Xeroderma pigmentosum is one of the hereditary dermatological diseases. It is extremely rare: 2 cases per 1 million births. Symptoms of the disease appear in early childhood and steadily progress without comprehensive treatment. The danger of xeroderma pigmentosum lies in its high oncogenic potential. Skin manifestations of the disease are an obligate precancer, that is, they are prone to malignant degeneration and in almost all cases turn into cancer.
At the same time, the first dermatological symptoms of xeroderma pigmentosum in a child are most often regarded by parents as a phenomenon of some kind of allergic dermatitis and do not cause unnecessary concern. Lack of alertness leads to late seeking medical help and delayed treatment.
- Causes and mechanism of development
- Kinds
- Clinical picture
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
- Forecast
Causes and mechanism of development
Xeroderma pigmentosum belongs to a group of hereditary diseases and is transmitted in an autosomal recessive manner. Autosomal recessive inheritance is understood when mutations occur in any chromosomes except sex chromosomes, and for the disease to manifest in a child, it is necessary that both spouses have a defective gene.
The main links in the pathogenesis of xeroderma pigmentosum are increased sensitivity to direct sunlight and the body’s inability to eliminate DNA damage caused by ultraviolet radiation. Disruption of DNA repair processes is associated with the absence or low activity in the skin of enzymes responsible for repair: nucleosides and proteases.
Irreversible damage to the genetic apparatus of cells leads to a number of pathological processes. Thus, at the early stage of the disease in the skin the following is observed:
- increasing the rate of division of the stratum corneum of the skin and exfoliation of dead scales;
- thinning of the spinous (intermediate) layer;
- excessive deposition of melanin in the basal (germinal) layer of the epidermis and in the papillary layer of the dermis;
- infiltration of leukocytes and other inflammatory cells in the perivascular spaces.
At later stages of xeroderma pigmentosum, areas of excessive keratinization (hyperkeratosis), acanthosis (hyperproliferative foci, often pigmented) with elements of cellular atypia, and degenerative changes in collagen and elastin fibers are found on the skin.
The terminal stages of the disease are predominantly characterized by atrophy (thinning) and ulceration of skin areas; warty or papillomatous growths are less common. These processes are especially pronounced on open parts of the body.
Hydration creams
If a person has developed dryness, it is important to use a high-quality moisturizer so as not to provoke increased xerosis. They use creams based on hyaluronic acid, glycerin, oils, collagen, and plant extracts. Natural ingredients help reduce the risk of allergic reactions and irritation. If skin xerosis is significant, use day and night forms of the cream.
- Garnier, series Life-giving hydration
. The skin type is first identified by selecting a high-quality composition. Most creams are suitable for both normal and combination skin. The product has a light texture, but deeply moisturizes the epidermis. - Loreal, Moisturizing expert
. The cream is based on camellia oil. Has a moisturizing effect, suitable for dry, sensitive skin. Additionally contains rose oil, currant extract. - Aloe vera
. This is a product from a range of pharmaceutical cosmetics based on hyaluronic acid, vitamins, minerals, and aloe vera extract. The ointment moisturizes but does not cause harm.
When choosing a moisturizer for the treatment of skin xerosis, you can choose any product. However, if a person has allergies, it is better to choose hypoallergenic structures. Then the risk of simple xerosis transitioning into the stage of dermatitis or eczema will be reduced.
Kinds
Depending on the damaged chromosome, there are 8 subtypes of the disease: A, B, C, D, E, FG and Young's pigmented xerodermoid. The first 7 types of xeroderma pigmentosum have a similar clinical course and are determined only after molecular genetic analysis. Young's xerodermoid pigmentosa has a more favorable prognosis - the symptoms of the disease appear later, and the pathological process itself is mild.
An independent clinical form of the disease is De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome. It is considered the most aggressive type of xeroderma pigmentosum and is characterized by pronounced changes in the central nervous system. The syndrome can develop with any chromosomal variant of the disease, but most often occurs with subtype A.
Ointments with urea
Urea is a substance that helps moisturize and heal the skin. The rate of increase in wrinkles is significantly reduced. Peeling and irritation deep in the skin stops.
The action of urea is based on stabilizing the nitrogen balance, saturation with protein and energy.
A number of urea-based drugs are used. They can be used for legs, face, hands. They effectively remove corns. The following means are used.
