Pediatrician
Sayfulina
Maryam Zakareevna
32 years of experience
Pediatrician of the highest category, member of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia
Make an appointment
Miliaria in children under one year of age and older is a fairly common skin lesion, which is a rash caused by severe sweating or poor care of the child’s delicate skin. It is important to understand that the baby’s thermoregulation processes are not yet perfectly established, and therefore the slightest negative factors can cause an undesirable reaction - parents should not be scared and think that this is a rare phenomenon. Almost all kids go through this.
However, you shouldn’t treat this problem negligently either: ordinary heat rash without treatment tends to become more complicated and worse, and in this case, longer and more complex treatment will be required - it’s better not to let it get to that point.
What is atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin disease characterized by a relapsing course.
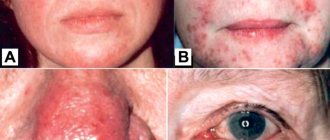
Babies with atopic dermatitis are bothered by itching and dry skin. Foci of inflammation can be located throughout the body, but they especially “love” children’s cheeks and folds, as well as the area under the diaper. Statistics indicate that atopic dermatitis occurs in every fifth baby [1]. Why is he dangerous? Lack of treatment can lead to the development of severe forms of atopic dermatitis, the spread of inflammation and the atopic march. In this condition, the disease begins to “march” through the child’s body, provoking the appearance or exacerbation of concomitant diseases. In 20-43% of cases, the development of bronchial asthma is possible, and twice as often - allergic rhinitis or eczema [2].
In addition, disruption of the hydrolipid barrier that occurs with atopic dermatitis in children can cause a secondary infection. Unfortunately, atopic dermatitis cannot be “outgrown.”
General characteristics of rashes
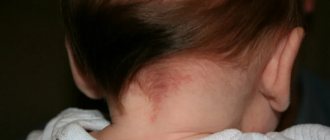
A slight redness on the back of the head is popularly considered a stork bite. It is not dangerous for the baby and does not cause discomfort. However, parents should additionally analyze the manifestation of the following symptoms:
- The spots appear only when crying or screaming. In a calm state they are practically invisible.
- Changing shade from light pink to crimson.
- The edges are uneven and torn.
- As the baby grows older, the formation becomes lighter and disappears completely.
- With detailed palpation of the area, it is impossible to detect any changes.
A red head can appear not only under the influence of harmless factors. That is why parents must seek advice from a specialist. A baby may have several types of formations.
Additionally, in this case, slight swelling appears. This clinical picture is observed immediately after childbirth and will disappear on its own within a short time. Violations are observed against the background of head injury during labor, hypoxia or minor changes in pressure.
A fiery nevus appears immediately after the baby is born. It will also resolve quickly, but you should first consult with your doctor.
It is impossible to completely eliminate the risk of hemangioma formation from capillary rupture. The growth is bright purple in color and may continue to grow as the child grows older. In medical practice, cases have been recorded when their diameter was about 10 centimeters. By the age of seven, it becomes brown in color. Only a doctor can prevent further increase. That is why it is categorically not recommended to hesitate in contacting him.
Against the background of improper proliferation of blood vessels, the risk of formation of cavernous hemangios increases. This spot is considered very dangerous. Among its additional disadvantages, discomfort should be highlighted. The disease is aggravated by itching and bleeding from the formation. That is why if there are stains, you should immediately consult a doctor. He will register the baby.
In the occipital region there is an increased risk of telangiectasia formation. The formation has fuzzy edges. Additionally, shoots may also extend from it. Externally, the formation has many similarities with a spider. If you observe him while crying, you can detect an increase in color intensity. This spot goes away without medical help by 1.5 years.
After birth, the risk of developing angiodysplasia increases on the baby’s skin. The rash consists of flat spots that can increase in size and can change color and color intensity. Under the formation, the vascular network noticeably increases. Only drug treatment prescribed by a doctor can prevent the negative effect.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis in children
According to recent studies [3], in 45% of babies, atopic dermatitis debuts between the ages of two and six months. In 60% of patients during the first year of life.
