Dirty hands are one of the common causes of the development of dangerous diseases. Neglect of personal hygiene rules and poorly washed products increase the risk of pathogenic bacteria entering the body. Infectious agents can exist and multiply for a long time on surfaces touched by humans. Harmful microorganisms can survive even when frozen. An acute intestinal infection can be caught from drinking a cocktail with ice if, for example, the ice was made from dirty water.
Causes
The main reason for the development of such defects is not only vascular diseases. Often, trophic ulcers occur against the background of neoplasms localized in the axillary, subclavian and mediastinal lymph nodes. In addition, injuries of various types (stabbed, cut, chopped, bitten), infectious and inflammatory diseases (chickenpox, helminthic infestations), pathologies of the immune system, systemic connective tissue diseases (lupus erythematosus, vasculitis), sepsis cause aggravation of the skin syndrome and the development ulcerative defects on the hands.
Parasitic diseases
Helminthic and protozoal infestations can easily be classified as diseases of dirty hands. The most common among them are ascariasis and giardiasis. Cysticercosis, or pork tapeworm infection, is a particular danger. A number of researchers in their scientific work indicate that “with damage to the brain and spinal cord, eyes, lungs, heart, liver, kidneys, the course of the disease becomes severe and acquires a serious prognosis (the danger of death remains constant)” (Polyakov V. E., Lysenko A. Ya., Konstantinova T. N. and Avdyukhina T. I., 2004, p. 57).
There are nonspecific symptoms of helminthic and protozoal infestations: fatigue, headaches, bruxism (teeth grinding), cough that cannot be effectively treated, allergic and neurological symptoms, bowel and digestive disorders, weight loss, etc. Timely consultation with a doctor is the only way to diagnose the species parasite and choose the right treatment tactics.
Education mechanism
As a result of exposure to the causative factor, the pressure in the venous capillaries of the upper extremities increases, and they begin to change their shape and direction. They become crimped and thinned. Their permeability increases, fibrin and blood clots are deposited between the venous vessels. This leads to hypoxia (low oxygen saturation of the blood vessels). The level of blood circulation decreases sharply, causing ischemia (circulatory failure). A prolonged absence of normal blood circulation provokes the development of necrotic processes. Plaques of various shapes form on the hands, which over time either dry out and turn into a dry form of necrosis or begin to quickly increase, reaching large sizes.
Inflammation of the fingers, or felon
25.09.2019
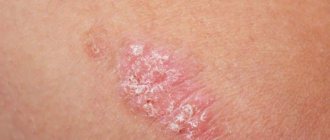
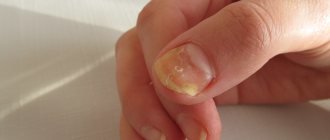
Inflammation of the fingers is medically called felon . Usually the disease manifests itself as a purulent abscess on the fingers or toes , as a rule, the abscess is localized near the nail plate. The affected area swells, turns red, and an inflammatory process begins to form inside.
Most often, pathology develops by introducing infection into the wound through cracks and microtraumas of the skin. As a rule, these are injuries, cuts, bruises, splinters. Sometimes the cause of the development of a purulent abscess is banal hangnails, torn to the point of bleeding . If not treated in time, an ordinary abscess can turn into a serious wound.
Types of panaritium by location
Depending on the location of the suppuration, doctors divide felon into several categories:
- cutaneous - develops on the surface or inside in the subcutaneous layer of the palm or finger. The tissues swell, filling with purulent contents, sometimes with admixtures of blood , a swelling forms externally, which is very painful;
- subungual – occurs as a complication or as a result of infection under the nail plate. In this case, the tissues located under the nail become soft and inflamed. Often the cause of the development of subungual suppuration is a blow to the finger with a heavy object;
- articular - spreads to all phalanges of the finger, causing swelling and immobility. It begins with an infection that accompanies cuts and bruises and small wounds. Due to swelling, the finger may stop straightening;
- bone - a severe form of panaritium , which is formed due to lack of treatment and damages the entire finger. Edema fills the periarticular tissues with serous fluid, which leads to serious consequences and hospitalization;
- tendon – the last stage of the disease, when all tissues of the joints and tendons are affected. It can act as a complication or after serious injuries to the phalanges of the fingers. With the tendinous form of panaritium, surgical treatment cannot be avoided.
Symptoms
Symptoms may vary depending on how deep the infection has penetrated into the tissue. The disease begins in several stages. At the beginning, tissue infection occurs, with the introduction of a microbial infection.
At this stage, felon sometimes occurs unnoticed, without causing any pain. After a few days, the affected area turns red, swells, and becomes hot to the touch. Characteristic pains appear that accompany the wound. At the last stage, a purulent boil , the joints of the phalanx are affected. Protracted forms of panaritium are treated surgically .
Some characteristic symptoms:
- severe swelling , redness at the site of the abscess;
- increase in temperature in the wound area;
- formation of pus around the nail, under the nail;
- constant throbbing pain;
- trauma to the cuticle under the nail plate;
- transfer of swelling to the remaining phalanges of the finger, difficulty in flexion.
