Papillomaviruses (HPV) are a group of viruses that includes more than 200 types (strains) of HPV. More than 40 types can be transmitted during sex, from infected skin and mucous membranes to the skin and mucous membranes of the sexual partner.
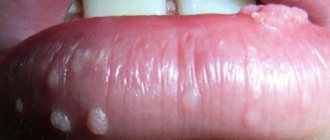
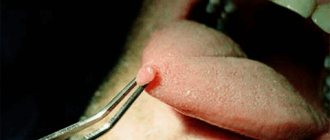
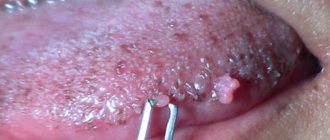
Infection with papillomavirus can lead to the development of benign neoplasms (papillomas, warts or condylomas) on the skin and mucous membranes almost anywhere. Some types of virus can cause malignant degeneration of the epithelium and lead to cancer. HPV types 16 and 18 account for the bulk of cancers induced by human papillomavirus infection.
Infection and incubation period of HPV 18
Papillomavirus spreads during sex.
The infection can also be transmitted through household contact.
But if the genitals are affected, most likely the infection occurred during sex.
The contagiousness of HPV 18 is extremely high.
With a single contact, the risk of infection reaches 70%.
Barrier contraceptives do not always save you.
Since HPV can penetrate not only into the urethra or vagina, like other STIs.
Microdamages on the skin of the pubis or inner thighs are sufficient for the virus to become infected.
If papillomavirus is present during pregnancy, the mother may also infect the child.
It can occur in utero or during childbirth.
The incubation period of HPV 16 and 18 in women lasts several months.
Then either signs of infection appear or the virus is spontaneously eliminated from the body.
This is facilitated by the activity of the immune system.
Why does HPV 18 make itself felt?
Doctors point out to their patients that their incubation period can vary greatly.
It all depends on the characteristics of the body, as well as on how active the immune system is.
There are people who live their entire lives with HPV 18 in their bodies.
Without even knowing it, or knowing but not suffering from symptoms or complications.
Whether the virus will manifest itself during a person’s lifetime depends on a number of factors.
Among them:
- exposure to various colds, ARVI, etc.
- presence of human immunodeficiency virus in the body
- frequent hypothermia or, conversely, regular exposure to high temperatures
- decreased immunity under the influence of stress factors, frequent nervous strain, etc.
Any of the factors, if not taken into account, can lead to the virus being activated in the body.
This happens due to the fact that the body’s immune system is simply unable to restrain the proliferation of the pathogen, preventing it from injuring other organs and cells.
Prevention from infection
The most reliable prevention against infection with HPV type 18 is to limit the number of sexual partners.
You can use a condom - it significantly reduces the risk of infection.
Vaccination is used before intimate life begins.
2 vaccines are used.
One provides protection against types 16 and 18 of human papillomavirus.
These are the most common etiological factors of cervical cancer.
The second vaccine additionally prevents infection with types 6 and 11.
These are the causative agents of anogenital warts.
Secondary prevention involves regular screening.
Tests make it possible to identify HPV and promptly carry out therapy, before pathological changes in the cervical epithelium.
How men become infected with HPV 18
Prevention from HPV infection is very difficult, since the virus is easily transmitted from one person to another.
To develop prevention methods, it is necessary to know exactly how the virus is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person.
There are several options for the spread of the disease:
- 1. Sexual tract. It is implemented most often in modern medicine. Viral particles are found in natural lubrication in women, in semen in men, and on mucous membranes. Contact with them is inevitable during sex, they enter a healthy body and begin their active reproduction. Doctors often remind their patients that it’s not just classic unprotected sex that is dangerous. You can also become infected through anal or oral contact.
- 2. Contact path. Another common way of transmitting the virus. You can become infected by kissing, using other people's personal hygiene items, or touching injured skin in areas where growths caused by HPV are located.
