Tongue cancer is a fairly common pathology in the structure of malignant neoplasms of the head and neck organs (about 55% of cases), and in the general structure of malignant neoplasms it accounts for 0.45%. The average age of those affected is 60 years, men suffer from it 3 times more often than women. But the tumor can also occur in young people and even children.
- Causes of tongue cancer
- Symptoms of tongue cancer
- Methods for diagnosing tongue cancer
- Treatment of tongue cancer
- Prevention
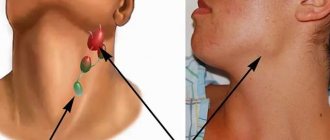
Most often, cancer is localized on the lateral surface, a little less often on the root of the tongue, and very rarely in the area of its back and tip. [1,2]
Anatomical structure of the tongue
Vincent's ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis
One of the reasons that the tongue hurts on the side is Vincent's ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis. With this disease, ulcers appear in the oral cavity, which can be located not only directly on the tongue, but also on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, and even spread further:
- on the gums;
- sky;
- tonsils.
The disease is caused by bacteria: spirochetes and fusobacteria. What is especially characteristic of this pathology is that the ulcers are covered with a dirty gray coating. Vincent's ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis is treated locally with antimicrobial drugs. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are also prescribed.
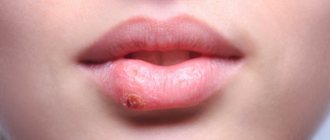
Reasons for the appearance of a lump
A tumor can appear for various reasons. If the pain is not severe, temporary, and goes away on its own within a day, there is nothing to worry about. And when the appearance of a growth causes significant discomfort and lasts for several days, you should be alarmed. A growth under the tongue near the frenulum can be caused by the following factors:
- Condylomatosis, that is, papilloma virus. In this situation, the cell growth mechanism is disrupted. The early phases of the disease have no obvious symptoms. The virus is actively transmitted through household and sexual contact, especially with weak immunity. The nature of warts is such that they act selectively. HPV is distinguished by genotypes. There are benign and life-threatening strains. Warts may rise above the muscular organ. Keratin, which is produced in such cells, gives the balls rigidity.
- Inflammation often appears when the frenulum is short from birth. It is better to correct the problem in childhood.
- The process of inflammation appears with vitamin deficiency, gastrointestinal diseases, allergies, abscesses in the oral cavity, and injuries.
- A pimple on the frenulum under the tongue is formed during tonsillitis, when streptococci and staphylococci are activated and the lymph nodes are affected.
- The problem occurs when the salivary duct is blocked. Mineral or mucus plugs can become an obstacle. This interferes with patency. In this situation, a ranula is formed, which contains liquid exudate. The bubble may be clear or cloudy. It can burst, then build up again. Provoking factors include stomatitis, herpes, candidiasis, and lichen planus.
Since the mucous tissues of the oral cavity are sensitive, they can be damaged by hot food or drink. In the burn area, bacterial microflora feels comfortable, which contributes to the formation of salivary plugs in the ducts.
Tongue injuries
Another reason why the tongue hurts on the side lies in mechanical injuries to the organ. They occur when eating food with sharp parts (seeds, nuts, undercooked cereals), hitting, or biting. Damage can occur due to a seizure, sports, falls, or various accidents.
If you are absolutely sure that the soreness is the result of an injury, then you just need to give the tongue time to recover. Nevertheless, examination by a specialist to clarify the diagnosis and treatment will not be superfluous.
General recommendations
For stomatitis in adults, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. The dentist can perform initial treatment of the oral cavity, then the patient will need to perform all the manipulations independently at home.
Antiseptic treatment of the entire oral cavity is a prerequisite for the successful treatment of stomatitis and the rapid recovery of the affected mucosa. For “disinfection”, solutions containing chlorhexidine, furatsilin or metronidazole are used. Dentists also recommend rinsing with a soda solution every 2-3 hours.
Locally in the affected areas, it is necessary to remove heavy plaque using gauze and apply anti-inflammatory and regenerating gels or ointments to the areas where ulcers accumulate. The procedure is unpleasant, but significantly speeds up recovery.
Treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults, subject to all prescriptions and recommendations of the dentist, takes no more than 10 days. Symptoms of the disease disappear after 3–5 days; a few more days are required to restore the affected tissues.
