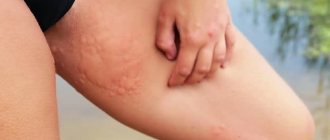
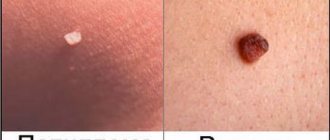
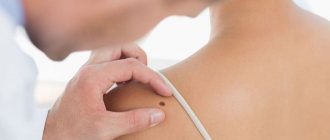
Genital warts in men appear on the mucous membranes of the genital organs when infected with human papillomavirus types 6 and 11. These seemingly harmless tumors can lead to serious complications. To prevent this, you should contact a specialist as soon as possible and remove the condylomas.
Genital warts in a man
At the Diana Clinic, patients can receive comprehensive medical care for diagnosing the HPV virus and removing genital warts in men.
Methods of infection with papillomas
If a papilloma appears on the pubis, most likely the infection occurred through sexual contact.
Human papillomavirus infection is a disease with a predominantly sexual transmission method.
Although it can also infect humans through close household contact.
But it is obvious that in everyday life people do not touch each other’s pubis or genitals.
Therefore, taking into account localization, if you find papillomas in yourself, this is a “gift” from your sexual partner.
Moreover, the infection could have occurred quite a long time ago.
It is likely that it took place several months ago.
For this reason, it is often not possible to determine the source of infection.
Incubation period of papillomas
The incubation period of human papillomavirus infection can be long and lasts several months.
The infectious process develops in two stages.
The initial stage is after the virus enters the body.
It is characterized by the persistence of HPV in episomal form.
During this period, the infected cell can produce viral particles.
Therefore, this stage is called reproductive.
During this process, the virus accumulates in the body.
Next comes the integrative stage.
The DNA of the virus is inserted into the genome of infected cells.
At the initial stage, the pathology is reversible.
Many go into remission.
Papillomas do not appear on the pubis, and malignant tumors do not develop.
If the disease enters the integrative stage, various skin formations begin to appear.
Causes
The main trigger for the occurrence of neoplasms is HPV activation. A large number of people are infected with different forms of the virus, but may not know it. The papillomavirus can remain latent for a long time, and then show itself in the form of external manifestations - papillomas. At the same time, their location can be completely different: from small tumors on the neck to large growths on the pubis.
Factors that provoke the development of the disease can be:
- chronic diseases;
- hormonal drugs;
- pregnancy period;
- the presence of infectious and inflammatory processes;
- frequent viral diseases.
All these processes can weaken the immune system, resulting in activation of the papillomavirus.
How contagious is the papilloma virus?
HPV is a highly contagious infection.
The risk of infection with one contact reaches 70%.
It penetrates through microdamages of the skin and mucous membranes.
Even a condom does not protect against the virus.
Because it can enter the body, for example, through the skin on the pubis.
Due to its high contagiousness, there is a high percentage of people infected with HPV at a young age.
Those infected in the age category of 15-30 years are about 20-25% of the general population.
After 30 years, the number of virus carriers decreases to 8-9%.
HPV persists in the body for a long time.
But for most people it does not cause symptoms.
After a few months or years, it is eliminated on its own.
Papillomas on the pubis appear only if a person has a weak immune system.
Then the virus actively multiplies and causes mutations in skin cells.
Benign and sometimes malignant oncological formations appear.
What causes the disease
The causative agent of papillomatosis is a virus that can penetrate the body by all available means. There is an opinion that HPV can only enter the body through sexual intercourse. However, doctors were able to prove that infection occurs not only during sex. A person runs the risk of becoming a carrier of HPV by not following the rules of personal hygiene and by coming into contact with objects that were used by an infected person. The papilloma virus is transmitted in utero through the placenta from mother to fetus.
It is worth noting that using a condom does not guarantee 100% protection against contracting this infection. If your partner has flat hanging warts in the pubic and groin area, most likely, after the first sexual intercourse, the virus will be transmitted to you. The epidermis of the genital organs is highly susceptible to various types of infectious agents, and the papilloma virus has the property of penetrating into the deep epithelial layers. Using a personal towel and washcloth will help minimize the risk of infection.
