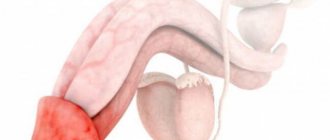
The vagina is an organ of the female reproductive system, which is a canal connecting the cervix to the vulva (external female genitalia). Its wall consists of muscles, the outside is covered with a sheath of connective tissue, and the inside is lined with mucous membrane. On average, the length of the vagina in adult women is 7.5 cm along the anterior wall and 9 cm along the posterior wall. The urethra and bladder are adjacent to the vagina in front, and the rectum is adjacent to the back.
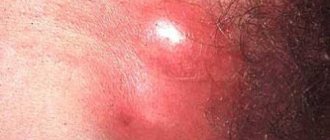
Vaginal wall cancer is a fairly rare malignant tumor.
Types and stages of vaginal cancer
Depending on the histological structure, there are two types of vaginal cancer:
- The most common type of cancer is squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina. It gets its name from the fact that it develops from the squamous epithelium that lines the organ from the inside. Such malignant tumors usually grow slowly, rarely invade neighboring organs and give distant metastases.
- Less common are more aggressive adenocarcinomas . They come from glandular cells that produce mucus. Adenocarcinomas are more likely than squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina to invade adjacent organs, spread to lymph nodes, and metastasize.
Stages of vaginal cancer:
- At stage 1, the tumor has a diameter of up to 2 cm (IA) or more (IB), but does not grow beyond the vagina.
- At stage 2, the tumor has a diameter of up to 2 cm (IIA) or more (IIB) and grows into neighboring tissues.
- At stage 3, the tumor grows more strongly into neighboring tissues and spreads to regional lymph nodes.
- Stage 4 vaginal cancer is characterized by invasion into the rectum, bladder, or beyond the pelvis (IVA), or the presence of distant metastases (IVB).
Causes of vaginal cancer
Up to 75% of vaginal and cervical cancers are associated with human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. There are different types of viruses, they can cause warts on the hands and feet, lips, tongue, and condylomas in the genital area. Some types of pathogens can lead to malignant transformation of cells.
Other risk factors for vaginal cancer in women:
- Age . In 85% of cases, squamous cell carcinomas develop in women over 40 years of age. Almost half of the cases occur in women over 70 years of age.
- Vaginal adenosis is a condition in which areas of the vaginal mucosa appear lined with glandular cells, characteristic of the cervix, uterus and fallopian tubes. The risk of cancer is slightly increased, and yet such women need increased attention from gynecologists. According to statistics, vaginal adenosis occurs in 40% of women.
- Cancer and precancerous changes of the cervix increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina. According to most researchers, this is due to the fact that vaginal and cervical cancer have similar risk factors. Sometimes vaginal cancer occurs after uterine cancer.
- Smoking harms more than just your lungs. It doubles the risk of vaginal cancer.
- Alcohol consumption . One recent study found that the risk of vaginal cancer was lowest among women who did not drink alcohol at all.
- HIV infection . _ The immunodeficiency virus also increases risks, according to some studies.
- There is a condition called uterine prolapse : in which the uterus descends and prolapses into the vagina. The pathology can be treated surgically or using pessary rings. There is some evidence that long-term pessary wear may lead to chronic vaginal irritation, which in turn increases the risk of cancer. These data do not have reliable evidence.
The presence of any risk factor or even a combination of different factors does not guarantee that a woman will definitely develop cancer. At the same time, sometimes cancer occurs in women who do not have any risk factors from this list.
Probability of infection
HPV infection of the genitals and perineum is highly contagious, or contagious. Infection during a single sexual contact with a partner who has the virus occurs in six out of ten cases. The possibility of genital warts increases even more in the presence of a number of conditions.
| Predisposing factor | Characteristic |
| Young age | Most often, clinical signs of HPV infection appear in patients aged 20 to 24 years. In general, the age range from 17 to 33 years is the most likely for women in terms of the growth of papillomas in intimate areas. |
| Early sexual debut | Early onset of sexual activity, when the processes of hormonal changes have not yet been completed, is a factor that increases the risk of genital papillomatous formations. |
| Frequent change of sexual partners | A large number of sexual partners, frequent and promiscuous sexual contacts significantly increase the chances of contracting human papillomavirus infection. |
| Unprotected sexual contacts | Barrier contraception - the use of a condom - still remains the only easily accessible and relatively inexpensive means of possible, but not absolute, protection against HPV. It is impossible to completely get rid of the likelihood of infection with its help, since a condom may not isolate all contacting areas of damaged skin. But unprotected sexual intercourse is an almost guaranteed infection. Unprotected anal sex is an even greater risk factor, as it is often accompanied by microtrauma to the mucous membrane and skin. |
A combination of factors greatly facilitates the possibility of infection.
