What is pityriasis rosea?
Pityriasis rosea is a disease that is diagnosed in children and adults, but more often occurs in young people. The causative agent of the disease is unknown, but there is an assumption that the disease occurs as a result of the penetration of a virus into the body. Most often, skin ailments occur in the off-season (spring and autumn), when the immune system is weakened and the risk of catching a cold is increased.
Inflammation can go away on its own with complete disappearance of symptoms, and then in most cases the patient develops immunity to the disease. But if pityriasis rosea does not go away, then it becomes chronic. And then not just treatment is required, but the development of a special program to prevent frequent relapses and strengthen the patient’s immunity.
Is pityriasis rosea contagious or not, transmitted from person to person or not?
There are several assumptions about how a person can become infected with this disease:
- transmission from person to person by airborne droplets, but with strong immunity this is impossible;
- pityriasis rosea can occur as a result of the body's reaction to hypothermia (this is why the disease often occurs in spring and autumn);
- severe stress, prolonged nervous tension and other factors that undermine the body's defenses can also trigger pityriasis rosea.
Pityriasis rosea and pregnancy
In pregnant women, pityriasis rosea can occur both when a virus enters the body and when there is a tendency to allergic reactions. An “interesting situation” causes a loss of strength, vitamin deficiency, fatigue, hormonal changes, which leads to a decrease in immunity, which means there is a risk of “catching” an infection.
What does pityriasis rosea look like in pregnant women? Exactly the same as in other patients, only treatment in this case is selected even more carefully - taking into account the patient’s condition and the duration of pregnancy.
In young children and newborns, cases of infection are extremely rare. Children's pityriasis rosea often occurs in adolescence, when the hormonal system undergoes restructuring. If pityriasis rosea is diagnosed in a baby in infancy or up to one and 2–3 years of age (the rash spreads throughout the body), then the causes are often intestinal or other past infections, and in rare cases, vaccinations.
Complications after pityriasis rosea, and why it reappears
Relapses of the disease occur rarely or never, but under different circumstances complications such as folliculitis, osteofolliculitis, eczema, streptococcal impetigo, etc. are possible.
Recurrence of the disease is possible when wearing tight clothing, frequent rubbing of the skin during water procedures, incorrect and illiterate treatment of an individual tendency to allergies and excessive sweating.
Secondary infection is manifested by rashes on areas of the skin that are subject to stretching to the greatest extent (along Langer's lines). Especially a lot of flaky spots appear in the groin area and on the inner thighs, as well as on the forearms.
Secondary infection is also possible in places where there are many sweat glands and on delicate areas of the skin. The face is rarely affected; the scalp and mucous membranes also remain clean.
Lichen ruber planus
Flat multi-colored (from pale pink to purple) nodules of lichen red often appear on the mucous membranes, nails (they crumble), and delicate skin of the chest and abdomen. Their appearance is accompanied by severe itching, which, as a result of scratching, leads to the rapid growth of foci of skin damage.
Dermatologists find it difficult to determine the cause of the appearance of lichen red, but note that it is quite common in patients with diabetes, as well as those suffering from diseases of the stomach, liver, and biliary tract. Moreover, women over 40 years of age are primarily at risk.
Pityriasis rosea: symptoms
The main symptom is pink, scaly spots that appear gradually. The disease begins with the appearance of one spot (maternal plaque) measuring 2 cm. After about a week, multiple pink spots of different diameters appear (smaller than the maternal plaque).
Location of rashes: pityriasis rosea appears on the face and other areas of the skin (sides of the body, back, shoulders, etc.). Peeling appears in the center, and a red border remains around the circumference. Individual spots may merge with each other. Patients may also be bothered by itching of varying intensity and increased body temperature (in cases with complications).
Sometimes pityriasis rosea has atypical forms with symptoms such as blistering, dotted and draining rashes in small quantities, but the spots can reach large sizes and also become chronic.
Pityriasis rosea: causes
As mentioned above, the causes of the disease are not fully understood. Perhaps it is a viral disease; pathogens like herpes are sometimes cited as the cause.
What else causes pityriasis rosea?
As a rule, this is a standard set of reasons that lead to a decrease in immunity and disruption of the normal functioning of the body’s protective functions, namely:
- past infections and diseases;
- colds;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system;
- stress and nervous tension;
- change of climate and time zone;
- allergic reactions;
- metabolic disease;
- insect bites, etc.
The medical department provides comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of skin diseases of various levels of complexity and causes. For diagnosis and treatment, dermatologists use specialized expert clinical and clinical-biochemical microscopy, as well as dermatoscopy and cultural diagnostics.
Initial appointment
Treatment of pityriasis rosea in children and adults begins with the first consultation with a specialist. As a rule, already at the first examination, the doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment with a plan of individual visits according to each specific clinical case.
If the disease is severe or has complications and concurrent infections, then appropriate tests and examinations are prescribed.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics includes:
- examination of the patient by a dermatologist;
- taking material for biopsy and histological examination to exclude parapsoriasis;
- scraping for bacteriological culture;
- scraping for pathogenic fungi;
- fluorescent diagnostics;
- conducting RPR tests for syphilis (in rare cases).
Repeated appointment
The main means of treating pityriasis rosea, its causes and consequences are ointments, gels and creams. But besides this (depending on the case) the patient:
- bathing is prohibited (only washing in the shower with gentle detergents is possible);
- It is advised to limit your time in the sun;
- It is advised to wear loose clothing made from natural materials;
- a hypoallergenic diet is prescribed during treatment and for some time after it;
- prescribe the use of antiallergic and anti-inflammatory ointments for severe itching;
- antibiotics are prescribed (in particularly difficult cases).