Symptoms and types of papillomas
The signs of papillomas are quite obvious.
Small pedunculated formations appear on the skin.
They rise significantly above the level of the skin.
The color may be red or flesh-colored.
Blood vessels are visible in them.
Types of skin lesions due to human papillomavirus infection:
- genital warts (the most common variant)
- spots
- papules
- bowenoid papulosis
- giant condyloma
In addition to the formation on the skin itself, other symptoms are possible.
Patients may complain of itching and pain.
Sometimes there is a tingling or crawling sensation.
Painful cracks in the skin may occur.
Tests for diagnosing papillomavirus
The very fact of detection of papillomas may be sufficient grounds for their removal.
It doesn't matter how dangerous they are.
The main thing is that these formations look ugly and can interfere with the quality of sexual life.
But still, a person who comes in with pubic papillomas is usually examined.
First of all, in order to find out what type of HPV affected his skin.
It can be low-, medium-, or highly oncogenic.
If oncogenic types are detected, the patient is monitored dynamically.
Because the risk of cancer remains even after papillomas are removed.
PCR is used to determine the type.
A scraping of the pubic skin is taken.
It is then examined to identify a fragment of the virus's DNA.
Women are also recommended to undergo smears for oncocytology.
Sometimes your doctor will order testing for other STDs.
Because in the presence of papillomavirus, they are detected quite often - in approximately 50% of patients.
The person himself is often unaware of them.
Because sexually transmitted infections may not be accompanied by symptoms.
Conservative treatment of the disease
If there are no clear indications for removal of growths, the doctor selects suitable medications for the patient from the group of antiviral and immunostimulating agents. Thanks to such medications, it is possible to reduce the activity of HPV infection and strengthen the body's defenses.
In addition to medications, patients with papillomatosis are often prescribed topical medications. Experts do not recommend purchasing such medications at your own discretion due to the high risk of burns and improper scarring of the wound. External agents include liquid solutions and ointments that contain trichloroacetic acid. The medicine is carefully applied to the warts, trying to avoid contact with the healthy epidermis.
Tests for an immunologist and an immunogram for pubic papillomas
Papillomas almost always appear against a background of reduced immunity.
Therefore, patients need to consult an immunologist and conduct a study of the activity of the immune system.
This is necessary because:
- allows us to predict the development of the disease
- makes it possible to select immunomodulatory therapy
A person with poor immunity suffers not only from papillomas.
He exposes himself to the risk of dangerous infectious diseases.
Nonspecific inflammatory processes may occur in the body.
Therefore, even after removal of papillomas, it is worth adjusting the immune system.
This will help avoid recurrence of the formation of anogenital warts.
It will also prevent other diseases of infectious origin.
Factors that provoke HPV activity
From the moment the infectious agent enters the body until the first manifestations of the disease, more than one month, and sometimes even several years, may pass. How the virus behaves depends largely on the state of the person’s immune system. Even with a slight weakening of the immune system, HPV can enter the active stage. The following reasons may contribute to the development of the disease:
- weight change and exhaustion of the body;
- pregnancy and long lactation;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- stress and nervous experiences;
- relapse of chronic diseases.
Histology and oncocytology for papillomas
HPV is dangerous for the body.
Especially for women.
In them, the presence of papillomas can result in cervical cancer.
But the virus is dangerous in men too.
In both sexes, HPV causes squamous cell carcinoma.
In total, about 180 types of virus are known.
Of these, 29 have oncogenic potential.
Therefore, it is advisable to examine women with identified papillomas.
They need regular monitoring while the virus is in the body.
Even if the papillomas are removed, the risk of cancer remains.
To avoid pathology, it is worth taking a smear for oncocytology once every six months.
It is taken from the cervix.
The doctor checks whether there are atypical cells in it.
If necessary, if the result of an oncocytology test is unfavorable, clarifying studies are prescribed.
The doctor performs a colposcopy.
Using a special device, he examines the vaginal part of the cervix under a magnification of several tens of times.
This way the doctor can see pathologically changed areas of the epithelium.
