You wake up and see bright marks on your legs, stomach, arms, and maybe other parts of your body. Sometimes they itch, sometimes they don't. We will analyze in detail where red spots on the body appear, like bites, what are the consequences and what are their differences. All answers are below. Let's start with an interesting story.
Allergic rash similar to mosquito bites - what is it and how to fight it
From the article you will learn which allergies manifest themselves as rashes in the form of mosquito bites and other insects, as well as how to distinguish a mosquito bite from an allergy.
Mosquito bites, although not a pleasant event, are quite common in our lives. And during the period of activity of these insects, we do not pay much attention to the individual itchy blisters that appear on the skin every now and then.
But what if mosquito bites appear on the body, and it’s winter, when there are no mosquitoes nearby; fleas, ticks and other parasites capable of leaving such marks were also not found, and the rash in the form of mosquito bites still does not go away, persisting for several weeks, or even months.
In this case, first of all, suspicion falls on an allergy, namely on one of the varieties of its manifestation – urticaria.
The main reasons for the development of urticaria, or allergies in the form of mosquito bites, are allergies to insects, food products, medications, and infectious agents.
However, urticaria is a symptom not only of allergies, but also of autoimmune processes (an allergic reaction to the body’s own cells), toxicoderma (occurring when active and toxic chemical compounds get on the skin and into the body, from insect bites), disorders of the liver, as well as may occur when the skin is subjected to excessive physical exposure to cold, heat, sunlight, vibration, or pressure.
There are also other diseases whose symptoms are a similar rash:
- infectious diseases;
- diseases of the circulatory system;
- rubella, measles, herpes and some others.
“I was bitten by a snake”: two dots around swollen skin
It was with these words that our friend Peter jumped up in the middle of the night. The whole family was alarmed. Mom began to examine the wound. The problem was also created by the fact that the people were in the village, 35 km from the nearest hospital. Then the question arose whether to go to the doctors at 3 am and whether our hero would die before the morning. You will say: “Of course, go, this is a man!”, but 15 years ago more severe morals reigned in the villages. Fortunately, the presence of a snake was quickly ruled out, because another creature was found in the room.
Two-tailed attack: 2 centimeters in length, huge whiskers and spread paws, and in the back there are pincers. This is exactly what the cute creature, also called an earwig, looks like.
- Threat No. 1 - our new “friend” does not have a stinger, and the scary-looking device is the cerci, the forceps with which it holds prey. You might get bitten by them too. Red dots on the body will look like bites from a cold-blooded animal, but will not cause harm;
- Threat No. 2 - in rare cases, a double-tailed fish gets into a person’s ear and swarms around in it. She won't eat your brain, but she's pretty scary. And don’t forget about ticks. If the population of a species in a house grows, then the likelihood of such an incident also increases.
The earwig looks scary, but does not pose an impressive threat, but by carrying out a comprehensive treatment of the more dangerous inhabitants of apartments, houses and offices, you will get rid of it too. Still, do not forget to inspect the premises for snakes. They usually don't crawl far.
What do mosquito bites look like?
Most often, mosquito bites manifest themselves as itching and the formation of reddish blisters on the skin. Below in the photo gallery you can see what the body’s usual inflammatory reaction to a foreign insect protein looks like.
What does a mosquito bite look like in adults and children: photo
Main symptoms of mosquito bites
Sometimes it is possible to distinguish manifestations of an allergy from a bite without visiting a doctor.
| Symptom | Photo |
| Mosquitoes most often bite exposed areas of skin, so you are unlikely to find marks under clothing (especially thick ones) | |
| Visually, the bite is quite pronounced, with reddish inflammation around it. Often this area is quite itchy. | |
| You may notice multiple bites after sleeping (especially in the summer). The presence of marks on several family members also speaks in favor of bites. |
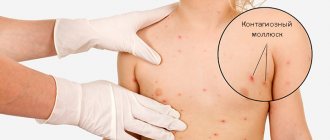
Parasites
Often parasitic diseases lead to pimples popping up all over the body and itching like mosquito bites. Indeed, sometimes a person is attacked by parasitic insects, such as bedbugs, ticks, fleas and others, which leave red areas on the skin. These itchy bite marks can become infected and complicated by purulent inflammation.
