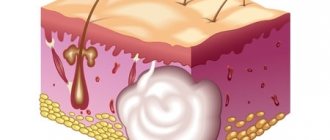
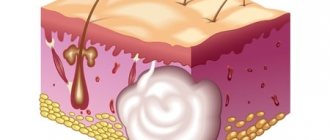
A benign neoplasm, which is formed from the synovial (articular) membranes, is called “hygroma” or “tendon ganglion”. This bulge inside is filled with mucus and fibrin protein strands. The tumor can appear on any joint (fingers, hands, feet).
Hygroma on the finger is one of the most unpleasant types of pathology. As a rule, the formation appears near the distal joints between the phalanges or in the area of the flexor muscles. The lump looks unsightly and causes pain. If left untreated, the mobility of the joint worsens and the nail becomes deformed.
Types of hygroma
A synovial cyst is usually located in the tendon sheath or joint capsule. It looks like a ball with a soft, flesh-colored consistency. Inside the formation there is serous fluid, mucus, and fibrin protein fibers.
Reference. A cyst of the phalanx of the thumb rarely causes discomfort. A mass in the knuckle of the index, middle, or little finger can limit mobility.
The tendon ganglion never becomes malignant, but requires proper therapy. Otherwise, the likelihood of spontaneous opening increases, which threatens the formation of new tumors.
Finger hygromas are divided into types according to location, number of capsules formed and type.
Types of synovial cysts depending on the number of capsules:
- Single-chamber are single growths.
- Multilocular – multiple tumors.
Types of formations by capsule type:
- Valve. In the area where the capsule connects to the maternal shell, a valve is formed, as a result of injury to which the viscous contents flow out or in from time to time.
- Anastomosis. The cyst cavity connects to the joint, while its contents periodically flow out and fill the maternal membrane.
- Isolated formation. The cavity of the tendon ganglion is separated from the maternal membrane.
Hygroma of the finger appears relatively rarely; it is often confused with nodes that form in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and rickets. To determine the nature of the tumor, you need to conduct a thorough diagnosis.
Formation mechanism
A synovial cyst is formed in this way:
- The elasticity and endurance of damaged tissue decreases.
- The joint is unable to retain joint fluid.
- The contents of the synovial membrane are poured into the surrounding tissues.
As a result, an elastic and dense tumor-like formation appears, filled with thick liquid inside.
Doctors still cannot accurately answer the question of why a synovial cyst occurs. However, they identify several factors that can trigger the appearance of a lump:
- Hereditary predisposition. If close relatives had a hygroma on the finger, then the likelihood of its occurrence in the child also increases.
- Systematic load on the hands.
- Inflammatory diseases and injuries (microtraumas, bruises, sprains, dislocations, fractures) of tendons and joints.
- Metaplasia is the pathological replacement of normal tissues with abnormal ones.
- Excessive tension in the arm muscles.
- Calluses on the fingers that appear regularly.
- Lack of adequate treatment for finger injuries and diseases.
Finger hygromas, which form after injuries, are diagnosed in 30% of patients. Tumors that are inherited occur in 50% of cases. In other cases, growths are formed due to repeated injuries and constant overstrain of the damaged area.
Reference. Tendon ganglion most often appears in women between 20 and 30 years of age. In children and the elderly, pathology is observed extremely rarely.
Symptomatic means problematic
The growths are visible to the naked eye. The reason for their occurrence can be judged by their appearance.
Hard and dense lumps on the joints, covered with smooth skin, usually form in men over 40 years of age and indicate gout. They are usually called gouty tophi. They grow during periods of exacerbation of the disease. The patient becomes weaker and complains of malaise. The temperature in the area of the tophi rises, and the pain sometimes becomes unbearable.
If the skin on the lump is rough and red, and the growth itself is round and elastic, it is a hygroma. It usually forms in women 20-30 years old and can be single-chamber or multi-chamber. Hygromas differ from other types of growths in that their size gradually increases, and pain is felt when pressed.
Formations on the interphalangeal joints that appear after 60 years are called Heberden's nodes. They are equally likely to be found on any phalanx and are signs of osteoarthritis. This disease leads to stiffness of the hands and deformation of the joints.
Nodules up to 2 cm in diameter, which form in 20% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, are rheumatoid nodules. They do not cause pain, but the course of the disease is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms: lethargy, fatigue, fever, and sometimes loss of body weight.
Symptoms
A synovial cyst is a dense, elastic formation with a smooth surface in the shape of a ball. The tumor shell is attached to the surrounding tissue, so it does not move. But sometimes during palpation you can notice that the growth moves.
