Causes of sun allergies
Although the exact cause of this condition is not fully known, it is believed that ultraviolet radiation from the sun or artificial sources such as solar lamps causes a reaction in some people who are sensitive to this type of light. This causes an immune reaction that results in a rash.
Risk factors for some types of rash may include:
- Female;
- Light skin;
- Hereditary predisposition.
Solar eczema
Refers to a type of common eczema - a non-infectious skin disease that is characterized by itching, redness, peeling and irritation. Solar eczema is most often diagnosed in women 16-40 years old, mainly with a mobile and easily excitable nervous system. Exacerbation occurs in warm spring and summer, and in winter the pathology does not manifest itself, or its symptoms are significantly mitigated.
Large symmetrical lesions with small blisters along blurry edges appear on the skin. They burst, dry out, turning into serous crusts. Rashes appear on the face, neck, hands, and much less often on the forearms and legs. The constant itching bothers me. Scratching the itchy areas can lead to a secondary infection causing inflammation. It is noteworthy that if during an exacerbation the sun factor is eliminated (for example, by not leaving the house), there is practically no improvement.
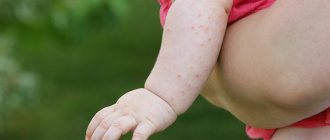
Symptoms of sun allergy
This condition usually develops 30 minutes or more after exposure to the sun.
Characteristics of the rash vary and include:
- Groups of small papules or blisters;
- Itchy red spots;
- Hyperemic areas of skin;
- Raised or rough areas of skin.
If a person receives a severe sunburn, it may be accompanied by nausea and fever.
A person with a sun allergy may also experience weakness, breathing problems, headaches, and other allergy symptoms.
Manifestations can occur anywhere on the body exposed to sunlight.
Some types of rashes occur on skin that is usually covered by clothing, such as the chest or arms.
Content:
- The dangers and causes of sun allergies
- Manifestation of the disease
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Treatment of sun allergies
The dangers and causes of sun allergies
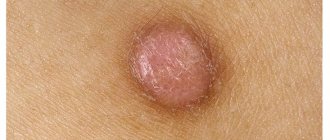
Polymorphic photodermatosis is a specific seasonal disease that occurs in response to exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin. It is characterized by the appearance of a rash on open areas of the skin, which can be represented by various elements - spots, plaques, nodules, blisters with severe itching.
In a normal body, ultraviolet radiation has an immunosuppressive effect (suppresses immune responses), due to which phototherapy is often used in the treatment of many skin diseases. The direct cause of the development of photodermatosis has not been established, but the mechanism is that when exposed to sunlight, specific substances (hitherto unidentified antigens) are formed in the skin, which trigger a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. These antigens are formed as a result of damage to cell components and a delayed reaction of their destruction under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Therefore, this disease is also called “sun allergy”. Photodermatosis occurs much more often in females of any age group, and the prevalence in some regions reaches 20% of the population. Predisposing factors include heredity, certain skin phototypes, and the effect of photosensitizing substances (increasing the skin's sensitivity to sunlight).
Manifestation of the disease
Clinical symptoms usually appear in the spring and summer, when there is a high level of insolation. Morphological elements of polymorphic photodermatosis appear on open areas of the skin that have been exposed to insolation. They appear some time after exposure, on average the next day. The main localization of rashes is the neck and limbs, the torso and face are affected much less frequently. Polymorphic photodermatosis can appear in the form of spots, nodules with vesicles, and sometimes larger merging elements. Any type of rash is accompanied by itching, burning or tingling. Several days or weeks pass from the moment the rash appears until it completely disappears. In severe cases, the rash may be excessively pronounced - large blisters, blisters or hemorrhagic elements, which may leave areas of depigmented skin. Usually in the same person, regardless of the number of relapses, the rashes are represented by one type of morphological elements. The phenomenon of adaptation in this disease is characterized by a decrease in manifestations after several exposure to the sun.
Additional symptoms include changes in the red border of the lips and the mucous membrane of the eye (cheilitis and conjunctivitis).
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis and treatment of hypersensitivity to sunlight is carried out by a dermatovenerologist. Additional consultation is usually not required.
Diagnosis of polymorphic photodermatosis is based on examination of the affected areas, medical history and laboratory tests. To confirm photodermatosis, special phototesting techniques using artificial ultraviolet sources are used.