With atopic dermatitis in children, clinical symptoms and localization of inflammation largely depend on age. There are infant (up to one and a half years), child (from one and a half years to puberty) and adult phases. The following symptoms are common to all phases:
- Severe dryness of the skin (xerosis), which cannot be treated with regular baby cream .
- Redness and inflammation on the skin (especially symmetrical ones).
- Itching, causing severe discomfort to the child.
- Recurrent course (alternating periods of remissions and exacerbations). Moreover, in the cold season, deterioration is more often observed, and in the warm season, improvement is observed.
According to the nature of the course, acute and chronic stages of atopic dermatitis are distinguished, which are expressed by different signs (symptoms):
● Acute stage. Rough red spots (erythema), nodular rashes (papules), swelling, and crusts (including weeping) may appear on the baby's skin.
● Chronic stage. Accompanied by lichenification (thickening of the skin), cracks on the soles and palms, scratching, and increased pigmentation of the skin of the eyelids.
Why do diaper rash appear on a baby's neck?
This phenomenon is provoked by a number of factors, such as:
- Lack of compliance with temperature standards;
- The child’s clothes are too hot/tight, do not allow air to pass through, and also rub the baby;
- Excessive use of skincare products that lead to acid imbalance and cause increased skin sensitivity (soaps, baby creams, oils, etc.);
- Irregular air baths;
- Untimely bathing of a newborn, especially in the summer (hot) period;
- Increased temperature due to ARVI.
All of the above points lead to increased moisture on the skin, and since during infancy there are natural folds in the neck area, irritation and redness of damp skin develop more actively there.
As for diaper rash in the neck area, the rash is most often caused by tight clothing in the collar area, which reduces the access of oxygen to these areas of the skin.
Causes of atopic dermatitis in children
Atopic dermatitis can be considered a hereditary disease, because the most important role in its occurrence is played by a genetic factor [3]:
- In 80% of children, it occurs if both parents have or have had atopic dermatitis.
- In more than 50% of children - if at least one of the parents was sick, especially the mother (this doubles the risk of transmitting the disease “by inheritance”).
Some prenatal factors can also provoke atopic dermatitis in a baby: for example, poor nutrition of the expectant mother, contact with toxic substances, infections suffered during pregnancy, as well as bad habits and stress.
In addition, atopic dermatitis more often develops in babies who suffered oxygen deprivation during childbirth, were born prematurely and were bottle-fed (perinatal factors).
Features of therapeutic measures
Most often, the tumor does not require treatment. This manifestation goes away on its own after a certain time. Only in rare cases does a small area of light skin appear in this area. Over time, hair will appear, so the area will become almost invisible. Additionally, it should be noted that many people are not even aware of the presence of such spots on their heads that they had in childhood.
Parents should immediately consult a doctor if their child has the following negative manifestations:
- The stain did not disappear from the skin even after a month of the child’s life.
- Discomfort in this area is periodically noted.
- The baby constantly tries to touch the spot.
- If you put pressure on the formation, it darkens.
In only 50% of all children, the spots disappear irrevocably by the age of three. If the formation is aesthetically unattractive, then it can always be eliminated with a laser. Cases have been recorded where the stain transferred to the face as the child grew older.
It is important for parents to adhere to the following pattern of behavior in case of detection of a tumor on the back of the head:
- Try to remember the period when they saw the speck for the first time.
- Study in detail the features of the neoplasm. Large spots that cause a lot of discomfort to the baby are considered dangerous signs. You should also seek help if it protrudes strongly above the surface of the skin.
- If severe discomfort is detected, you should also come for an unscheduled examination.
- Not only an increase in size, but also a change in color is considered a dangerous factor.
Doctors are convinced that most often there is no reason to worry about the formation of red color on the skin. It only speaks of certain physiological changes. In this case, the spots disappear without medical intervention before reaching the age of one year.
Many new mothers, having discovered a scattering of red spots on the back of their newborn’s head, fall into a completely unnecessary panic.
More experienced mothers and grandmothers, on the contrary, treat this completely calmly, as a harmless and widespread phenomenon. What to do if there are red spots on the back of the baby’s head?
What is this disease called? Is this even a disease? This article will answer all these questions.
