Sometimes the disease develops over years, and sometimes it debuts abruptly and for no reason - arthritis of the hands is unpredictable. Sometimes the inflammation goes away after 2-3 days, and sometimes it lasts for weeks. Sometimes the pain in the arms is so severe that patients need heavy hormonal therapy. And sometimes they practically don’t notice the disorder until the final stages. But in all cases without exception, advanced disease leads to disability. It all starts with arthropathy - inflammation of the joint membrane. Without treatment, arthritis of the hands quickly spreads to the entire joint: it successively affects synovial cartilage, tendons and ligaments, muscles, and bones. Inflammation destroys cells, joints lose mobility, and every movement is accompanied by pain. What are the causes of hand arthritis and is it treatable?
Arthritis of the hands is a common joint disease that makes life much more difficult.
Why does eczema occur on fingers?
The exact causes of eczema on the fingers are still unknown. Immunological disorders play a decisive role in its development. The onset of the disease is provoked by external or internal factors, and they may differ from person to person.
What causes eczema on the fingers:
- constant contact with aggressive chemical components or metals;
- dry air, severe frost and other types of thermal effects;
- insufficient hand hygiene;
- frequent mechanical damage, wounds and abrasions on the hands;
- allergic reaction to food;
- hereditary predisposition;
- disorders in the endocrine and digestive system.
Dyshidrotic eczema on the fingers is especially widespread. Its name is explained by the fact that previously the development of the disease was associated with blockage of the sweat glands. The pathology often affects the skin of the palms. Its development is promoted by hyperhidrosis - excessive sweating.
Causes of red fingers
Red fingers and palms of the hands can be the result of various factors. Here are just a few reasons for redness:
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Allergies to medications, food, environmental factors.
- Insect bites.
- Erysipelas and other infectious diseases of a bacterial nature.
- Fungal skin lesions.
- Dyshidrotic eczema.
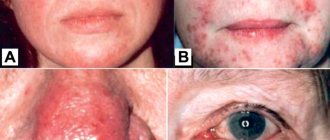
- Inflammation in autoimmune diseases: systemic scleroderma, dermatomyositis.
Many of these conditions are still considered quite rare. In most cases, redness and peeling of the skin occur due to atopic dermatitis and allergies.
Can water cause irritation?
Patients often associate redness of the skin of their hands with exposure to water. This is indeed possible under the following conditions:
- Weeping eczema. With this pathology, due to autoimmune disorders and pathology of the neuroendocrine system, bubbles with clear liquid appear on the hands. With increased skin moisture at the site of the lesion, they have difficulty healing and only progress. If work or household activities involve frequent washing or laundry, then it is very difficult to overcome such a disease.
- Allergy to substances contained in water. Only distilled water is considered absolutely pure, while running and spring water contains a large amount of trace elements and other substances. A person may be intolerant to any of the components of this “cocktail”. Therefore, it is likely that allergies will develop.
Skin reaction to water is often observed when a person moves. The skin has already adapted to one composition of the liquid, but serious changes in the composition cause an intolerance reaction.
Features of a child
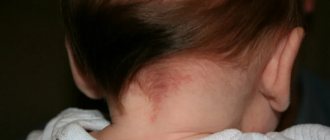
Skin changes on the hands and wrists can occur at any age: in the newborn period, at 2 years and beyond. The following may contribute to the reaction in children:
Symptoms of eczema on fingers
In the early stages of eczema, only increased dryness of the skin is observed. It is almost impossible to eliminate with conventional moisturizers. Due to severe dryness, cracks appear, and inflammation occurs at the site of their formation. They cause itching and burning.
The general list of symptoms of eczema on the fingers includes:
- increase in epithelial pattern on the skin;
- constant feeling of skin tightness;
- roughening of the skin;
- swelling and redness of the affected skin;
- red sprinkle elements.
The rash rapidly spreads across the skin, enlarges and merges into large plaques. All this causes severe itching in a person, which prevents normal sleep and causes nervous disorders. Very deep cracks form in the bends of the fingers, which hurt and do not heal for a long time. The skin in this area continues to peel off, and if a bacterial infection occurs, purulent discharge appears.
What to do if your hand ligaments become inflamed
A brush is a complex mechanism consisting of different elements. If one of these is damaged, the mobility of the entire limb is impaired. Inflammatory processes in the ligaments are a common problem that leads to discomfort and decreased performance. If left untreated, serious complications may occur or complete immobility and joint pain
and other negative consequences.
The ligaments in the hand are a dense elastic formation, which helps stabilize the joints and their mobility. There are a large number of joints in the hand, each of which supports a specific ligament and helps strengthen the muscles and bones. You need to understand that they are exposed to heavy loads every day. Sometimes situations arise that lead to an inflammatory process. Most often, the reason for this is injury or prolonged performance of the same type of actions. Inflammation of the hand often occurs in people:
- going in for sports;
- involved in the construction industry;
- artists;
- office employees;
- musicians.
Elderly people also have similar problems.