Glossitis
Glossitis
is an inflammation of the tissues of the tongue, manifested in its soreness, changes in color and structure, and the appearance of a dense coating. There is a burning sensation, hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels), food loses its taste, and salivation increases.
If the doctor has diagnosed the patient with glossitis, then the next step is to find out whether this indicates a pathology of other organs. This could be a herpes virus, poisoning with heavy metal salts, etc. Treatment is prescribed depending on the initiating cause, trying to exclude it. It usually includes local antiseptic therapy.
Congenital pathologies
Sometimes neoplasms on the root of the tongue can be congenital. They appear as a result of developmental disorders of the fetus during the intrauterine period. Most often, such tumors are diagnosed in childhood. Let's take a closer look at congenital pathologies of the tongue:
- Hemangioma. This is a tumor consisting of blood cells. Its etiology is associated with a violation of embryogenesis. More often girls suffer from hemangioma; the disease is detected either at birth or in early childhood. The neoplasm looks like a red spot or a blue-purple lump. When the tumor is injured, heavy bleeding occurs.
- Lymphangioma. The tumor grows from lymphatic vessels. The rashes look like warts. Often the tongue is greatly enlarged in size. Lymphangioma is diagnosed in childhood. The tumor often becomes inflamed due to injury from hard food or teeth.
- Struma of the root of the tongue. This is a very rare disease. If embryonic development is disrupted, thyroid cells may enter the developing tongue. This is the cause of the pathology. The struma consists of thyroid tissue. It looks like a nodule under the tongue up to 3 cm in size. This disease is otherwise called goiter of the tongue. Clinically, it usually manifests itself during puberty. It becomes difficult for the child to swallow and speak. This tumor must be removed surgically, as it is prone to malignant degeneration.
Catarrhal glossitis
If the tongue hurts on the side and a white coating covers its surface, then this is most likely catarrhal glossitis - a special case of this disease. It can be considered as a symptom of other pathologies. In particular, it is called:
- caries;
- stomatitis;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- various infections (measles, diphtheria, etc.).
In addition to pain and plaque, symptoms of catarrhal glossitis include swelling of the tongue and a burning sensation, which is especially worse after eating or talking. The disease is treated by eliminating its causes and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions.
Prevention
Prevention of tongue cancer involves reducing exposure to risk factors and regular dental checkups. In order to minimize the likelihood of developing this disease, it is necessary to give up smoking and alcohol abuse, as well as the use of chewing mixtures. Monitor your oral health carefully. Chronic injury to the tongue should not be allowed; teeth must be treated and dentures adjusted in a timely manner. If long-term (more than 2 weeks) formations are detected, you definitely need to consult a doctor as soon as possible. [1.7]
| More information about treatment at Euroonco: | |
| ENT oncologists | from 5,100 rub. |
| Chemotherapy appointment | RUB 6,900 |
| Emergency oncology care | from 12,100 rub. |
| Palliative care in Moscow | from 44,300 rubles per day |
| Radiologist consultation | RUB 11,500 |
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Bibliography:
- Clinical recommendations. — Malignant neoplasms of the oral cavity. Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. — 2022.
- MM. Soloviev. — Practical Oncology • T. 4, No. 1 – 2003, Cancer of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue (reserves for improving treatment results), 2003
- A.L. Yudin. — Cancer of the tongue and floor of the mouth: modern aspects of diagnosis — Bulletin of Radiology and Radiology No. 5, 2015.
- Clinical protocol for diagnosis and treatment. — Malignant neoplasms of the oral cavity. The Republic of Kazakhstan. — 2015.
- Malignant tumors of the organs of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue. Educational method. manual./O.P. Chudakov, L.E. Moiseichik, T.B. Lyudchik, L.G. Bykadorova. - Mn.: BSMU, 2007. - 39 p.
- V.A. Soloviev. — Possibilities of ultrasound diagnosis of tumors of the tongue and floor of the mouth. — Oncology. Journal named after P.A. Herzen, 4, 2015. doi: 10.17116/onkolog20154418-21.
- A.R. Gevorkov. – Independent conservative and combined treatment of tongue cancer. – Oncology. Journal named after P.A. Herzen, 4, 2014.
