We all want to have an attractive appearance. However, it often happens that existing diseases prevent us from making our dreams come true. Nowadays, it is quite common to encounter skin diseases, which, of course, do not have the best effect on our appearance.
And so, let's talk in this article about such a topic as hyperkeratosis of the facial skin, and also consider its causes and treatment methods.
Naturally, at the very beginning of our conversation it is necessary to clarify what hyperkeratosis of the facial skin is. This is a disease that occurs due to the strong development of the stratum corneum of the skin.
The reasons for its appearance can be two types of factors - external and internal. The former include friction, the effect of lubricating oils, and pressure.
Symptoms of hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is not an independent disease; it is a consequence of various disorders in the body. The main symptom of hyperkeratosis is thickening of the skin in various parts of the body. At first, the skin gives the impression of being rough, but does not cause discomfort. Then the thickness of the stratum corneum increases, the skin begins to peel off or partially peel off, its sensitivity decreases, and color often changes.
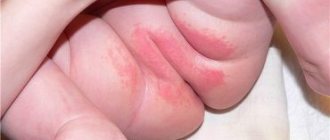
Hyperkeratosis on the hands. Photo: Pai VV, Shukla P, Godhge R, Bhandhare P – Indian dermatology online journal / Open-i (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0)
In the thickest and driest areas, painful cracks may appear, which take a long time to heal and become a gateway to infection. Hyperkeratosis is often accompanied by dry skin, hair loss, and decreased function of the sebaceous glands.
How long do the symptoms of hyperkeratosis last?
It depends on the form of hyperkeratosis. For example, corns and calluses usually persist as long as a person continues to wear tight shoes and plays sports with special equipment (in the case of calluses on the palms). Actinic and seborrheic keratoses do not go away without treatment. Hereditary forms of hyperkeratosis are lifelong. In this case, only symptomatic treatment is possible (relieving symptoms, but not eliminating the causes of the disease).
Treatment of hyperkeratosis
Despite the fact that the symptoms of all forms of hyperkeratosis can cause significant discomfort to a person, you can completely get rid of them or significantly alleviate your condition. The doctor draws up a treatment plan after determining the form of keratosis.
It is important to understand that conservative (medicinal) treatment of skin diseases does not always give quick results. It is achieved only when the patient carefully follows the instructions of the attending physician.
Who treats hyperkeratosis?
With the initial manifestations of any disease, you can contact a general practitioner.
He conducts a basic examination, orders laboratory tests, and determines which specialist the patient should be referred to. However, this step is not always necessary. Thus, a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist deals with the treatment of skin diseases. Based on the results of the initial examination, if necessary, he refers the patient to a consultation with an allergist, oncologist, geneticist and other specialists to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
The first stage of treatment for many forms of keratosis usually consists of emollients, topical keratolytics, and re-evaluation of the condition. If there is no improvement, additional tests may be ordered and the treatment plan revised.
Depending on the diagnosis, drug therapy may include corticosteroids, retinoids, topical anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamin D derivatives, phototherapy and laser treatment.
If you have symptoms of hyperkeratosis, you can consult a therapist or dermatologist. Photo: AndreyPopov / Depositphotos
Local remedies used in the treatment of hyperkeratosis:
- Salicylic acid destroys the protein keratin, thereby softening and reducing the thickness of the keratinized skin.
- Urea-based products (may be contained in emollients). Used to increase the water content of the skin and soften it. Also involved in the destruction of keratin (protein), although to a lesser extent than salicylic acid.
- Alpha Hydroxy Acid exfoliates the upper layers of the skin's epidermis, revealing softer layers that better absorb moisture.
- Tretinoin (a retinoid) is also used to stimulate the exfoliation of the top layers of dead skin.
- Corticosteroid creams and gels are used to relieve skin inflammation in lichen planus, eczema, and other inflammatory forms.
