Vulvar itching is one of the most common complaints in gynecological practice. Usually the disorder occurs against the background of another pathology or under the influence of external factors. It is extremely rare that a disorder is regarded as an independent disease. Today, over 300 diseases are known that are accompanied by itching in the genital area. Often the reasons for its development are directly related to the patient’s age. In girls, adolescents and girls, itching is provoked by inflammatory processes, in women over 30 years old - gynecological, somatic and endocrine diseases, during menopause - hypoestrogenism and associated involutive changes in the mucous membranes of the genital organs.
Causes
Unpleasant itching sensations in the area of the external genitalia appear as a result of unfavorable external influences, genital and extragenital diseases. In some cases, the factors that provoke the occurrence of itching remain unknown. Specialists in the field of obstetrics and gynecology identify five main groups of reasons for which this disorder develops:
- Inflammatory urogenital pathology
. Burning and itching in the genital area are a characteristic symptom of vulvitis, vaginitis, bacterial vaginosis, endocervicitis, urethritis, cystitis caused by opportunistic flora or pathogens of specific infections - chlamydia, genital herpes, candidiasis, mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, etc. When the mucous membrane is inflamed constantly irritated by discharge. - Non-inflammatory diseases of the vulva
. They usually result from age-related involutive changes caused by a decrease in estrogen levels. Itching due to dry mucous membranes is accompanied by kraurosis (lichen sclerosus), leukoplakia (squamous hyperplasia), post-castration syndrome after removal of the ovaries. Itchy sensations are also characteristic of vulvar cancer and genital psoriasis. - External factors
. The disorder occurs due to mechanical irritation from rough fabric, contaminated linen, parasites (scabies mites, pinworms, other pathogens of helminthic infestations). Itching of the vulva can be provoked by thermal effects (especially hypothermia), chemical agents, allergens, and observed when taking phenothiazine derivatives, hormonal contraceptives, erythromycin, aspirin, etc. - Extragenital diseases
. A burning sensation in the vulva is observed with an increase in the concentration of certain metabolites in patients suffering from diabetes, hepatitis, renal failure, leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, gout, thyroid dysfunction, Sjogren's syndrome and other autoimmune processes. Complaints also appear with skin diseases - lichen planus, lichen rosea, eczema. - Mental and neurological disorders
. According to many obstetricians and gynecologists, the sensation of itching in the external genitalia and the degree of its severity largely depend on the state of the peripheral and central nervous system. Provoking factors include psychological and sexual trauma, neuroses, depression, prolonged or severe stress. These disorders are highly resistant to treatment.
Itching of the vulva
Starting period of therapy
If a person is bothered by itching, he should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment as early as possible. Many infections can affect the genitals, causing many complications, including infertility. The earlier therapy is started, the lower the risk of their development.
Lack of quality hygiene
This is one of the most common problems that cause itching in the groin. You are required to shower at least once a day. To relieve disturbing symptoms, use a decoction based on plant extracts:
- chamomile, calendula, string;
- oak bark, celandine.
To prepare a decoction, take one or several plants at once and pour boiling water over it. After infusion and straining, wash the area of the penis and adjacent tissues.
After treatment, wipe the skin dry with a towel. Next, apply a regenerative and moisturizing cream. For example, Sinaflan.
Sinaflan is a glucocorticosteroid intended for external use. It eliminates inflammation, allergies, exudate, and active itching. The action is formed by suppressing the negative influence of the immune system. The drug is applied to the affected skin. Sinaflan is recommended for use for dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, and skin itching of various origins. It is used up to 3 times a day. The drug has a small list of side effects that develop extremely rarely:
- purpura, telangiectasia, skin atrophy;
- hypertrichosis, secondary infection, perioral dermatitis.
The product is not recommended for pregnant women with bacterial, fungal, or viral infections. With prolonged use, the steroid causes a decrease in blood supply to tissues, so atrophic processes may develop. Because of this factor, doctors prescribe the drug in a short course, up to 1 week.
Food allergies
Itching is provoked by foods that cause allergies. Treatment is required to relieve the acute condition:
- taking an oral antihistamine;
- application of an intimate gel with a neutral acid-base state;
- treatment with an antiseptic solution, for example, Furacilin;
- applying baby powder.
During therapy, they refuse synthetic underwear and do not visit the sauna, bathhouse, or swimming pool. Any sexual intercourse is possible after completion of therapy.
After 3-4 days, the patient’s condition completely normalizes. But in the future you will need to eliminate foods that cause hypersensitivity.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis in other words is called thrush. To eliminate it, use the following measures:
- frequent hygiene procedures, you can use herbal decoctions for treatment;
- applying antifungal ointments containing clotrimazole or fluconazole;
- in severe cases, an oral antifungal drug is used, but in a short course, so as not to cause a load on the liver.
Follow a diet low in dairy products, sugar, and baked goods.
Ureaplasmosis
It is almost impossible to completely destroy ureaplasma from the body. But it is necessary to reduce its concentration by using antibacterial agents. For example, Doxycycline, Josamycin. Additionally, immunostimulants are used so that the body can fight the infection on its own.
