Today, human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common viral infections. According to statistics, it is present in almost 90% of the world's population. Scientists have also proven that two types of the virus (16 and 18) occur in approximately 70% of patients diagnosed with cervical cancer and precancerous pathological conditions of the cervix.1 It has been established that in women with long-term persistence of the virus in the body, the risk of developing cervical cancer increases 80 times. For this reason, doctors pay increased attention to the fight against this disease.
- Types of virus that can cause cancer
- Varieties of the virus
- Viferon suppositories for HPV Release form and composition
- Indications for use
- Suppository dosages
- Use during pregnancy
Human papillomavirus (HPV) belongs to the genus Papillomavirus and belongs to subgroup A of the Papovaviridae family. It inhabits the deep layers of the epithelium (skin and mucous membranes), and its reproduction occurs in the upper layers of the epithelium. The entire life cycle of the virus takes place only inside the cells of the body, but for some time it can also exist in the external environment, which explains its high contagiousness - the ability of infectious diseases to be transmitted from sick people to healthy people by transmitting the pathogen through direct contact or through transmission factors. Re-infection is possible because immunity to this virus is not developed.
Types of HPV with oncogenic risk
Currently, there are more than 600 types (strains) of papillomavirus found in humans. Of these, approximately 40 can cause damage to the anogenital tract of men and women, which is manifested by the formation of condylomas or the development of precancerous changes within the epithelium with the subsequent development of cancer of the cervix, vagina, vulva, anus, and penis.
All types of papillomaviruses are divided into three groups according to their oncogenic danger to humans1:
- human papillomaviruses of low oncogenic risk: 6, 11, 40, 42, 43, 44;
- viruses of intermediate oncogenic risk: 35, 51, 52, 58;
- viruses of high oncogenic risk: 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 56.
The oncogenicity of the virus is explained by its ability to integrate its DNA into the genome of human cells.
What types of HPV exist?
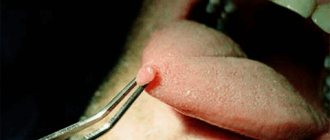
HPV infection of anogenital localization can occur in latent, subclinical and clinical forms. In the latent form, the virus is detected, but there are no changes in the epithelium. Subclinical infection is detected only using a test with 3% acetic acid and manifests itself as small flat warts. The clinical form of human papillomavirus infection can occur in the form of intraepithelial lesions (within the epithelium) in women and men, which are not visible to the naked eye, but are detected by colposcopy and cytological/histological examination and can lead to precancerous diseases and cancer. And also in the form of genital warts, which are soft papillary formations on a stalk, prone to fusion. Merging, they form colonies that look like cauliflower.
The manifestations of human papillomavirus are variable and depend on the type of virus. HPV of low oncogenic risk also leads to the appearance of warts and papillomas:
- Vulgar warts are hard growths more than 1 mm in diameter with a rough, keratinized surface. It is possible for papillomas to merge to form large areas of damage.
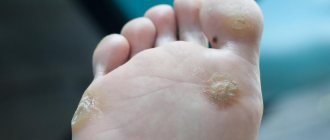
- Plantar warts are hard, flat formations on the skin of the foot, rising above its level and covered with a layer of keratinized epithelium. They have a protruding rim. Sometimes one wart produces daughter warts.
- Flat warts are skin formations in the form of flat nodules up to 5 mm in size. Flat warts, as a rule, are multiple and are located in groups on the face, back of the hands, and legs.
- Threaded papillomas affect the area around the eyes, groin, neck and armpits. They are elongated formations of elastic consistency measuring 5-6 mm.
There are three known routes of transmission of HPV:
- contact and household;
- sexual (genital, anal, oral-genital);
- in childbirth from mother to child.
Predisposing factors that contribute to infection and the development of infection are vitamin deficiency, immunodeficiency, smoking, endometriosis, physical overload and chronic fatigue, pregnancy, urogenital infections, as well as any chronic diseases that negatively affect the immune system. The risk of infection increases with frequent contact with bare human skin, for example during massage.
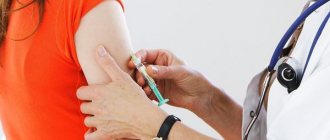
VIFERON Suppositories for HPV
Since infection with the virus and the appearance of papillomas and condylomas on the skin and mucous membranes are inextricably linked with the state of the immune system, treatment when the human papillomavirus is detected in the body includes drugs that not only fight viruses, but also help restore immunity. One of these drugs is VIFERON, which has a wide spectrum of antiviral activity and strengthens the immune system. Recombinant interferon alpha-2b, which is part of this drug, has immunomodulatory, antiviral properties (blocks virus replication) and helps restore the immune system. It is identical to human interferon alpha-2b, but is produced using modern technology without the use of donor blood.