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in children
For a long time it was believed that atopic dermatitis in children is predominantly an allergic disease. However, it has now been proven that this is, first of all, a disease with dysfunction of the epidermis! And food allergies are detected only in 30-40% of children with atopic dermatitis.
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis are almost always influenced by certain environmental triggers. This could be chlorinated or “hard” water, soap, contact with an allergen, unfavorable climate and even stress. Another common trigger is bacteria that enter the skin through a damaged epidermal barrier.
Only a doctor (pediatrician, dermatologist, allergist) can make a diagnosis of “atopic dermatitis in children”! It takes into account the presence of external signs of disease and itching, as well as hereditary factors. Laboratory tests may be prescribed for children to carry out diagnostics. For example:
- General detailed (clinical) blood test.
- Biochemical general therapeutic blood test.
- General (clinical) urine analysis.
- Study of the level of total immunoglobulin E in the blood.
- Skin testing with allergens.
- Skin biopsy.
In what cases is specialized help needed?
Unfortunately, red spots on the skin are not always harmless. Some problems require mandatory consultation with a specialist and appropriate treatment (including surgery). There are two main disorders that require medical help:
- hemangioma;
- angiodysplasia.
Hemangioma is a congenital disorder of the blood vessels of the skin. Due to improper development of capillaries, a spot appears on the skin, which can be easily felt. It can be either red, or purple, or even blue. The main trouble with this disorder is the possibility of severe bleeding when the tumor is damaged. Hemangiomas can increase in size and do not go away on their own. Often no treatment is prescribed. The child may be referred for ultrasound examinations periodically. But if the hemangioma forms in internal organs (for example, in the liver), surgical intervention may be required.
Angiodysplasia is also a congenital malformation of blood vessels. Unlike hemangiomas, this type of spots cannot be felt, although it is clearly visible on the skin. The color of the spot can be either red or purple. Angiodysplasia can occur in the fetus in the first five months of the mother's pregnancy, because during this period the formation of the circulatory system occurs. Therefore, experts recommend paying special attention to your health in the first two trimesters. Also, chromosomal abnormalities can be the culprits of angiodysplasia. There are several treatment options, such as laser photothermolysis. In any case, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor.
Please note that none of these disorders can be treated on their own. Do not try to use any creams or ointments that your friends have recommended to you. If you have any suspicions, contact a specialist immediately.
- General characteristics of rashes
- Key causes of manifestations
- Features of therapeutic measures
From the very first days of her child’s life, mother tries to closely monitor his health. It is not surprising that red spots on the back of a baby’s head can greatly bother her. Especially if they are systematic. There is no need to worry. Most often, the rash is harmless. However, it is also not recommended to ignore its appearance. Only a pediatrician can correctly assess the overall clinical picture.
According to statistics, 50% of newborns have a red spot on the back of their head. Their number and color directly depend on the individual characteristics of the baby’s body. They do not cause discomfort. Only the external manifestation of such a sign plays a negative role.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children
In modern medicine, there are three degrees of severity of atopic dermatitis in children:
- Easy. The child responds well to treatment, remission can last more than 10 months, the itching is minor, the redness is slight. Exacerbations occur no more than twice a year.
- Medium-heavy. Exacerbations occur 3-4 times a year, and periods of remission are reduced to 2-3 months. The therapy gives less pronounced results, the redness “stubbornly” returns.
- Heavy. Long-term exacerbations are interrupted by short periods of remission - up to one and a half months. Treatment helps little or for a short period of time; the baby’s behavior is greatly affected by itching [4].
At all stages of atopic dermatitis, pediatricians and dermatologists recommend emollients - cosmetic skin care products. They moisturize the skin and help restore the level of lipids - the most important structural components. During periods of exacerbation, emollients can be applied frequently and generously.
Pay attention to the composition; it is advisable that emollients are not addictive. Their main tasks are to help the skin produce its own lipids, providing effective hydration and softening. In addition, the constant use of emollients prolongs periods of remission and alleviates the symptoms of atopic dermatitis.
The Mustela Stelatopia line of cosmetics will help restore skin comfort for a long time! Stelatopia emollients are effective at all stages of atopic dermatitis , incl. at its first signs - increased dryness of the skin.