The symptoms of the pathological condition, when after a parasitic infection a rash similar to mosquito bites appears and itches, depends on the type of insect. In such cases, the appearance of itchy blisters may be accompanied by:
- a burning sensation and itching at the site of the lesion,
- swelling of soft tissues,
- increase in local body temperature,
- peeling after flea and bedbug bites.
Read also: Itchy scrotum: causes of testicular itching, treatment
Allergy symptoms
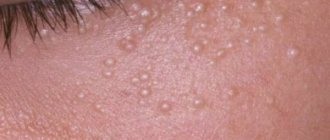
Urticaria, or urticaria, is characteristic of an immediate allergic reaction, and therefore occurs within a few minutes after contact with the allergen.
Photo: characteristic appearance of allergic urticaria
The symptomatic manifestations of urticaria are similar to those caused by a nettle sting or an insect bite. It is due to the identity of the type of rash that allergies are similar to mosquito bites. Below are the main symptoms indicating an allergy.
- With this condition, blisters appear on the skin throughout the body - small, dense, swollen, raised elements of a round or irregular shape that can merge with each other. Please note that the rash in this case also occurs in areas covered by clothing
- The blisters are pale pink in color, and the surrounding skin is normal or reddened. The rash is accompanied by severe itching.
- Unlike a bite mark, which can remain unchanged for a long time, the rash disappears without a trace after the cessation of exposure to the allergen.
- The allergic reaction disappears quite quickly or becomes symptomatic when taking antihistamines
- People around you do not have any symptoms of the rash.
Actually, allergic reactions also occur to mosquito bites and other insects (especially in children) and there are few of them that can be confused with.
Familiarize yourself with the characteristics and treatment of this allergy, as well as photographs of allergic reactions to mosquitoes and other midges.
Atopic dermatitis: symptoms and treatment methods
The causes of atopic dermatitis are still unknown for sure. It can appear in both infants and adults. As a rule, at first the skin simply turns red. Over time, itching, burning, and small blisters begin to appear. “Favorite” places for atopic dermatitis: cheeks, lower back, shoulder blades, calves, forearms.
There is only one non-drug way to get rid of the manifestations of atopic dermatitis: a strict diet. As a rule, through selection, those products are determined, against the background of which dermatitis becomes less and eventually disappears completely.
There are also medicinal methods of treatment: for example, Advantan cream is highly active due to the content of corticosteroids in its composition. Already on the second or third day of treatment, the patient feels significant relief. The disadvantage of this remedy is that, as a rule, after stopping the drug, all the symptoms return again. The main key to the success of treatment is to eradicate the cause that caused the blisters to appear. Itchy legs, like insect bites, but there are no other symptoms - it is likely that the cause of this condition is atopic dermatitis.
Treatment of allergic urticaria
The action of the allergen that caused the reaction ceases. In addition, the patient should switch to an elimination diet that excludes foods with a large number of allergens (chicken, citrus fruits, nuts, eggs, strawberries, spices, foods with a high content of dyes).
In acute cases of urticaria, antihistamines are prescribed.
In the case of the development of a severe form of the disease, infusion antihistamines, corticosteroids (prednisolone, dexamethasone), calcium preparations that reduce sensitivity to allergens (calcium chloride or gluconate) are used; when the allergen is taken orally, gastric lavage is performed, and activated carbon and other sorbents are also used.
Preventive measures
People who experience attacks of allergic urticaria are also prone to developing urticaria in response to other external factors: light, heat, cold, pressure, mechanical damage to the skin.
To ensure that allergies similar to mosquito bites bother you as little as possible, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid stress; on the recommendation of a doctor, it is possible to take mild herbal-based sedatives.
- Avoid allergenic factors to which the patient is hypersensitive.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Be exposed to direct sunlight as little as possible (sunbathing is contraindicated). Also avoid prolonged exposure to high and low temperatures, use creams that protect from ultraviolet radiation and heat, and from cold.
- Take a shower, wash your face and wash your hands only with warm water, using soaps with skin-softening and moisturizing additives, and dry with soft towels.
- Do not take aspirin, codeine, ACE inhibitors.
