Comfoderm and Advantan are glucocorticosteroids widely used in the treatment of skin diseases. Medicines are structural analogues and are prescribed for the same pathologies.
Comfoderm and Advantan are glucocorticosteroids widely used in the treatment of skin diseases.
pharmachologic effect
Manufacturer: LEO Pharma A/S, Denmark
Release form: cream, ointment, emulsion, fatty ointment
Active ingredient: methylprednisolone aceponate
Synonyms: Comfoderm, Comfoderm K, Methylprednisolone aceponate, Metizolone, Sterocort
Advantan is a drug based on the glucocorticosteroid methylprednisolone for external use. All effects of the drug are provided by the mechanisms of action of methylprednisolone. When used externally, Advantan has the following effects:
- elimination of inflammation;
- reduction of skin allergic manifestations.
When using the drug under a bandage, there is an increased likelihood of developing systemic adverse reactions.
Characteristics of Comfoderma
The drug is sold in the form of ointment and cream. The active ingredient is methylprednisolone aceponate. This component is a synthetic steroid.
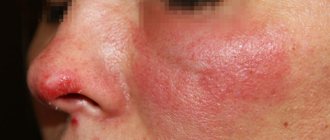
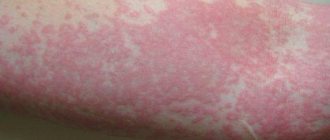
External use of the drug eliminates inflammatory and allergic reactions on the skin. Relieves erythema, swelling and weeping, itching and irritation.
The active substance binds to glucocorticosteroid receptors. The resulting complex interacts with certain regions of the cells' DNA. Against the background of this process, the synthesis of macrocortin is induced. It leads to inhibition of arachidonic acid release and the formation of inflammatory mediators.
Instructions for use Advantan
Advantan and its full analogs are used externally in patients older than 4 months, including on the scalp. The product should be applied once a day to the affected areas of the skin. The duration of therapy should not exceed 1 month for children and 3 months for adults.
The product should be applied in a thin layer without intense massage movements. The choice of dosage form should be entrusted to the doctor.
Advantan is contraindicated in purulent processes, dermatitis around the mouth, acne, post-vaccination skin reactions, allergies to glucocorticoids, ulcers and wounds, fungal and viral infections, syphilis and skin tuberculosis. The drug should not be used under bandages, since this method of application enhances the absorption of hormones into the bloodstream.
When using the product, the following local reactions may occur: skin atrophy, rash, fungal or bacterial infections.
Comparison of the effectiveness of Advantan and Comfoderm
The effectiveness of Advantan is quite similar to Comfoderm - this means that the ability of the drug substance to provide the maximum possible effect is similar.
For example, if the therapeutic effect of Advantan is more pronounced, then using Comfoderm even in large doses will not achieve this effect.
Also, the speed of therapy - an indicator of the speed of therapeutic action - is approximately the same for Advantan and Comfoderm. And bioavailability, that is, the amount of a drug reaching its site of action in the body, is similar. The higher the bioavailability, the less it will be lost during absorption and use by the body.
Advantan cream or ointment - which is better, what is the difference
Advantan is produced in different external dosage forms: ointment, fatty ointment, cream and emulsion. The cream is a form of release with a low content of fatty base and a high concentration of water. This drug is recommended for oily skin, as well as for acute inflammation and allergic reactions on the skin and scalp without wet surfaces.
An ointment is a form that contains a fatty base and water in approximately equal proportions. In this form, the drug is ideal for the treatment of dry skin, as well as for chronic inflammatory processes, unlike Advantan cream. Emulsion is the “lightest” form of the drug, which is excellent for treating sunburn and other inflammatory processes that are not accompanied by dry skin.
Advantan's analogs
Complete analogues of Advantan with the same active ingredient include the following:
- Sterocort;
- Comfoderm;
- Comfoderm K;
- Metizolone;
- Methylprednisolone aceponate.
Such drugs are the best options when looking for a replacement for Advantan.
The list of close group analogues includes the following Advantan substitutes in the form of hormonal creams, lotions, ointments, emulsions with different prices and low hormonal activity:
- hydrocortisone-based products - Highton, Hydrocortisone, Akortin, Hydrocort, Cortade, Lokoid, Laticort;
- analogues with betamethasone - Beta-Val, Valison, Celestoderm, Valoderm, Betnovate, Mesoderm;
- products with desonide - Dezoven, Lokara, Tridesilone;
- drugs with aclomethasone - Afloderm.