Release form and composition
The drug, which is available in the form of suppositories, gel and ointment, was developed as a result of fundamental research in the field of immunology, which has proven that in the presence of antioxidants (vitamins C, E), the antiviral effect of interferon is enhanced.
VIFERON Suppositories are produced in the form of bullet-shaped rectal suppositories of white-yellow or yellow color. The drug suppresses the activity of viruses and increases the effectiveness of the body's own immune response to pathogenic microorganisms. Cocoa butter, which is part of the drug, contains phospholipids, due to which the medicinal substances are evenly distributed throughout the suppository, which ensures their rapid and almost 100% entry into the blood. Unlike cocoa powder, butter does not contain natural allergens and does not irritate the mucous membrane. The properties of cocoa butter make it possible to avoid the need to add synthetic toxic emulsifiers, which, in the case of using solid fat as the basis of suppositories, are used to uniformly distribute and increase the bioavailability (absorption) of the active substance.
Indications for use for HPV
The drug in the form of suppositories can be used during pregnancy (from the 14th week), as well as during breastfeeding and when treating children.
The drug is used in children and adults as part of complex therapy to combat a number of diseases, including infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract in adults (human papillomavirus, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus infection, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gardnerellosis, bacterial vaginosis, recurrent vaginal candidiasis, mycoplasmosis). It reduces the frequency of relapses and prevents the progression of cervical pathology associated with HPV infection.
VIFERON suppositories for HPV: drug dosage
Information on how to use VIFERON Suppositories for human papillomavirus is contained in the instructions. The recommended dose for adults is VIFERON 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5-10 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued.
Before using suppositories, check their expiration date. It is not recommended to use candles that have expired. Before using a rectal suppository, you should wash your hands thoroughly. The candle wrapper must be carefully cut with scissors and its contents removed. Then you need to lie on any side convenient for the procedure, completely straightening your lower leg and bending your upper leg towards your stomach. Then you need to slowly insert the suppository into the anus, pushing it past the muscle sphincter with the tip of your finger. After inserting the suppository, the buttocks should be brought together and held in this position for several seconds.
The use of Viferon suppositories against HPV during pregnancy
Pregnant women from the second trimester of pregnancy (starting from the 14th week of gestation) are prescribed VIFERON 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours daily for 10 days, then for 9 days 3 times with an interval of 3 days (on the fourth day) 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours. Then every 4 weeks until delivery - the drug in a dosage of 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours every day for 5 days. If necessary, the drug is prescribed before delivery (from the 38th week of gestation) at a dosage of 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 10 days.
Warts are skin growths, mostly benign, caused by different types of human papillomavirus (HPV).
HPV, getting on the skin or mucous membrane, penetrates the cell and penetrates into the nucleus, where it can remain inactive for a long time. Under conditions leading to immunosuppression, the virus begins to multiply in the nucleus, causing proliferation of epithelial tissue.
At present, it is obviously impossible to achieve a complete cure for HPV infection through monotherapy. However, the therapeutic methods of modern medicine make it possible to inactivate the virus and achieve stable long-term remission [1].
Methods that reliably ensure the removal of warts are the external use of drugs based on salicylic acid (possibly used at home) and cryotherapy prescribed by a doctor. Injection immunotherapy in the treatment of nongenital common (vulgar) warts can be used on large warts that are difficult to treat with other means (Table 1).
Warts occur in 10% of children and adolescents. The age group 12-16 years old is at greatest risk. Girls get warts more often than boys. The peak incidence occurs at 13 years in girls and 14.5 years in boys [4].
It has been established that without special treatment, warts disappear after 2 years in 40% of children [5]. They usually continue to increase in size and may become more resistant to treatment over time [6]. Children with treatment-resistant warts can become active carriers of HPV. In addition, depending on the location, warts can be painful (for example, if they are located on the sole or periungual fold), and can also be perceived as an obstacle to communication if the warts are located on visible areas (for example, the hands or face) [7].
