Moles or nevi are present on the skin of any person. Some of them are present at birth, others appear in the first weeks of life, and others are formed on the body during adolescence and adulthood. Usually these benign formations do not cause concern to their owner. But when a mole grows, if it has changed color or changed in size, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist for advice and examination. Well, based on the results of the visit to the doctor, you can decide whether to remove the mole or whether it is not necessary.
Why do moles appear?
Moles vary in size, color, and location. They can appear on the face, neck, scalp, back and arms, absolutely on any part of the body. Black, brown, red moles are small, barely noticeable, and can be the size of a pea or even a chicken egg. Flat and protruding moles above the surface of the skin (not to be confused with papillomas) are a consequence of the pathology of epidermal cell division. And the reason for their appearance may be genetic, internal or external factors.
Interesting: Many dermatologists are inclined to believe that a person’s map of moles is laid down during intrauterine development. That is, when a child is born, there is not always a mole on the body. But its location is already determined by genetic factors.
Internal factors that lead to the appearance of moles are hormonal changes (not to be confused with age spots). External factors for the appearance of moles include skin trauma, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation, and burns.
Important: Often teenagers who have entered the phase of puberty discover that they have grown a mole. And during pregnancy, a woman may discover a new formation. With age, the number of nevi on the body increases.
And, by and large, if two or three new moles appear on the skin, there is no reason to worry. Well, if a mole begins to grow, begins to hurt, itch, or bleed, you should consult a doctor. So, if a mole has appeared and is growing rapidly, this is a direct signal for medical consultation.
Types and characteristics of moles
A nevus (this is the scientific name of a mole) is a benign formation consisting of an accumulation of cells with excess melanin (so-called melanocytes) in different layers of the skin. Nevi can be congenital or acquired.
Let's look at the different types of nevi. In medicine, it is customary to distinguish epidermal, border and intradermal nevi. They all differ in localization in the thickness of the skin - the epidermal one is located in the uppermost layer, and the intradermal one, accordingly, in the deepest. Such moles are a cluster of melanocytes of small size (usually from a few millimeters to a centimeter), round in shape, smooth, with clear boundaries.
The following classification of moles has also become widespread:
- Complex nevus (also mixed) . This mole is located simultaneously in several layers of the skin. Otherwise, it is no more different from the above-mentioned formations.
- Pink and blue (blue) nevi . The first can most often be observed in blondes with very fair skin, since the melanin pigment in this case has a pinkish or reddish tint. The second type of nevus also differs only in the shade of the skin pigment, which in this version will be blue-violet.
- Halonevus (Setton's nevus) is a mole with a white halo around it.
- Papillomatous nevus . This mole is similar to a papilloma, which is why it got its name. It is characterized by a bumpy surface protruding above the skin level and may have a stalk (the so-called “hanging” mole).
- Congenital nevi . This is a large group that includes dysplastic nevus (Clark's nevus or atypical nevus), giant congenital nevus, nevus of Ita, nevus of Ota, vascular nevus, Jadassohn's nevus, etc. What they all have in common is that they develop in utero and the child is born with a spot on the skin. These spots can be of absolutely any shape, size, they can have a surface with a very different structure: from smooth to resembling brain convolutions and overgrown with hair, they can be localized on any part of the body, including the skin of the eyelids and genitals.
The last group, due to its size, can be classified as birthmarks rather than moles, however, if these nevi are small in size, then it will be difficult for a non-specialist to distinguish between these formations.
Can a benign mole grow?
Moles grow, as already mentioned, under the influence of internal and external factors. They change appearance throughout life - they evenly thicken, turn pale, darken, and grow along with the skin. And if the mole begins to grow, but its increase in size occurs slowly, in proportion to the growth of the body, then this condition should not cause any special concern. These are natural changes in which the risks of the tumor degenerating into melanoma are minimal. Well, if this growth is rapid, the mole shows signs of a dysplastic nevus, it is recommended that it be examined and removed.
Is an enlarged mole a sign of melanoma?
As you know, rapid growth is one of the hallmarks of malignant tumors. This, in the vast majority of cases, also applies to melanoma. How can one distinguish between a normal enlargement of a mole and its transformation into a tumor? Unfortunately, doing this reliably “by eye” can be very difficult even for an experienced specialist.
