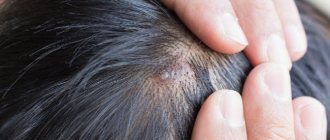
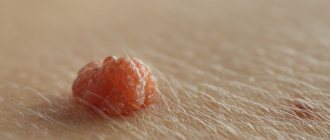
Nevi (moles) often appear on the scalp, representing benign neoplasms. They arise during life or be congenital. Often moles are hidden in the scalp and for many years may not cause aesthetic or other problems. Discomfort usually occurs if the moles are too large, protruding above the surface of the skin, or hanging. Inconveniences may be associated with the risk of injury when visiting a hairdresser, combing hair, or performing hygiene procedures.
If a mole grows, is it melanoma or cancer?
As we have already found out above, cell division in a mole is a normal phenomenon. Moreover, from my practice I have found out that almost all moles can increase during a person’s life. At the same time, it remains unclear - after all, cells of malignant tumors are also prone to rapid division and growth.
Unfortunately, without a microscope, we will not be able to determine by eye whether growth is associated with the degeneration of a mole. To find out this, a histological examination after removal of a mole is well suited. However, there is a less accurate, but simpler method - read on about it.
Causes
There are several main factors.
- Local defects in fetal development lead to the appearance of congenital formations. In most cases, they occur due to failures in cell division during late pregnancy. Such nevi are small in size, so they are difficult to detect immediately after the birth of the child.
- The hereditary factor plays an important role. If the parents had congenital moles, then the likelihood that the child will also have similar nevi on his head increases several times.
- Ultraviolet radiation stimulates the work of melanocytes in the basal layer of the skin. Over time, this process can lead to the growth of moles.
- Hormonal factors are another cause of formations. Quite often, nevi on the head appear in adolescents during puberty, in women during pregnancy, as well as in patients with endocrine pathologies.
Some experts call mechanical damage to the head the cause of moles, but this happens extremely rarely.
How to distinguish malignant growth of a mole from normal one?
First: almost every mole on our body can grow at a rate of about 1-2 mm per year. In my opinion, such a rate of increase should not raise suspicions among the oncologist.
There are rare types of melanoma (lentigo melanoma) that can grow very slowly. More on them later. For now, I’ll just note that in most cases, this tumor grows quickly. Its increase often occurs at a rate of 1-2 cm over six months to a year.
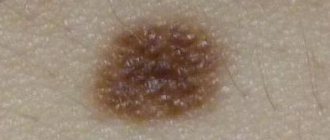
Second: when answering the question “is it melanoma?” You always need to analyze the complex of symptoms. Rapid growth alone is rarely enough to cause serious suspicion. This is because lentigo melanoma can grow very slowly, sometimes over decades. At the same time, it will definitely reveal itself by the presence of other signs or during dermatoscopy. The benign nature of a mole will be confirmed by its smooth edge, symmetrical shape, hair on the surface, and its existence for 5 years or more. In favor of malignancy - “geographical” edge, asymmetry along two axes, bleeding without trauma, etc.
Kinds
Experts identify several types of moles that can appear on the head.
- Large nevi are congenital and gradually increase in size. It is these neoplasms that occur most often and require medical intervention.
- The convex formations are hemispherical in shape and protrude strongly above adjacent areas of the skin. Dermatologists recommend removing such moles, since they can be easily injured when combing your hair or over-dried with a hairdryer.
- Flat nevi are the most common and safest nevi. As a rule, they do not cause discomfort, do not grow and do not require special care.
- Blue neoplasms have an unusual color: the shade varies from light blue to purple. Usually they protrude slightly above the surface of the skin.
- Hanging formations are quite rare on the head. But if they occur, immediate removal is required.
Nevi of all types are prone to malignancy when injured. To avoid dangerous complications, it is necessary to constantly monitor them and properly care for them.
How to accurately determine whether a mole is growing or not?
Sometimes it may seem that the mole that we have been carrying all our lives has grown in size. Sometimes it may seem that it has increased greatly. Unfortunately, the words “seems to have increased” will not help the doctor make a diagnosis. Accurate data required. There is an easy way to get them:
- Take a good photo of the mole against the background of a ruler with millimeter divisions. It's better to use a camera with a flash in macro mode. The photo must be taken by another person.
- If you have the slightest doubt about the size of the mole, you need to attach a ruler to it and compare the size with that in the original photo.
Rules of care
Your doctor will tell you what to do if a nevus appears on your head. However, there are several universal rules of care:
- you should avoid using scrubs and peelings at the site of formation,
- if the nevus is located under the hair, you need to comb it carefully and try not to touch the skin in this place with the comb,
- it is important that the hat or glasses do not put pressure on the skin defect,
- it is necessary to protect your head from exposure to ultraviolet radiation, wear hats in summer,
- You need to constantly monitor the size, color and shape of the tumor, and if there are any changes, immediately consult a doctor.
