclusively aesthetic problem. However, this is a serious disease that occurs chronically and in cases of immunodeficiency or decompensation of endocrine diseases can cause the development of widespread mycosis of the skin and its appendages. Onychomycosis is often accompanied by the development of severe complications, such as diabetic foot, chronic erysipelas of the extremities, lymphostasis, and elephantiasis [9, 10]. In patients receiving cytostatic or immunosuppressive therapy, the disease can cause the development of invasive mycoses. That is why treatment of onychomycosis is necessary and should be carried out in a timely manner [11].
Just a few decades ago, treatment of onychomycosis was labor-intensive, lengthy and unpromising. Medicines used to treat fungal diseases of the skin and its appendages were characterized by low effectiveness and high toxicity. To achieve a positive result, long-term treatment or an increase in the dose of drugs was required, which was often accompanied by severe complications. Some treatments were potentially life-threatening for patients. For example, X-ray therapy, the use of thallium and mercury led to the development of skin cancer, diseases of the brain and internal organs in patients.
The emergence of highly effective and low-toxic antimycotic drugs has greatly facilitated the treatment of fungal diseases of the skin and its appendages. However, the results of using new antimycotics were not satisfactory. Controlled clinical trials have shown that the effectiveness of systemic antimycotics after treatment is from 40 to 80%, and after 5 years - from 14 to 50% [12]. At the same time, the effectiveness of therapy for onychomycosis increases with the use of complex treatment methods, which involve the use of etiotropic drugs and agents that influence the pathogenesis [13]. Also, as a result of clinical trials conducted in European countries, it was found that the effectiveness of treatment of onychomycosis can be increased by an average of 15% with the combined use of systemic antimycotics and antifungal varnish containing amorolfine [14].
Treatment
For the treatment of onychomycosis, drugs are used that differ in chemical composition, mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, and spectrum of antifungal activity. A common property for them is a specific effect on pathogenic fungi. This group consists of azoles (itraconazole, fluconazole, ketoconazole), allylamines (terbinafine, naftifine), griseofulvin, amorolfine, ciclopirox. To treat onychomycosis, systemic drugs are used that belong to the azole group - itraconazole, fluconazole, as well as to the allylamine group - terbinafine. Griseofulvin and ketoconazole are currently not prescribed for the treatment of onychomycosis due to low effectiveness and a high risk of adverse events. Varnishes and solutions containing amorolfine and ciclopirox are used as external agents for onychomycosis.
Allylamines are synthetic antimycotics. Allylamines primarily act on dermatomycetes, while they have a fungicidal effect. The mechanism of their action is to inhibit the enzyme squalene epoxidase, which takes part in the synthesis of ergosterol, the main structural component of the cell membrane of dermatomycetes. Allylamines include terbinafine and naftifine.
Allylamines are active against most dermatomycetes (Epidermophyton spp., Trichophyton spp., Microsporum spp., Malassezia spp.), the causative agent of chromomycosis and some other fungi.
Indications for the administration of terbinafine orally are onychomycosis, common forms of dermatomycosis of the skin, mycosis of the scalp, chromomycosis. Indications for external use of terbinafine and naftifine include limited skin lesions due to mycoses, pityriasis versicolor, and skin candidiasis. Terbinafine has high bioavailability and is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract regardless of food intake. In high concentrations, the drug accumulates in the stratum corneum of the skin, nail plates, hair, and is secreted with the secretions of the sweat and sebaceous glands. Absorption of terbinafine when applied topically is less than 5%, naftifine - 4-6%. The concentration of terbinafine and naftifine in the skin and its appendages significantly exceeds the MIC for the main pathogens of dermatomycosis. Correction of the terbinafine dosage regimen may be required when combined with inducers (rifampicin) or inhibitors of microsomal liver enzymes (cimetidine), since the former increase its clearance, and the latter reduce it.
As a result of numerous controlled multicenter comparative clinical trials, it was found that terbinafine is the most effective antimycotic in the treatment of onychomycosis [12] (Table 1).
| Table 1. Comparative effectiveness of antimycotics in the treatment of onychomycosis (based on the results of a meta-analysis of 27 randomized studies) |
Terbinafine is used for widespread skin lesions, onychomycosis, chromomycosis, in such cases terbinafine is prescribed orally. Terbinafine is the drug of choice in the treatment of onychomycosis, as it is most effective against the main causative agents of onychomycosis - dermatomycetes. Contraindications for the use of allylamines are allergic reactions to drugs of the allylamine group, pregnancy, breastfeeding, age under 2 years, liver diseases accompanied by impaired liver function (increased transaminases).