- 3. Vertical path. It is often implemented, since HPV is easily transmitted from mother to child. Even if infection does not occur in utero, there is a high probability of the virus entering the child’s body during the birth itself, when the placenta no longer provides protection to the baby.
HPV 18: preventive vaccination
Due to the fact that HPV 18 provokes malignant tumors in women, vaccination against this pathogen is becoming increasingly popular.
Their introduction is carried out in adolescence, before contact with the virus.
After the start of intimate life, vaccinations are not given.
The vaccine reliably protects against certain types of papillomavirus.
These are types 16, 18, as well as 6 and 11.
However, there is no guarantee that the patient will not develop cervical carcinoma in the future.
Firstly, only 90% of cases of this cancer are associated with HPV.
This means that 10% of women develop pathology without papillomavirus.
Secondly, among cancer cases that develop as a result of HPV infection, types 16 and 18 of the virus become the culprits in 70% of cases.
Another 30% of cases occur with other highly oncogenic HPV types.
So vaccination reduces the risk of cancer by 3 times.
But it does not guarantee protection against this infectious disease.
Therefore, a woman still needs to undergo regular screening for timely detection of precancerous processes.
The importance of correctly determining the HPV type
Patients are often interested in the question of what types of tests they should know, and why correct diagnosis is so important in general.
After all, it would seem that a diagnosis of HPV can be made only by looking at the growths.
The fact is that there are a huge number of varieties of the HPV virus.
Today there are at least 100 of them known, and new ones are being discovered regularly.
Some of these viruses have low oncological activity, provoking malignant degeneration only in exceptional cases.
Some, on the contrary, have high oncological activity.
Among them is the type 18 virus.
Naturally, it is impossible to determine the type of virus by examining the rash.
Additionally, diagnosis is necessary to choose the right treatment tactics.
To do this, concentration PCR is done.
What does concentration mean, patients want to know.
Everything is very simple.
It shows how many viral particles are present in the body.
The concentration determines what treatment and in what volume is needed.
Additionally, doctors may prescribe oncocytology.
This analysis helps determine whether the processes of malignant degeneration have already begun in the patient’s body.
Daijin test for HPV 18
The Digene test or hybrid capture method is one of the most commonly used methods for laboratory diagnosis of papillomavirus.
It is prescribed when the results of a smear for cytology are unclear.
It is used mainly in women after thirty years of age.
The Daijin test makes it possible to detect clinically significant amounts of the virus.
That is, the amount of HPV that can lead to dysplastic changes in the cervix.
The method is also used as an independent screening study.
If the Daijin test is positive in women under 30 years of age, the patient is monitored dynamically.
The study is repeated after 9 months.
Most likely the test will be negative.
Because a woman’s body usually gets rid of the virus on its own.
But after 30 years, the risk of long-term persistence of HPV increases.
Therefore, if the result is positive, the patient should be examined every six months.
They take a smear from her for oncocytology and perform a Daijin test.
The method can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
If negative results are obtained, further observation is carried out once every 3 years.
PCR for HPV 18 with concentration
An alternative to the Digene test is PCR.
The analysis can be quantitative and qualitative.
A qualitative test allows you to determine whether a pathogen is present in the body.
But the fact of detection of HPV type 18 does not mean a high risk of developing uterine neoplasia in the patient.
Since it is likely that the virus is present in minimal quantities.
But PCR is such a sensitive method that it can detect a pathogen even if the clinical material contains only a few dozen copies of DNA.
For more reliable diagnosis, quantitative PCR is used.
It's more informative.
The amount of virus gives the doctor the following information:
- is the HPV concentration clinically significant?
- Has it increased or decreased recently?
- how high is the risk of developing dysplasia or its progression in the near future?
- what will be the outcome of the disease (cure or development of neoplastic processes)
- How successful is the treatment?
Initially, PCR is carried out for various types of HPV.
Usually a DNA fragment is determined that is universal for all types.
Separately, they check a section of the genetic code that is characteristic only of HPV types 16 and 18.