The main causes of the inflammatory process
A similar problem appears when various diseases occur, and the cause may be:
- injury;
- stretching;
- arthritis;
- osteoarthritis;
- peritendinitis.
Here are the most common causes of inflammation in the hand:
- lifting something heavy;
- performing physical exercises without preparation;
- regular and equal loads on the arm;
- fall or injury;
- joint infections;
- hypothermia;
- allergy;
- cartilage deformation;
- age-related changes;
- metabolic disorders.
Hand injury and joint problems
You must be careful, as injuries lead to inflammatory processes in the ligaments. People of any age are prone to them. Your hand can be injured both at work and at home. The wrist and thumb are most often affected. The symptom of a bruise is sharp pain when moving. There may be swelling, redness, and the hand begins to lose mobility. If such symptoms are observed, you should urgently consult a specialist for advice. It is necessary to understand that serious injuries lead to rupture of ligaments and the appearance of cracks in the bone.
Peritendinitis and arm pain
This is one of the most popular causes of inflammation in the hand area. Peritendinitis occurs due to prolonged stress on the hand. This is associated with embroidery, sedentary work, knitting, and playing sports. Sometimes an allergy or infection leads to inflammation. The pathology is manifested by pain in one of the damaged ligaments, which begins to intensify during palpation or movement. Over time, swelling and redness appear.
Joint pathology
The problem affects people of any age, but most often it is typical for those over 40. One of the most common inflammatory diseases is arthritis, which develops as a result of injury or infection.
Arthrosis affects the joints and fingers. The disease is chronic and progresses over time, destroying cartilage. Without treatment, joint deformation begins.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Inflammation of the wrist ligaments is diagnosed, and the problem is typical for those who experience a variety of stress for a long time. The ligament begins to compress the nerves, causing severe pain, tingling, and numbness in the fingers. Without proper treatment, muscle atrophy is detected.
De Quervain's disease
This is what is called stenosing ligamentitis in the dorsal ligament of the hand. The disease is caused by trauma, infections, and monotonous movements. Pain in a certain place begins to bother you, swelling forms, which appears over time. There is usually no redness on the hand.
Main symptoms of inflammation
Inflammatory processes in the hand have signs:
- pain of varying intensity;
- discomfort while moving the hand;
- limited mobility;
- clicking or creaking due to joint instability;
- redness.
Symptoms and further treatment depend on what caused the problem. It is necessary to understand that the signs of inflammation can be different, so it is important to correctly diagnose. Only after an examination can a correct diagnosis be made. In addition to an external examination, an ultrasound, MRI, and radiography will be required. This is the only way to identify the affected joints and detect a pinched nerve or injury.
Features of therapy
As soon as discomfort appears in the hand area, measures must be taken. A little pain can lead to serious pathology. The inflammatory process will not go away on its own. Treatment will require special ointments with a warming effect and painkillers. Complex therapy is usually used, which is aimed at treating the underlying disease. Antibacterial agents are prescribed for infectious arthritis.
If the hand has been injured, first aid is provided to avoid swelling and cold is used. Compresses, physiotherapeutic procedures, therapeutic exercises, and massage are selected. If conservative therapy does not have the desired effect, surgical intervention must be resorted to. You should contact a specialist and follow all recommendations to avoid loss of arm mobility or surgical intervention.
You can use the recommendations of traditional medicine.
Potatoes, radishes, and horseradish root help well. One of these products is applied raw to the affected area. You can lubricate your brushes with clove, lavender, and geranium oil to speed up recovery. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Types and forms of the disease
Treatment for finger eczema depends on what stage of development the disease is at. It is characterized by a wave-like course: exacerbations are replaced by periods of remission. Hands are most often affected by dry eczema, in which papules with exudative fluid do not form on the skin. The disease can occur in one of the following ways:
- Ostrom. Symptoms appear suddenly, swelling quickly develops, and redness forms. The disease develops within a couple of days, and sometimes even in a matter of hours.
- Subacute. Eczema does not develop as rapidly and is less pronounced than in the acute form. The disease itself lasts for several months and only then subsides for an indefinite period of time.
- Chronic. The most common form of eczema, in which relapses and periods of improvement regularly follow each other.
What is urticaria?
Urticaria, also known as nettle fever or urticaria, is a skin disease, most often of allergic origin. This is a fairly common phenomenon that every third person encounters at least once in their life, and only a quarter of all cases of urticaria become chronic. Sometimes the symptoms of hives appear for no apparent reason, and, as a rule, some triggers contribute to this:
- allergenic foods, including peanuts, eggs, nuts;
- taking antibiotics, aspirin and ibuprofen:
- insect bites;
- pet hair;
- physical irritants: thick clothing, especially synthetic fabrics and latex;
- cold, heat, prolonged exposure to the sun;
- bacterial and viral infections, including ARVI, mononucleosis, hepatitis;
- pollen from plants or certain plants, such as oleander and wild ivy;
Thanks to its name, it is quite easy to imagine what hives looks like, since it causes a skin reaction that is easy to get if you fall into a nettle thicket: sharp redness of the skin, raised blisters or blisters, itching, and sometimes burning pain. As a rule, all these symptoms disappear within a day, but in the chronic form they can persist for several weeks or even months.