In case of severe disease, external topical steroids with moderate and high activity can be used at the beginning of therapy:
- analogues based on triamcinolone - Kenalog, Triacort, Kenalog, Polcortolon, Focort, Cinacort;
- products based on mometasone - Momat, Mometasone, Avecort, Momecon, Silkaren, Elokom;
- analogues with fluocinolone - Sinoderm, Flucort, Flucinar, Fluciderm, Eatsinon, Sinaflan;
- products with betamethasone dipropionate - Belosalik, Diprosalik, Diprozon, Akriderm, Beloderm;
- analogues based on clobetasol - Dermovate, Cloveit, Cloderm, Etrivex;
- Cutivate;
- Westcourt;
- analogue of Cordran.
Treatment is often started with stronger drugs, and as the patient’s condition improves, they are transferred to drugs with low activity.
Combined analogues of Advantan are also used in the form of creams, ointments and other forms for adults and children:
- Akriderm;
- Betaderm;
- Kremgen;
- Lorinden S;
- Trimistin;
- Flucourt;
- Fusiderm B;
- Celestoderm B with garamycin;
- Mycozolon;
- Akriderm GK;
- Pimafucort;
- Candiderm.
Such drugs cannot be considered very close substitutes for Advanatan, since they contain, in addition to the steroid, several other active components, which changes not only the mechanisms of action, but also the effects and indications for use.
List of Advantan analogues with prices
| Drug name | Active substance | Release form | Manufacturer | Minimum dosage cost |
| Advantan | Methylprednisolone aceponate | Ointment, cream, emulsion, greasy ointment | LEO Pharma A/S, Denmark | From 500 rub. |
| Comfoderm | Ointment, cream | Akrikhin JSC, Russia | From 280 rub. | |
| Akriderm GK | Clotrimazole, gentamicin, betamethasone | Cream, ointment | Akrikhin JSC, Russia | From 420 rub. |
| Celestoderm | Betamethasone valerate | Shering-Plough Labo NV, Belgium | From 200 rub. | |
| Triderm | Clotrimazole, gentamicin, betamethasone | From 335 rub. | ||
| Elokom | Mometasone furoate | Cream, ointment, lotion | From 80 rub. | |
| Sinaflan | Fluocinolone acetonide | Ointment | Nizhpharm JSC, Russia | From 50 rub. |
| Lokoid | Hydrocortisone butyrate | Cream, ointment, emulsion | Temmler Italia SrL, Italy | From 260 rub. |
Advantan or Comfoderm
Manufacturer: Akrikhin JSC, Russia
Release form: ointment, cream
Active ingredient: methylprednisolone aceponate
Synonyms: Advantan, Comfoderm K, Methylprednisolone aceponate, Metizolone, Sterocort
Comfoderm is a complete analogue of Advantan. The drug is used to treat allergic dermatitis and inflammatory skin diseases in children over 4 months and adults. The difference between the products is only in the manufacturers. Comfoderm is an inexpensive Russian-made analogue of Advantan, which is not inferior to it in effectiveness and safety.
The drug should be used only externally as prescribed by a doctor for the shortest possible period of time to prevent the development of adverse reactions and complications.
Comparison of Comfoderm and Advantan
Advantan and Comfoderm are structural analogues. Their therapeutic actions are based on the same substance, which is active for both drugs. Therefore, both drugs have the same indications and contraindications.
Medicines are produced by different manufacturers and therefore have different prices. Advantan is considered an original drug from the Italian company Intendis Manufacturing S.p.A., sold at a price of 540 rubles. Comfoderm is produced by the Russian company Akrikhin. Its cost is from 250 rubles.
Advantan or Akriderm GK
Manufacturer: Akrikhin AO, Russia
Release form: Cream, ointment
Active ingredient: clotrimazole, gentamicin, betamethasone
Synonyms: Triakutan, Triderm
Akriderm GK is a combined drug based on antifungal, antibacterial and hormonal components. The product is considered a fairly distant substitute for Advantan, since it differs not only in composition, but also in pharmacological properties, indications and features of use. In addition to dermatitis of various etiologies, this medicine is widely used in the treatment of dermatomycosis.
The medication is used to treat children over 2 years of age. Given the composition of the drug, caution should be exercised when using Akriderm in patients under 18 years of age, especially due to the high likelihood of absorption into the blood and systemic effects.
Advantan or Celestoderm
Manufacturer: Shering—Plough Labo NV, Belgium
Release form: cream, ointment
Active ingredient: betamethasone valerate
Synonyms: Betnovate, Persivat, Betazon, Mesoderm, Soderm, Betamethasone
Celestoderm is a more active analogue of Advantan in the form of ointment and cream, which is used for external use in children and adults. Pronounced powerful anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory effects allow the product to be used for eczema, dermatitis, as well as psoriasis and skin itching of various etiologies.