Azoles are the largest group of synthetic antimycotics. In 1984, the first systemic antifungal drug from the azole group, ketoconazole, was introduced into practice, in 1990, fluconazole, and in 1992, itraconazole.
Azoles used as systemic drugs have predominantly fungistatic activity. An important advantage of azoles over other drugs is their wide spectrum of antifungal activity. Itraconazole is active in vitro against most pathogens of onychomycosis - dermatomycetes (Epidermophyton spp., Trichophyton spp., Microsporum spp.), Candida spp. (C. albicans, C. parapsilosis, C. tropicalis, C. lusitaniae, etc.), Aspergillus spp., Fusarium spp., S. Shenckii, etc. Fluconazole is active against dermatomycetes (Epidermophyton spp., Trichophyton spp., Microsporum spp. .) and Candida spp. (C. albicans, C. parapsilosis, C. tropicalis, C. lusitaniae, etc.), but does not affect Aspergillus spp., Scopulariopsis spp., Scedosporium spp.
The pharmacokinetics of different azoles is different. Fluconazole (90%) is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. For good absorption of itraconazole, a normal level of acidity is necessary. If a patient taking these drugs has low acidity, their absorption decreases and, consequently, their bioavailability decreases. The absorption of itraconazole solution is higher than that of itraconazole capsules. Itraconazole capsules should be taken with food, and Itraconazole solution should be taken on an empty stomach.
Itraconazole is metabolized in the liver and excreted from the body through the gastrointestinal tract. It is also secreted in small quantities by the sebaceous and sweat glands. Fluconazole is partially metabolized and is mainly excreted unchanged by the kidneys (80%).
Itraconazole interacts with many drugs. The bioavailability of ketoconazole and itraconazole decreases when taking antacids, anticholinergics, H2 blockers, proton pump inhibitors, and didanosine. Itraconazole is an active inhibitor of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes and can alter the metabolism of many drugs. Fluconazole affects drug metabolism to a lesser extent. It is unacceptable to take azoles with terfenadine, astemizole, cisapride, quinidine, as deadly ventricular arrhythmias may develop. Concomitant use of azoles and oral antidiabetic drugs requires constant monitoring of blood glucose levels, as hypoglycemia may develop. Taking indirect anticoagulants of the coumarin and azoles group may be accompanied by hypocoagulation and bleeding; therefore, hemostasis control is necessary. Itraconazole can increase the blood concentration of cyclosporine and digoxin, and fluconazole - theophylline and cause the development of a toxic effect. Dose adjustments and constant monitoring of drug concentrations in the blood are required. The combined use of itraconazole with lovastatin, simvastatin, rifampicin, isoniazid, carbamazepine, cimetidine, clarithromycin, erythromycin is contraindicated. Fluconazole should not be used with isoniazid and terfenadine.
Itraconazole is used for dermatomycosis (athlete's foot, trichophytosis, microsporia), pityriasis versicolor, candidiasis of the skin, nails and mucous membranes, esophagus, vulvovaginal candidiasis, cryptococcosis, aspergillosis, phaeohyphomycosis, sporotrichosis, chromomycosis, endemic mycoses, for the prevention of myco call for AIDS.
Fluconazole is used for the treatment of generalized candidiasis, all forms of invasive candidiasis, including in immunocompromised patients, genital candidiasis, candidiasis of the skin, its appendages and mucous membranes. Recently, due to its safety and good tolerability, fluconazole is increasingly used for the treatment of patients with dermatomycosis with damage to both the skin and its appendages (nails and hair).
Amorolfine is part of a varnish used to treat onychomycosis. The mechanism of action of amorolfine is to disrupt the synthesis of ergosterol, the main component of the cell membrane of the fungus. It has fungistatic and fungicidal effects. Has a wide spectrum of action. The concentration of amorolfine in the nail plate significantly exceeds the MIC for the main pathogens of dermatomycosis for 7 days. Therefore, the drug can be applied no more than 1–2 times a week, which makes its use economically profitable. Contraindications: allergic reactions to amorolfine, infancy and young children. Varnish as monotherapy is prescribed when no more than 1–3 nail plates are affected and no more than 1/2 of the area from the distal end is affected. Amorolfine can also be used in combination with systemic antimycotics for more widespread nail lesions (Table 2).