- Doctor
. They produce creams for night and day action. Softens the epidermis, eliminating dryness and flaking. The base contains natural ingredients, urea. With constant use, recurrent cracks are prevented. - Urea from L'Adeleide
. The ointment is suitable for all skin types and does not cause allergic reactions. Has a softening and anti-inflammatory effect. Used for face and body. - NutriExtra Mains from Vichy
. The ointment is based on thermal water and additionally contains urea. The skin quickly returns to normal. Protection is carried out within 24 hours. Therefore, the cream is applied in the morning, immediately after waking up. - Super Moisture
. Cream with dispenser. It has a light structure and is quickly absorbed into deep layers. Eliminates corns and rough skin.
After a long course of use, take a break. This is important, since the epidermis can form an addiction. After a break from the cream, re-administration begins to eliminate the risk of relapse.
Clinical picture
Newborn children have no symptoms of the disease. The first signs of xeroderma pigmentosum begin to be noticed between the ages of 3 months and 4 years. In rare cases, the onset of the disease is possible in adulthood. The literature contains data on the appearance of symptoms in patients aged 25-30 years.
Xeroderma pigmentosum is characterized by seasonality and stages of progression. An exacerbation of the disease occurs in the sunny season (spring - early autumn). The first stage is called inflammatory and is manifested by a specific triad of symptoms:
- photosensitivity - intolerance to direct sunlight;
- erythema - redness of the skin of exposed areas of the body after exposure to the sun;
- foci of hyperpigmentation - the appearance of areas of excess color.
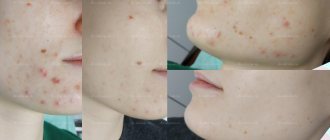
Erythema of the skin is persistent. It is often accompanied by severe swelling, peeling and the formation of small bubbles with transparent contents. After the inflammatory processes subside, at the site of the erythema, foci of hyperpigmentation appear in the form of light or dark brown spots of different sizes. In most cases, they resemble a scattering of freckles, but can be large (lentigines).
The second stage is poikilodermic. It begins at the age of 3-7 years and is characterized by pronounced changes in the skin in the form of telangiectasia (spider veins), areas of hyperkeratosis with abundant peeling, areas of atrophy and thinning of the skin. A typical manifestation of the second stage is also the formation of small, smooth, whitish scars with a shiny surface. Upon careful examination, areas of skin atrophy have an uneven, rough appearance and resemble a burn surface.
Pronounced changes in the skin lead to a number of serious consequences:
- deformation of the external nose and nasal passages, resulting in difficulty breathing;
- curvature of the mouth;
- deformation of the ears due to cartilage atrophy;
- eyelash loss;
- eversion or inversion of the eyelids.
In patients with xeroderma pigmentosum, areas of hyperpigmentation persist, and as the disease progresses, hypopigmented spots appear. As a rule, they are localized on the back and wings of the nose, on the chin.
In 75-80% of patients at the second stage, signs of damage to the organ of vision are also determined: lacrimation and photophobia, blepharitis, ulceration of the conjunctiva and its inflammation, clouding of the cornea and the appearance of spots on it. In 20% of patients, symptoms of dysfunction of the central nervous system are detected in the form of decreased sensitivity, mental retardation, changes in coordinated muscle function (ataxia) and decreased or absent unconditioned reflexes (for example, tendon reflexes).
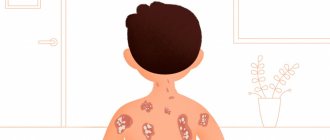
The disease enters the third (tumor-like) stage in adolescence. It is characterized by the appearance of benign or malignant neoplasms of various shapes and sizes on the affected areas. Benign tumors can be represented by papillomas, nevi, fibromas, angiomas and have a high risk of oncological transformation. Often, neoplasms are also detected on the mucous membrane of the mouth and nose.
De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome has a severe clinical course. Its main symptoms are impaired mental development (idiocy) due to a decrease in the size of the brain and skull, dwarfism and typical skin manifestations of xeroderma pigmentosum. Additional signs of the syndrome are delayed sexual development and severe disturbances of the nervous system (paresis, paralysis, ataxia). Skin manifestations appear early in patients with De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome. They are pronounced, rapidly progress and develop into oncological neoplasms already in childhood.
How to restore the health of the epidermis?
The use of emollients and moisturizing lotions will not solve the problem unless the cause of increased dryness is eliminated. It is important to review your daily care and adjust your diet. Some simple tips to get rid of flaky skin include:
- choose high-quality cosmetics that do not contain allergens, dyes or synthetic fragrances;
- for dry skin types, use moisturizing lotions based on shea butter, coconut, grape seed or wheat germ;
- monitor the humidity level in the room during the heating season;
- eat right, do not exclude vegetable fats and fiber from the diet, take multivitamins;
- observe the drinking regime, reduce the consumption of coffee, tonics, give preference to clean water without gas.