Before developing into cancer, the papilloma virus causes dysplasia.
At first it has the first degree, then the second.
Both are reversible.
The first degree regresses on its own in most women, the second - only in 30%.
With the third degree, the risk of degeneration into cancer reaches 80%.
Therefore, grade 2-3 dysplasia is an indication for surgical treatment.
Pathological areas of the altered epithelium are “cauterized.”
This helps prevent cancer.
Timely performance of oncocytology is of utmost importance in the early detection of dysplasia.
A woman who is not lazy to visit a gynecologist once every six months can prevent cervical cancer with almost 100% success.
Sometimes, at the time of removal, papillomas already look suspicious.
In unfavorable cases, they can degenerate into squamous cell carcinoma.
Then they are sent for histological examination after removal.
The doctor examines the structure of the tissue and looks for signs of malignancy.
Histological diagnosis is also used if it is necessary to distinguish papilloma from other benign skin tumors.
If signs of malignancy are detected, the scope of the operation can be expanded.
Next, we will consider what methods are used to remove papillomas, what advantages and disadvantages they have.
Signs of defeat
The first symptom of infection is the appearance of warts in the pubic area.
This mainly occurs through sexual intercourse, the virus is transmitted from an infected partner to a healthy one. A person becomes infected with one of the types of virus - pointed or filamentous papillomas, as in the photo. They differ in their natural origin, shape and color. Pointed growths look like small flesh-colored or pink papillae and affect the pubic area in several places at the same time. They are particularly dangerous for women as they can lead to cervical cancer.
Thread-like, cone-shaped papillomas are pale yellow in color. They have the ability to grow, enlarge and merge with each other over time. This pathology is typical for women approaching menopause.
Symptoms of the disease:
- warts appear on the inside of the genitals;
- formations inside the vagina, on the internal membranes;
- In case of injury, bleeding and pain are noted;
- strong growth;
- the growths acquire a flesh-colored, pale brown color;
- constant feeling of discomfort in the pubic and genital area;
- sexual intercourse causes pain;
- frequent infectious pathologies;
- unpleasant smell.
In women, against the background of papillomavirus, it is possible to develop pelvic cancer. Timely diagnosis and removal of warts will help prevent the further development of pathology.
Diagnostics
If there are tumors on the pubis, women should visit a gynecologist, men a urologist. A dermatologist can consult patients.
An examination is necessary to establish the correct treatment and determine the type of papillomavirus that provoked the pathology. Diagnostics is very important, because the results will show how dangerous the virus is to human life and will help create the correct treatment regimen.
There are several categories of papillomavirus:
- The first group – there is no oncogenicity (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 28, 49).
- The second group is rare oncogenicity (6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 51, 72).
- The third group is medium oncogenicity (26, 30, 35, 52, 53, 56, 58, 65).
- The fourth group is increased oncogenicity (16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 45, 50, 59, 61, 62, 64, 68, 70, 73).
Diagnostics consists of conducting a PCR analysis, which is necessary to determine the strain of the virus and its concentration. The test is so accurate that no further laboratory procedures are required. The doctor may prescribe a biopsy or cytological examination.
Removal of papillomas with liquid nitrogen
Cryodestruction is one of the oldest methods in dermatology.
It is also the most accessible.
Any dermatologist, including a public clinic, can remove pubic papillomas with liquid nitrogen.
Because this does not require special equipment.
You just need to take a stick with cotton wool, dip it in liquid nitrogen and press it onto the papilloma for a few seconds.
This is how tissue is frozen.
And frozen tissue subsequently dies.
The method has both advantages and disadvantages.
Its advantages:
- no anesthesia is required, since removing pubic papillomas with nitrogen is almost painless
- low costs for the procedure itself
- no need to buy anesthetics or pay for an anesthetic injection
- You can remove papillomas with nitrogen from any doctor - it’s a simple and affordable procedure
But there are also disadvantages.
After the procedure, an inflammatory reaction is observed and the patient experiences pain.
Only the smallest papillomas can be removed.
And if they are large, there is a risk of freezing the tissue too deeply.
In this case, scars will appear on the skin.