Table 1. Recommendations for the treatment of individual forms of hyperkeratosis¹
| Form of hyperkeratosis | Treatment |
| Psoriasis | Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and can range from topical ointments (mild to moderate cases) to light therapy and oral or injectable medications (more severe cases). The main thing in treatment is proper skin care |
| Calluses and corns | They usually disappear on their own after eliminating the source of irritation to the skin of the feet. Changing shoes to more comfortable ones, using orthopedic and silicone pads, and moisturizing rough areas often helps solve the problem without a scalpel. However, in more advanced cases, it is recommended to consult a specialist (podiatrist), who will use instruments to treat the skin of the foot and carefully remove the corn. You should not do this yourself - improper removal of the keratinized area of skin can provoke a relapse and aggravate the problem |
| Warts | Both conservative and surgical treatment are possible. Since the formation of warts is caused by the human papillomavirus, in some cases the immune system itself copes with it and the warts disappear. If they do not go away on their own, are constantly injured or cause discomfort, salicylic acid can be used (except for anogenital warts). It is applied pointwise to the wart itself, while it is necessary to protect the surrounding tissues from its effects. Treatment may take several months. Cryotherapy may be used for surgical removal of formations |
| Actinic hyperkeratosis |
|
| Seborrheic hyperkeratosis | Non-drug treatment methods are mainly used: cryotherapy, curettage, excisional biopsy, dermabrasion and laser surgery. In some cases, superficial peeling can speed up the skin cleansing process |
| Follicular hyperkeratosis (“goose bumps”) | Daily exfoliation and moisturizing of the skin - peelings, creams, emollients are used |
Prevention
General preventive measures include:
- Compliance with sun exposure and solarium use.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- A rational diet that corresponds to energy costs.
- Prevention of trauma to the skin (wear comfortable, appropriately sized shoes, clothing made from natural fabrics).
- Maintain personal hygiene, correct (according to type) skin care.
- Regular use of medicinal/cosmetic products to moisturize and soften the skin and prevent peeling of keratinized plates.
- Avoid injury to the skin.
- Don't freeze.
- When working with any chemical reagents, avoid contact with skin (use special protective equipment).
- If you are prone to hyperkeratosis, regularly carry out hardware treatment methods and visit a podiatrist.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hyperkeratosis usually includes not only an external examination of the affected areas of the skin, but also a careful collection of the patient’s personal and family history³.
Depending on your symptoms, your doctor may ask the following questions:
- Do your relatives have skin problems?
- Have you had allergies before, including in childhood)?
- Do you often have to be exposed to direct sunlight?
- Are dentures or other orthodontic structures used (the question is relevant for hyperkeratosis on the oral mucosa)?
In most cases, the cause and form of hyperkeratosis can be determined based on symptoms and complaints, the results of an external examination and anamnesis.
Corns, calluses, warts and chronic eczema are fairly easily diagnosed. If the doctor suspects a connection between eczema and allergies, the patient may be prescribed allergy tests.
Hyperkeratosis on the elbows. Photo: Lernia VD, Ficarelli E, Zanelli M – Indian dermatology online journal / Open-i (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0)
To confirm the diagnosis, a biopsy may be required: a small piece of skin is removed for testing in the laboratory. In this way, it is possible to diagnose actinic and seborrheic hyperkeratosis, as well as carry out differential diagnosis with malignant neoplasms of the skin.
If hyperkeratosis affects multiple areas of the body in a newborn child, the question is raised about the hereditary nature of the disease. In this case, a consultation with a geneticist is scheduled and appropriate research is carried out.
Forecast
For most forms of hyperkeratosis, the prognosis is favorable. Moreover, for some types (calluses, warts) a complete cure is possible, while for others (chronic eczema, lichen planus, psoriasis) it is only a relief of symptoms. Sometimes actinic keratosis (even less commonly, seborrheic keratosis) can develop into skin cancer.
The condition is alleviated by eliminating irritating factors, changing lifestyle, and treating underlying diseases.
Prevention
To prevent hyperkeratosis and avoid worsening existing symptoms, the following rules must be followed:
- regularly wash, scrub, moisturize the skin on your feet (emollient creams will help);
- avoid hypothermia in the cold season;
- do not come into contact with aggressive detergents, chemicals or reduce their negative effects on the skin (use rubber gloves);
- Avoid prolonged exposure of the skin to direct sunlight;
- wear comfortable shoes (if your foot is bent, use orthopedic insoles);
- treat any diseases (especially skin diseases) in a timely manner;
- Provide in your diet a sufficient amount of animal protein (at least 1 g per 1 kg of body weight per day) and vitamins of groups A, B, C and E.