Any formation is at risk of malignancy, but it is higher if the mole is large or frequently injured. In this case, doctors recommend removal without waiting for complications. You should also contact a dermatologist if the following symptoms appear:
- the nevus has increased in size or acquired an asymmetrical shape,
- the surface of the neoplasm has changed, the skin began to peel off, tubercles, cracks and black spots appeared,
- the mole has changed color, turned black or red, the skin around it has become white,
- the formation hurts or itches.
In case of injury to the nevus, you must also consult a doctor. Any dynamics should be a cause for concern.
Summary or briefly about the main thing:
If your mole has enlarged, wait a minute to sound the alarm. First, answer the question: does the mole grow faster than 1-2 mm per year? If the rate is not higher than indicated and there are no other symptoms of melanoma (“geographical” edge, asymmetry along two axes, bleeding without injury, etc.), then most likely everything is fine with the mole. At the same time, if there is even the slightest doubt about the correctness of your conclusions, the oncologist should say the last word during an in-person examination.
If you still have questions, the following will help you:
- In-person appointment with an oncologist
(St. Petersburg) - Mole removal
with histology (St. Petersburg) - My online consultation (from anywhere in the world)
Prices for removing nevi on the head
Removal of nevi (moles), fibroids in adults and children over 12 years of age
| Delete area | Size | Price, rub |
| Initial appointment with a cosmetologist, consultation free of charge - subject to completion of procedures on the day of application Make an appointment | 1000 0 | |
| Head removal Make an appointment | up to 1 cm. | 1 500 |
| Head removal Make an appointment | more than 1 cm. | 2 000 |
What are nevi
They are a formation consisting of melanocytes. The surface of the mole is smooth and dark in color. There are up to 40 such formations on the body of the average person. Some moles appear on the baby's body immediately after birth. Others are formed during growing up. Nevi can change their appearance and color. Most changes occur during adolescence during puberty. Also, degeneration in a nevus can begin when a person is exposed to direct sunlight for a long time. Ultraviolet radiation in large quantities has a negative effect on the skin. According to statistics, the more time a person spends in the sun, the more moles there are on his body.
The changes concern not only color, but also appearance. An ordinary mole can become flabby and soft, or, on the contrary, develop into a dense and colorless formation. There are a large number of different types of nevi. The main danger of such formations, when exposed to certain factors, is that they can degenerate into malignant ones. Particularly dangerous are complex moles, as well as large formations. They must be constantly monitored by the attending physician in order to prevent a dangerous transformation.
Treatment
Not all nevi can be removed. In most cases, it is enough to follow simple recommendations to prevent complications. If a mole is often injured or there are signs of malignant degeneration, such a formation must be removed.
What to do at home
All activities carried out at home are aimed at preventing complications. No home treatment can effectively remove the formation.
Care Tips:
- try to wash and comb your hair carefully so as not to damage the nevus;
- do not use scrubs and peels on the scalp;
- if the mole is localized on the open part of the head, cover it with a sun bandage.
Under no circumstances should you remove the formation yourself! Such an attempt at treatment can damage the nevus and provoke the development of complications (malignancy, bleeding).
One of the most important things you can do at home is preventative checkups. It is necessary to regularly examine the nevus and evaluate it using the ACORD algorithm.
Only a doctor under appropriate conditions should remove moles; self-medication is unacceptable.
Surgery
The final decision on the need to remove the nevus should be made by the patient together with the doctor after a complete examination. Surgical treatment is indicated for all patients with suspected melanoma. To remove the formation, different methods can be used - laser therapy, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, surgical excision.
| Treatment method | Description, advantages and disadvantages |
| Laser therapy | Suitable for removing nevi, which are often injured (especially on open areas of the head). This is a modern treatment method that uses a laser to remove the formation. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia; no scars are left at the removal site. The main disadvantages include the high cost of treatment and the impossibility of removing malignant tumors. |
| Electrocoagulation | The method is based on exposure to electric current. The nevus is cauterized, and after some time the necrotic tissue is rejected on its own. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. |
| Cryodestruction | Exposure to liquid nitrogen is often used to remove small lesions. Freezing and subsequent destruction of the mole occurs. The procedure is painless, does not require anesthesia or local anesthesia, but is not suitable for removing large nevi. Sometimes several sessions are required for complete removal. |
| Surgical excision | Surgical excision is the main treatment method for melanoma and large benign tumors. A scalpel is used for removal; the operation is performed under local or general anesthesia. After excision of the nevus or melanoma, the wound is sutured, and the formation is sent for histological examination. |
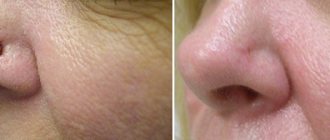
Removal
Removing a mole on the head will allow you to forever forget about the discomfort that the neoplasm causes. The doctor will choose the optimal method of excision after examination. Today there are five most effective methods:
- surgical intervention - a traditional operation during which removal occurs using a scalpel;
- electrocoagulation - the skin defect is excised with high frequency current;
- cryodestruction - ultra-low temperatures are used for removal: liquid nitrogen or a special cryodestructor that freezes tissue;
- laser surgery - the mole is burned out with a laser beam;
- radio wave method - the nevus is irradiated with high frequency waves using the Surgitron device.