When you feel the cyst, you may feel clots, cholesterol crystals, and “rice bodies” inside. They are quite mobile, often changing their position. Usually, when you press on the tumor, there is no pain or minor discomfort.
Reference. If painful sensations occur during palpation, this indicates that the pathology has become chronic. The formation increases gradually; at the early stage, there are no pronounced unpleasant sensations.
Hygroma on the finger has the following external signs:
- spherical shape, size - about 5 cm, sometimes more;
- the surface of the cyst is elastic, smooth;
- when pressing, a slight nagging pain appears in the area of the damaged joint;
- the skin over the tumor is thick and rough;
- During the inflammatory process, the skin turns red.
Symptoms depend on the stage of the pathological process: at first there are no pronounced signs, and in advanced cases they are clearly expressed. Clinical manifestations of hygroma (early stage):
- tumor size – from 5 mm;
- the cyst is inactive;
- the growth is soft, elastic;
- there are no painful sensations;
- the skin over the capsule is smooth and even.
The hygroma on the finger is practically invisible. At first, the tumor does not affect surrounding structures and is not accompanied by other pathologies.
Symptoms of an advanced stage of pathology:
- growth size – from 10 cm;
- when palpated, the tumor practically does not move;
- the cyst is dense and hard;
- nagging or sharp pain, which sometimes radiates to the arm;
- the skin over the cyst turns red, becomes rough, rough.
The hygroma on the finger is clearly visible, as its size has increased. It compresses the surrounding nearby joints, nerves, tendons, and blood vessels. The pathology is accompanied by limited mobility in the affected joint, numbness, tingling, redness of the skin, inflammatory, purulent process.
Establishing diagnosis
If a patient notices a suspicious tumor on his finger, he should contact a traumatologist, surgeon or orthopedist.
Reference. The specialist will conduct a differential diagnosis to distinguish the hygroma from the leak (capsule with purulent contents), ganglion (nerve ganglion), epithelial cyst, chondroma (cartilaginous tumor), osteoma (bone tumor), aneurysm (protrusion of the artery wall), malignant formations, etc. d.
First, the doctor collects anamnesis, conducts a visual examination, and palpates the neoplasm.
To clarify the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed the following studies:
- Ultrasound helps evaluate the structure of the formation.
- Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are performed if nodular structure is suspected.
- X-ray.
To analyze the contents of the formation, a puncture is performed. During the examination, the pathological formation is punctured, the necessary cellular material is collected, and then it is studied in the laboratory.
To clarify the diagnosis and create an effective treatment regimen, doctors prescribe the following tests:
- Clinical examination of blood and urine.
- Biochemistry of blood.
- X-ray of the lungs.
- Tests to detect sexually transmitted infections, hepatitis, HIV.
- Electrocardiography.
Once the diagnosis is made, treatment is necessary.
Diagnostics is everything
To identify the root cause of the disease and select an effective course of treatment, the doctor gives the patient appointments for ultrasound, X-ray, MRI, and urine testing. The study of uric acid salts will determine the presence of gout. An x-ray will reliably demonstrate the presence of osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. However, the results of a visual examination and verbal complaints from the patient are often sufficient to make a diagnosis.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Treatment of finger hygiroma at an early stage is carried out using medications and physiotherapy. The patient should refuse physical activity.
Reference. Conservative treatment is associated with frequent relapses.
Medicines are used for non-purulent inflammation:
- Nimesil is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
- Diclofenac in the form of an ointment demonstrates a pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Clemastine in tablet form is an antihistamine that accelerates the destruction of histamine and reduces its concentration in tissues.
Physical therapy is carried out to reduce the size of the tumor, relieve or eliminate inflammation that has arisen due to compression of the surrounding tissues by the formation.
For hygroma, the following physiotherapeutic techniques are used:
- Deep heating of tissues with high frequency and intensity current. After the procedure, the inflammatory process is alleviated, blood circulation is normalized, and tissue restoration is accelerated.
- Ultrasound therapy improves blood circulation in small vessels, reduces the tone of striated and smooth muscles. Under the influence of ultrasound, more oxygen enters the tissues, and they recover faster.
- Magnetic therapy weakens the inflammatory process in cartilage and bones.
- Balneotherapy is treatment with mineral waters (sodium chloride, radon, hydrogen sulfide baths). After the procedures, adhesions and structures become softer, lengthen, and the severity of the inflammatory process decreases.
In addition, electrophoresis with glucocorticosteroids, radiotherapy, mud or paraffin wraps are used to eliminate the tumor.