- Do not use wardrobe items that put excessive pressure on the skin (tight clothing, belts, suspenders). Give preference to cotton clothes.
- Hypoallergenic diet, healthy eating.
- Treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver, infections in a timely manner.
- Maintaining a daily routine, alternating work and rest.
All this will prevent the occurrence of an attack of hives, which will make life much easier for allergy sufferers.
Diet and skin condition
Changing your diet almost always brings relief of symptoms, whatever the diagnosis - allergies or dermatitis (except for infectious diseases). You should exclude the following categories of foods from your diet:
- fast food;
- hot and spicy spices;
- salt and sugar - reduce to a minimum;
- carbonated, sweet and alcoholic drinks;
- confectionery;
- vegetables and fruits of bright colors.
Reviews from patients indicate that after switching to proper nutrition, the number of rashes is reduced, and overall well-being improves and performance increases.
When does allergy in the form of mosquito bites occur?
Skin is one of the most sensitive anatomical structures of the human body. The appearance of an itchy rash on its surface, reminiscent of the consequences of contact with insects, suggests the presence of blisters. This is an element that does not have a cavity; it is swelling of the papillary layer of the connective tissue part of the skin. It is characterized by such symptoms as:
- existence for a short period of time (on average up to a day);
- combination with itching, burning;
- pink, in some cases – porcelain shade;
- round or irregular shape;
- tendency to merge.
The blisters disappear without transforming into secondary elements of the rash (cracks, erosions, ulcers, scars). Only in the case of intense scratching, scratches and wounds remain in the area of the affected areas - the consequences of active mechanical action, which heal within a few days and can serve as an “entry gate” for infection.
An allergy in the form of a mosquito bite is usually urticaria.
Before making a final diagnosis, other etiological (causal) factors not related to individual sensitivity, such as infection, must be considered. Some types of bacterial, viral, and fungal agents can cause redness, swelling, and rashes. In addition, insect bites (bugs, ticks) that were not noticed by the patient are quite likely.
Bad habits as a factor in the appearance of blisters
If a patient has been suffering from dermatological pathologies for a long time, and neither pharmacological drugs nor diet help him get rid of them, then he should think about his lifestyle. How often does the patient drink alcoholic beverages and does he smoke? These bad habits slowly but inevitably “undermine” the body’s defenses; over time, large blisters appear on the body, itching like bites - this is a symptom of dermatological pathologies. Over time, the body can become so exhausted that it is simply unable to resist even the spread of fungal spores.
If no treatment helps with the appearance of dermatitis and blisters, or only helps for a short period of time, then you should think about the need to completely stop smoking and drinking alcohol, even in small quantities. Judging by the experience and reviews of people who were able to get rid of dermatitis, this method really helps. At the same time, you should minimize or completely avoid the consumption of salt and sugar.
Causes
Urticaria is a group of pathologies of an allergic nature, the basis of the pathogenesis (mechanism of development) of which is an immediate hypersensitivity reaction. The leading symptom is the presence of rapidly emerging and severely itchy blisters that disappear without a trace within up to 24 hours without secondary skin changes. There are several main reasons for the development of urticaria:
- Food products (citrus fruits, fish, nuts, peanuts).
- Medicines (antibiotics, vitamins, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Insect bites (wasps, bees, hornets).
- Infectious agents (viruses, bacteria, fungi, helminths).
- Autoimmune pathologies (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis).
- Physical triggers (low and high temperature, vibration, sunlight, pressure, humidity).
Factors that contribute to the development of urticaria include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- diseases of the digestive tract, endocrine and nervous systems;
- infections and neoplasms.
Stress plays a part. It has been proven that nervous tension (including due to a change of place of residence, climatic conditions) affects the immune system and can lead to malfunctions in its functioning, which sometimes results in allergic sensitivity.
Mycotic (fungal) diseases of the skin
You can get a fungus anywhere. But few people know that almost every person has fungal spores in one quantity or another on their body. They just begin to develop when the body’s defenses fall. And when the skin is not able to limit the proliferation of the fungus. Then the person complains of blisters on the heels: they itch like bites, bring pain and discomfort, and spread over a large area over time. The “favorite” places for fungus are the heels, the space between the fingers, and the nail plates of the hands and feet.