Since they provoke 70% of all cases of cervical carcinoma.
Classification
There are 2 clinical forms of HPV infection:
- 1Anogenital form: skin papillomas, condylomas form on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs, perineum, anus and perianal area.
- 2Non-genital form: damage to the skin of the head, neck, torso, limbs, palms and soles.
Table 1 - Types of HPV that lead to damage to the skin and mucous membranes.
Table 2 - Types of HPV leading to damage to the genitals and perianal area
Along the flow they distinguish:
- 1Asymptomatic infection (the presence of infection is confirmed only by PCR and DNA hybridization methods). In most cases, the infection occurs latently and is not accompanied by any symptoms: no complaints, no skin manifestations. However, the patient is contagious to his sexual partner.
- 2Subclinical (damage to the epithelium is determined only after treatment with a solution of 3-5% acetic acid and microscopy).
- 3Clinically pronounced infection (various skin neoplasms - papillomas - can be detected with the naked eye).
Sexually transmitted HPVs are divided into 2 categories:
- 1 Strains of low oncogenic risk - viruses of this group do not cause cancerous transformation of the epithelium, but only lead to the appearance of condylomas and papillomas.
- 2High oncogenic risk strains can lead to the development of cancerous tumors. There are approximately 12 strains, most often detected in cancer (including 31, 35, 33, etc.). 2 of them (types 16 and 18) are responsible for the majority of cancers caused by HPV.
Oncocytology
The PAP test, along with testing for HPV type 18 DNA in women, is considered the most important stage in cancer screening.
This disease is completely controllable.
It can be detected visually.
In addition, cancer formation is predicted.
After all, a tumor does not develop on unchanged mucosa.
A malignant neoplasm is preceded by long-term processes in the epithelium of the cervix.
They can be detected at any stage.
Therefore, if a woman visits a gynecologist at least once every 3 years and gets tested, the risk of missing oncological processes will be minimal.
A smear for oncocytology is prescribed:
- first time - 3 years after the first sexual intercourse, but no later than 21 years of age
- at 30-40 years old - once every 3 years
- after 40 – annually
- when pathology or highly oncogenic papillomavirus is detected - once every 6 months
The PAP smear is assessed as follows:
- Type 1 – normal, absence of atypical cells
- Type 2 – signs of inflammation
- Type 3 – single cells with minor signs of atypia
- Type 4 – the presence of cells with obvious signs of atypia
- Type 5 – a large number of malignant cells
With type 3 smears, additional studies are prescribed for oncocytology.
This may involve repeating an oncocytological smear after some time.
PCR is performed for oncogenic HPV types, if this has not been done previously.
A colposcopy may be prescribed.
For type 4 or 5 smears, a biopsy and histological examination of a tissue sample is indicated.
Prevention of complications
Cancer can be prevented.
Moreover, a woman has years to do this.
On average, after infection with HPV, grade 1 dysplasia occurs only after 5 years.
Before the development of dysplasia, stage 3. 10-15 years pass.
Cancer appears in place after a total of 20-25 years.
And even in this case, a woman’s life can be saved.
Since for several more years the cancer does not spread beyond the cervix, and it can be easily removed.
Most patients who are diagnosed with cancer locally are in the age category of 40-50 years.
But complications can only be prevented if you are examined regularly.
Therefore, neither dysplasia nor cancer on site manifests itself as symptoms.
They occur only at the stage when the malignant tumor becomes invasive.
In this case, it grows quickly and metastasizes.
A complete cure may be impossible already at stage 2 of cancer.
To prevent cervical cancer, you need to get tested by your doctor:
- be tested for HPV 18 and other high-risk papillomaviruses
- smear for oncocytology for timely detection of tumor cells
- colposcopy – helps determine indications for biopsy with histological examination in the case of type 3 smears for oncocytology
If oncogenic viruses are identified, treatment is necessary.
Moreover, it consists not only in the removal of papillomas and warts.