They can also form if a person's skin is too thin and vulnerable.
Then even the usual time of exposure to liquid nitrogen on the papilloma may become excessive for the patient.
Once the formation is frozen, it will not be possible to send it for histological examination.
This is another disadvantage of this procedure.
But it still remains one of the tools for removing papillomas for dermatologists.
Because it makes it possible to quickly and effectively remove many small formations on the pubis.
Electrocoagulation of pubic papillomas
The method of electrocoagulation of pubic papillomas in women and men allows the papillomas to be cauterized or separated from the body due to temperature exposure.
The tissues become very hot and are destroyed.
Using electrocoagulation, you can both “burn” the papilloma and separate it from the body.
This makes it possible to send the formation for histological examination.
Other advantages of the method:
- possibility of removing even large pubic papillomas
- absence of bleeding, as simultaneous coagulation of blood vessels occurs
- low risk of relapse
Electrocoagulation also has disadvantages.
The method has a greater risk of scarring than other methods, which will be discussed below.
When removing pubic papillomas using electrocoagulation, the doctor needs to use anesthesia.
Because this procedure is painful.
After it, pain may occur.
Because nearby tissues also heat up and become damaged.
Intimate condylomas
Having penetrated the body, human papillomaviruses penetrate the basal layer of the epithelium, especially in the zone of transition of stratified squamous epithelium to columnar epithelium. In a cell, HPV can exist in two forms - outside the cell’s chromosomes or integrated into the genome. Regardless of its location in the cell, the virus will be detected when the smear is tested for PCR. Being in a cell outside the chromosomes, the virus can either not cause clinical changes (latent, hidden course), or lead to increased reproduction of unchanged (!) cells and clinically manifest in the form of warts or papillomas, for example, in the same intimate places.
Another variant of virus behavior is integration into the cell genome. In this case, it either leads to the development of neoplasia (grade 1-3 dysplasia), which ultimately becomes the cause of the development of carcinoma (malignant process - invasive cancer).
Hidden form
A less common variant of the clinical course of intimate condylomas in women and girls. Latent course of human papillomavirus infection without any changes in the skin or other manifestations, i.e. in this case, visible growths of genital warts in the intimate area or any other area of the body are not always observed. At the same time, the virus behaves “autonomously”, without interfering with the life activity of healthy human cells (there are types of papillomaviruses that do not manifest themselves in the human body throughout his entire life).
Active form
In this form, the body reacts to its presence in the cells and makes attempts to “limit” the further spread of the papillomavirus. This is achieved due to the compensatory proliferation of cells in the basal layer of the skin, resulting in the creation of a kind of “sarcophagus” of cells. As you probably guessed, this formation is called a “genital wart” or “intimate condyloma.” In this case, the virus integrates with the genome of human cells, as a result of which they are modified, which leads to dysplasia of the affected tissue area, or even cancer (the most common location of this process is the cervix, provoked by HPV types 16 and 18). A woman can be infected with several types of HPV at the same time.
As a rule, from the moment of infection to the appearance of papilloma (whether it is a wart or genital wart in the intimate area) time passes from several weeks to 9-10 months, and until the appearance of cervical or rectal cancer - from 5 to 15 years, depending on the type of HPV , its concentration (viral load) and, of course, the state of the human immune system. The relevance of condylomas in women is also due to the fact that highly oncogenic types of the virus increase the risk of developing precancerous diseases of the vulva and vagina by 60 times. Removal of condylomas in a clinic by a gynecologist (not self-medication at home!) is the main way to prevent this complication!
Questions - answers
1. WHERE CONDYLOMA GROWS. In women, they appear most often on the external genitalia in the area of the labia minora, less often on the labia majora, often in the vagina, on the cervix, in the urethra, perineum and near the anus. They are much less common on the clitoris, mouth, throat and anal canal. In masturbating girls or virgins who practice sexual games “without penetration” into the vagina, a gynecological examination can often reveal papillomatosis of the vestibule and hymen. See photos of condylomas in women.