Ureaplasmosis is dangerous because it does not cause negative clinical symptoms for a long time. But gradually, without treatment, it penetrates deeper and deeper into the urethra, spreading to the internal genital organs. This can lead to infertility. If a man transmits a pathogenic microorganism to a woman, reproductive dysfunction occurs much faster.
Antibiotics are used for treatment, but it is impossible to completely eliminate the pathogenic microorganism, since it belongs to the bacteria of opportunistic microflora. Therefore, a man must monitor the condition of the penis and the discharge from it. If any changes occur, immediately make an appointment with a urologist.
Chlamydia
The earlier treatment for chlamydia is started, the lower the risk of damage to the reproductive system, including infertility. Treatment methods:
- oral antibiotics - Ceftriaxone, Amoxiclav, Azithromycin, Macropen;
- immunostimulating drugs - Lysozyme, Dekaris;
- enzymes to improve intestinal microflora - Mezim;
- probiotics - Normobact.
If you use drugs in combination, recovery occurs faster.
Genital herpes
If a person has genital herpes, the condition is accompanied by a profuse rash, it is necessary to immediately begin antiviral therapy:
- an antiviral agent containing acyclovir;
- interferon-based immunostimulants.
Herpes is a rather dangerous disease that causes complications. Therefore, the choice of drug depends only on the doctor; it is forbidden to change its dosage on your own.
Scabies mite
The microorganism quickly causes severe, long-lasting itching. The place where it is located needs to be lubricated with special creams. For example, Crotamiton, Lindane. Therapy is long-term, at least 10 days.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of formation of vulvar itching is based on the peculiarities of the innervation of the perineum, labia minora and labia majora. The branches of the iliac, pudendal, femoral and rectal nerves approach this area. When various stimuli are applied to the endings of unmyelinated C-fibers, poorly differentiated impulses, perceived as itching, tingling, burning and even pain, enter the sensitive zone of the cerebral cortex through the spinal cord.
The nature of the stimulus is usually determined by the immediate cause of the pathology. These may be drying secretions, local changes in the mucosa, metabolites, thermal, mechanical and chemical factors. Sometimes the action of irritants leads to the release of histamine, causing swelling and itching in the affected area. The pathogenesis of the disorder in mental disorders is apparently associated with a decrease in the threshold of sensitivity and increased excitability of brain structures.
Symptoms of the phenomenon
Regardless of the considerations and suspicions that women and men may have regarding the causes of the problem, the initial step in solving it should be to seek qualified help.
The doctor will refer the patient for tests, which will reveal the exact reason why the pubic area began to itch.
Symptoms accompanying pubic irritation can be numerous. But as a rule, in the intimate area in men and women the following manifestations are observed:
- rash;
- redness;
- swelling;
- secretion of mucus in the intimate area.
Based on these symptoms, as well as the results of laboratory tests, the causes of itching on the pubis are determined. As already noted, provoking factors can be both physiological and infectious.
Symptoms of vulvar itching
A woman complains of burning, tingling, itching, and other uncomfortable sensations that bother her constantly or occur in attacks, more often in the evening or at night. With a long course of the underlying disease, areas of redness, scratching, cracks, and ulcerative defects appear on the genital mucosa. Often the itching spreads from the perineum and labia to the skin near the anus and inner thighs. With the development of the inflammatory process, pain, light yellow, greenish, grayish-white, cheesy or copious liquid discharge with an unpleasant odor are noted.
Mechanical damage and itching
Mechanical damage can occur due to improper hair removal in the groin area. Especially often, skin rashes appear after shaving at home with a regular razor or epilator; sometimes women can accidentally damage the skin. There are also cases when hair grows back after removal and small pimples form, most often painful.
During salon hair removal, there is also a possibility of irritation, so the specialist immediately after the procedure treats the skin with a fatty cream or a special solution.
Complications
To relieve intense discomfort, women often rub or scratch the itchy areas. Mechanical stress increases irritation, which leads to the formation of scratching, erosion, and ulceration. Infection of the mucous membrane aggravates the course of the underlying pathology due to the addition of vulvitis. In chronic somatic, endocrine and inflammatory genital diseases, dysplastic and neoplastic processes may occur against the background of prolonged irritation of the vulvar mucosa. Constant discomfort in the genital area causes the development of anxiety-depressive, hypochondriacal and other neurotic disorders.
Vulvoscopy
Traditional methods of treatment
The above remedies will help relieve itching
If there are external causes of itching, you should not rub the skin until it bleeds, but try to help yourself.
- Treat acne with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, soda, herbal decoctions, furatsilin, hydrogen peroxide.
- Apply aloe leaves after cutting them to improve the flow of juice. You can apply a gauze strip soaked in aloe juice or Vishnevsky ointment to the inflamed area, securing it with a “breathable” plaster.
- Douche with soda solution (1 teaspoon per liter of water) 3 times a day.
- Take vitamins, royal jelly in capsules or tablets.
- Include more vegetables, fruits, berries, juices in your diet, exclude fast food, fatty foods, and alcohol.