The use of Celestoderm is permitted in patients over 6 months of age. Caution should be exercised when using the drug in this category of patients due to the increased likelihood of affecting adrenal function. In most cases, this analogue of Advantan is used 1-2 times a day.
Elidel and corticosteroids: allies or rivals?
N
Topical corticosteroids (CS) are the basis for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD), as they have anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive and antiproliferative properties. These drugs act quickly and effectively, which satisfies both the doctor and the patient. However, steroids have a number of serious side effects. Systemic complications are especially dangerous, developing, as a rule, as a result of the absorption of drugs from large-area lesions with prolonged use. The No. 1 risk group in this regard is children under 2 years of age, whose skin permeability is much higher than that of adults [1]. The most serious systemic complications include inhibition of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system and associated growth retardation, Cushing's syndrome, hypertension, and diabetes [2–6]. Long-term use of topical steroids carries a risk of immunosuppression, manifested by bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. These effects are predominantly characteristic of early generations of CS, especially fluorinated CS. In recent decades, drugs have been created whose absorption when applied externally does not exceed 1%, however, they also have a number of disadvantages. Among local complications, skin atrophy, striae, telangiectasia, pigmentation disorders, and acneiform rashes predominate [7]. Important disadvantages of external CS include tachyphylaxis - addiction and loss of effectiveness.
All these side effects and complications have led to the fact that 73% of patients with AD suffer from the so-called “steroid phobia” - anxiety of varying degrees, up to a complete refusal to use CS [8]. For this reason, 24% of adult patients and 36% of parents of sick children admit to violating the external therapy regimen. “Steroid phobia” affects not only patients, but also doctors themselves, so treatment with these drugs is often started late, the duration of therapy is insufficient, and the doses, especially in children, are too small. All this leads to inadequate relief of exacerbation, early relapse and the formation of tachyphylaxis.
In this regard, the question arises: how to shorten the period of use of CS during exacerbation of blood pressure and at the same time prolong the remission of the disease?
To solve this problem, a selective inhibitor of the synthesis and release of proinflammatory cytokines, pimecrolimus (SDZ ASM 981), is currently used. It has been established that this substance is in vitro
selectively binds to macrophilin-12, and inhibits calcineurin and thereby the synthesis of inflammatory cytokines in T cells (IL-2, INF-g), as well as the release of inflammatory mediators (for example, histamine) from mast cells [9–12]. At the same time, pimecrolimus does not affect keratinocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells and Langerhans cells. In vivo, the drug has high anti-inflammatory and slight immunosuppressive activity [9–12] and does not cause atrophy [13]. Pimecrolimus has a high affinity for the skin, therefore it penetrates well into it and practically does not penetrate the skin [11].
Clinical trials have established the safety and effectiveness of 1% pimecrolimus cream - Elidel® (Novartis, Switzerland) for short-term and long-term use in children and adults with AD.
In order to try to reduce with the help of Elidel the frequency and duration of relapses and the dependence of patients on external CS for blood pressure in adults, a multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled trial lasting 24 weeks was conducted [14].
We observed 192 patients with AD aged 18 years and older. The diagnosis was made in accordance with the criteria of Hanifin [15] and Rajka [16]. The affected area before treatment was at least 5%, with an average of 17% in both groups. In each group, patients with moderate AD predominated (3 points on the IGA scale).
Based on the results of randomization, 96 patients were included in the main group and 96 in the control group. There were no statistically significant demographic or clinical differences between the groups (Table 1).
Patients in the main group received external treatment with Elidel cream 2 times a day, while patients in the control group received only the base of the cream. In the first week of the study, this treatment regimen was mandatory. Subsequently, in case of exacerbation, external CS (prednicarbate 0.25% cream) was prescribed twice a day for 7 days and once a day for the next week. After CS therapy, treatment with the study drug was carried out for another 1 week to relieve residual symptoms of exacerbation (Table 2). The main efficacy criterion was the number of days (%) during which CS were used for acute treatment of exacerbations. Additional evaluation of effectiveness was carried out according to the following parameters: number of exacerbations, IGA results, EASI, itching intensity. The last parameter was assessed by the patients themselves, using the following point scale: 0 – no itching, 1 – slight itching, 2 – moderate itching, 3 – severe itching, 4 – very severe itching. Tolerability was assessed based on clinical and laboratory data.