2. CAN CONDYLOMAS GO AWAY BY THEMSELVES AND DISAPPEAR? At a young age, the immune system works very well, there are no chronic diseases, so condyloma in an intimate place can either suddenly appear or suddenly disappear. Especially if it is caused by non-oncogenic types of HPV and in a low titer (see quantitative analysis for condylomas in the table below).
3. WHEN ARE INTIMATE CONDYLOMAS CONtagious? If HPV enters a healthy body with good immunity, it may not appear clinically for some time. Sometimes this period lasts months and years (the incubation period can last from several weeks to 2-3 years). If the HPV that enters the human body is not an oncogenic type, it does not pose any threat to the carrier itself and is not transmitted to others. But as soon as an exacerbation begins, and genital warts or papillomas grow in the intimate area or on the skin, it begins to be transmitted to the contactee upon any contact.
4. CONDYLOMAS WITHOUT HPV - DOES IT HAPPEN? Are genital warts possible without HPV? In women and men, these formations are a consequence of the human papillomavirus entering the body. However, when asking questions to a gynecologist or on medical forums, many people discuss a negative HPV test, but there are papillomas or condylomas. Let’s clarify this situation and give a few reasons why this could be:
- Violation of the rules for collecting material for analysis;
- The NGE laboratory conducts this range of research;
- Failures in the technological process of performing the analysis;
- More than 100 types of HPV are known to medicine, and many of them can cause various formations on the body. As a rule, laboratories diagnose only 14 main, clinically significant, types of high oncogenic risk, for example, 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 56, etc. Therefore, negative HPV in the presence of condylomas indicates that your disease is caused by non-oncogenic types of the virus. This is prognostically more favorable (of course, if paragraphs 1-3 are irrelevant).
5. IS IT POSSIBLE TO COMPLETELY CURE HPV IN WOMEN? There are currently no treatments for condylomas with reliably proven effectiveness. Systemic therapy for HPV infection has not been developed and is only necessary in the case of complicated HPV infection (papillomas, condylomas, dysplasia, erosion), or long-term, recurrent HPV infection, especially when high cancer risk types of the virus are identified. For example, in the presence of HPV and condylomas, it is necessary to remove formations as a source of infection and carry out complex antiviral therapy.
As for the use of immunomodulators, their use should be balanced, reasoned and after a blood test for immune status. Afterwards, dynamic monitoring should be carried out - regular HPV Digen test, PAP test (cervical oncocytology), colposcopy and vulvoscopy to identify possible foci of relapse of genital papillomatosis. Consider getting vaccinated against HPV. The Gardasil vaccine, of course, will not protect against the type that already exists, but it will help prevent infection with other dangerous types of HPV.
6. HOW TO REMOVE CONDILOMAS AT HOME? If you really want to, you can find tips on how to remove genital warts at home. For example, on the Internet there are tips on how to cauterize intimate warts with acid, lubricate them with ointments and creams, herbal recipes from “grandmother..., grandfather...” and other all-scientific and sometimes downright harmful recommendations. I will quote one patient of our gynecology, who tried to get rid of papillomas between her legs on her own, received a rather strong side effect from the so-called “folk recipes” and came to the conclusion that “... a woman has only one pussy and she must be treated with care, with trepidation, and trust her health, well-being and appearance only to medical professionals!”
7. CAN CLEANING THE BODY FROM PARASITES HELP? Attempts to cleanse the body of papillomas in the intimate area instead of removing them, as well as to expel other parasites (germs, worms, viruses, including HPV) with various microwaves, UHF currents, exposure to resonant frequencies and other similar undertakings - shamanism, quackery or It's just pure fraud. By expelling uninvited intestinal inhabitants with a pharmaceutical drug, you will certainly be doing your body a favor, but you will not get rid of HPV and genital warts from your intimate area!