Ciclopirox has a fungistatic effect. Active against dermatomycetes, yeast-like and filamentous fungi, molds, as well as some gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Ciclopirox (varnish) is used as monotherapy when no more than 1-3 nail plates are affected by no more than 1/2 of the area from the distal end. Ciclopirox can also be used in combination with systemic antimycotics for more widespread nail damage. Contraindications: allergic reactions to ciclopirox, infancy and early childhood, pregnancy and lactation.
List of recommended laboratory tests when prescribing systemic antifungal drugs.
- Clinical blood test.
- General urine analysis.
- Biochemical blood test (ALT, AST, bilirubin, creatinine).
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys (preferred).
- Pregnancy test (preferred).
Treatment of underlying diseases. The effectiveness of the use of antimycotics increases with the correction of pathological conditions that contribute to the development of onychomycosis. Before starting antimycotic therapy in patients with somatic, endocrine, neurological diseases, and with circulatory disorders in the extremities, it is necessary to conduct an examination to identify the main symptom complex that contributed to the development of dermatomycosis. Thus, the main objectives of pathogenetic therapy are to improve microcirculation in the distal parts of the extremities, venous outflow of the extremities, normalize the level of thyroid-stimulating hormones in patients with thyroid diseases, carbohydrate metabolism in patients with diabetes mellitus, etc. As a result of many years of research conducted at the Military Medical Academy and St. Petersburg Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, it has been established that one of the main causes of the development of dermatomycosis is disorders of the pituitary-hypothalamus-gonadal system. This leads to circulatory disorders in the distal extremities, microcirculation disorders, and peripheral innervation. A set of measures aimed at correcting these disorders includes acupuncture, transcranial electrical stimulation of the subcortical centers of the brain, and the prescription of drugs that correct the functioning of the sympathetic and parasympathetic autonomic nervous system. All this makes it possible to achieve a faster clinical effect in the treatment of dermatomycosis. It is advisable to prescribe pathogenetic therapy in patients with dermatomycosis with underlying diseases before the start of etiotropic treatment and continue it during the entire course of taking antifungal drugs.
Symptomatic therapy of dermatomycosis, aimed at reducing subjective complaints of patients and objective manifestations of the disease, cannot replace etiotropic therapy. However, its use in combination with antifungal drugs makes it possible to quickly improve the condition of patients, reduce the feeling of discomfort and eliminate cosmetic defects. With onychomycosis, the greatest concern for patients is caused by deformed, significantly thickened (hypertrophied) nail plates - onychogryphosis. To correct this condition, hardware pedicure is used. Using a device that resembles a dental turbine, in a short period of time, altered areas of the nails, hyperkeratotic areas, horny masses from the skin, and calluses are mechanically removed. In this case, there is no trauma to the nail matrix, and the patient remains functional after the procedure.
For limited damage to nails (no more than 3 nail plates and no more than 1/2 in area from the distal edge), topical preparations are used. It is recommended to begin treatment by cleaning the affected area of the nail plate using the Mycospor set, hardware pedicure or keratolytic agents. Next, antifungal drugs are applied to the affected nail plate. An amorolfine solution containing ciclopirox is applied to the nail plate 1–2 times a week. Before applying the varnish, you do not need to first clean the nail plate of previous layers of the preparation. The varnish is applied daily until the healthy nail plate grows completely. On the 7th day, the nail plate is cleaned using any cosmetic nail polish remover. There are conflicting reports in the literature about the effectiveness of this treatment method. The percentage of cure for patients is indicated from 5–9 to 50%.
In case of widespread damage to the nail plates on the fingers, a complex of treatment measures should include the prescription of a systemic antimycotic, cleaning of the nails and external therapy with antifungal drugs. In order to prevent re-infection, it is necessary to treat the patient’s gloves and disinfect personal hygiene items (washcloths, towels, nail files, graters and scrapers for treating skin and nails).
The drug of choice for the treatment of onychomycosis of any localization is terbinafine. It is prescribed to adults and children weighing more than 10 kg, 250 mg per day for 6 weeks. Children over 2 years old weighing less than 20 kg are prescribed terbinafine at the rate of 67.5 mg/kg per day, from 20 to 40 kg - 125 mg/kg per day for 6 weeks. Reserve drugs are products containing itraconazole and fluconazole. Itraconazole is used in two regimens: 200 mg daily for 3 months or 200 mg twice daily for 7 days in the first and fifth weeks from the start of therapy. Itraconazole is not prescribed for the treatment of onychomycosis in children. Fluconazole is recommended to be taken 150 mg once a week for 3–6 months.