Treatment approaches
Currently, there are different approaches to treating warts, including observation and a combination of several methods to increase effectiveness. The choice of treatment method should be made on a case-by-case basis based on the physician's experience, patient preference, and application of an evidence-based approach. In immunocompromised patients who complain of warts, treatment may not lead to significant improvement, and the warts may be resistant to the drugs used. The two most common methods for removing warts are the use of salicylic acid and liquid nitrogen cryotherapy [8].
Salicylic acid preparations
The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials assessed that topical salicylic acid is a safe and effective treatment for wart removal [8]. In addition, according to the report, there is no information to support the superiority of other methods in terms of treatment effectiveness or fewer side effects. Pooled data from 6 randomized controlled trials indicate a 75% effectiveness of treatment in patients using salicylic acid preparations, compared with 48% in the control group [8]. The manual by J. Sterling et al. [7] Salicylic acid has been named the drug of choice for the treatment of flat warts on the face, plantar warts, and flat and common warts on the hands.
Currently, there are various salicylic acid-based products on the market. Over-the-counter medications contain less than 20% salicylic acid, while prescription medications may contain up to 70% salicylic acid [9]. However, 15-20% salicylic acid is usually enough to cure a wart.
The effectiveness of treatment with salicylic acid preparations, according to various sources [10], is 40-84% (on average 61%). The therapeutic benefits of topical salicylic acid-containing products, both prescription and over-the-counter, are supported by randomized controlled trials [11–14]. The use of salicylic acid preparations is considered first-line therapy in the treatment of nongenital common warts (Table 2)
[9].
In the Russian pharmaceutical market, among over-the-counter drugs based on salicylic acid, Collomak
, produced in the form of a liquid varnish with a shaving brush lid.
Collomak
is a modern multicomponent drug that contains active ingredients: keratolytics - salicylic (20%) and lactic (5%) acids, emulsifier polidocanol 600 (2%), as well as special fillers that form the basis of the varnish dosage form - a film-forming substance ( ethylcellulose 5.5%), plasticizer (dibutyl phthalate 1%), solvents (acetone 6.65%).
The polidocanol component of Collomac
also causes sclerosis and obliteration of small veins and arteries at the site of application.
Collomak
applied to a wart or callus, after which the horny layers are easily removed.
If necessary, this treatment is carried out several times. To avoid damage to the surrounding skin when applying Collomac
, it is protected with indifferent zinc paste.
You can protect the surrounding skin with adhesive tape by cutting a hole in the middle. The duration of treatment is determined depending on the effectiveness of the drug. For adults, the maximum dose of Collomac
is 10 ml/day, which corresponds to 2 g of salicylic acid, for children - 1 ml, which corresponds to 0.2 g of salicylic acid.
It is not recommended to exceed the indicated dose and treat several areas of the skin and mucous membranes at the same time. During pregnancy, the use of Collomak
is permissible only when applied to a limited surface (no more than 5 cm).
When using the drug in the maximum daily dose in adults and children, the duration of treatment should not exceed 1 week. Positive experience with the use of Collomac
allows us to recommend this drug for widespread use in gynecological and dermatological practice in the treatment of warts and genital warts [1].
Cryotherapy
The effectiveness of cryotherapy treatment varies widely depending on the treatment regimen. As a rule, the wart is frozen for 10-30 seconds until a ring 1-2 mm thick forms around the frozen ball of the treated area. The maximum effectiveness of therapy is achieved when treated at intervals of 2-3 weeks. A positive result of therapy lasting more than 3 months is not documented [10, 11]. The best rate of effectiveness in the treatment of plantar warts was achieved when cutting off the hyperkeratotic surface and using two freezes with intermediate complete thawing [11, 13]. For common warts not located on the palms or soles, it is preferable to use one-time freezing [9]. One scientific report recommends the use of cryotherapy as first-line therapy for the treatment of flat and simple warts [7].
Cryotherapy is also offered as second-line therapy for flat and simple warts on the face [7]. A report by R. Brodell et al. [9] Cryotherapy is proposed as an effective treatment for simple and plantar (cutting with two freezing cycles) and flat warts. According to a report from the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials [8], cryotherapy is not superior to topical medications for nongenital common warts.
Laser therapy
With the help of laser therapy, it is possible to influence the hemoglobin of red blood cells contained in the blood vessels of the wart. In this case, thermal energy is extrapolated to adjacent tissues, which leads to coagulation of blood vessels. As a result of the procedure, a necrotic area with a wart remains, which is easily rejected [15]. Studies examining the effectiveness of laser therapy after 2-3 sessions show a positive result in 48-83% of cases for warts located on different parts of the body [16, 17].