Patients were examined during the initial examination, and then at 1, 3, 6, 12 and 24 weeks of treatment. In addition, additional telephone contact was carried out at 9 and 18 weeks. In cases of severe exacerbation, unscheduled examinations were performed.
results
In the main group of patients treated with Elidel cream, a statistically significant (compared to the control group) reduction in the number of days during which patients were forced to use CS was recorded (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Number of days patients used corticosteroids (%)
In the main group, patients used CS on average for 14.2% ± 24.2% of 168 days (total study duration), and in the control group - in 37.2% ± 34.6% (p < 0.001). Moreover, half of the patients receiving Elidel did not require the use of CS for the entire 24 weeks (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Number of days patients required treatment with topical corticosteroids (%)
The frequency of exacerbations and time to first exacerbation also differed significantly between the two groups of patients. In the main group, on average, 1.1±1.4 cases of exacerbation were registered, in the control group – 2.4±2.3 (p<0.001). Almost half (44.8%) of patients treated with Elidel showed no exacerbations for six months. In persons receiving traditional therapy, this figure was 18.8% (Fig. 3.4).
Rice. 3 Frequency of exacerbations (%)
Rice. 4. Time until first exacerbation
When assessed on the IGA scale, 82.3% of patients in the main group showed an improvement of at least one point versus 51.0% in the control group, and the EASI score decreased by an average of 48.3% versus 15.9% (respectively) (p<0.001) . Among patients treated with Elidel, half as many people stopped treatment due to its ineffectiveness compared to traditional therapy (15.3% and 27.1%, respectively).
The dynamics of itching are presented in Figure 5. Noteworthy is the decrease in itching during the first three days of therapy in the main group and a temporary increase in the control group.
Rice. 5. Dynamics of itching during the first week of treatment
Elidel cream was well tolerated by patients; pathologies in traditional laboratory tests were not detected in any of the patients throughout the study.
Thus, external treatment of patients with blood pressure with Elidel cream allows:
- reduce the use of local CS or completely abandon them,
- reduce the number of exacerbations,
- increase the duration of the period without exacerbations of blood pressure,
- leave the CS as a reserve for short courses of treatment for exacerbation of blood pressure and minimize the risk of complications from long-term steroid therapy,
- improve control of the disease in general, the general well-being of patients, and, consequently, the quality of life of patients.
References:
1. Giusti F, Martella A, Bertoti L, Seidenari S. Skin Barrier, Hydration, and pH of the Skin of infants under 2 years of age. Ped Derm 2001; 18:93–6.
2. Keipert JA, Kelly R. Temporary Cushing's syndrome from percutaneous absorption of betamethasone-17-valerate. Med J Austr 1971; 1:542–4.
3. Pascher F. Systemic reactions to topically applied drugs. Int Dermatol 1978; 17: 768–75.
4. Bode HH. Dwarfish following long long–term topical corticosteroid therapy. JM Med Assoc 1980; 244:813–14.
5. Bartorelli A, Rimondini A. Severe hypertension in childhood due to prolonged skin application of mineralocorticoid ointment. Hypertension 1984; 6:586–8.
6. Walsh P, Aeling JL, Huff L, Weston WL. Hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal axis suppression by superprotent steroids. J Am Acad Dermatol 1999; 29:501–3.
7. Fisher DA. Adverse effects of topical corticosteroid use. West J Med 1995; 162:123–6.
8. Charman C, Morris A, Willians H. Topical corticosteroid phobia in patients with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 2000;142:931–6.
9. Meingassner JG, Grassberger M, Fahrngruber H et al. A novel anti–inflammatory drug, SDZ ASM 981, for the topical and oral treatment of skin diseases: in vivo pharmacology. Br J Dermatol 1997; 137:568–76.
10. Grassberger M, Baumruker T, Enz A et al. A novel anti–inflammatory drug, SDZ ASM 981, for the treatment of skin diseases: in vitro pharmacology. Br J Dermatol. 1999 Aug;141(2):264–73
11. Stuetz A, Grassberger M, Meingassner JG. Pimecrolimus (Elidel(, SDZ ASM 981) – Preclinical pharmacological profile and skin selectivity. Seminars Cutan Med Surg 2001; 20(4):233–41.
12. Zuberbier T, Chong SU, Grunow K et al. The ascomycin macrolactam pimecrolimus (Elidel, SDZ ASM 981) is a potent inhibitor of mediator release from human dermal mast cells and peripheral blood basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001 Aug; 108(2): 275–80.
13. Queille–Roussel C, Paul C, Duteil L et al. The new topical ascomycin derivative SDZ ASM 981 does not induce skin atrophy when applied to normal skin for 4 weeks: a randomized, double–blind controlled study. Br J Dermatol. Mar 2001; 144(3): 507–13.