Symptoms of vaginal cancer
In the early stages there are usually no symptoms. Often the first manifestation is vaginal bleeding not associated with menstruation. However, this symptom is nonspecific; it also occurs with other pathologies, for example, with submucosal fibroids - benign formations in the muscular layer of the uterine wall.
Other signs of vaginal cancer are also nonspecific and occur in other pathologies:
- Feeling of discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse.
- Vaginal discharge.
- Seal, node, formation in the vagina.
- Pain in the pelvic area.
- Painful urination.
- Constipation.
The last three symptoms on the list usually occur in the later stages, when the tumor has spread beyond the vagina.
The occurrence of any of the above-mentioned manifestations is not a reason to panic, but definitely a reason to consult a doctor as soon as possible. Most likely it is not cancer. But you won't know for sure until you get tested.
Symptoms
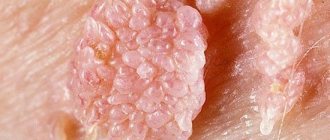
Genital papillomas in women can be single or multiple (see photo), small or large in size. Usually, during initial growth, they look like small flesh-colored or pink nodules, and later turn into growths in the form of papillae, similar in appearance to the comb of a rooster or cauliflower inflorescences. They are soft in consistency and have a so-called stem. Sometimes they grow up to several centimeters in diameter. The most common sites of localization in women:
- vaginal part of the cervix;
- walls and vaults of the vagina;
- labia;
- urethra;
- perineal skin;
- area around the anus;
- groin area.
Genital warts often exist asymptomatically. In this regard, women do not complain, especially with small lesions. Bleeding and weeping appear when the growths are traumatized, itching, pain, and sometimes an unpleasant odor - when ulceration and the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. Discomfort during urination occurs when papillomas are localized in the urethra, and during defecation - in the anus.
Diagnostic methods
The examination begins with an examination by a gynecologist and a PAP test (other names are Papanicolaou smear, cytology smear). If the doctor finds pathologically changed areas, and the analysis reveals atypical cells, colposcopy . During the procedure, mirrors are inserted into the vagina and it is examined using a special device - a colposcope - which magnifies the image using lenses. In order to better examine and evaluate pathologically changed areas, the gynecologist applies a solution of acetic acid or iodine to the vaginal mucosa.
The colposcope is not inserted into the vagina; during the examination it is kept at some distance. This is a safe test and can be performed even during pregnancy.
During colposcopy, you can perform a biopsy - obtain a piece of tissue from pathologically changed areas and send it to the laboratory to study the structural features of cells and tissue. A biopsy is the most accurate method for diagnosing cancer.
Write to an oncologist
If necessary, other studies are carried out:
- Chest X-ray
- Computed tomography helps to clearly assess the shape, position, size of the tumor, damage to the lymph nodes and neighboring organs. Sometimes contrast is used during a CT scan: the solution is given to drink or administered intravenously. If a suspicious formation is detected, a needle can be inserted into it under the guidance of a computed tomography scan and a biopsy can be performed.
- Magnetic resonance imaging helps assess the extent of cancer spread. This is a more complex and time-consuming study compared to CT, but sometimes has advantages.
- Positron emission tomography for metastases. A special substance with a radioactive label is injected into the body and images are taken with a special apparatus. Cancer cells accumulate this substance, and all lesions become visible on photographs.
- Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the rectum and colon. Indicated for large and/or vaginal tumors located close to the intestine.
- Cystoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the bladder. During this, a biopsy may be performed.