How to treat eczema on fingers
Comprehensive treatment of eczema between the fingers includes local and systemic therapy. This approach gives the most pronounced and fastest results. The basis of local treatment at the PsorMak clinic is the use of a non-hormonal ointment on a natural basis. It does not cause side effects and has no contraindications, and also has a very simple treatment regimen - a single application per day is enough.
Systemic treatment of eczema between the fingers is aimed at:
- to eliminate an allergic reaction;
- general strengthening of the immune system;
- elimination of diseases that contribute to the development of eczema.
Treatment continues when the exacerbation subsides. During periods of remission, it is aimed at preventing relapses. The patient is assigned to work with a psychotherapist to relieve stress and stabilize the activity of the nervous system. Additionally, general restorative treatment methods are practiced, in particular acupuncture.
Hundreds of patients have already undergone a similar original therapy program at the PsorMak clinic. You can find out about the results of their treatment on the website. Many years of experience allows us to cope with the most difficult clinical cases. To schedule a consultation, use the online form or contact numbers +7 (495) 150-15-14 and.
How to cure?
Since redness can be caused by various diseases, it is impossible to list a universal treatment.
The key point in successful therapy is timely and complete diagnosis. Depending on its results, drugs from various groups may be prescribed:
- Glucocorticosteroids.
- Antibiotics.
- Antifungal agents.
- Cytostatics.
- Other drugs.
Their prescription is possible only after consulting a doctor and establishing the exact cause of the rash.
How to treat with tablets?
Before being examined by a specialist, you can alleviate the condition and reduce skin itching by taking antihistamines. These medications are symptomatic and do not address the cause of the redness and itching.
Some examples of tablets:
- Suprastin.
- Cetirizine.
- Loratadine.
- Desloratadine.
The first two drugs relieve symptoms more effectively, but cause side effects such as drowsiness. Loratadine and desloratadine are more modern antihistamines and are less likely to cause side effects, but have a less pronounced effect.
Ointments and gels
For eczema and dermatitis, hormonal ointments, creams and gels are an excellent remedy. They help relieve inflammation and reduce skin itching. Local forms are not absorbed into the systemic circulation if used for less than two weeks in a row.
Use the following:
- Hydrocortisone ointment.
- Advantan.
- Lokoid.
- Ecolom.
Long-term use of such drugs is addictive and can cause side effects.
If your brushes are dry
Moisturizing cosmetic skin creams help cope with dryness and flaking. They are sold not only in pharmacies, but also in cosmetics stores. A doctor's prescription is not required, but the products are quite effective in achieving their goals.
As an alternative, you can use emulsions with lipids, which moisturize the skin well and even prevent inflammation. One of these drugs is Lipobase, but it also has a number of analogues.
HOW TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT at the PsorMak Institute for Healthy Skin
1. Click the button you see below -
Make an appointment
2. Fill in the fields in the form that appears. Be sure to check the correct phone number so that our specialist can reach you. After filling out, click on the “Submit” button.
3. Wait for our specialist to call. He will answer any of your questions and agree on the date and time of your visit to PsorMak.
The initial appointment includes:
- Visual examination , which will allow the specialist to get a general understanding of the condition of your skin and the pathology itself.
- Collecting anamnesis - finding out information about the development of the disease, living conditions, previous diseases, operations, injuries, chronic pathologies, allergic reactions, heredity, etc. Together with a general examination, this allows you to make a fairly accurate diagnosis and choose a method of treatment and/or prevention.
Additional symptoms
Some clinical features of the disease help to make a diagnosis. Here are several options for redness.
Only red spots
If there is no itching on the skin, and only red spots bother you, the most likely causes of the disease are the following:
- Insect bites.
- Some fungal diseases, for example microsporia.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus and cutaneous forms of lupus.
- Disorders of the autonomic innervation of the skin.
Isolated redness of the skin without other symptoms should not be ignored. After all, additional manifestations may arise later.
If it itches
The most common clinical picture is a combination of redness and itching. It can occur with all of the diseases listed above.
Autoimmune diseases rarely cause itching, but other factors (allergies, insect bites, atopic dermatitis and others) may well cause this symptom.
In this case, a dermatologist helps to establish the cause; it is not always possible to independently determine the etiology of itching and redness.
For diagnosis, additional research methods are often required:
- Dermatoscopy.
- Skin scraping culture.
- General clinical studies.
- Skin allergy tests.
Contact a specialist in a timely manner for treatment, do not blur the clinical picture by using symptomatic remedies.
Cracks at the knuckles
Itching, redness and peeling on the “bones” of the fingers are more common in the following pathological conditions:
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Dyshidrotic eczema.
- Contact allergy.
If there is a culprit allergen that you attribute the development of symptoms to, you should avoid contact with it. This way you will narrow down your search for the culprit disease.
Sores on the fingertips
This symptom is called digital ulcers. They are often found in systemic scleroderma. With this disease, the skin becomes red, thickened and tightened. Small abrasions appear on the fingertips, which become scars.