You should visit a dermatologist: modern anti-fungal medications will help get rid of the pathology in a matter of days. If the disease has reached an advanced stage, longer treatment will be required.
Symptoms in adults
Urticaria is classified as:
- acute (episodes of rash observed over a period of time lasting less than 6 weeks);
- chronic (repeated for more than 2 months);
- localized (rash occurs in separate areas of the skin);
- systemic (blisters cover the entire body).
Urticaria is a disease in which not only the skin is involved in the pathological process. There are likely additional signs that determine the severity of the sensitivity reaction.
Dermatological manifestations
The dominant group of symptoms, characterized by damage to the skin. Observed:
Blisters due to urticaria can be localized on absolutely any part of the body. Location on the scalp, palms and soles is not excluded. They itch very much.
If the rash occurs on the face, it practically does not rise above the skin level. The elements start out pink and soon become porcelain. This occurs due to compression of blood vessels as a result of increasing edema. Then, as the swelling decreases, the blisters turn red again and then disappear from the surface of the skin.
Quincke's edema
This form of reaction can be classified as a dermatological manifestation, but it is worth considering it separately. According to statistics, more than half of the episodes of urticaria are accompanied by angioedema; it is a dense swelling affecting the subcutaneous tissue. There is no intense itching. Changes can be localized in areas such as:
- face (lips, cheeks, eyelids, ears);
- external genitalia;
- oral cavity, nasopharynx;
- mucous membranes of the digestive and urinary organs.
The most dangerous is Quincke's edema in the larynx - it causes a narrowing of the airway and can lead to asphyxia (suffocation).
Additional manifestations
Allergies that look like mosquito bites can be characterized by the following symptoms:
- General weakness.
- Increased body temperature.
- Runny nose.
- Watery eyes, swelling of the eyelids.
- Pain in muscles and joints without specific localization.
Sometimes patients are bothered by a cough; symptoms of damage to the digestive tract are likely - lack of appetite, nausea and vomiting, as well as diarrhea in combination with flatulence and abdominal pain. These signs can be associated either directly with urticaria or with Quincke's edema.
An allergy sufferer may complain of fatigue, poor sleep, becomes irritable due to itching, and is unable to concentrate on everyday tasks.
Briefly about disinfestation
Many people are afraid to call the SES. They think it's difficult. In fact, the processing procedure takes less than an hour. Surfaces can be washed, and the active ingredients remain odorless and health threatening for up to 2 months. Even after their action ends, insects prefer not to approach the potentially dangerous zone - this is an instinct. For some reason, many people waste time going to the store, buying non-working products (have you heard anywhere other than advertising that a spray will make all mosquitoes or cockroaches disappear?). Then it takes hours to spray them. Later, the lack of results is monitored, new expenses are incurred, etc. But you just need to order a professional pest control. One call → 50 minutes → clean house.
Symptoms in children
Patients belonging to the younger age group often experience urticaria associated with food or drugs, as well as other triggers. Allergies in a child are characterized by the following symptoms:
- swelling and itching of the skin;
- the appearance of a rash in the form of blisters;
- increase in body temperature.
Fever can be observed even in infants and often causes misdiagnosis of infection, as it can reach high numbers. Children can suffer a systemic or generalized form of urticaria, which is combined with angioedema and is considered a life-threatening condition. But even with a mild reaction, the need to itch can lead to skin defects (wounds, ulcers) and infection.
Domestic burns as a cause of blisters
If blisters appear on the hand, itch like bites, swell and burst over time, and the person is guaranteed not to suffer from fungal diseases or mycotic pathologies - most likely these are household burns. Often housewives who are forced to spend a lot of time at the stove and perform their duties “automatically” simply do not notice how they get burned. As a result, blisters form on the body. They itch like bites, swell slightly (typical of a second-degree burn), and go away after a few days.
To prevent burns, you should be more careful about your actions in everyday life: do not touch hobs, hot kitchen utensils, or radiators.
Diagnostics
There are several main clinical criteria in favor of urticaria:
- Sudden onset of itching and blisters.
- The presence of a connection with the allergen (most often, contact with it occurs 30–60 minutes before signs of a reaction appear).
- The fleeting nature of the rash (that is, rapid disappearance without secondary elements).