This is why oncologists always evaluate a complex of symptoms. The history of the existence of the mole, the changes that have occurred to it during this time, the nature of the edge, the degree of asymmetry, bleeding, lack of hair, etc. are important. If only one sign speaks in favor of melanoma, most likely everything is fine with the mole. Two, and even more so three signs of melanoma indicate that you urgently need to see an oncologist.
Based on my experience, I can say that the growth of an ordinary mole by 1 mm per year, as a rule, is not a reason to worry. Although, I must repeat, you cannot evaluate the nature of a mole by only one parameter - you need a complex.
What changes in education are alarming?
The following symptoms should not be ignored:
- The mole has increased to 6 or more millimeters in diameter.
- The color of education has changed. Light or dark spots appeared on its surface.
- The texture, texture, and density of the nevus have changed.
- The edges of the mole have become uneven.
- Both during palpation and at rest, the mole hurts and itches. The skin around the formation is red and swollen.
These changes are unfavorable signs. It is recommended that you seek professional advice immediately.
Are they dangerous?
After the dermatologist explains to the patient why large moles appear and what is the reason for the specific formation, the doctor finds out the nature of the pigment spot and its type.
An increase in size and the appearance of new moles is usually observed after harmful exposure to UV rays and hormonal changes. Whether large moles are dangerous can be determined by the following factors:
- cessation of growth and loss of hairs on the surface of the spot;
- change in outline;
- the appearance of pronounced asymmetry;
- an increase in size of more than 5 mm in diameter;
- itching and burning in the area where the nevus is located;
- redness and swelling of the tissues around the spot;
- discharge;
- bleeding
For an experienced specialist, there is no problem in determining at first glance whether large moles can be removed and how dangerous they pose. But even the most expert dermatologist can evaluate a spot subjectively. Therefore, if there are more than three signs of danger, the doctor prescribes a test.
What to do if a mole starts to grow?
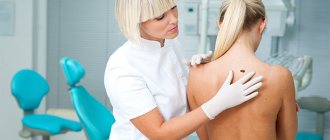
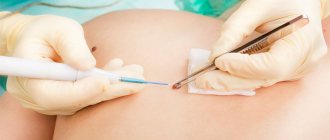
Make an appointment with a dermatologist. The specialist will collect anamnesis and conduct a visual and hardware examination (dermatoscopy). If necessary, he will remove the formation and send a tissue sample for histological examination.
What can’t be done if a mole has increased in size? You should absolutely not try to “remove” the tumor at home using pharmaceutical or folk remedies. Any unprofessional manipulation is extremely dangerous; “treatment” is fraught with serious damage to the skin and can cause the mole to degenerate into melanoma due to damage and bleeding.
Also, dermatologists strongly do not recommend removing moles in beauty salons that are not suitable for such procedures. Only an experienced dermatologist can determine the need for removal and histological analysis.
How quickly does malignancy occur?
Malignancy is the process of transforming healthy cells into cancer cells. Daughter cells acquire malignant features. Pathology occurs at different speeds depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Stages of development
Malignancy occurs in several stages.
- Initiation External and internal harmful factors provoke cell mutation. The appearance of oncogenes causes rapid growth and reproduction of affected cells. In a healthy body, such cells die, but due to initiation they continue to divide. However, this stage is not yet the beginning of the development of oncology.
- Promotion At the second stage, oncogenes are activated, provoking the proliferation of diseased cells.
- Evasion of diseased cells from differentiation Differentiation is changes in the functions, size, and shape of a cell that allow it to perform its genetic functions. Poorly differentiated cells eventually form an altered area of tissue, which later becomes the basis of the tumor. Such a mole already leads to skin cancer.
- Tumor progression Uncontrolled proliferation of altered cells leads to the germination of a diseased area of tissue, which begins to destroy the walls of blood vessels. The affected cells spread throughout the body, ending up in the lymph nodes and distant organs. There the cells settle and the formation of metastases begins.
How is the diagnosis done?
The most accurate method for diagnosing moles is dermatoscopy. The digital device dermatoscope allows you to “enlighten” the formation and enlarge its image. It becomes possible to study the texture and nature of skin pathology. Diagnosis is painless, safe and does not take much time.
