One of the types of neoplasms on the skin is keratoma - a skin disease that is practically asymptomatic and does not cause obvious inconvenience to its owner. Keratomas are essentially benign formations that do not pose a serious health hazard. The only possible problem is the likelihood of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm, which can already directly threaten a person’s life. For this reason, skin tumors, moles, tumors and keratomas must be constantly monitored by a doctor - a dermatologist or oncologist, and in some cases, therapeutic measures must be taken to remove them.
Causes of keratoma formation
Keratomas have a multifactorial etiology. First of all, age-related degeneration of skin cells is important. In addition, the following factors are important:
- Excess ultraviolet radiation.
- Age-related decrease in immune defense. As a consequence, intensive growth of epidermal cells and the formation of areas of hyperkeratinization and keratinization occur.
- Neuroendocrine pathology.
- Vitamin A deficiency.
- Endocrine disorders and sexual involution (menopause).
- Long-term use of certain medications.
- Skin exposure to chemicals.
Keratomas: causes of appearance?
Keratoma, according to dermatologists, develops for one of two reasons - excessive ultraviolet radiation and the physiological processes of aging of the skin. The predisposition to the development of pathology, according to medical experts and geneticists, is inherited. But there are no clear reasons for the appearance of a formation, such as, for example, in condyloma, which is caused by the human papillomavirus. At one point, an accumulation of cells is observed, which leads to an anomaly.
Skin keratoma, as a rule, does not pose a threat to health. But dermatologists strongly recommend observing the spots. After all, individual formations have a tendency to reproduce and grow. And in rare cases, they degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
Classification of keratomas
Keratoma is a group of skin pathologies, among which there are several options:
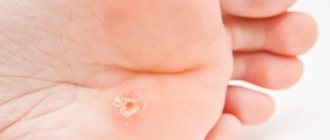
- Senile keratoma is the most common type of neoplasm of this type. Looks like a brown spot. Tends to increase in size and at the same time change its structure, for example, becoming convex and soft, and may become loose. Its surface begins to peel off over time. This type of keratoma can disappear spontaneously, or it can transform into a cutaneous horn, which is prone to malignancy.
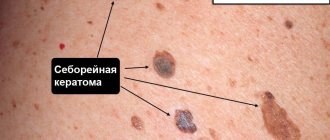
- Seborrheic keratoma. It grows slowly, and seborrheic multilayer crusts form on its surface. At the initial stages, the keratome looks like a yellowish spot, then, when the work of the sebaceous glands in them is disrupted, scales appear on the surface. Their thickness can reach one centimeter. The spots increase in size, merge with each other and change color to brown. If the keratoma is damaged, it bleeds and becomes painful.
- Cutaneous horn. It begins as a red spot, in its place the epidermis thickens and a tubercle forms. It is dense and rises above the skin (cases of cutaneous horn about 10 cm in height have been described). Its surface is uneven and peeling. Can transform into cancer. Horny keratoma can act as an independent disease or be a symptom of another pathology.
- Follicular keratoma is localized at the base of the hair. It looks like a flesh-colored knot. Its size does not exceed one and a half centimeters. In the center there is a cone-shaped depression with scales.
- Solar keratoma. At the initial stages it looks like multiple scaly pink papules. Gradually they grow and transform into plaques, around which there is an area of inflammation. The plaques are covered with scales, which have a dense structure, but are easily removed from the keratome. The disease is considered a precancerous condition because it is prone to spontaneous malignant transformation. At the same time, it can also disappear spontaneously, but then a relapse occurs in the same place. Solar keratoma is localized in open areas of the skin.
- Angiokeratoma is a group of neoplasms originating from skin capillaries with symptoms of keratinization disorder (hyperkeratosis). They look like burgundy elevations, dense to the touch.
What is a keratoma and why does it appear?
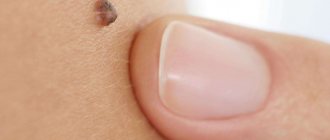
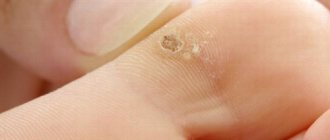
Keratoma is a specific skin formation that is formed from epidermal surface cells. It can have different sizes - from a few millimeters to 3-5 centimeters in diameter. Typically, keratomas are brown, gray or brown in color, and may look like freckles. Over time, its surface becomes keratinized.
Content:
- What is a keratoma and why does it appear?
- Types of cutaneous keratomas known to doctors
- Why are keratomas dangerous and why do they need to be treated?