In addition, anamnesis is important - information about past episodes of pathology, the presence of allergies (not necessarily urticaria) in close relatives. Additional methods are used to clarify the diagnosis.
Laboratory tests
May include different types of tests - from basic general clinical ones (determining the level of hemoglobin, red blood cells, counting leukocytes, examining urine and feces) to complex special ones:
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect antibodies to reaction provocateurs - food products, insect venom, etc.;
- determination of markers of infections (in particular, viral hepatitis);
- serum tryptase level test;
- assessment of thyroid function indicators (hormonal panel).
It is also important to identify signs of helminthiasis, for which stool is examined for worm eggs and the use of ELISA to detect antibodies to parasites (giardia, opisthorchid, toxocara).
Skin tests
These are provocative tests to check for sensitivity. They involve applying a potential trigger to the forearm or back and waiting within a specific time period (minutes, hours).
For example, if the patient reacts to cold, a piece of ice in a moisture-proof wrapper is applied to the skin (to prevent contact with water, which can also cause urticaria). In case of intolerance to drugs or food, use special media that contain the suspected allergen. If signs of a reaction (redness, swelling, itching, blister) occur during the observation period, sensitivity is considered proven.
General recommendations
Each insect bite causes a local response of varying severity. People who don't have allergies just wait for it to go away. To alleviate your condition, you can take certain measures:
- Applying ice to the bite site;
- Applying a vinegar solution to the affected area;
- Rinsing the wound under cold water (in case of stings from wasps, bumblebees, bees, etc.)2.
You should not get carried away with folk remedies, especially herbal decoctions or alcohol tinctures, which can aggravate the situation. It is recommended to avoid any foreign protein structures at the site of the allergen.
Treatment
Treatment for urticaria is carried out both at home and in a hospital department - it depends on the patient’s condition, the severity of symptoms and the presence of life-threatening signs. We must not forget that blisters on the skin can be a harbinger of anaphylactic shock - a reaction manifested by a sharp drop in blood pressure (collapse) and, like angioedema in the larynx, requiring emergency care.
Stopping contact with the trigger
It forms the basis of the treatment of any variant of urticaria and implies the absence of contact with the substance or physical factor that causes the reaction. Experts call this method elimination; it includes:
- Regular wet cleaning (elimination of dust and mites).
- Refusal to keep pets (relevant if you are sensitive to hair and secretions - saliva, urine).
- Excluding allergenic foods from the menu (in case of food intolerance).
- Selection of cosmetics that do not contain trigger components.
- Avoid using medications that cause reactions.
Elimination measures are observed throughout life. In children, sensitivity may disappear as they grow older, so control may be weakened - but only if you are sure that the immune system does not respond to contact with the provocateur.
Hypoallergenic diet
Must be strictly observed during the period of acute manifestations of the reaction (that is, when a rash or itching occurs); after the condition improves, the list of permitted products expands.
- bran bread;
- dull fruits and vegetables in heat-treated form;
- dryers, crackers;
- lean meat, fish;
- dairy products;
- cereals
Drinks allowed are still water, dyes, weak tea, and compote. You shouldn't eat:
- citrus;
- strawberries;
- chocolate;
- whole milk;
- mushrooms;
- red meat;
- canned food;
- tomatoes;
- radish;
- processed cheese;
- spicy seasonings.
You need to eat dishes prepared by boiling, stewing or baking in the oven. A great way is steam treatment. Excess sweets, semolina and legumes should be avoided. Oatmeal, offal (liver, kidneys) are limited.
Drug therapy
Various medications may be used to treat hives:
| Pharmacological group | Representatives | Destination purpose |
| Histamine H1 receptor blockers | Loratadine, Erius, Zyrtec, Fenistil | Rapid reduction of itching, swelling, elimination of rash. Therapy of Quincke's edema. |
| Glucocorticosteroids | Elokom, Prednisolone, Dexamethasone | |
| Adrenergic agonists | Adrenaline, Epinephrine | To provide emergency care for severe urticaria, laryngeal edema, anaphylactic shock |
| Mast cell membrane stabilizers | Ketotifen, Sodium cromoglycate | For long-term therapy with frequent relapses (repeated episodes) of urticaria. |
For children from 6 months old, you can use Zyrtec, Desloratadine, and if the child is younger, with the permission of the doctor, a short course of treatment with Dimetindene is allowed.