Interesting: After dermatoscopy, all examined formations are recorded. At a subsequent visit to the doctor, you can monitor changes in nevi, their size, and shape.
During the examination, the dermatologist decides on the need for histological analysis. Most often, there are no contraindications for mole removal. It remains for the doctor to choose the optimal method.
Prevention of degeneration
In order to prevent the transformation of an ordinary nevus into a malignant one, it is important to promptly contact a specialist with a request for diagnosis. The question of whether large moles are removed will be clarified at the first appointment. Doctors usually recommend getting rid of pigment formation as early as possible from the point of view of aesthetics and safety.
But measures to prevent degeneration are still worth taking:
- do not get carried away with tanning;
- in the hot season, go outside, applying cream with SPF 30 - 50 to areas of the skin not protected by clothing;
- protect yourself from injury;
- Do not take hormonal drugs uncontrollably.
And most importantly, do not ignore scheduled examinations by specialists. Especially during periods of hormonal changes in the body, it is necessary to constantly see a doctor.
The specialists at the Desir clinic specialize in various areas of medicine. We have some of the best dermatologists and highly specialized specialists: dermatologists-oncologists. Make an appointment and get your moles examined. If you are concerned about the presence of a large mole, we will provide qualified assistance. Our innovative equipment allows us to conduct research as accurately as possible and use the latest techniques to remove formations of various types.
Indications for mole removal
Direct indications for removal are, as already mentioned, that a mole has begun to grow. Manipulation is also carried out if the formation spoils a person’s appearance or develops complexes. For example, a nevus that appears on the face can look extremely unattractive.
Another reason for its removal may be poor location. If a mole is located on the neck, on the scalp, under the armpits and gets caught by clothing and accessories, this can cause bleeding and secondary infection. And the process itself can cause pain.
What are the main risks
Moles today cause serious concern among people. First of all, the risk of developing melanoma is one of the most dangerous and fastest-growing types of cancer. In addition, the fact of their active spread also raises questions - why some have more of them and others have less. Naturally, many people worry about their health and are interested in how to prevent the development of moles on the body.
What is the reason for the active appearance of new moles? More details
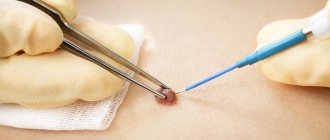
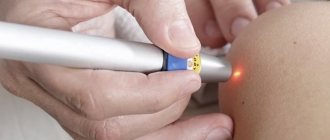
Laser mole removal
The laser method of treating skin tumors is the most effective today. After all, it is painless, safe, fast and has a minimum of consequences. The laser device allows you to adjust the depth and intensity of the effect on the tissue, so the skin around the formation does not suffer, and very soon the wound heals. This allows micro-surgery to be performed on the face, neck, and other open areas of the body if there is an increase in the size of the mole, without the consequences of the appearance of a scar.
The laser beam vaporizes pathological tissue. And you can remove a mole in one procedure. The rehabilitation period is minimal. Healing of the wound takes 5-7 days. The wound is immediately cauterized with a laser beam, so there is no risk of bleeding or infection.
Important: The procedure is painless, there is no need for general anesthesia. And all because the laser device works in short pulses, pain receptors do not have time to react. The patient does not feel pain. But after the procedure, the wound may burn a little.
After surgery, some restrictions are recommended. For two weeks, it is forbidden to be in the open sun, visit the sauna and steam bath, or apply aggressive ointments and creams to the skin. A dry crust forms at the site of exposure. It cannot be torn off or removed. The wound will heal, and the skin underneath the crust will be completely restored.
Important: The most important advantage of laser surgery for mole removal is the complete safety of the procedure and a minimal list of contraindications.
Surveillance for safety
For those who have many moles, we can advise, in addition to the rules of sun protection, constant monitoring.
“Only control of moles. If we are talking about hard-to-reach places, you need to ask help from loved ones - husband, wife, children, parents, friends. They should help fix moles in places where you yourself cannot. The optimal solution is photographic recording. If any mole bothers you, it must be recorded using a photo at the same time, under the same lighting, using the same camera. And it would be good to take additional centimeter measurements to better monitor the condition of the mole,” says the specialist.