In addition to physical destruction, lasers have a toxic effect on HPV, but the recurrence rate for this method is quite high - 4-22% [18]. K. Robson et al. [19] in a prospective randomized study showed that the effectiveness of laser therapy and conservative treatment methods is comparable. The use of laser therapy is recommended as second-line therapy for plantar warts and third-line therapy for common and flat warts [9].
Immunomodulators and antiviral drugs
The main mechanism of action of drugs in this group (imiquimod, kagocel) is the ability to induce the production of late interferon (IFN; a mixture of α-IFN and β-IFN), which has high antiviral activity. For chronic viral infections, they are recommended to be prescribed simultaneously with external therapy.
J. Sterling et al. [7] do not consider the available information on the use of imiquimod to be sufficient to recommend this drug for the treatment of nongenital common warts.
Cytotoxic drugs
The mechanism of action of cytotoxic drugs (bleomycin, podophyllotoxin) is based on inhibition of DNA synthesis of cells and viruses. Cytotoxic drugs are an alternative treatment for warts that do not respond to other treatments or are difficult to remove surgically. The pain of treatment (especially with bleomycin) is the main limiting factor in the use of this method. Possible side effects include scar formation, pigmentation, nail damage, and Raynaud's phenomenon (bleomycin) [20].
According to the report of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, there is no statistically significant evidence of the effectiveness of intralesional bleomycin in the treatment of non-genital common warts, and the available data cannot be generalized for analysis [8]. However, R. Brodell et al. [9] based on 4 randomized controlled trials and a number of case series studies provide evidence of the effectiveness of bleomycin and recommend it as third-line therapy for simple and plantar warts.
Retinoids
Systemic retinoids are used to treat warts due to their ability to influence keratinization processes, which speeds up wart removal [21].
J. Sterling et al. [7] provide compelling evidence for the effectiveness of topical retinoids in a prospective case series study and a limited number of trials of systemic retinoids. R. Brodell et al. [9], based on a series of case studies, recommend oral and topical retinoids as second-line therapy for the treatment of flat warts.
Injection immunotherapy
Injectable immunotherapy relies on the ability of the immune system to recognize specific viral and fungal antigens. A skin antigen test for Candida is commonly used. It is generally accepted that delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions caused by these antigens increase the immune system's ability to recognize and eliminate HPV. In a study by M. Clifton et al. [6] showed complete (100%) removal of warts in 47% of patients and 75–99% removal of warts in 13% of patients. In 34% of those participating in the study, complete removal of all warts distant from the injection site was noted. In 22% of study participants, the effectiveness of therapy was 75-99% for warts located at a considerable distance from the injection site. No cure of warts in distant areas was observed with the use of other drugs.
S. Johnson et al. [22] analyzed the removal of warts by administering Candida and mumps antigens and compared their effectiveness with that of cryotherapy. Complete removal of warts was achieved in 49% of cases in those treated with mumps immunotherapy and in 70% of cases in those treated with Candida antigen immunotherapy, while the same figure for cryotherapy was 42%. The most common side effect was itching at the injection site [6]. A flu-like condition lasting less than 24 hours and improving with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs was also noted. The high therapeutic efficacy of injection immunotherapy indicates that it is a promising method for the treatment of warts, although it requires clinical trials and safety assessment. R. Brodell et al. [9] recommend injection immunotherapy as second-line therapy for plantar warts and third-line therapy for simple and flat warts.
Conclusion
The drugs of choice for external treatment of HPV are currently salicylic acid-based products. Modern combination drugs, such as Collomac
, allow you to increase the effectiveness of treatment using salicylic acid, while maintaining a high level of safety. In addition, it is important that such treatment is safe and inexpensive. Other methods can be used for individual intolerance to salicylates, as well as as part of combination therapy.
Truths and myths about human papillomavirus
FACT 1. Human papillomavirus can cause cervical pathology in the form of precancerous changes and cervical cancer.
This is true. Certain types of virus can cause serious health problems. The virus is found in most patients with cervical cancer. Human papillomavirus of medium and low oncogenic risk leads to the appearance of condylomas, papillomas and warts throughout the body and genitals. These lesions are not precancerous and require treatment for cosmetic reasons.
FACT 2: Condoms and other barrier contraceptives protect against HPV transmission.