This procedure only provides a cosmetic effect.
But it does not reduce the risk of cancer.
Therapy should be aimed at eliminating the virus.
If the concentration of HPV type 18 in a woman decreases, this leads to regression of dysplastic changes in the cervix.
If grade 2 or 3 dysplasia is detected, surgical treatment is required.
Foci of altered epithelium are “cauterized” with a laser or conization of the cervix is performed.
This helps prevent cancer.
However, most operations do not have a negative impact on a woman’s fertility.
Treatment and observation
There are no uniform standards of treatment and drugs with proven effectiveness yet. The main recommendation for a patient with an asymptomatic infection is regular monitoring and screening with the attending physician.
Treatment is indicated for patients who have signs of HPV infection (appearance of papillomas/condylomas). The main approach to therapy is the removal of visible papillomas (physical methods, local use of drugs) and the prescription of immunostimulants.
Immunotherapy and removal of papillomas do not rid the patient of HPV, but contribute to its regression. Consequently, the patient remains at risk of relapse.
In women, when changes in the cervix and human papillomavirus infection are detected, local anti-inflammatory therapy is recommended.
The patient needs regular monitoring by a doctor (every 3-6 months) with a smear taken from the cervix to assess the degree of epithelial dysplasia. Chronic inflammation, an increase in the degree of dysplasia of erosion cells, and cancer in situ may be indications for conization (indications are determined by a gynecologist).
Effect of HPV 18 on pregnancy
In pregnant women, HPV types 18 or 16 are detected with a probability of 20-30%.
Such a high prevalence is primarily due to the young age of most pregnant women and an active sexual life.
Moreover, HPV 18 is often detected in high concentrations.
Because physiological immunosuppression occurs during pregnancy.
Immunity is reduced under the influence of progesterone and adrenal hormones.
HPV can cause:
- spontaneous abortions
- papillomatosis of the bronchi or larynx in a newborn
1 in 2,200 pregnant women develop cancer during gestation.
There are no generally accepted standards for the management of pregnant women with papillomavirus.
Many doctors, when identifying oncogenic types, prescribe antiviral drugs.
They allow:
- increase the likelihood of virus elimination
- improve the cytological picture in smears
- improve colposcopy results
- reduce the risk of complications
- reduce the likelihood of vertical transmission of infection
If HPV type 18 is detected, testing for other STIs is carried out.
Because concomitant infections are no less dangerous for the developing fetus than papillomavirus.
Why is HPV a health risk?
Patients often wonder why HPV is such a concern for doctors.
Since the virus itself rarely reminds of itself with symptoms, and in general practically does not bother the patient during his life.
It's all about the possible consequences of the presence of a pathogen in the body.
Oncological complications are the most common problem faced by doctors and patients when the body is affected by type 18 of the virus.
The microorganism is capable of changing the DNA of healthy cells, turning them into cancerous ones.
As a result, a man may develop penile cancer, which is quite difficult to treat.
Do not forget that HPV affects potency.
The action of the microorganism can lead to the fact that a representative of the stronger sex will feel impotence and will not be able to have sex.
There may also be a negative impact on reproductive functions.
It is also worth remembering that the virus can affect the reproductive activity of a representative of the stronger sex.
Infectious complications are also dangerous.
They inevitably develop if a man often injures the tumors and does not care for his genitals carefully enough.
How the effectiveness of treatment is monitored
The effectiveness of treatment is monitored using laboratory tests.
A Digene test is prescribed.
It helps determine whether the concentration of HPV 18 is clinically significant.
If yes, then treatment is continued.
If not, it is stopped.
A smear is performed for oncocytology.
Because one of the goals of therapy is to improve the cytology results of scrapings of the cervical canal.
Sometimes treatment fails.
The concentration of the virus is growing, and dysplastic phenomena are progressing.
In this case, surgical treatment is indicated.
Areas of dysplasia are removed in one way or another.
Laser, radio wave treatment, and conization of the cervix are used.