Cosmetic procedures help with severe peeling: mesotherapy with the introduction of hyaluronic acid, alginant masks, biorevitalization, wraps with oils.
Increased dryness of the skin in most cases is associated with improper and irregular care. But with severe peeling, which is accompanied by itching, burning, and the appearance of cracks, it is necessary to exclude chronic diseases, allergies, and consult a dermatologist.
Complications
The main complication of the disease is the appearance of skin and visceral (internal) malignant tumors. Multiple warty neoplasms have the highest risk of oncogenic transformation. The incidence of malignant tumors also correlates with the severity of skin pathological processes. With the early onset of the disease and its aggressive course, oncological tumors appear in adolescence (12-14 years) and quickly metastasize to internal organs.
Among malignant tumors, squamous or basal cell carcinoma most often develops, and melanoma of the skin or eye is the least common. Cases of more than 50 different types of oncology have been described: fibrosarcomas, angiosarcomas, histiocytes and others.
The disease can also lead to severe deformities of the face (mouth, nose, ears). The result is social maladjustment of the child and psychological problems.
Diagnostics
A detailed history taking is of great importance in making the correct diagnosis. The collected data (onset of the disease in early childhood, seasonality of symptoms, high photosensitivity, consanguineous marriages) suggest xeroderma pigmentosum. The diagnosis is confirmed after cytological and histological examination of the affected areas of the skin.
Additional examinations include examination by a dentist, otorhinolaryngologist, ophthalmologist and neurologist to exclude damage to the central nervous system, oral apparatus, visual and hearing organs. For De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome, an X-ray examination or computed tomography of the skull bones, and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain are also performed. In this case, small sizes of the sella turcica, a decrease in the volume of the cranium and brain, and underdevelopment of the cerebellum and pituitary gland are detected.
Treatment methods
There is no etiopathogenetic treatment for xeroderma pigmentosum. In essence, any methods of therapy are symptomatic and are aimed at eliminating the existing manifestations of the disease. Comprehensive treatment of the disease includes:
- vitamin therapy courses;
- antimalarial drugs - the effectiveness of drugs from this group in eliminating the inflammatory process and sensitization of the body has been noted;
- aromatic retinoids;
- cytostatic antitumor drugs.
Patients are also advised to adjust their lifestyle, limit exposure to the sun as much as possible, and before going outside, take care to protect their skin from sun rays.
All benign skin elements are subject to mandatory removal and histological examination. When a neoplasm transforms into a malignant one, treatment tactics are determined based on the type of tumor and the stage of the oncological process.
Forecast
The quality and length of life depend on several factors, primarily on the timing of seeking medical help, making the correct diagnosis and early initiation of comprehensive treatment. With timely diagnosis of the disease and constant dynamic monitoring by a dermatologist or oncodermatologist, the prognosis is relatively favorable.
With warty growths on the skin, about 35% of patients do not survive to adulthood and die at the age of 13-15 years. This is due to the high tendency to malignancy and rapid metastasis of the tumor to internal organs.
De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome has a poor prognosis. The aggressive course of the disease leads to death from oncopathology in childhood in 70% of patients.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Keratolytics for rough skin
Keratolytics are ointments, gels, creams designed to exfoliate and remove dead particles from the surface of the skin. They are prescribed for a short course so as not to provoke dermatological pathologies. Use one of the following inexpensive remedies.
- Kerasal
. Dermatological ointment that softens and protects the skin. It is used for skin pathologies accompanied by peeling and the formation of dry plates. Contains salicylic acid and urea. After prolonged use, softening appears, combined with the keratolytic effect of the active ingredients. - Akriderm
. Keratolytic ointment based on salicylic acid and glucocorticosteroid. Exfoliates, relieves inflammation, eliminates allergies. - Betasalik
. Contains betamethasone and salicylic acid. Eliminates swelling, inflammation, redness, itching. Apply to the skin in the form of lotion or ointment. The course of application is short. - Retasol
. Based on isotretinoin. It is a keratolytic, enhances healing, relieves inflammation. Used for xerosis of the skin, seborrheic dermatitis.
If the cream contains a steroid substance, it should be used with extreme caution and for a short course. Hormonal substances have a large number of side effects and quickly penetrate the systemic bloodstream. It is better to first consult with a therapist or dermatologist.