Traditional methods of treatment if blisters pop up and itch like bites
Some traditional methods of getting rid of blisters that cause itchy skin are also popular. Judging by the reviews, these are:
- infusion of oak bark (a tablespoon per glass of boiling water): wipe the affected area with a cotton pad soaked in the decoction several times a day (has an astringent and anti-inflammatory effect);
- calendula infusion (a tablespoon per 200 ml of boiling water) has a calming and anti-inflammatory effect; blisters should be wiped several times a day;
- baths with salt and soda - this method is suitable if the blisters are located in the extremities.
Prevention and useful tips
To avoid recurrence of urticaria, you must:
- Avoid contact with triggers.
- Stick to a hypoallergenic diet.
- Take a course of treatment.
People who are aware of a tendency to sensitivity reactions should carry antihistamine tablets (for example, Cetrin). You should choose drugs without a sedative (calming) effect - otherwise drowsiness and decreased ability to concentrate are possible.
If a child suffers from urticaria, you need to warn the adults around him about the diagnosis. These are older relatives (grandparents, etc.), a kindergarten teacher, a school teacher, and a teacher in a club or sports section. It is better if your son or daughter always has with him the medications recommended by the doctor to relieve the symptoms of urticaria, as well as a card indicating the diagnosis and the contact number of the family.
- Spring Fever: Let's Say Yes! healthy lifestyle
- Fitness from the cradle: introducing your child to a healthy lifestyle
- Healthy eating pyramid
- Cold allergy: what you need to know
- What you need to know about allergies
Healthy lifestyle © 2022 Attention! The information published on the site is for informational purposes only and does not constitute a recommendation for use. Be sure to consult with your doctor!
What cosmetics to use for sensitive skin
For people with sensitive, irritated skin, we can recommend the La Cree series of safe cleansers. Instead of your usual shower product, you can use La Cree cleansing gel every day. This product is designed specifically for the most sensitive skin. Thanks to its special composition, it strengthens its protective function and helps reduce redness and itching. You can use it even during the period of exacerbation of blisters.
Since the gel contains no dyes or fragrances, it can be used for bathing very young children (as a detergent and instead of bubble bath). The gel is ideal for gently cleansing, nourishing and moisturizing the skin, as it contains natural oils and extracts. They fight inflammation and microbes, helping to heal microtraumas faster.
You can use this product to wash your face and cleanse your body, wash your hands, instead of bubble bath. After a shower, the skin can be moisturized with a hypoallergenic emulsion or La Cree cream.
Ringworm and its variety - eczema
When a child itches and becomes covered with red spots, it is quite logical to assume that he has lichen - a disease of a fungal or viral nature. You can become infected with it from animals (ringworm), as a result of damage to the skin or diseases of internal organs (eczema), after infection with a fungus (pityriasis versicolor), as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the immune system (lichen planus), as a result of infection by viruses (lichen rosea) .
Depending on the type of disease, it is characterized by different types of rashes:
pityriasis rosea is characterized by the appearance of small round pink or red spots; Pityriasis versicolor is characterized by darker red or even red-brown rashes; with ringworm, in addition to red spots, peeling and itching of the skin appears; eczema is characterized by the appearance of red spots, crusts, peeling, cracks, blisters; With lichen planus, shiny nodules of a reddish-purple hue of irregular shape are formed.
Despite the fact that lichen is treated mainly at home, it is impossible to do without medical help - only a doctor can confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of illness. Depending on the type of disease, antihistamines, corticosteroids and antifungals are used to treat it. It is also recommended to give up bad habits and adhere to a special diet.
To prevent the disease, it is important to strengthen the immune system and limit the baby’s contact with street animals.
How to treat
For proper treatment, specific therapy must be carried out to confirm scabies. If the doctor was unable to identify the mite and scabies, a trial treatment will be prescribed. In addition, preventive treatment is prescribed to all family members and people in contact with the patient.