Recipes for home care for feet and heels
Foot baths, compresses and peeling are easy to make yourself using natural ingredients. We are happy to share the most effective recipes.
Foot baths
- Milk-soap bath . Fill a container with warm water at a comfortable temperature no higher than 40 degrees. Add half a liter of milk and a tablespoon of soap crumbs. Take a bath for about 15-20 minutes until the water cools down.
- Bath against profuse sweating . Brew 2 tea bags for every liter of water, wait until the temperature of the “tea” becomes comfortable and dip your feet in the resulting decoction. Black tea has the ability to tighten pores and also contains tannins that reduce sweating.
- Soda bath for corns . Dissolve 2 tbsp in water. spoons of baking soda and 1 tbsp. a spoonful of soap or shower gel. Take a bath for 15-20 minutes. The shower gel in this recipe can be replaced with sea salt, and you can also add your favorite essential oils.
- Lemon bath . Lemon juice destroys the stratum corneum of the skin and works as an acid peel. Dilute lemon juice with water in a ratio of 1:10. Add the resulting mixture to warm water and soak your feet for 10 minutes. Afterwards, rinse your skin with water to avoid drying out.
Home peeling
- Coffee peeling . Ground coffee is one of the main exfoliating ingredients in natural cosmetics. It improves blood circulation and also stimulates the production of collagen and elastin for renewed and firm skin. Mix 1 tbsp. spoon of coffee, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of cocoa and the same amount of cinnamon. Add 150 ml of any oil (olive, grape seed, macadamia) and tbsp. a spoonful of Dead Sea salt. Apply to skin with massaging movements, rinse after 10 minutes. If desired, you can use ready-made coffee scrub “Coffee Cocktail”.
- Classic salt peeling . Mix 50 gr. Dead Sea salt or Himalayan salt with 1 tbsp. spoon of olive oil. Add 5 drops of tea tree or lavender essential oil. Massage the mixture onto your feet and leave for a few minutes. Afterwards, rinse with warm water and apply cream.
- Kefir peeling . Heat 100 ml of kefir to 39 degrees, pour into a bag and lower your feet there for 2 hours. Afterwards, rinse off the residue with water and you can start sanding.
- Citrus peeling . Fruit acids perfectly soften rough skin and saturate it with vitamins. Any citrus fruits that you can find in the kitchen are suitable for peeling: orange, grapefruit, lemon, lime, tangerine. Grind a fruit weighing about 200 grams in a blender instead of peel and seeds. Add a sprig of finely chopped mint. Apply the mixture to rough areas of the skin and leave for 10 minutes, then rinse with water. Repeat acid peeling every week. The Slim Citrus mixture is also suitable for citrus peeling.
Foot compress
- Honey compress for the night . Mix a tablespoon of honey with 2 tablespoons of flour. Form a dense cake from the resulting mass and apply it to the steamed legs, covering the top with film. It is advisable to leave the compress overnight.
- Moisturizing compress with aloe juice . Mix aloe juice with onion juice and olive oil in equal proportions. Apply the mixture to your feet, cover with foil and go to bed.
- Softening compress with vinegar and glycerin . Glycerin is loved by cosmetologists for its ability to quickly heal wounds, moisturize and soften the skin. Mix 2 tbsp. tablespoons of pharmaceutical glycerin with an equal amount of 9% apple cider vinegar. Apply the solution to gauze and apply to areas of rough skin. Leave for several hours or overnight, covering with film and warm socks.
- Onion compress for rough skin on heels . For the recipe you only need one medium onion. Cut it in half, apply it to your heels and secure it with film and leave it overnight, putting socks on top. In the morning, throw away the onion, wash and file your heels.
Mask for feet and heels
- Nourishing potato mask . Mash the warm boiled potatoes with a fork and apply the resulting puree in a thick layer to your feet. Cover with cling film for half an hour, then rinse with warm water and apply your favorite cream.
- Moisturizing oatmeal mask . You will need 2 tbsp. spoons of oatmeal, 2 tbsp. spoons of olive oil and a spoonful of honey. Mix the ingredients thoroughly and apply to your feet. Cover with cling film and rinse with warm water after half an hour.
- Softening mask with semolina . Mix 2 tbsp. spoons of sea salt, 1 tbsp. spoon of honey, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of sour cream and half a glass of semolina. Apply the resulting mixture to your feet for 20 minutes, then rinse with warm water.