It is a myth. Of course, using condoms reduces the risk of contracting the virus, but they are not able to completely protect against infection. Especially in cases where formations in the intimate area are located outside the organs protected by the contraceptive.2
FACT 3. The presence of human papillomavirus in the body is determined by a blood test for antibodies.
It is a myth. Antibodies in the blood can be detected as evidence that the body has previously encountered HPV. The virus itself can only be detected in squamous epithelial cells, which are present on the mucous membranes and skin.
FACT 4. You can completely get rid of the human papillomavirus.
It is a myth. At the moment, there is no method of combating the virus that would permanently eliminate it from the body. However, the manifestations of the virus can be successfully combated with a course of treatment with immunomodulatory drugs with antiviral activity, including the drug VIFERON.1,2
FACT 5. Human papillomavirus can disappear on its own without treatment.
This is true. This phenomenon is called “self-elimination”, which is possible within 6-24 months after infection, as a consequence of an adequate immune response. Most often it happens to women under 26-30 years of age.2 After 30 years, the likelihood of self-healing decreases significantly and the majority remain carriers of the human papillomavirus.
Reference and information material
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
Sources
1. Early pregnancy. From prenatal preparation to healthy gestation” / Ed. V.E. Radzinsky and A.A. Orazmuradova. – 3rd ed., revised. and additional – M.: Editorial office of the magazine StatusPraesens, 2018. – 800 p.
2. Gynecology: national guide / ed. G.M. Savelyeva, T.G. Sukhikh, V.N. Serova, I.B. Manukhina, V.E. Radzinsky. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2022. – 1008 p.
Loading...
Take other surveys
Remedy for papillomas
Ointments against papillomas
Ointments for papillomas are recommended as a gentle way to inhibit HPV activity. Their effect is aimed directly at neoplasms, nearby skin or mucous membranes. The ointment is prescribed by the doctor, guided by the indications. It is worth noting that drugs for external use against papillomas can be used throughout the entire period of treatment, as part of complex therapy.
Before turning to radical methods of getting rid of papillomas, many resort to the help of such common and accessible means as: Oxolinic ointment.
The active ingredient of the drug suppresses the activity of the virus, slowing down or eliminating the appearance of new formations. To get rid of papillomas, oxolinic ointment is used 2-3 times a day for at least two weeks. Oxolinic ointment for papillomas can be used on any area of the skin, including children over 2 years old, pregnant women, and women during lactation.
Panavir.
A gel based on herbal components eliminates the external manifestations of HPV and, moreover, quite successfully fights directly against the virus, penetrating into the deep layers of the skin. After just a week of using the product in recommended doses, the concentration of active ingredients reaches an effective level.
Aldara cream.
This remedy eliminates neoplasms and blunts the activity of HPV. Effective in the fight against warts and genital warts, including on the genitals.
Salicylic ointment.
The active substance has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect and is a good antiseptic. Recommended for eliminating warts.
Viferon
. The drug has an antiviral effect and is an immunomodulator. Viferon ointment for papillomas is used up to 4 times a day for 7-10 days.
Zinc ointment.
Softens and dries the neoplasm, promotes better exfoliation of keratinized tissue.
Zinc-salicylic ointment.
Has softening and exfoliating properties. Effectively reduces the concentration of local manifestations of HPV. With regular application (up to 2 times a day), neoplasms, as a rule, disappear completely.
Antipapillomas.
The gel has a good exfoliating effect and is an effective means of removing warts and papillomas. After treatment, the neoplasms disappear within 2-3 days. Removal of large tumors is carried out in 2-5 steps.
Malavit.
The ointment is effective in the fight against flat papillomas and condylomas. Has pronounced anti-inflammatory properties. It is recommended for use until the tumors completely disappear or their concentration decreases to a satisfactory level.
Bonafton.
Ointment for papillomas concentrated on the eyelids. The doctor determines the duration of the course and frequency of treatment of the affected area individually.
Vishnevsky ointment.
A powerful antiviral, bactericidal, healing agent that has proven its effectiveness against growths in different locations. Can be used both on the skin and mucous membranes. Has no contraindications. Proper use eliminates side effects.
Among the existing drugs, gel and ointment against papillomas are the most convenient to use. The dense structure of the drugs allows for a targeted effect on the tumor. In addition, ointment for papillomas usually does not have a systemic effect, which means it can be used to treat children and pregnant women. The appropriate drug format, dosage and course duration are selected by the doctor, taking into account the indications. By self-medicating, you can trigger the disease or provoke complications. Remember that the effectiveness of treatment depends on how well the therapy is selected.