- Treatment of keratosis: what methods exist
- Treatment of neoplasms at home, traditional medicine
The formation grows precisely from epithelial cells, which have a multilayer structure, where each layer lies on top of each other. The outer layer of cells gradually dies, becomes horny and turns into scales, which fall off under mechanical influence, for example, during washing. They are replaced by deeper layers, which also die and fall away over time - this is how the continuous process of renewal of the skin takes place.
If normally the speed of the process of development of new cells and death of old ones is balanced in such a way that the number of newly appeared cells corresponds to the number of keratinized and dead cells, then in cases when a disorder occurs in this system, various formations are formed on the skin, including benign tumors from keratocytes - cells of the epidermis.
The formation is benign because it consists of unchanged cells, and appears only due to their excess quantity. However, on average, in 8-20% of cases, a keratoma can degenerate into a cancerous tumor if some external factors contribute to this, for example, excessive tanning or work associated with contact of toxic substances with the skin.
Keratomas can be single or localized in groups. They can be located on any part of the body, most often on the chest, neck, face, arms, and less often on the lower extremities.
The reasons for the appearance of these tumors are not yet fully known to medicine, but doctors emphasize that frequent and prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays, on the beach or in a solarium, promotes the growth of keratomas.
Treatment
Treatment includes drug therapy and surgical removal. Drug therapy involves the local use of cytostatics or other antitumor drugs selected according to an individual regimen. Treatment may require hospital stay.
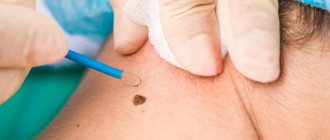
Surgical methods for removing keratomas are varied:
- Traditional excision within healthy tissue using a scalpel. Used in cases of suspected cancer.
- Curettage of the hair follicle - the keratoma is scraped out with special instruments with sharp edges.
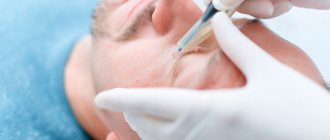
- Laser removal - using laser radiation, the tumor is evaporated layer by layer. In its place, a crust remains, which disappears after healing, and “young” skin remains in its place.
- Electrocoagulation - the tumor is excised under the influence of high-frequency electric current. It leads to local heating of tissues and their evaporation. At this point, they separate and form a cut. After removal, a wound with a crust remains in place, healing occurs, as after exposure to a laser.
- Radio wave surgery is a non-contact method of removal using radio waves. A modern, effective method with minimal risk of the formation of rough scars.
- Cryodestruction is the effect of liquid nitrogen on the keratoma, which leads to its immediate freezing and necrosis. After a few days it disappears on its own.
Surgical removal is performed on an outpatient basis using local anesthesia. After the procedure, the patient can leave the clinic almost immediately.
Our clinic has all the necessary equipment for keratoma removal, and experienced specialists will offer treatment based on specific clinical features.
Book a consultation around the clock +7+7+78
Where to remove keratoma
malignant skin keratoma can become malignant at any time. An effective and safe treatment method is laser removal. The skin keratoma is evaporated layer by layer, without affecting healthy tissue.
IN LASER REMOVAL CLINICS, experienced dermatologists and oncodermatologists treat skin tumors. After laser removal of a keratoma, a small crust forms, which falls off on its own after a few weeks. There will be new healthy skin under the scab. It is recommended to protect it from UV rays for several months using sunscreen.
Diagnostics
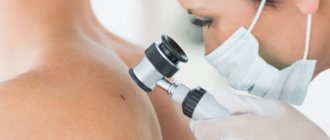
An appointment with a dermatologist begins with taking an anamnesis. The doctor clarifies how long ago the formation was, asks the patient about sensations - painful manifestations, itching, and studies the symptoms. Next, the skin is examined to determine the size and location of the keratoma. The instrumental method - dermatoscopy - allows you to clarify the diagnosis and exclude other skin diseases.
A special device allows you to identify the formation, examine the structure of its tissues, and the depth of its occurrence. The dermatoscope magnifies the image many times, so errors are excluded. And if there is a risk of the keratoma degenerating into a tumor, the doctor will determine this. In some cases, histology is recommended - the formation is sent to the laboratory to determine the cellular composition.
Stages of keratopapilloma
The formation of keratopapillomas is usually divided into two main stages.
initial stage
At the initial stage of their development, keratopapillomas look very similar to freckles or moles on the human body. The color of the spots can be either brown or gray. The surface of the tumors may also peel off. If you do not seek the help of a specialist at this stage, keratomas can transform into squamous cell carcinoma due to the rapid spread of spots throughout the body.
How to remove keratomas
In our clinic, keratomas can be removed on the day of treatment, after dermatoscopy and determination of the nature and benignity of the formation. Our doctors practice several modern methods of removing keratomas. The choice of removal method is made based on the location of the tumor, its size and the risk of malignancy.