Features of HPV 18 in HIV
HPV type 18 associated with HIV is one of the common causes of death from AIDS-associated malignancies.
Because the virus provokes cervical carcinoma.
Moreover, twice as often as other carriers of the virus.
This is due to the resulting immunosuppression.
Also, against the background of HIV, the risk of infection with oncogenic types of HPV increases by 2 times.
In severe immunosuppression that occurs at the final stage of HIV infection, papillomavirus is detected in more than 50% of patients.
Moreover, in 90% of them persistence lasts more than 3 years.
Treatment of human papillomavirus infection against the background of HIV should be carried out using immunostimulants.
All patients should receive adequate antiretroviral therapy.
Under its influence, immunity levels are normalized, and the risks of complications of HPV 18 are reduced to average in the population.
When highly oncogenic viruses are detected, smears for cytology are taken every six months.
Methods for removing external manifestations of HPV
HPV not only increases the risk of dysplastic changes in the epithelium.
This virus also has external manifestations.
Condylomas appear on the reproductive organs, including the ectocervix.
Their removal does not affect the risk of malignancy.
But it prevents other complications.
Condylomas can be injured during sexual intercourse or become infected.
In addition, they look ugly and worsen the quality of sexual life.
Various techniques are used to remove formations:
- 1. Physical methods. Cryodestruction, laser treatment, and electrocoagulation are used. These techniques are the most effective among all. Because most physical methods can eliminate condyloma with 100% probability. The removal procedure is painless and bloodless. There is no pain because infiltration anesthesia is performed. The doctor injects a local anesthetic into the skin at the base of the condylomas. It blocks the sensitivity of nerve endings. Therefore, during the process of removal or destruction of a formation, a person does not have any sensations. There is no bleeding either. Laser or high-temperature exposure coagulates blood vessels. At the same time, microorganisms are destroyed. Therefore, the risk of infectious complications is minimal. After the procedure, the affected organs are treated with antiseptics for several days. Sometimes the doctor prescribes oral antibiotics.
- 2. Chemical methods. Treatment of genital warts with solutions of alkalis or acids is suggested. These methods attract patients because the procedure can be performed at home. No need to go to the doctor. There are no large financial costs either. But in reality, chemical treatments have disadvantages. Firstly, the patient cannot independently treat condylomas in hard-to-reach places. After all, they can be inside the vagina or on the cervix. Secondly, chemical burns of healthy tissue often develop. Thirdly, scars form after the procedure. Fourth, the procedure can be painful. Finally, the main disadvantage is that after treatment, all the torment and side effects, the condyloma may not disappear. Therefore, in medical practice, chemical methods of destruction are rarely used. Most often they are used by patients independently.
- 3. Cytotoxic method. Condylomas are treated with the drug. The most commonly used is podophyllotoxin. It is more or less effective in treating leather. But when used to eliminate warts of the vulva and vagina, it is practically useless. It is used over a long course – up to 5 weeks. Often treatment does not work. 57% of patients develop local inflammatory reactions. Half of patients experience pain or itching. In 40%, erosions form at the site of application of the solution. The cost of podophyllotoxin treatment is comparable to physical removal of condylomas. However, the effectiveness and tolerability of therapy leave much to be desired.
Use of traditional methods of therapy for HPV 18
Often the reasons for failures and relapses are the patient’s attempt to self-prescribe medications or use folk remedies in the fight against HPV.
As doctors note, traditional therapy in the fight against viruses is completely ineffective.
The fact is that all the recipes used by our ancestors were aimed only at eliminating the symptoms of HPV.
But not to remove the virus from the body or stop its reproduction.
And this is the main problem with drugs from the traditional medicine group.
The most striking example is celandine.
Using its juice, you can remove formations located on the surface of the skin.
But coping with the virus that caused it is no longer realistic.
Doctors note that traditional methods of treatment in men with HPV 18 can be used very limitedly.
Their use is permissible as an adjuvant, but not as the main therapy.