1) Photoprovocation tests - using a UVA and UVB source, they try to cause characteristic rashes to appear on the patient’s skin. 2) If sensitization (hypersensitivity) to medicinal or chemical substances is suspected, then photo-patch tests are carried out (initially, the suspected substance is applied to the skin area, after which a test with UVAV is carried out). To exclude a disease such as systemic lupus erythematosus (which is characterized by an increased reaction to sunlight and the development of a similar rash, but more often on the face), laboratory tests are performed: antinuclear factor, antibodies to double-stranded (native) DNA, Sm, Ro/SS are determined -A and La/SS-B antigens. To exclude porphyria, a hereditary disease with impaired porphyrin metabolism and the development of photodermatosis, neuropsychiatric disorders and other symptoms, the content of porphyrins in the blood and urine is determined. Histological examination of the skin is extremely rare in diagnostically difficult cases.
Treatment of sun allergies
Treatment primarily involves limiting sun exposure as well as using highly effective sunscreens. To relieve symptoms, glucocorticoids are used internally and externally. To prevent the occurrence of rashes in early spring, it is effective to use courses of narrow-band, broadband mid-wave or PUVA phototherapy, which allows the skin to adapt to sunlight and reduce the manifestations of the disease.
Treatment of sun allergies in Samara at the FIRST NEUROLOGY clinic
Allergies do not always require treatment, as they often go away on their own within 10-14 days. This depends on the type of rash, as well as on the overall clinical picture.
However, if the rash is itchy, a hydrocortisone steroid cream may be helpful, as may oral antihistamines. Cold compresses or a cool bath can also relieve itching. If you cannot cope with your allergies, contact an allergist-immunologist at the FIRST NEUROLOGY clinic at the address: Samara, st. Stara Zagora 142 B.
Administrator's phone number
Food photodermatitis
These are mainly pellagra and pellagroid - complex systemic diseases that affect the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, liver, vitamin and protein metabolism. Provoking factors are gastrointestinal diseases and alcoholism, which disrupt the absorption of proteins and vitamins. Their lack triggers a protective reaction in the body, which is expressed in increased photosensitivity. The pathology is chronic and worsens in spring/summer.
The main symptoms of food photodermatitis:
- dermatitis (rashes, itchy skin);
- diarrhea (loose stools);
- dementia (deterioration of memory and thinking abilities).
Read also
Allergic conjunctivitis
What is allergic conjunctivitis With prolonged exposure of the human body to allergens, such as pollen, yeast spores, eye symptoms associated with inflammation may appear.…
Read more
Allergic vasculitis
Most often, this is a reaction to the administration of antibiotics, vaccines, contact with perfumes, fuels and lubricants, food intake, and the course of infectious and systemic diseases. There are various…
More details
The concept of secondary immune deficiency
The concept of secondary immune deficiency Immunodeficiency disorders can be congenital or acquired. A congenital or primary disorder is something that a person is already born with. Purchased...
More details
Food allergies
What is the difference between food allergy and food intolerance? Food allergy is the response of the immune system to the intake of a particular food that causes an allergic reaction. Even a small amount of associated...
More details
Pollen allergy
What is a pollen allergy? Pollen is a fine mist produced by trees, flowers, grasses and weeds for the purpose of reproduction. Many people have an unfavorable immune response...
More details
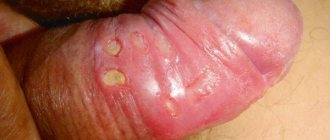
Solar prurigo
It is seasonal: it appears in the spring, when the sun's rays gain strength, and can last almost the entire summer, weakening towards its end. However, exacerbations are possible even on winter days if they are sunny. The disease can begin at any age, starting from 16 years7.
In the affected areas, the skin turns pale (white dermographism), thickens, loses elasticity, and plaques form on the surface. The rashes are very itchy and crusts form due to scratching.
Pruritus often appears on the face and exposed parts of the arms. The rashes resemble small nodules in shape. At first they form in small quantities, then there are more and more of them, and they merge into single spots. The skin is dry. Over time, the skin may become covered with small pigment spots. If the disease is chronic and severe, atrophic scars may form. Additional symptoms are irritability and withdrawal7. Due to itching, a person suffers from insomnia.
How to treat sun irritation with traditional medicine?
Grandma's recipes can be very effective, but you shouldn't rely solely on them. Combine them with the products prescribed by your doctor - in this case, you can quickly bring sun-damaged skin to normal condition:
- Potato. Grate 1-2 medium-sized tubers on a fine grater and apply the resulting pulp to the affected area.
- Aloe. Cut a suitable-sized leaf from an indoor aloe flower and rinse it under running water. Cut lengthwise and wipe the damaged area of skin. You can also make aloe juice. To do this, peel the leaf and grind it in a blender/pass through a meat grinder. Dilute the resulting mass with clean water in a 1:1 ratio, soak a bandage or napkin in it and apply to the affected areas for 10-15 minutes.