Routes of infection
HPV is very easily transmitted from person to person. Entry into the body occurs in several ways.
| Method of infection | Description |
| Sexual | When genital warts occur in intimate places in women, this is the main method of infection. The virus can enter the body through oral-genital and anal contact. |
| Contact and household | The virus can survive for a short time in exfoliating skin cells, so the presence of damage to the skin and mucous membranes, even of a microscopic nature, allows viral particles to penetrate the human body. Infection occurs when visiting public toilets, swimming pools, baths, and gyms. |
| Autoinfection | The woman herself can spread the virus to new areas of the skin when shaving and epilating. This route of infection is also called autoinoculation. |
| From mother to child | The viral infection can be transmitted from mother to child during childbirth. This causes the appearance of papillomas in a newborn on the mucous membranes of the mouth, pharynx, genitals, and in the anus. |
The likelihood of infection increases in the presence of predisposing factors.
Surgery
Depending on where the tumor is located and how far it has spread beyond the organ, different types of surgery are used for vaginal cancer:
- Sometimes, for small stage I tumors, local resection . The vagina is preserved, and the tumor is removed along with a portion of surrounding healthy tissue.
- Vaginectomy - removal of the vagina. It can be partial (when part of the organ is removed), complete and radical (when the vagina and surrounding tissues are removed).
- Trachelectomy - removal of the vagina along with the cervix. Such surgical intervention is resorted to in rare cases when the tumor is located in the upper part of the vagina.
- Hysterectomy - removal of the vagina along with the uterus. Often, some surrounding tissue, fallopian tubes and ovaries are also removed. The operation can be performed through the vagina or through an incision (or, in the case of laparoscopic surgery, a puncture) in the abdomen.
- Pelvic evisceration is the most radical and serious operation, when the rectum and part of the colon and bladder are removed along with the vagina, uterus and uterine appendages.
Often, nearby (regional) lymph nodes are removed along with the vagina.
Removal of papilloma
Unfortunately, there is currently no universal cure for papillomas in intimate places. In addition, the viral infection is incurable, that is, with a single invasion, it remains in the body for life, periodically showing activity. However, it is still necessary to remove the external manifestations of the disease, that is, papillomas from the genitals, since there is a risk of developing malignant neoplasms.
There are many ways to remove intimate papillomas. To get rid of small tumors, it is enough to use antiviral agents for local action and oral administration. To remove large tumors, it may be necessary to use more radical measures, which include surgery, laser and radio wave therapy, cryodestruction, and many others.
Drug treatment
For small tumors, treatment of papillomas in intimate places, for example, in the groin area or on the genitals, can be done through the use of antiviral drugs. It is important to remember that the choice of the appropriate medication should be made only according to the recommendations of the attending physician.
The following products are particularly effective:
- Acyclovir. The product is presented in the form of tablets and ointments. It has a powerful antiviral effect, quickly suppressing the activity of pathogenic flora. In addition, its regular use to eliminate papillomas in intimate places helps to increase the body's protective functions.
- Oxolinic ointment. A simple but highly effective remedy for the treatment of papillomas. It can be used to remove small tumors.
- Panavir. A broad-spectrum medicine that helps increase the body’s resistance functions and suppress the activity of viral flora. It is recommended to use it to remove existing growths, as well as their reappearance.
- Viferon. One of the most effective immunomodulatory agents, which also has antiviral properties.
To effectively treat intimate papillomas, a specialist can prescribe the patient the complex use of two or more drugs.
The most common combinations of medications are complexes of products for internal and external use.
We should also talk about radical methods for removing papillomas in intimate areas.
If large growths are present on the skin and mucous membranes, the following methods for eliminating them are recommended:
- cryodestruction. The method involves exposing papillomas to liquid nitrogen, which literally freezes pathological tissue, promoting their destruction. Due to the somewhat painful nature of the method, the procedures are carried out using anesthetics.
- Electrocoagulation. One of the most effective methods, which involves removing tumors using high-frequency current. This method allows you to get rid of even large growths.
- Laser therapy. One of the most gentle methods, the use of which allows you to avoid the occurrence of inflammation and bleeding at the site of removal of the growth.
- Surgery. Removal of intimate papillomas using a scalpel is practiced quite rarely, since the use of this technique is fraught with the development of complications. More often, this method is used only for large tumors, the removal of which by minimally invasive methods is not possible.