The doctor will prescribe medications that kill ticks. Most often they are:
- aerosols
- ointments
- creams
- suspensions
- emulsions
The prescribed drugs will be based on the following substances:
- benzyl benzoate
- permitrina
- sulfur
- piperonyl butoxide
- esbiola
Sometimes treatment includes washing with soap or treating the skin with emollient ointments before using the drug.
Only a doctor can prescribe a medicine and treatment method. It is based on the following criteria:
- clinical picture
- complications
- person's age
- pregnancy
Self-medication can cause complications, apathetic forms of infection or a protracted course of the disease.
When and which doctor to contact
Experts say “that the earlier the diagnosis is made, the easier it is to cure the disease.” Therefore, if you experience small pimples that itch and swell, it is advisable to consult a doctor the next day.
This is a therapist or pediatrician, an allergist, a dermatologist. After passing the necessary tests, the healthcare professional will prescribe appropriate therapy.
Complications
If treatment is not started on time, a number of problems will arise that affect both appearance and future health. These are depressions, scars, increased pigmentation. Skin imperfections will remain for a long time, and maybe forever.
A person’s immunity will decrease, therefore, colds will be his constant companions. Complications from the disease can lead to malfunctions of internal organs, as well as death.
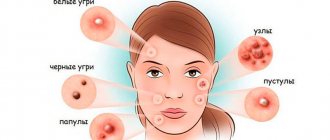
Diseases accompanied by rashes
Any type of rash on the body is a symptom of the disease. They can be very different in appearance. The rash can be papular, pinpoint or, conversely, in the form of large dots or pimples. It comes in a variety of colors, ranging from clear or white to bright red. The characteristics that describe rashes directly depend on their etiology or the illness that they accompany.
Dermatological diseases
Among the diseases of dermatological etiology, the symptoms of which are a variety of rashes, the following can be noted:
- dermatoses (for example, diaper dermatitis);
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- candidiasis and other diseases of the epidermis.
Almost always, skin diseases are caused by problems with internal organs and systems combined with exposure to external factors. For example, neurodermatitis can be triggered by malfunctions of the nervous and endocrine systems due to decreased immunity. In such a situation, complex therapy is required using medications, and not just ointments or creams.
Psoriasis on the hands of a child
As for psoriasis, at the initial stage it looks like an allergic reaction, but over time the plaques acquire a characteristic appearance. Another name for the disease is lichen planus. Psoriasis and eczema are very rare in children of one month of age. Genetic predisposition to these diseases only after 2 years.
Allergic reaction
One of the main symptoms of allergies is a rash. A negative reaction is the result of taking medications or eating certain foods. Having different shapes and sizes, the rashes can spread throughout the body, including the face, chest, and limbs.
The main characteristic difference between an allergy rash is that it increases in severity when exposed to an allergen and disappears after eliminating the irritant. Another feature is the presence of severe itching.
The most common manifestations of an allergic rash are:
- Hives. Occurs due to foods, medications and temperature factors. Sometimes it is impossible to determine the true cause of hives.
- Atopic dermatitis. It is a papular red rash that, as it develops, merges and becomes crusty. It most often occurs on the face, cheeks and places where the arms and legs are bent. Accompanied by itching.
Atopic dermatitis or eczema
Infectious diseases
Quite often, a rash is a sign of an infectious disease. The most famous of them:
- Chickenpox. The child develops characteristic watery blisters, which dry out and form a crust. They are characterized by itching. The temperature may also rise, but sometimes the disease goes away without it.
- Rubella. The main symptoms are enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and a rash in the form of small red spots or dots that first appear on the face and then move to the neck, shoulders and then spread throughout the body.
- Measles. It appears as round spots and nodules behind the ears, spreading throughout the body. The disease is also accompanied by peeling, pigmentation disorders, fever, conjunctivitis, cough and photophobia.
- Scarlet fever. Initially, the rashes are localized on the cheeks, then move to the limbs, chest and torso. Gradually the rash becomes paler. Scarlet fever is also characterized by a bright red coloration of the palate and tongue.
- Roseola. It starts with an increase in temperature. The fever lasts about three days, after which a pinpoint red rash appears on the body.
- Scabies. It is characterized by a red rash that is very itchy.
Chickenpox symptoms are difficult to confuse with symptoms of another infection Rubella rash Signs of measles Roseola rash