To remove the tendon ganglion without surgery, a puncture is prescribed. To do this, the joint capsule is punctured, the contents of the cyst are pumped out, after which the cavity is treated with antiseptics or glucocorticosteroids (Diprospan). If the hygroma becomes infected, antibacterial drugs (Neomycin, Amicil) are injected into its cavity after aspiration (suction of the contents). The puncture is performed under local anesthesia, so the patient does not feel pain.
After the procedure, a pressure bandage and an orthosis (a medical device that relieves stress on the joints) are put on the affected area. During the rehabilitation period, it is forbidden to subject the finger to stress.
The most dangerous methods include crushing the hygroma. During the procedure, the doctor squeezes the tumor with his hands or plastic objects. When the membrane ruptures, the fluid spreads throughout the surrounding tissues, which is accompanied by intense pain.
Carefully. Crushing a hygroma is a painful method that provokes dangerous complications (inflammation, suppuration) and frequent relapses. After the procedure, the cyst shell remains inside, so the risk of new ganglia forming is high.
Surgical intervention
If conservative treatment is unsuccessful, which happens in most cases, then doctors prescribe surgery.
Bursectomy is an effective method for removing finger hygroma.
It is necessary to treat the growth surgically in the following cases:
- Education is increasing rapidly.
- Painful sensations occur that intensify during movement.
- The mobility of the joint is limited.
- Aesthetic discomfort.
Removing the growth lasts no more than 30 minutes. The area around the tumor is numbed. The surgeon excises the formation along with the membrane and fluid and carefully separates it from the joint. Then stitches are placed on the surgical wound and removed after 7–10 days.
Reference. If the tumor is large, then bursectomy is performed under general anesthesia in the hospital.
Laser treatment is an effective alternative to classical surgery. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, so there is no pain.
Using a laser beam, the skin over the cyst is cut, and the membrane with liquid is removed. Then the cavity is treated with antiseptics, stitches are placed on the wound, and the top is covered with a sterile bandage to prevent infection.
After treatment, the affected joint is fixed with brace and immobilizing plaster orthoses. They are comfortable and do not interfere with joint mobility.
Reference. After laser removal of hygroma, there are no scars. The procedure lasts approximately 15 minutes, after which the patient can go home.
Alternative Treatment
In the early stages of development of the tendon ganglion, you can use traditional medicine (complex therapy). They will not replace traditional treatment, but can speed up recovery.
Folk remedies against synovial cysts:
- Take a copper coin, heat it on a fire, and dip it in an aqueous solution of salt. Then bandage it to the damaged area. After 3 days, remove the bandage, rinse your finger and repeat the procedure.
- Take a piece of the jellyfish’s body and secure it on your finger with a bandage. After 3 hours, remove. Repeat the procedure every day. Kombucha can be used in the same way.
- Grind the cabbage leaves using a blender or meat grinder, squeeze out the juice through cheesecloth. Drink it 200 ml per day for 4 weeks.
- Squeeze the juice from celandine leaves (25 ml), apply to the tumor, after steaming your finger in hot water. Bandage it, cover it with cling film, and then wrap it in a warm cloth. Treatment lasts about 20 days.
There are many more recipes for the treatment of pathology, but they can only be used after the approval of a doctor.
Rehabilitation
The duration and complexity of the recovery period are determined by the type of surgery performed. After marginal resection, discharge can be carried out on the day of surgery, but patients are advised to limit physical activity for 2 days. Drug therapy is also prescribed to reduce the risk of developing infectious complications and eliminate pain. After 2 days, a dressing is required, the stitches are removed after 7-10 days.
When performing a corrective osteotomy, recovery is more complex and lengthy. It involves immobilization of the operated finger, which is necessary for the healing of an artificial fracture.
Thus, exostoses of the fingers and toes are a rare phenomenon, but can significantly reduce the level of physical activity, cause cosmetic defects, pain, and generally worsen the quality of life. The solution to the problem is only possible through surgery. In this case, the operation is usually simple and does not require complex recovery. The main thing is to contact an orthopedic traumatologist as soon as possible after signs of exostosis appear, before its active growth provokes deformation of the fingers.
Prevention
To prevent cyst formation, you must follow the following rules:
- If there is a hereditary predisposition to hygroma, you need to avoid injuring your hands, protect your joints, and limit monotonous mechanical loads on your hands.
- During physical work, distribute the load evenly between your hands. If you regularly engage in such activities, then use elastic bandages.
- Treat tendovaginitis (inflammation of the tendon sheath) and bursitis (inflammation of the mucous bursae of the joints) with a chronic course in a timely manner.
The latter pathologies often cause the appearance of a tumor.
As you can see, finger hygroma is not a dangerous pathology. But in order to avoid unpleasant consequences, you need to seek medical help in time and carry out competent therapy. You should not self-medicate, as this will only worsen your condition.