8. EROSION AND CONDYLOMA In gynecology, cervical erosion is a collective concept that simply describes certain changes in the cervical mucosa, but is not a diagnosis as such. Accordingly, not all erosion requires treatment. In order to determine what exactly led to its formation, it is necessary to do a cytological examination of the scraping and an extended colposcopy. If you just have ectopia (false erosion associated with hormonal characteristics in the period up to 22 - 25 years, in women who have not given birth), it is uncomplicated and small in size, then it does not require treatment. If you are diagnosed not with ectopia, but with any transformation of the mucous membrane, especially in the presence of intimate warts or papillomas, you need to be examined for HPV types (Digen test) and hidden infections. The next step may be a biopsy of the cervix (taking a section of tissue). Histological examination allows us to understand the nature of changes in the cervix, confirm or refute the presence of flat “cervical” warts, which will give the correct final diagnosis and help the doctor choose the optimal method of treatment or cauterization of condylomas.
Laser vaporization of pubic papillomas
A laser is used to destroy pubic papillomas.
With short pulses, the tissues are heated to such an extent that they simply evaporate.
In this case, the areas of skin located next to the papilloma are not affected.
The laser allows you to evaporate papilloma with maximum precision.
There is a risk of scarring, but it is small.
Less than when using electrocoagulation.
The laser coagulates blood vessels more effectively.
This is a non-contact technique.
Therefore, there is not the slightest risk of wound infection during the procedure.
If the infection gets into the skin, this can only happen after removal, if the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations.
But there are also disadvantages.
Only small or medium-sized papillomas can be removed.
Large formations are usually not removed with a laser, preferring other methods.
Plus, there is no material left for histological examination.
If it is necessary, then preference is given to other methods of combating pubic papillomas.
Radio wave removal of papillomas
For medium and large papillomas, radio wave removal is often used.
It has a number of advantages compared to other methods.
The doctor can control the depth of exposure.
Therefore, if removed correctly, scars usually do not appear.
After this procedure, there is a minimal risk of relapse.
The resulting tissue can be sent for histological examination.
Removal of pubic papillomas is performed under local anesthesia.
Application or infiltration anesthesia can be used.
More often it is infiltrative.
The doctor uses a syringe with a thin needle to inject anesthetics into the skin.
He punctures the base of the papilloma.
Then, during its removal, the person does not feel anything.
Consequences of deletion: reviews
The procedures for excision of warts themselves are easily tolerated - this is evidenced by many comments from patients. During removal, people often experience unpleasant sensations such as burning, tingling, and mild pain.
Data also differ about the healing time of the wound. Depending on the type of procedure, for full recovery patients need:
- 14-18 days after cryodestruction;
- 7-10 days after laser removal;
- 4-7 days after radio wave excision;
- up to 30 days after removal with a scalpel.
The recovery period lasts the longest in patients who have had several papillomas removed at once. In their reviews, many complained about the difficulty of subsequent care of the wound surface, constant itching, swelling and a strict ban on visiting solariums, baths, swimming pools, saunas, and open-air reservoirs for the next three weeks.
Keloid and hypertrophic scars after removal of papillomas
Sometimes scars form after removal of papillomas.
More often they occur if the removal was carried out at home or by an incompetent specialist.
A greater risk of scarring occurs when using folk remedies or chemical cauterization.
Correct implementation of destructive procedures reduces the risk of scar formation to a minimum.
But still, in a certain percentage of patients they appear.
Even if the most modern methods are used and the papilloma is removed by an experienced doctor, scars may appear.
This occurs when the deep layers of the skin are damaged.
Subsequently, such scars can also be removed.
There are also drugs that significantly reduce their size.
Chemical coagulation of papillomas
Chemical coagulation is one of the methods for removing pubic papillomas.
Concentrated solutions of acids or alkalis are used.
They cause a chemical burn to the skin at the site of application.
After this, the damaged tissues die.
The drugs Feresol and Solcoderm are used.
These methods are effective, but sometimes they can be quite traumatic.
Patients often use these drugs on their own.
In this case, the solutions enter the surrounding tissues, causing their necrosis.
In the future, scarring is possible if the impact was too deep.
Localization of condylomas in men
In men, genital warts appear in the following places:
- glans penis;
- surface of the inner layer of the foreskin;
- coronal sulcus;
- near the external opening of the urethra;
- in the perianal zone (near the anus);
- crotch area.
The growths can be single or multiple. They don't hurt or itch. Other unpleasant symptoms appear only when tumors are injured. In this case, the growths may bleed, hurt, and cause other discomfort.