- Cleansing mask with Dead Sea salt . Mix Dead Sea salt and olive oil in equal quantities, add a teaspoon of cinnamon. Apply to skin with massaging movements, rinse after 10 minutes.
Causes and types of hyperkeratosis
As a result of frequent skin irritation, a natural reaction occurs in the form of division of new cells and their thickening - hyperkeratosis (for example, rough skin on the knees and elbow joints).
The skin reacts to the influence and produces additional layers of keratin to protect damaged areas. Such a reaction can occur not only in response to physical impact, but also as a result of the following factors:
- chronic inflammation;
- infection;
- UV radiation, which is part of the sun's rays;
- irritating chemicals, etc.
Hyperkeratosis and improper footwear
One of the common reasons for the development of keratosis on the feet is improperly selected shoes.
Moreover, pressure on the sole comes not only from tight, but also from excessively loose shoes: in the absence of normal fixation of the foot, friction occurs, which quickly leads to pathological changes in the skin. Less commonly, hyperkeratosis develops on non-irritated skin. In this case, internal factors come into play. These may be hereditary diseases, dry skin due to metabolic disorders, deficiency of vitamins A and C, liver disease, gall bladder, thyroid disease, diabetes mellitus, congenital pathologies. In addition, symptoms of hyperkeratosis accompany chronic skin diseases - eczema, psoriasis, lichen planus, seborrhea, keratoderma, etc.
Wart. Photo: PiLens/Depositphotos
Hyperkeratosis can manifest itself in various forms:
- actinic keratosis, which causes rough, sandpaper-like patches of skin due to overexposure of the skin to ultraviolet rays (mostly sunlight);
- follicular hyperkeratosis - flakes of exfoliating skin clog the ducts of the hair follicles, which is why numerous small tubercles appear on the skin, reminiscent of “goose bumps”. People whose relatives suffered from follicular hyperkeratosis become ill more often. Deficiency of vitamins A and C, as well as violations of personal hygiene rules are risk factors. When the skin is exposed to cold, hard water and other physical factors, follicular hyperkeratosis can also develop in people with normal skin. After eliminating the irritating factors, the symptoms of hyperkeratosis disappear;
- calluses and corns - accumulation of dead skin cells due to constant friction and pressure on the soles of the feet, palms or other areas;
- warts are small bumps on the skin and mucous membranes of different parts of the body. Occur on the skin in response to the human papillomavirus entering the body;
- Eczema is a chronic inflammation of the skin that can be caused by allergies, chemicals and other factors. Eczema is also called dermatitis. It is characterized by symptoms such as itching, redness of the skin and small blisters;
- Seborrheic hyperkeratosis - small brown or black spots that look like moles usually appear on the face, neck, shoulders and back. They are benign, but often look suspicious. This is one of the most common benign skin tumors in adults;
- Lichen planus is characterized by white patches in the mouth and/or itchy, scaly, pink or purple patches on the skin caused by an abnormal response of the immune system to the skin's own proteins;
- Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin disease that causes hyperkeratotic, scaly silver plaques on the skin.
Leather and its features
Human skin is a multifunctional organ, the condition of which is in close relationship with other organs and systems of the body. It has 3 layers, the thickness of which differs in different parts of the body. This:
- epidermis;
- dermis;
- subcutaneous fat tissue.
The epidermis is the top and thinnest layer of the skin. Moreover, it itself has a multilayer structure and is formed:
- stratum corneum;
- glassy or shiny layer (present only in the skin of the palms and soles);
- granular layer;
- spinous layer;
- basal layer.
The epidermis is 85% composed of keratinocytes - cells that contain keratin and successively undergo stages of differentiation, shifting from the basal layer to the spinous, granular and gradually losing water, the nucleus and turning into prismatic scales of the stratum corneum. The latter are called corneocytes. At the same time, the epidermis is constantly renewed due to the desquamation of corneocytes of the uppermost stratum corneum and its replacement by other keratinocytes, which also transform over time into corneocytes and are ultimately desquamated.
Thus, the skin is constantly renewed. If this process is disrupted due to the action of certain factors and desquamation slows down with thickening of the granular and stratum corneum of the skin or excessive formation of creatine is observed, hyperkeratosis develops.