During treatment procedures, do not depilate, because this can only aggravate the discomfort. This does not apply to lice, in which hair removal is the first step in treating the disease.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic task for complaints of vulvar itching is to determine the cause that caused it. At the first stage of the examination, the gynecologist examines the external genitalia and perineum. Upon examination, changes in the color and condition of the mucous membranes (redness, areas of hyperkeratosis, damage due to friction and scratching), condylomas, other formations, and discharge in the vestibule of the vagina are revealed. Next, a comprehensive laboratory and instrumental examination is prescribed. The most informative methods are:
- Vulvoscopy
. Examination of the vulva and perineum under a colposcope is performed to detect local inflammation, dysplasia, hyperproliferation, atrophy, and malignant degeneration of the skin and mucous membranes. If necessary, the procedure is carried out in an expanded version with surface treatment with various medications. - Histological examination
. In the presence of local changes in the tissue of the vulva, it is recommended to take a biopsy sample with subsequent examination of the obtained material. The method makes it possible to accurately determine the nature of changes in the external genitalia and promptly identify oncopathology. - Microscopy and culture of secretions
. Microbiological examination allows us to detect possible pathogens of infectious and inflammatory processes and clarify their sensitivity to antibiotics. According to indications, microbial antigens and antibody titers are additionally determined (RIF, ELISA, PCR).
To establish the genital causes of itching, speculum examination, bimanual examination, cervicoscopy, hysteroscopy, and other special methods for diagnosing gynecological diseases are used. Tests and studies to identify extragenital pathology are prescribed by specialized specialists - urologists, therapists, gastroenterologists, dermatologists, venereologists, infectious disease specialists and allergists-immunologists. If there are no morphological prerequisites for the occurrence of vulvar itching, the patient is examined by a neurologist and a psychiatrist. Differential diagnosis is carried out with vulvodynia, as well as between diseases and conditions for which discomfort is observed in the vulvar area.
Treatment for vulvar itching
Therapeutic tactics are aimed at eliminating the causes of the disorder, reducing its severity or completely eliminating it. Depending on the etiology, the patient is prescribed antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory drugs, eubiotics, estrogens, immunomodulators, drugs for the treatment of somatic, endocrine, and other extragenital pathologies. For intense itching that significantly reduces a woman’s quality of life, the following are effective:
- Detoxification therapy
. Means for the active, rapid removal of pathological metabolites are usually used in the form of droppers, if necessary supplemented with forced diuresis. It is possible to use enterosorbents. - Antihistamines
. Some of the symptoms of inflammatory, allergic and autoimmune reactions are due to the effects of histamine. Drug blocking of histamine receptors can reduce itching and swelling of tissues. - Novocaine blockade of the pudendal nerve
. For patients with persistent, painful sensations, the affected area is injected with anesthetic solutions. Although this method provides only a temporary effect, it is chosen when it is important to ensure normal sleep. - Sedatives
. For unspecified etiology of the disorder or emotional disorders, herbal sedatives, tranquilizers and mild antidepressants are used. Psychotherapy is carried out according to indications.
Drug therapy is usually combined with physiotherapeutic techniques, the most effective of which are laser therapy and calcium electrophoresis. The patient is recommended gentle care for the vulvar area using mild pH-neutral hygiene products, sitz baths with decoctions of string, calendula and chamomile, the use of moisturizers, and wearing cotton underwear with frequent changes. Diet correction involves avoiding fried foods, canned food, smoked foods, sweets and baked goods. As a rule, complex conservative therapy can completely eliminate itching; only in extreme cases, in severe cases, surgical resection of the pudendal nerves is performed.
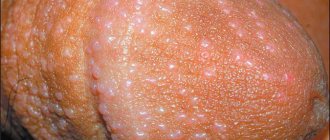
Fungal skin lesions in the intimate area
Fungus is one of the most common causes of itching and irritation. Fungal diseases are not the most dangerous, but quite unpleasant, and with proper treatment you can quickly get rid of them. All infections occur due to pathogens that spread the infection throughout the groin area, and itching often appears in the vagina. Of all fungal diseases, the most popular disease is thrush. When it occurs, the following symptoms are observed: severe itching in the pubic area, on the labia; curd-white discharge for a long time; the occurrence of pain during urination or sexual intercourse.
When these symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a specialist. Perhaps we are talking about another type of fungal disease, and a self-selected course of treatment in this case provokes complications. A long wait can lead to the appearance of a purulent rash, which is even more unpleasant for a person, and ulcers are seedlings of infection, so you should not delay going to a specialist.
Prognosis and prevention
With adequate diagnosis and treatment, in most cases it is possible to completely get rid of vulvar itching or significantly reduce its manifestations. Longer treatment is required for atrophic diseases of the vulvar region, neoprocesses, and mental etiology of the disorder. For preventive purposes, timely treatment of extragenital and gynecological diseases, giving up bad habits, proper care of the genitals, and the use of soft cotton underwear are recommended. It is important to maintain a sleep and rest schedule, eat rationally, and avoid significant psycho-emotional stress and exposure to harmful environmental factors.