Folk remedies for removing pubic papillomas
The use of folk remedies is ineffective in most cases.
Often folk recipes are not pathogenetically justified.
They are based on conspiracies, ineffective plants, etc.
Sometimes such methods work, because in 15% of cases papillomas disappear on their own.
Usually, no result can be achieved.
The exception is when plants that have a cytotoxic effect or can cause a chemical burn to the skin are used.
The fight against papillomas can be effective if you use:
- thuja juice
- celandine
Podophyllotoxin used in medicine is also of plant origin.
But the plant from which it is made grows in North America.
Pubic papillomas: immunological treatment and antiviral drugs
After papillomas are removed, doctors often prescribe treatment to suppress the virus.
Applicable:
- means for stimulating the immune system
- general antiviral drugs
Interferons are most often prescribed.
They simultaneously stimulate the immune system, kill viruses and have antiproliferative activity.
Used locally and systemically.
Local interferons have low effectiveness against HPV.
Therefore, they are rarely used in monotherapy.
Mostly prescribed in addition to systemic medications.
For pubic papillomas, alpha interferon is prescribed intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
It is used in a dose of 1.5 to 3 million IU, every other day.
The course of treatment is 1 month.
After such a course, papillomas sometimes disappear even without their physical removal.
Local therapy is also used.
The drugs are injected into the lesions or applied in the form of a gel.
Cytokine inducers are also used.
Imiquimod is prescribed as a 5% cream at night.
It is used in a course of several months.
Warts disappear in 50-60% of cases.
Without treatment, over the same period they disappear in only 15% of patients.
For the treatment of HPV, inducers of endogenous interferon synthesis can be prescribed.
They are mainly used in combination with the destruction of pubic warts.
The drug Gepon is used.
Mechanisms of action:
- increased interferon production
- suppression of HPV replication
- increased macrophage activity
- decreased cytokine production and decreased inflammatory response
- increased antibody production
- increased nonspecific resistance of the body
The drug is prescribed orally at a dose of 2 mg, 3 times a week.
Other medicines that may also be used include:
Isoprinosine - a course of 5 days, 50 mg per kg per day in three doses, a total of 3 courses are needed.
Panavir - after one injection increases the level of leukocyte interferon by 3 times.
Glycyrrhizic acid – activates local immunity, blocks the introduction of the virus into the cell.
There are many other drugs that destroy viruses or enhance immunity.
Which of them should be prescribed is decided by the immunologist.
The decision is made based on the results of the immunogram.
Symptoms of papillomatosis
It is not difficult to recognize this disease. It is impossible to confuse hanging warts on the pubis with anything else. The characteristic rashes in the genital area resemble spiky or thread-like growths. Their structure is heterogeneous, the shape and type of neoplasm differs from hanging nevi. The hue of papilloma is mostly pale flesh-colored, but sometimes it can turn red or darken, becoming almost black. The latent period of the disease lasts from several months to several years. The first rash appears suddenly, is cone-shaped and slightly yellowish in color. The size of papillomas can reach 5-7 mm.
Side effects of immunomodulators for papillomas
Flu-like conditions often develop when interferons are used.
Body temperature rises, signs of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract appear.
There is a headache.
The higher the dose, the greater the risk of side effects.
They can be relieved by using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
When using cytokine inducers, local reactions may occur.
This is redness, swelling, and the formation of erosions on the skin.
Control tests after treatment of papillomas
After treatment of pubic papillomas, laboratory monitoring is needed.
It is required for:
- viral load estimates
- prevention of recurrence of papillomas (by timely administration of a course of antiviral therapy)
- determining the likelihood of malignant oncological diseases
Control involves performing quantitative studies for human papillomavirus infection.
If it decreases, the virus is likely to be eliminated soon.
In the future, papillomas will not appear.
An increase in the number of papillomavirus DNA copies indicates the need for further antiviral therapy.
Recurrence of skin formations is possible.
In this case, they will have to be deleted again.
In addition, women regularly undergo smears for oncocytology.
This is required if oncogenic HPV types are detected during PCR.