Methods of treating felon
At first, it is best to resort to conservative methods of treatment, as they can quickly stop the penetration of pus into the deep layers of the finger. Treatment methods must be discussed with the surgeon.
In the later stages, panaritium is treated with antibacterial drugs that suppress the purulent process. In some situations, you have to resort to surgical opening of the wound. The formation of a persistent abscess requires immediate medical ; in this case, you should not self-medicate, as this can be dangerous.
Published in Surgery Premium Clinic
Diagnostics
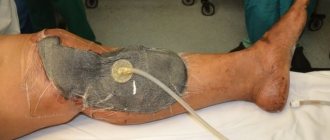
Diagnosis of trophic ulcers on the hands consists of carefully collecting data on the development of the underlying disease. Upon examination, the doctor determines the nature of the ulcerative defect, linking it with the cause of its development. After this, laboratory and instrumental research methods are carried out. Laboratory methods include a complete blood count. It is used to determine the presence of blood diseases (anemia), the presence of inflammation (the level of leukocytes and erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases), the presence of an oncological focus (young and mature forms of blood cells). In addition to a general blood test, microbiological cultures are performed on various media. This is necessary to determine the infectious pathogen and prescribe appropriate antimicrobial drugs. Also, in the presence of immunological pathologies, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is performed. It is used to determine the presence of foreign particles. Instrumental methods include: ultrasound diagnostics and computed tomography. With their help, blood flow in the vessels, the presence of pathological neoplasms and areas of ischemia are determined.
Sources of disease
An infected person, an asymptomatic carrier of the disease, water or food can be a source of intestinal infections. Infection with a viral infection occurs through contact with another person, consumption of contaminated products, or use of shared hygiene products.
Many bacterial and viral intestinal infections are transmitted through dirty dishes, toys, household items and even a smartphone. At the same time, the causative agents of the disease are quite resistant to environmental factors - they can live on fruits and vegetables for weeks, and in water for months. Their favorite habitat is dairy, meat and fish products.
A pathogen such as Giardia cysts can live quietly in a humid external environment for up to 2 months or more. In this case, infection is possible by drinking unboiled water; contact with the carrier is not necessary.
Treatment
After identifying the main cause that led to the development of trophic ulcers on the hands, adequate therapeutic measures are selected. For antibacterial purposes, antibiotics are prescribed - Ceftriaxone, Amoxicillin, Tetracycline. Venarus and Detralex are used to strengthen blood vessels and restore impaired blood flow. For shallow/superficial ulcerative defects, the use of healing ointments is recommended for topical application. These include Zinc ointment, Argosulfan, Solcoseryl and Levomekol.
Surgical treatment consists of excision of the edges of the ulcer and rinsing with antiseptic drugs (Betadine, Furacillin). If purulent contents are present, drainage is installed.
Treatment of diseases transmitted through dirty hands
Accurate diagnosis is the key to effective treatment. A doctor will help you establish a diagnosis; he will direct you to a number of studies: bacteriological analysis for infections, serology. Sometimes hardware diagnostic methods may also be required.
The course of treatment is aimed at eliminating the causative agent of the disease. So, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- antibiotics, intestinal antiseptics;
- antiviral drugs;
- antifungal agents;
- antiprotozoal and anthelmintic drugs.
Painkillers and antispasmodics, antihistamines, antipyretics and other medications are prescribed as symptomatic therapy. For skin manifestations of parasitosis, the doctor may supplement the course with local antipruritic and anti-inflammatory drugs. Also, in most cases, a special diet will be required.
Most diseases of dirty hands manifest themselves with acute symptoms. But even in the absence of such, it is important to maintain an optimal diet - this will help you recover faster and alleviate the condition.
Acute bacterial and viral intestinal infections require a gentle diet. It is important to avoid foods that irritate the intestinal mucous membranes and also cause increased gas formation. Sweets, fatty foods, fried and peppered foods, soda, strong coffee, alcoholic drinks, concentrated juices, baked goods and brown bread, pasta, raw fruits and vegetables are prohibited.
If you have diarrhea, you need to eat small portions. It is better to give preference to astringent products, rice, crackers, jelly, etc. Poultry, fish and meat should be carefully processed - boiled or steamed.
For pathologies of viral origin, symptomatic treatment is most often recommended:
- Drink plenty of fluids to replenish fluid balance. The use of dehydration agents is also allowed.
- A gentle diet and proper rest. In the acute period, bed rest and symptomatic treatment are indicated.
- Taking sorbents that relieve intoxication and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
One of the effective means for eliminating the consequences of intestinal infections is the English biocomplex “Fitomucil Sorbent Forte”. The drug contains plantain seeds (psyllium), a prebiotic (inulin) and an active probiotic complex. The product reduces the manifestations of intoxication, stimulates the growth of beneficial intestinal microflora, and has a beneficial effect on the immune system. "Fitomucil Sorbent Forte" is gentle on the intestinal walls and does not cause bloating or abdominal pain.
If you experience any intestinal or other infection, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only a specialist can determine the cause and prescribe the correct treatment.