Studies have confirmed that the use of Stelatopia emollient cream can reduce the likelihood of developing atopic dermatitis by 51% ! [6]
Treatment (use of hormonal drugs) for atopic dermatitis in children can only be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account age, symptoms, concomitant diseases and test results. Self-medication can be dangerous!
- For external therapy for moderate and severe degrees of atopic dermatitis, topical glucocorticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors and others are used.
- In case of mild disease, the use of Stelatopia Emollient Cream reduces the severity of inflammation after 32 hours, due to the presence of sunflower oil in the distillate [5].
- In systemic therapy, the drugs dupilumab, cyclosporine, glucocorticosteroids and others are used orally or in injection forms.
- To relieve itching - clemastine, hifenadine, cetirizine, chloropyramine, levocetirizine and others. The use of Stelatopia emollient cream as a cosmetic skin care product reduces the severity of itching in 80% of cases [7].
- Physiotherapy treatment may include phototherapy. Sometimes, in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, diet therapy, acupuncture, plasmapheresis and some other methods may be prescribed.
In what cases is it not necessary to see a doctor?
First of all, it is necessary to mention the so-called stork bite. In medicine, there is such a term as “telangiectasia”, or nevus of Unna. It looks like one or more spots on different parts of the baby's body. The characteristic features of this phenomenon are as follows:
- red or pink skin color;
- there is no way to feel the spot; it feels the same as the rest of the skin;
- reduction in size and color intensity until complete disappearance from the skin;
- manifestation is possible only in cases where the baby screams.
The cause of such problems is excessive compression of the skin during the passage of the birth canal.
If this happens, deformation of small blood vessels is noted at some point in the body, causing a red spot of various sizes to form. Also, capillary disorders can occur due to oxygen starvation of the fetus. It is important to know that Unna’s nevus does not pose any danger, and over time it may even disappear or become almost invisible. The only possible treatment is laser removal.
Also, red spots sometimes arise due to birth hematomas, which are also quite common. However, they rarely appear on the back of the head; much more often they can be found on other parts of the body. Characteristic signs of this problem are:
- Redness of the skin.
- Blueness of the integument.
- The appearance of tissue swelling.
In the vast majority of cases, the hematoma goes away on its own and no specialized treatment is required. But if you are still worried about this, consult a specialist.
Another problem that requires special attention is prickly heat. It occurs infrequently on the back of the head, but occurs almost regularly on other parts of the body. It appears as small red pimples on the body of a newborn, vaguely reminiscent of a rash. In addition to their unaesthetic appearance, they itch and cause additional discomfort to the baby.
The reason for the appearance of prickly heat is the hypervigilance of mothers who constantly worry that the child does not feel cold. Children's skin is very sensitive to temperature conditions, and if you wrap your baby in “seven clothes without fasteners” during a hot period, the baby will sweat intensely. Also, prickly heat can occur due to an excess of cream, which is applied to the skin and clogs the pores.
Miliaria itself is not dangerous to health, but it can cause some discomfort to the baby. The spots may be itchy, and scratching the pimples can cause infection. No specialized treatment is required in this case. Just make sure your baby is always dressed appropriately for the weather. Do not wear too warm clothes on him in hot weather.
So, we have looked at relatively harmless cases in which no special measures should be taken. Next, we’ll talk about disorders that may require you to see a doctor.
Prevention of atopic dermatitis in children
For atopic dermatitis, primary, secondary and tertiary preventive measures are distinguished.
Primary prevention
is aimed at preventing the occurrence of atopic dermatitis in children.
Recommended:
- Expectant mothers with a tendency to allergic reactions should exclude allergenic foods from their diet.
- Introducing complementary foods to babies begins at four months of age.
- Pregnant women and newborns at risk should take probiotics containing lactobacilli.
- Practice breastfeeding whenever possible.
- Eliminate exposure of your baby to tobacco smoke.
- Maintain humidity levels and regularly ventilate the children's room.
Secondary prevention
is aimed at eliminating risk factors that, under certain conditions (stress, weakened immunity, etc.) can lead to the occurrence, exacerbation and relapse of atopic dermatitis.