Carrying out complex therapy, consisting of taking a systemic antimycotic, cleaning nails, local use of antifungal drugs, as well as anti-epidemiological measures, ensures high efficiency in curing onychomycosis of the feet. Terbinafine is prescribed to adults and children weighing more than 10 kg, 250 mg per day for 12 weeks or more. For children over 2 years old weighing less than 20 kg, the drug is prescribed at the rate of 67.5 mg/kg per day, from 20 to 40 kg - 125 mg/kg per day for 12 weeks. Fluconazole is recommended to be used at a dose of 150–300 mg once a week for 6–12 months. Itraconazole is used in two regimens: 200 mg daily for 3 months or 200 mg twice daily for 7 days in the first, fifth and ninth weeks. If the big toes are affected, it is recommended to carry out the 4th course of pulse therapy in the thirteenth week from the start of therapy. Itraconazole is not used for the treatment of onychomycosis in children.
The criteria for mycological cure of onychomycosis are negative results of microscopic and cultural examination of the nail plate. After treatment with itraconazole and terbinafine, healthy nail plates do not grow back completely, so complete clinical recovery can be observed only 2–4 months after the end of taking antifungal drugs.
Literature
- Kornisheva V. G. Mycoses of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, clinical pathogenesis, treatment: abstract. Dis... Dr. med. Sci. St. Petersburg, 1998. 34 p.
- Levy A. Epidemiology of onychomycosis in special-risk populations // J. Am. Podiatr Med. Assoc. 1997; 87:546–550.
- Herikkila H., Stubb S. The prevalence of onychomycosis in Finland // BJ Dermatol. 1995; 133:699–703.
- Rukovishnikova V. M. Mycoses of the feet. M., 1999. 317 p.
- Sergeev Yu. V., Sergeev A. Yu. Onychomycosis. Fungal nail infections. M.: GEOTAR - Medicine, 1998. 126 p.
- Cribier BJ, Bakshi R. Terbinafin in treatment of onychomycosis: a review of its efficacy in high-risk populations and in patients with nondermatophyte infections //BJ Dermatol. 2004; 150: 414–420.
- Yosipovitch G., Hodak E., Vardy P. et al. The prevalence of cutaneous manifestations in IDDM patients and their association with diabetes risk factors and microvascular complications // Diabetes Care. 1998; 21:506–509.
- Rich P. Special patient population: onychomycosis in the diabetic patient // J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1996; 35: 10–12.
- Lykova S. G., Nemchaninova O. B., Petrenko O. S., Borovitskaya O. N. Rational antimycotic therapy of foot mycoses in patients with metabolic syndrome // Russian Journal of Skin and Venereal Diseases. 2005. No. 6. P. 58–60.
- Sotirion E., Konssidon-Eremondi Th., Kastoridon Ch. et al. Erysipelas and tinea pedis: a 4 year review // JEADV 2004; 18 (2): 385.
- Kornisheva V.G., Shlyapnikov S.A., Nasser N.R., Pak E.Yu. Frequency of occurrence of mycoses of the feet in patients with erysipelas of the lower extremities // Problems of medical mycology. 2005. T. 7. No. 2. P. 51–52.
- Gupta AK, Ryder C., Johnson S. Cumulative meta-analysis of systemic antifungal agents for the treatment of onychomycosis // Br J Dermatol. 2004; 150:537–544.
- Raznatovsky K.I., Rodionov A.N., Kotrekhova L.P. Dermatomycoses. St. Petersburg: Publishing house SPbMAPO, 2003. 159 p.
- Baran R., Feuilhade M., Datry A. et al. A randomized trial of amorolfine 5% solution nail lacquer combined with oral compared with terbinafine alone in the treatment of dermatophytic toenail onychomycosis affecting the matrix region //Br J Dermatol. 2000; 142:1177–1183.
L. P. Kotrekhova , Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor K. I. Raznatovsky , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor N. N. Klimko , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of St. Petersburg Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, St. Petersburg
What measures can be taken to prevent nail plate fungus?
To prevent a fungal infection from affecting your nails, you need to follow a number of simple rules every day:
- change socks, stockings, tights;
- wash your feet and hands in soapy water twice a day;
- wipe your feet dry after washing;
- do not use other people’s manicure accessories, especially for items that were previously used by people with nails affected by fungus;
- do not walk barefoot in public places and on beaches;
- monitor the level of sweating of the feet and hands;
- wear shoes made from natural materials.