To remove moles on the head, specialists at our clinic use various methods. The doctor will select the optimal method during a preliminary consultation. We guarantee excellent cosmetic results, complete safety and painlessness of the procedure.
What does it look like
The appearance of the formation in the photo may vary. All of the following options are normal:
- The color is most often brown, but can be black, red and even purple. A white rim may appear around.
- They rise (convex) or do not rise (flat) above the skin level.
- The mole can be located on any part of the head: the scalp (back of the head, crown), face.
- The size ranges from a pinpoint to 5 cm or even more. Birthmarks are often larger in size.
- There are no additional symptoms. The patient should not be bothered by pain, numbness, or burning. The appearance of these symptoms most likely means that we are talking about another pathology.
Types of nevi
There are moles on every person's body. Most often they do not pose any danger. If the quantity exceeds 50 pieces, it is advisable to visit a doctor. Such patients are at risk for developing melanoma. Particularly alarming should be asymmetrical formations with an uneven surface, which have a non-standard color, more than 6 mm in diameter, and began to form on the body already in adulthood.
Congenital
This category includes formations with which a person is immediately born. Congenital nevi vary in shape, color and size. In some cases, the mole may occupy a large part of the child's body. Such neoplasms are cause for concern as they often degenerate into cancerous tumors.
Regular
The category of common moles consists of formations that have a symmetrical shape, uniform color and smooth surface. Most often the color is brown or pinkish. There are no foreign inclusions on the surface. Also, such moles can have a dome shape.
Atypical
Moles with non-standard size and appearance. There are few of them on the body, several times less than ordinary moles. The main danger of such neoplasms is that under certain factors they can degenerate into melanoma. Another feature of such formations is that they have an uneven color, uneven edges, and the nevus itself is asymmetrical. For people with atypical moles, it is important to control their number on the body; the more formations, the higher the risk of melanoma. Constant monitoring by the attending physician and completion of the necessary studies is required.
Blue
Neoplasms are divided into two categories: they can appear on the body already in the womb or develop during a person’s lifetime. They got their name due to their bluish color. But this category also includes nevi, the color of which varies from light gray to black. Most often, formations characteristic of the skin of Mongoloids; in other races they develop in extreme cases.
Miescher's nevi
Formations are brown or flesh-colored. The most common place for moles to appear is in the neck and face. The surface is hard, dome-shaped, but smooth, without foreign inclusions. Hair often grows on the nevus.
Nevi of Unna
In appearance they are similar to the moles from the previous description. Features include their appearance: they resemble raspberries. The color of the new growth is brown.
Meyerson's nevus
It is not difficult to determine the problem around such a mole, a rash with red papules begins to develop and spread. In some patients, eczema in the area is not registered. Another feature of Meyerson nevi predominantly develops in men over the age of 30 years. Women are much less susceptible to this problem.
Nevi halo
They got their name due to the atmospheric phenomenon of the same name. A pale whitish ring begins to appear and develop around the mole. Such education does not last until the end of life, even if nothing is done with it. First the ring changes its color to pink, and then disappears. In some cases, new haloes may appear around the tumor throughout the patient's life.
Spitz nevi
Moles are slightly raised above the skin and have a dome shape. The formation itself is pinkish in color; it is acquired and appears on the skin of patients at a young age. Color may be different. The surface of the nevus is often damaged and begins to bleed. As a result, doctors often confuse such moles with malignant ones, referring the patient for histological examination.
Reed's nevi
The color of the formations varies; they can be black or dark brown (closer to a black tint). Mostly develop in women. The peculiarity of the neoplasm is that it increases in size very quickly, which is why it causes concern among doctors. In fact, such moles are mostly harmless and rarely develop into cancer.
Agminated
They are several moles at once, which are concentrated on a small area of the skin. The peculiarity of formation is that all nevi are not the same. Some may be more, some may be less. Also, among flat formations, dome-shaped ones, etc., may appear.
Only the main types of moles are listed above. In fact, there are a huge number of such neoplasms on the skin. To determine what type of mole a particular mole on the body of a patient seeking medical help belongs to, doctors perform dermatoscopy.
What to do with huge nevi
The overwhelming majority of nevi are small formations on the skin with a diameter of several millimeters, which are practically invisible to the naked eye. Exceptions are formations that exceed 20 centimeters in diameter. They are classified as huge. The mole can cover most of the arm, leg, back, etc. Such moles can appear on the body of representatives of any race. They develop in almost 2% of the population of our planet. The main danger of large nevi is that they often degenerate into malignant ones. Formations that appear in the area of the spinal column are considered extremely unstable. Moles that continue to rapidly increase in size and also change their color should cause concern.
The most unpleasant huge nevi on the body of newborn children. As the child grows over time, it seems to parents that the mole is decreasing in size, but in fact it continues to grow, almost not keeping up with the whole body.
In 30% of cases, such nevi become melanoma. They should be under the supervision of a doctor. Rebirth can occur at absolutely any age. Removal of giant nevi is indicated. The most commonly used method is surgical excision. If the mole is located in a hard-to-reach place, the patient may be offered alternative treatment methods. Removal is also possible using laser therapy.