Recommended:
- Regular consultations with specialists.
- Maintaining awareness of new research and drugs in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
3.Tertiary prevention
is a set of measures aimed at preventing exacerbations or development of complications of atopic dermatitis.
Recommended:
- Avoid contact of the baby with provoking factors: soap (it dries the skin), clothes made of rough or synthetic fabrics, low-quality cosmetics, etc.
- Take care of your child's skin and apply emollients on a regular basis, including during periods of remission.
- Bath your baby daily using cosmetic cleansers for atopic skin.
[1] Isaac Steering Committee. (1998). Worldwide variation in prevalence of symptoms of asthma. The Lancet, 351, 1225-1235. (International Committee on Asthma and Allergy in Childhood 1998. Worldwide differences in the prevalence of asthma symptoms. The Lancet, 351, 1225-1235). [2] Studies Watson W., 2011, Larsen F.S., 2002, Draaisma E., 2015, ISAAC Steering Committee, 1998. (Studies Watson W., 2011, Larsen F.S., 2002, Draaisma E., 2015 International Committee on the study of asthma and allergies in childhood, 1998). [3] Clinical guidelines. Atopic dermatitis, 2022. [4] Atopic dermatitis: recommendations for practitioners. Russian national consensus document on atopic dermatitis. Ed. P.M. Khaitova, A.A. Kubanova. M.: Pharmacus Print, 2002. 192 p. [5] ODT and inflammation June 2010 [6] Scientific dossier “Atopic-prone skin: latest discoveries” [7] Test report “Stelatopia” emollient cream, self-assessment by users
How to treat heat rash in newborns
The best treatment is prevention. To prevent heat rash from occurring, try to maintain the temperature in the apartment no higher than 22 degrees, regularly ventilate the baby’s room, and dress him according to the weather in loose clothing made from natural fabrics. At home in the heat, do not put on diapers for your baby, or at least change them promptly (once every 3 hours, regardless of how full they are). When changing, be sure to wash your baby and leave him to wallow without a diaper for 10-15 minutes so that the skin dries and ventilates. Do not apply greasy creams or cosmetic oils to your child’s skin in hot weather.
It is important!
If prickly heat has already appeared, then all of the above measures will also be relevant.
The task of parents is to keep the skin clean, provide air access to it, and prevent overheating. Usually this is enough for prickly heat to go away on its own in 3-7 days. If the rashes do not decrease or even become stronger, then pharmaceuticals will be required for treatment. But they can only be prescribed by a doctor after examining the child. Depending on the nature of the rash, the pediatrician will recommend antiseptics, products with dexpanthenol, zinc oxide or glucocorticosteroids.
Varieties
According to statistics, 40-50% of newborns can “boast” redness of the skin on the back of the head in the form of numerous spots or one large spot.
Pragmatic doctors have given the so-called “stork bites” a less romantic name - telangiectasia, nevus of Unna or birthmarks. They are completely safe for the baby’s health, and their characteristic features are:
- Color red or pink;
- Flat surface – that is, the skin is pigmented, but the spots are not convex and cannot be detected by touch;
- Reducing the size and intensity of staining spots over time;
- “Stork bites” in a one-year-old or two-year-old child may not be noticeable at all, but appear only when the baby screams and cries.
Parents should know that red spots on the back of the head are not always harmless “stork bites.” The table shows the main signs by which you can distinguish “normal” red spots on the back of the head from those that require mandatory consultation with a doctor.
Name of formation on the skin Color Size and shape Dynamics Prognosis Nevus Unna or “Stork bite” or birthmark Red May be different, non-convex with uneven edges Present at birth, does not increase over time Favorable, resolve over time Hematoma Red or bluish Rarely occurs on the back of the head , accompanied by swelling Appears during childbirth, goes away after a few days Favorable Hemangioma Purple, blue, red Nodular formation that rises above the surface of the skin Appears immediately after birth, can increase Requires consultation with a doctor Angiodysplasia From light pink to purple Large flat spots Present at birth , may darken and increase in size Requires consultation with a doctor