Is vinegar effective in treating mycoses?
Vinegar has a powerful antiseptic effect, destroys fungal spores, and stops their reproduction. Procedures carried out daily for several weeks can completely get rid of onychomycosis.
Additionally, vinegar has a softening, anti-inflammatory effect on the affected tissues, eliminates itching and redness of the skin, which are annoying due to fungus.
Begin treatment with minimal concentrations. 70% vinegar essence against nail fungus is used only in diluted form. The concentrate content in any product should not exceed 50%.
How to avoid relapse
To protect yourself from re-infection, you must disinfect your bed, towels, shoes, socks, tights, clothes and household items that have touched the infected skin.
Fungus is not a death sentence. His disputes can be treated, the main thing is to see a doctor as soon as possible and follow all his instructions. All activities and procedures must be carried out until the complete disappearance of not only the symptoms, but also the fungus as a whole.
After the first results appear, under no circumstances should you stop and stop treatment. If after 20 days of procedures there are no changes for the better, this is a good reason to consult a doctor.
Alexandr Popov
Author of the article. Practicing doctor
Diagnosis of the disease
To diagnose the disease, you need to seek help from a specialist; only an experienced doctor can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
To do this, the doctor first examines the patient, then sows the nail and skin underneath, checking them for the presence of fungus.
Once the presence of a fungal infection is established, the type of fungus and its sensitivity to drugs are determined. After this, the doctor prescribes the type of therapy to be performed and tells how to treat the fungus. In addition, you can use traditional medicine recipes, for example, iodine, tar, salicylic acid. These remedies are also used by doctors and various healers.
Recipe for making an ointment from vinegar and eggs against fungus
Onychomycosis, an infection known as nail fungus, can cause a lot of discomfort. There are many different ways to help get rid of the disease, but they may not work and are contraindicated for children and pregnant women.
If you need long-term therapy, you will have to spend an impressive amount of money on the necessary drugs. Or you can use folk recipes for getting rid of nail fungus.
Treating fungus with vinegar
Acetic acid is an accessible, inexpensive and reliable remedy against nail fungus. It provides productive treatment in a variety of ways. Doctors advise changing the prescription every two weeks to prevent the infection from becoming resistant.
For treatment to be effective and safe, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- Carry out the necessary preparation of the feet (wash and disinfect).
- Prepare the mixture correctly (start treatment with a 9% solution, gradually increasing the percentage of acid).
- Do not use recipes with vinegar if there are skin lesions on your feet, otherwise inflammation or burns may occur.
- For greater efficiency, experiment with various recipes and additives (egg, iodine, glycerin).
The easiest way to process it is with lotions. To do this, you need to lubricate your nails with vinegar every evening and do not wash it off for a day. It is also recommended to take baths with it.
The basic recipe for preparation is as follows: dilute a liter of acid in three liters of water, you can add potassium permanganate. Take 20 minutes for two weeks.
For greater effectiveness, you can apply tea tree ether to damaged areas.
How to prepare vinegar baths against nail fungus
Water must be disinfected by boiling in a fireproof container. After cooling to an acceptable body temperature, treatment can begin. A regular bath of 9% table vinegar and water will take longer without additives. Therefore, it is better to use additional ingredients.
After boiling water with vinegar, you can pour table or sea salt into the solution. The recipe is as follows: 150 ml of acid and 4 tablespoons of salt per 3 liters of water. Keep your feet in it for 20 minutes, then dry and apply vegetable oil (pine, tea, thyme). Suitable for healthy legs and relieves fatigue well.
Adding baking soda instead of salt will soften the skin and help get rid of nail fungus by neutralizing the acidic environment. After 10 minutes of use, adding 2 tablespoons (2 tablets) of hydrogen peroxide, after use the infected skin will turn white and part of the fungus can be removed with a pumice stone.
After this treatment, you need to dry your feet with a disposable towel and put on clean socks. Boiling them in a solution of water and 70% vinegar essence will improve the result. Wearing wet socks at night further disinfects your feet.
Treatment of fungus with eggs
Antifungal egg is used in combination with additional antifungal ingredients. An ointment with added wax will relieve nail fungus, burns, and wounds.
To prepare, you need to boil 500 ml of vegetable oil, mix with beeswax (1/2 teaspoon) until completely dissolved, add chopped boiled yolk. Keep on fire for 6 minutes, then strain and cool.
Apply to the surface of the nails and damaged skin until healing.