Possible complications and consequences of laser intervention
Laser surgery of neoplasms can leave scars - small and unnoticeable, or larger ones if the keratoma was initially large. In addition, patients note the appearance of numbness in the tissue at the site where the tumor was removed.
Such manifestations are natural consequences of the procedure.
It is necessary to pay attention to some dangerous symptoms of poorly carried out destruction of the tumor, for example, the appearance of redness around the crust formed after removal, severe itching or rash at the site of the keratoma.
If the crust has fallen off on its own, and underneath it an ulcer in the form of a red spot with an uneven surface is found that has not healed for a long time, you need to visit a dermatologist as soon as possible.
In addition, allergic reactions or dermatitis may develop around the procedure site due to constant wearing of a bandage, as well as the use of various ointments on the skin. At the first manifestations of dermatitis or allergic rashes, you must stop treating the area with any medications and also consult a dermatologist.
Types of keratopapilloma
If we talk about appearance, keratomas may differ from each other, depending on their type. Formations can be presented in the form of growths, plaques, spots . Keratopapillomas can disappear on their own without any treatment, but this happens in rare cases. So you should not hope for such a favorable outcome and think about removing the formations at the initial stage of their appearance.
In medicine, there are several types of keratomas, which are described below.
ARVE Error: src mismatch url: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HblTCuMsirU&list=PL8qf1F3sywhHLF0OLE6iVECB8HUBbc7Ws src in: https://www.youtube-nocookie.com/embed/HblTCuMsirU?list=PL8qf1F3sywhHLF0OLE6iVECB8HUBbc7Ws src gen: https ://www.youtube-nocookie.com/embed/HblTCuMsirU
Wound surface care techniques
After laser destruction of the keratoma, a characteristic dark brown crust forms in its place. It covers the surface of the wound, and underneath it the tissue healing process is actively occurring. It is strictly forbidden to rip off or comb the scab, as this opens the door for pathogenic microorganisms to enter the wound until the need for it disappears - then it disappears on its own. For the first two days, it is not recommended to wet the wound site.
Postoperative care includes the following rules: once or twice a day, the procedure site must be washed with water and baby soap, after which it is necessary to treat the surface with antiseptic drugs and healing ointments. Next, a sterile gauze bandage is applied to the wound. If possible, it is better not to use an adhesive plaster, as it restricts air flow into the wound, thereby slowing down its healing.
Complete skin restoration occurs after 4-6 weeks. During this entire time, it is prohibited to visit the bathhouse, sauna, or swim in pools or open reservoirs. Exposure to ultraviolet rays is also undesirable, and not only during postoperative recovery, but also in the next 6-8 months, in order to avoid recurrence of keratoma, so it is better to forget about beaches and solariums for a while, and go outside in clothes or a hat that covers the affected area and treat it with sunscreen with a high UV filter.
Removal of keratomas using diathermocoagulation method
In this case, the removal of pathological tissues is carried out under the influence of very high temperatures (about 2500 oC) using the Plasmaskin apparatus. The advantages of the method include non-contact (which eliminates the risk of contamination by infections) and a disinfecting effect.
After removal of the keratoma, observation by a dermatologist is necessary.
IMPORTANT!!!Given the frequent cases of degeneration of keratomas, especially multiple ones, we advise you to keep these neoplasms under the supervision of doctors!!!
Come to our clinic. We will conduct a diagnostic study of the keratoma, select the optimal destruction method for you, and professionally carry out the removal procedure.
Complications of senile keratoma
Due to the slow but constant growth of the nevus in length, a noticeable cosmetic defect can form, especially if it is located in a visible place. The course of the disease can be significantly complicated by the constant appearance of new keratomas. This brings discomfort to the patient, since keratomas have a convex shape and are very easily injured.
The most severe complication of senile keratoma is considered to be its malignancy. Senile keratoma is a benign neoplasm of the skin, but it is possible to transform the keratoma into basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Such a change from a benign to a malignant formation can be facilitated by regular trauma to the keratoma or excessive ultraviolet irradiation.
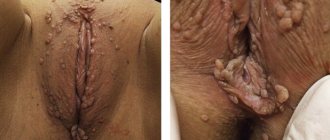
Angiokeratoma
Angiokeratomas on the body can appear either in groups or individually. Externally, angiokeratoma is a formation in the form of dark nodules. The most common formations are purple. The size of angiokeratomas is not very large.
You might be interested! Perianal area: what is it and what diseases can occur there?
Symptoms of angiokeratoma
Angiokeratomas have a number of symptoms:
- The formations are nodules that rise above the skin
- The color of the nodules can be black, burgundy or blue
- The diameter of the formations is small and reaches 1 cm
- Nodules have blurred, irregularly shaped boundaries