Since pityriasis rosea looks like an unpleasant and unaesthetic skin reaction, and can be contagious, it creates psychological discomfort in the patient. A common reaction to any skin rash is a reluctance to leave the house and communicate with people, embarrassment when communicating, isolation and detachment. Accordingly, if necessary, consultations with a psychotherapist or psychologist may be prescribed during treatment. If a dermatologist suspects a hormonal imbalance, an endocrinologist will also conduct a consultation.
If treatment of pityriasis rosea in an adult or child with ointments and other means has already been prescribed, then at a second appointment the doctor evaluates the results. If no improvement is observed, then a new course of treatment and restorative procedures are selected to strengthen the immune system.
Treatment of pityriasis rosea in children depends on the age of the child, his condition and the stage of development of the disease. Means and methods of combating the disease are also selected individually, but the treatment regimen is similar to that for adult patients. As a rule, a child recovers from a disease several times faster than an adult.
Control reception
A follow-up appointment is required 21–30 days after treatment to assess the patient’s condition and treatment results. If the outcome is positive, methods of restoring the patient are prescribed (physiotherapy, immunotherapy, etc.).
Treatment result
Achieving positive results is only possible if you strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and prescriptions. The duration of treatment is also individual in each case and is discussed with the doctor at the appointment: treatment usually takes from 2 to 6 weeks. If the patient has excessive sweating or allergic reactions, the treatment period is increased.
Prevention
To avoid the need to treat pityriasis rosea in a person, he should be warned: with what and how?
Good prevention is:
- proper nutrition or a hypoallergenic diet if you are prone to allergic reactions;
- strengthening the immune system through sports and active recreation;
- wearing high-quality clothes made from natural materials;
- individual selection of cosmetics and care products for body and face;
- local therapy, including taking medications to strengthen the immune system;
- careful use of water procedures;
- wearing warm clothes in the off-season and cold season to avoid hypothermia.
Making a diagnosis on your own is not recommended, nor is it recommended to prescribe treatment on your own. How and with what to treat and cure pityriasis rosea, get rid of symptoms and prevent the causes of relapses, only a dermatologist
. So don't delay visiting your doctor. High-quality and timely prescription of a course of treatment will allow you to quickly get rid of the disease and significantly improve your quality of life.
To make an appointment with a dermatologist in our center, just leave a request on the website (there is a special registration form) or call the phone number listed on the page.
Pathogens and carriers of lichen
The content of the article
Dermatologists distinguish several types of lichen, caused by different pathogens.
Most often, the appearance of lichen on human skin is initiated by fungi:
- zooanthropophilic - transmitted to humans from an infected animal, including from pets;
- anthropophilic - live only on human skin;
- geophilic - live in the soil and come into contact with human skin upon contact with the ground.
In addition to fungi, viruses are often the causative agent of lichen. Their cunning lies in the fact that they can live asymptomatically in the human body for a number of years and become more active when the immune system is weakened. This is exactly how, for example, those familiar to many with herpes or shingles behave.
Are all types of lichen contagious?
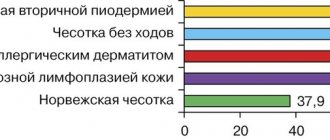
Many people believe that absolutely all types of lichen are dangerous to others. Meanwhile, this is not entirely true. So, with pink, ringworm or shingles, the patient will really need to be isolated. But, for example, pityriasis or scaly ones are not dangerous for others.
And this is another reason why any change in the skin should be the reason for going to a specialist - only he will be able to correctly determine the type of lichen, assess the degree of its danger, give recommendations for treatment, and finally select a set of medications and therapeutic measures aimed at including general strengthening of the body.
How to relieve pain from shingles
The main symptom of herpes zoster, which distinguishes it from other infectious diseases with skin manifestations, is pain, which can occur both before the rash appears and after it has healed. For pain relief, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
A common complication of herpes zoster is postherpetic neuralgia, a severe pain syndrome that lasts at least 120 days. Pain can bother a person for several months and even years after recovery. Postherpetic neuralgia develops mainly in older people - for example, about 50% of cases are recorded in patients over 60 years of age.
What does lichen look like in humans?
The external manifestation of the pathology is obvious - lichen is accompanied by a number of signs:
- rash in the form of spots of different colors - red, pink, brownish, yellow;
- itching, burning, unpleasant (painful) sensations;
- scales, bubble formations on spots;
- bald spots on the head in the hairline area (clipping form);
- fever (rare);
- malaise, lethargy.
Ringworm on the skin: treatment
Treatment of the disease is especially effective at an early stage. Ringworm can be cured in all patients, regardless of age. In this case, you need to consult a doctor even with minor manifestations. For diagnostic purposes, a dermatologist conducts a visual or instrumental examination (using a special lamp), prescribes a series of tests - studying urine, blood, as well as immunological studies and skin scrapings.
After establishing the exact cause and type of lichen, treatment is prescribed. Most often it is associated with the use of special ointments externally (antifungal drugs). The course of therapy lasts from 2 weeks to 3-4 months.
Main areas of treatment:
- Etiotropic – the use of drugs that eliminate the cause of the disease. These can be fungicides or antiviral agents (based on Acyclovir).
- Elimination of itching, spots and other unpleasant symptoms.
- Carrying out procedures - UV therapy, physiotherapy, increasing resistance (strengthening the immune system), maintaining personal hygiene.
- In rare cases, it is necessary to disinfect the premises, especially linen, furniture, and personal belongings.
It is not recommended to treat lichen yourself at home. This is dangerous because you can waste time and also infect other people. In addition, the patient often cannot determine which drug to treat the pathology with. For example, a person “prescribes” an antimicrobial ointment while he develops herpetic (viral) lichen. In rare cases, lost time can result in severe consequences such as blindness, arthritis, and other complications.