Egg yolk ointment will help get rid of the effects of nail fungus. Ten eggs need to be hard-boiled, the yolks separated, placed in a tightly closed container and kept in the oven for at least three hours. Cool the resulting mass and use it as a healing cream. It will help restore nails and exfoliate the dead layer.
It is advisable to use homemade eggs, having previously washed and disinfected them. Store prepared ointments in the refrigerator for no more than 10 days. A product prepared using acetic acid will help extend the shelf life and increase effectiveness.
Remedies with egg and vinegar to combat onychomycosis
The most convenient and common way to fight against nail fungus is ointment. You can buy it at the pharmacy or prepare it yourself at home. The recipe with vinegar and egg is the safest and has virtually no contraindications. Only if you have an allergy should you look for alternative options for getting rid of the fungus.
Product with dimethyl phthalate and olive oil
Ingredients:
- Vinegar - 2 tablespoons.
- One chicken egg.
- Dimethyl phthalate (available at any pharmacy) - 1 teaspoon.
- Olive or sunflower oil - 1 tablespoon.
Recipe for making ointment:
- Beat the whites with the yolk.
- Mix with vinegar essence.
- Add dimethyl phthalate and oil.
- Place in the refrigerator for 24 hours.
Application: every day before going to bed, rub the ointment into the surface of damaged nails, wrap with a bandage or film and insulate with socks. Use until complete recovery.
Vodka remedy
Ingredients:
- Vinegar - 2 tablespoons.
- Three chicken squirrels.
- Vodka or medical alcohol - 2 tablespoons.
Mix the whites with vinegar essence, add vodka or alcohol, and apply a lotion to the infected areas using a napkin or sponge. You need to keep it all night, wrapped in film or bandage, and also insulated with socks. Use until complete recovery.
Cream with butter
Ingredients:
- Vinegar - 1 glass.
- One chicken egg.
- Butter - 1 tablespoon.
Recipe for making ointment:
- Wash and dry the egg thoroughly. Place it in a glass and fill it with vinegar essence.
- Wait until the shell dissolves (3-5 days).
- Use tweezers to carefully remove the film from the glass.
- Mix the infused egg with vinegar and add pre-softened butter (if the mixture is too liquid, add more).
Application: before going to bed, apply ointment to the surface of damaged nails, wrap with a bandage or film and insulate with socks. Use until complete recovery, taking breaks of 2-3 days every 6 days.
What helps the fungus develop?
The most suitable environment for the growth of fungus is neutral or slightly alkaline. The skin of a healthy person is a slightly acidic environment, not suitable for fungal infections.
Often shoes are made from non-natural material, so your feet sweat and are in an uncomfortable position most of the time. This is what encourages foot fungus to develop.
Many people do not want to waste time on doctors and try to treat foot fungus with vinegar on their own.
A humid environment is good for the development of fungus, so swimming pools, baths and showers have the greatest risk of infection. In addition to the fact that you should wear slippers in such places, you cannot use other people’s towels, washcloths or pedicure tools.
Although, on the other hand, it feels great in a dry environment, even if the temperature is low. Only in this case it does not reproduce, but is simply waiting for a favorable moment to spread.
Exfoliated skin infected with fungus can persist for a long time in clothes and shoes, as well as on carpets. After contact with healthy skin, its development and spread begins.
To disinfect clothes, you can boil them for five minutes, after which the fungal cells die. Shoes must be wiped with a 1% formaldehyde solution, and furniture with chloramine.
The causes of infection are:
- Diabetes.
- Traumatic injuries to the skin of the foot.
- Poor blood supply to the legs.
- Weak immunity.
- Tight and unnatural quality shoes.
Types of onychomycosis
Nail fungus comes in many forms, and each type manifests itself differently:
- Subungual . Partially affects the nail plate, forming yellow dots or stripes on its surface. Damage to areas under the nail layer makes the skin wet, flaky, and the nail crumbles and changes in shape.
- Proximal . The deformation occurs closer to the middle of the nail, involving the skin around the fingers. The skin turns red, cracks, and gets wet. This form of fungus is characterized by itching and an unpleasant odor after removing socks and shoes.
- Superficial . This form of mycosis infects the entire nail plate, also affecting the skin between the fingers. It develops only on the legs. The fungus completely destroys the structure of the nail, causing new wounds for the proliferation of fungal spores.
New forms of the fungus may be added to the above-mentioned forms, depending on the degree of the disease and the type of pathogen. For effective therapy, it is first necessary to determine the type of fungus by passing medical tests.