- Cucumber. Wash the cucumber, cut off the skin and grate the vegetable. Squeeze the resulting mass through gauze and apply to damaged areas. It is recommended to keep the cucumber mixture on the skin for at least half an hour.
- Cabbage. Divide the head of cabbage into sheets. Apply the leaf to red, itchy areas.
Clinical researches
Based on the results of numerous clinical studies, La-Cri products, including cream for sensitive skin, are recommended by the St. Petersburg branch of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
The effectiveness, safety and tolerability of the products have been proven by a clinical study. The cream is also suitable for daily skin care of children with mild to moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
Sources:
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Clinical dermatology. A short guide to the diagnosis and treatment of dermatoses, Notabene, 2017.
- Reken Martin, Schaller Martin, Sattler Elke, Burgdorf Walter, Atlas of Dermatology, MEDpress-inform, 2022.
- Schneiderman Paul, Grossman Mark, Differential diagnosis in dermatology. Atlas, Binom, 2022.
In what cases does the likelihood of allergies increase?
The sun is most active in spring. The peak of circulation is the May holidays. “In spring, everyone wants the sun, everyone misses it, so they try to be in the sun’s rays as much as possible, which can lead to allergies,” added Nadezhda Magarina.
An allergic reaction can also occur during a vacation, as the time of exposure to sunlight increases. It is also important where a person travels - the closer to the equator, the higher the likelihood of allergies due to the activity of the sun's rays and the proximity of the sun to the surface of the earth.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment for solar urticaria begins with taking antihistamines. In case of illness, doctors most often resort to using remedies that belong to the new generation.
- The drug Erius helps block histamine and eliminate the inflammatory process on the surface of the skin. It can be used during pregnancy due to the absence of side effects.
- To relieve itching and inflammation, you can take Kestin. In addition, it has an antiseptic effect. The disadvantage of the drug is the presence of negative reactions with the wrong dosage and duration of therapy.
- Solar urticaria can be treated with Claritin. Within 30 minutes it helps relieve allergy symptoms. The effect of the product lasts throughout the day.
In addition to these commonly prescribed medications, therapy may be prescribed:
- Diphenhydramine;
- Suprastin;
- Tavegil;
- Lomilan;
- Diazolin.
With pronounced symptoms of the disease, the use of external agents is required. Treatment can be carried out using non-hormonal (Fenistil-gel, Bepanten, D-panthenol, Gistan) and hormonal (Elocom, Soderm, Flucinar, Advantan) drugs. The latter have the most powerful effect on the body, eliminating symptoms in a short period of time. However, if there are wounds, they should not be used. They can enter the bloodstream, disrupting the hormonal balance in the body.
The advantage of non-hormonal therapy is its availability for all categories of patients. Such ointments and creams are allowed to be used by pregnant and lactating women and children. They cool the surface of the skin, eliminating itching, burning and redness.
If peeling occurs, you can lubricate the damaged surface of the skin with any cosmetic product with high fat content. Children's cream copes well with the task.
Causes of the disease
Solar urticaria more often appears in people with Celtic skin type, photos of which are presented on the Internet. They tan poorly, which causes red spots and burns to appear on the surface of the skin. Pregnant women and children are also particularly susceptible to the disease.
The occurrence of the disease, the signs of which can be seen in the photo, is caused by a malfunction of the body’s immune system. Photodermatosis also often appears when the functioning of the liver, kidneys and gastrointestinal tract is disrupted.
The disease can occur when consuming foods that trigger the photosensitization process. A particularly strong influence on the body in this direction is:
- carrots;
- figs;
- bell pepper;
- parsley;
- coffee;
- celery;
- citrus fruits;
- alcohol;
- nuts.
Also, the allergic reaction, which is shown in the photo, appears under the influence of certain plants and herbs. They are found in medicines, cosmetics, and food. Urticaria from the sun can be caused by a negative reaction when consuming:
- nettle;
- hawthorn;
- quinoa;
- wormwood;
- St. John's wort;
- clover;
- immortelle.
In addition, essential oils and medications can have irritating properties. The latter are especially dangerous, therefore, when exposed to the sun for a long time, people at risk are prohibited from taking antibiotics, fungal remedies, hormones, and antidepressants.
If signs of illness appear, the patient should be examined by a doctor. Depending on the symptoms, the necessary treatment will be prescribed.
The main cause of solar urticaria is sun exposure.