The choice of a suitable treatment method for papillomas is made individually after examining the patient by a specialist. In case of significant damage to the skin, complex therapy can be used, combining invasive and medicinal methods of treatment.
Folk remedies
Procedures for removing papillomas on the genitals can be carried out independently using folk remedies. However, this is only permissible when the growths are small in size. In addition, before removing papilloma in intimate places at home, you need to consult a specialist.
The following methods are popular:
- aloe or kalanchoe juice. To obtain this antiviral agent, it is enough to grind several leaves of the selected plant to a pulp and squeeze out some juice using gauze. Next, you need to regularly apply fresh juice to the surface of the papillomas, as well as to healthy skin, which will help prevent the spread of infection.
- Propolis infusion. To remove growths, it is recommended to use pharmaceutical medicine. Using it is more than simple: to get the effect, it is enough to treat the growths at least three times throughout the day. It should be remembered that treatment of mucous tissues requires special care.
- Celandine juice. One of the most effective natural remedies for treating papillomavirus is fresh celandine juice. To remove tumors, it is enough to apply it to the surface of the growths. When processing, it is important to be careful not to get the product on healthy tissue, as this can cause severe burns.
Treatment of papillomas in intimate places with the help of folk remedies should be carried out until the growth is completely removed and the affected area is healed. You should know that even with small growths, treatment with home methods can take more than one week.
Features of treatment during pregnancy
Genital papillomas on a woman’s genitals, identified during the gestational period, can cause many problems. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy the use of most antiviral agents is not recommended. However, treatment is still recommended, since there is a high risk of infection of the fetus when passing through the birth canal.
If a woman has papillomas on her intimate organs, the use of invasive treatment methods is recommended. It is recommended to remove growths using a laser, radio wave technique, scalpel or other methods. It is important to remember that any manipulation is permissible only after receiving medical advice.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for vaginal cancer is given before surgery to shrink the tumor, combined with radiation therapy to enhance its effect. Various drugs are used: cisplatin, carboplatin, 5-fluorouracil, docetaxel, paclitaxel. It is often difficult to say which chemotherapy regimen will be most effective, since vaginal cancer is rare and there is not much research done at the moment.
Diagnosis of genital warts
Typically, diagnosing skin growths in intimate areas is not difficult. A doctor can visually identify condylomas. If several neoplasms grow and merge into a single focus, a characteristic colony is formed. It looks like cauliflower.
To accurately confirm the type of pathogen and exclude a malignant process, the following additional studies are carried out:
- colposcopy;
- PCR diagnostics;
- cytological screening;
- biopsy.
Before deciding to remove condyloma, it is important to exclude the possibility of the presence of atypical (malignant) cells.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is used before surgery along with chemotherapy, or, if the tumor has spread to neighboring organs and lymph nodes, as an independent type of treatment. Radiation for vaginal cancer can be done in different ways:
- From an external source . The woman is placed next to a special apparatus and the vaginal area is irradiated.
- Brachytherapy is irradiation of a tumor from a miniature source placed inside the vagina.
External radiation for vaginal cancer is often combined with brachytherapy.
Survival prognosis. Are there relapses after treatment for vaginal cancer?
To assess the prognosis for cancer, there is a five-year survival rate. It indicates the percentage of patients who are alive 5 years after diagnosis. For vaginal cancer, this indicator is quite optimistic:
- At stage I - 84%.
- At stage II - 75%.
- At stages III and IV - 57%.
Find out the exact cost of treatment
The prognosis is least favorable for vaginal cancer with metastases. But it is relatively uncommon because such tumors grow and spread slowly.
Sex life after treatment
In order for a woman to be able to have a sexual life after surgical treatment and removal of the vagina, they resort to reconstructive plastic surgery. The vagina can be reconstructed, for example, using a section of intestine.
Usually, after reconstructive surgery, orgasm becomes impossible. But, if it is possible to preserve the clitoris, the woman retains the ability to experience a clitoral orgasm.
Radiation therapy can cause the vagina to narrow, making sexual intercourse painful. Moisturizing creams with hormones and special dilators help cope with this symptom.