14. Meurer M, Folster–Holst R, Brautigam M. Pimecrolimus (SDZ ASM 981) cream reduces the need for corticosteroids in the long–term management of atopic dermatitis in adults. Study, presented at the 60th annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in New Orleans, USA, February 2002
15. Hanifin JM, Thurston M, Omoto M et al. The eczema area and severity index (EASI): assessment of reliability in atopic dermatitis. EASI Evaluator Group. Exp Dermatol. Feb 2001; 10(1): .11–8.
16. Rajka G. Natural history and clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis. Clin Rev Allergy. 1986 Feb; 4(1): 3–26.
Advantan or Triderm
Manufacturer: Shering—Plough Labo NV, Belgium
Release form: cream, ointment
Active ingredient: clotrimazole, gentamicin, betamethasone
Synonyms: Triakutan, Akriderm GK, Candiderm
Triderm is a combined preparation for external use with complex antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antifungal activity. A wide spectrum of activity allows the cream or ointment to be used in the treatment of dermatoses of various etiologies, mainly complicated by fungal and bacterial infections.
The product is applied in a thin layer 1 or 2 times a day, depending on the doctor’s prescription. The drug is not used in the treatment of children under 2 years of age. Caution should be exercised and strict adherence to the recommended dose when using this analogue in childhood.
Characteristics of Advantan
The active component of the drug is methylprednisolone aceponate. This substance is a synthetic steroid belonging to the GCS group.
The medicine can be used on different parts of the body and on any skin type. This is facilitated by the fact that Advantan is produced in several dosage forms - ointment, fatty ointment, cream and suspension. The additional components included in these drugs are different, so it is possible to choose the most suitable medicinal composition.
What else to read Comparison of Viferon and Oxolinic ointment
Advantan has anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects and is prescribed for the following diseases:
- atopic, allergic, contact dermatitis;
- degenerative, simple, dyshidrotic, seborrheic, true, microbial, acute eczema;
- neurodermatitis;
- sunburn;
- bites from mosquitoes and other insects.
The main contraindication is hypersensitivity to the composition of the drug. Before applying the medication for the first time, you should perform a test by applying a small amount of the product to the elbow bend. If within half an hour no rashes or redness appear on the skin, then the drug can be used.
Advantan should not be used in the treatment of children under 4 months of age. The medicine is not contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women, but its use must be agreed with a doctor.
Advantan should not be used in the treatment of children under 4 months of age.
Contraindications are also:
- skin manifestations of syphilis and tuberculosis;
- skin lesions from the herpes virus;
- rosacea, perioral dermatitis;
- negative skin manifestations of vaccination.
Side effects are possible. If itching, burning, swelling and other unpleasant symptoms appear, you must stop treatment and consult a doctor. In rare cases, more severe side effects are observed - skin atrophy, stretch marks, acne.
Advantan can be applied to large areas of the body. Overdose is unlikely.
Pimafucort or Advantan
Manufacturer: Temmler Italia SrL, Italy
Release form: cream, ointment
Active ingredient: natamycin, neomycin, hydrocortisone
Synonyms: Pimafukort
Pimafucort is classified as a combined analogue. Unlike Advantan, this product contains not only a corticosteroid, but also antifungal and antibacterial components. Pimafucort in the form of an ointment or cream is used in the treatment of dermatoses that are complicated by a bacterial or fungal infection.
The drug can be used in patients from 12 months. It should be borne in mind that this analogue of Advantan is not recommended to be applied under a bandage in order to eliminate the possibility of systemic action and the development of side effects.
Advantan or Elokom
Manufacturer: Shering—Plough Labo NV, Belgium
Release form: cream, ointment, lotion
Active ingredient: mometasone furoate
Synonyms: Momederm, Mometox, Uniderm, Elozon, Silkaren, Momat
Elokom is a highly active drug based on the steroid hormone mometasone. This remedy is quite cheap and turns out to be stronger and more effective than Advantan for various dermatitis, allergic reactions in children and adults, eczema accompanied by severe inflammation, swelling, and itching.
The use of this analogue is permitted in patients over 2 years of age. Particular care should be taken when using the Elokom analogue in any form in children, since in them the active substance penetrates the skin and is absorbed into the blood much faster. Like Advantan, there is the possibility of choosing different dosage forms depending on the type of skin, the location of the pathological process and the characteristics of the course of the disease. For dry skin, it is recommended to use ointment, for other types, as well as for lesions of the scalp - lotion or cream.