- Rodrigo Arrangoiz. — Oral Tongue Cancer: Literature Review and Current Management. - Сancer Rep Rev, 2022. - Volume 2(3): 1-9. - doi: 10.15761/CRR.1000153.
Inflammation of the salivary glands
This disease is called sialadenitis. Any salivary glands can be affected by it, but painful sensations in the tongue, closer to the base, occur if the sublingual gland is affected. Pathology is caused by viruses or bacteria. Symptoms of sialadenitis include:
- pain at the base of the tongue;
- the formation of a compacted swelling underneath;
- decreased salivation.
How to treat the disease if the tongue hurts on the side precisely for this reason? Antibacterial and antiviral drugs.
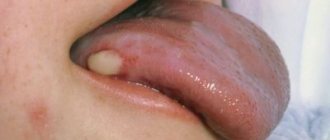
Papilloma
This is a formation in the form of a wart on a stalk. The causative agent of the disease is the human papillomavirus. It enters the body through damage to the mucous membrane.
Papilloma looks like a papillary or bumpy lump on the base of the tongue. Often it is diagnosed only at an appointment with a dentist or otolaryngologist. But in most cases, the neoplasm still causes serious discomfort to the patient. The papilloma is easily injured while eating and may bleed slightly.
It is important to remember that a wart on the tongue is dangerous. When injured, it can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Stages of the disease
Stages of tongue cancer
We offer you a table of correspondence between tongue tumor stages and clinical TNM classification, which uses the following designations:
- T – indicates the primary tumor: Tx – the primary tumor cannot be assessed;
- T0 – no data on the primary tumor;
- Тis – cancer in situ (pre-invasive stage);
- T1-T4 – the primary tumor is enlarged and/or widespread.
- Nx – regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed;
- M0 – no distant metastases;
Correspondence table for stages of tongue cancer TNM classification
| TNM stage | |
| 0 (carcinoma in situ) | Tis, N0, M0 |
| I | T1, N0, M0 |
| II | T2, N0, M0 |
| III | T3, N0, M0 or T1-T3, N1, M0 |
| IV | 4a: T4a, N0 M0 or T4aN1, M0 or T1-T4a, N2, M0 4b: T4b, any N, M0 or any T, N3, M0 4c: any T, any N, M1 |
Diagnostics
To accurately diagnose tongue cancer, laboratory and hardware tests are required. However, first of all, the patient should consult an ENT oncologist, who will give the necessary directions. Among the diagnostic methods:
- blood for tumor markers, other laboratory blood tests;
- biopsy of the affected area followed by histological examination;
- revision (revision) of the biopsy;
- MRI of soft tissues of the neck and face using contrast;
- CT scan of the neck and head with contrast;
- PET-CT.
Preventive measures
The main methods of prevention are strengthening the immune system and maintaining good hygiene.
How to prevent growths from appearing:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- exercise regularly, spend more time outdoors;
- avoid stressful situations, learn to relax, master meditative techniques;
- wash your hands frequently and thoroughly, especially after going outside or visiting the toilet;
- Always use only your own towels and personal items;
- adjust your diet - give up unhealthy and heavy foods, eat more vegetables and fruits, fermented milk products, cereals, lean meat and fish;
- observe the drinking regime - you need to drink 1.5-2 liters of clean still water per day;
- promptly identify and treat dental diseases and pathologies of internal organs.
An effective method for preventing the formation of papillomas on the tongue is HPV vaccination. The Cervarix and Gardasil vaccines have contraindications and side effects, so they are not suitable for everyone. Vaccination does not completely protect against infection, but it does promote the production of antibodies that help the body fight infection more quickly.
It is advisable to vaccinate up to 26 years of age. The protective effect is designed for 8 years. Contraindications: pregnancy and breastfeeding, any gum problems.
What not to do
If you notice a tumor on the root of your tongue, you should never touch it. This can lead to trauma to the tumor and serious complications.
If the lump looks like a purulent pimple or cyst, there is no need to try to puncture it and squeeze out the contents. This will cause infection. Only a doctor can open abscesses on the tongue under sterile conditions.
What to do if your tongue hurts? Many neoplasms are accompanied by unpleasant sensations and discomfort. Before visiting a doctor, you can rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile, sage or oak bark. This will help reduce pain. You can also use the anti-inflammatory gel Metrogyl Denta. However, these are temporary measures. Only a specialist can prescribe complete treatment.