Risk factors
Infection with the papilloma virus most often occurs through sexual contact with an infected person. All types of unprotected sex are dangerous - vaginal, anal, oral. Due to the small size of the virus, a condom does not provide 100% protection against infection. Therefore, people who are promiscuous have a particularly high risk of infection.
Some types of HPV can be transmitted even through simple contact of mucous membranes. Contact and household transmission of the virus is less common.
In total, medicine knows more than 100 types of HPV. HPV strains 6 and 11 can provoke the development of genital warts. The presence of these pathogens in the body before the appearance of skin growths is almost impossible to notice. In such a latent state, the infection can exist until provoking factors arise.
The activation of HPV and the formation of condylomas can be caused by:
- infection with another sexually transmitted infection (chlamydia, herpes virus, Trichomonas, etc.);
- weakened immunity, including immunodeficiency;
- vitamin deficiency, malnutrition;
- frequent stress, tension;
- pregnancy;
- undergoing surgical operations.
Prevention and early diagnosis
Measures to prevent vaginal cancer come down to preventing papillomavirus infection and giving up bad habits:
- Avoid promiscuity.
- Have sex with condoms: This reduces the risk of HPV infection, although it does not completely protect.
- Regularly visit a gynecologist and take smears for cytology - this will help you detect precancerous changes in time and take action.
- If you smoke, give up the bad habit.
- The Gardasil vaccine protects against human papillomavirus infection.
Regular examinations by a gynecologist and Pap smears help diagnose a tumor in a timely manner. If you begin to be bothered by certain symptoms, do not put off visiting a doctor.
Treatment of genital papillomas
Therapy for genital papillomas should solve the following key problems:
- improve immunity;
- remove existing papillomas;
- prevent the appearance of new growths.
It is extremely difficult to completely get rid of papillomavirus due to its variability and significant species diversity, so treatment is predominantly symptomatic and restorative.
It is necessary to treat not only the woman, but also the sexual partner.
The main goal of therapy is to convert the virus into an inactive, or dormant, state.
| Medical direction | Ways to achieve |
| Boosting immunity | A decrease in the protective properties of the immune system contributes to the appearance of genital warts in the genital area in women. With good immunity, the body is able to cope with HPV contained in cells in 80-90% of cases within 24 months. The effectiveness of the local immune response can be increased with antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs: Interferon, Isoprinosine, Allokin-alpha, Cycloferon, Genferon, Epigen Intim, Lykopid, Aldara, Immunomax, etc. It is possible to use various dosage forms: injection solution, tablets, vaginal and rectal suppositories , ointments, creams, sprays. |
| Removal of papillomas | Therapy cannot be limited to just removing existing papillomatous growths. The patient should be treated comprehensively. The disappearance of small papillomas and regression of large papillomas can sometimes be achieved with immunostimulating and antiviral treatment. In addition, papillomatous formations should not be removed without systemic treatment, as this promotes infection of adjacent areas of the skin and mucous membranes, increasing the possibility of relapse. Removal of papillomas in intimate areas can be carried out in several ways: surgically, using alternating electric current, laser, liquid nitrogen, using coagulation with chemicals. |
| Prevention of HPV infection | A healthy lifestyle is a factor that helps increase nonspecific immunity, and it is necessary to reliably resist HPV infection. You should create the correct stereotype of sexual behavior: choose one sexual partner, avoid casual relationships, use a condom. For primary prevention, there is a vaccine called Gardasil, which is effective against HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18. Vaccination is effective only for preventive purposes and is not intended to treat an existing disease. The best result is achieved if vaccination is carried out before the onset of sexual activity. Side effects when administering the vaccine are minor. |
Gardasil is a vaccine that allows you to protect against papillomavirus, which is responsible for the formation of papillomas in the intimate area
Cost of treatment for vaginal cancer
The cost of treatment depends on a number of factors: the stage of the tumor, the treatment program, the length of hospital stay, and the clinic’s pricing policy. At Euroonko you can get medical care at the level of leading Western oncology centers, but at a lower price. We have all the necessary original drugs, an excellently equipped operating room in which surgical interventions of any degree of complexity are performed.
| More information about treatment at Euroonco: | |
| Tumor markers for women | from 1,600 rub. |
| Oncologist consultation | from 5,100 rub. |
| Emergency oncology care | from 12,100 rub. |
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78