How to care for your ears?
Our skin is the first barrier that protects the body from the harmful effects of the environment. Negative processes occurring in the body also affect the condition of the skin. The skin may become red, flaky, rash, and blistered.
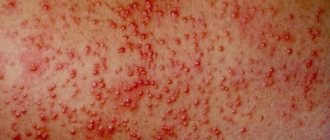
Blisters are perhaps the most unpleasant phenomenon of all of the above. They not only spoil the aesthetic appearance, but cause discomfort in the form of itching, and can even cause pain.
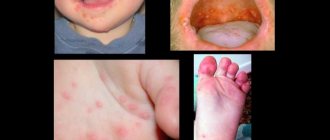
It is especially unpleasant when a blister appears on the ear, pinna or on the thin skin behind it. In this case, even touching the pillow can cause pain and discomfort.
Treatment of herpes in the mouth
Can herpes be in the mouth?
Maybe! Herpes in the mouth requires the same responsible approach and competent treatment as other diseases of the oral cavity. Despite the fact that the infection is often mild and goes away naturally, there are still risks of serious complications, and the possibility of infecting other people remains. Many factors influence the degree of development of the pathology and the presence of possible dangers for the patient. Complete diagnosis and comprehensive treatment can completely stop the manifestations of the infection, although complete elimination of the virus is considered impossible. Herpes, a viral disease known to many as a “cold sore,” is often perceived as a minor problem that does not require treatment. It is characterized by the appearance of a moderately painful blistering rash, but not many people know that this disease is not limited to appearing only on the lips , but can also develop on the oral mucosa . The disease is often accompanied by weakness, general malaise and severe itching, and in some cases can cause complications. During the active phase of the virus, a patient can easily infect others with it through household items, close contact or by airborne droplets.
Causes of blisters on and behind the ear
Blisters on the ears can be either independent formations on the skin or symptoms of serious diseases. The causes of blisters (single or multiple) can be:
- allergic reaction of the body;
- insect bites;
- burns (including sunburn);
- taking individually inappropriate medications or non-compliance with their dosage;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- skin fungus;
- viral infection;
- inflammatory processes in the body.
Blisters from sunburn or insect bites are not particularly dangerous, except that in rare cases they can lead to skin infections.
Bubbles that appear as a result of infection with viruses or the formation of a focus of inflammation in the body carry a much greater danger and require special attention from the sick person.
The appearance of blisters, just like any other neoplasm on the body, is a reason to seek medical help, especially in cases where it is impossible to determine the cause of their occurrence on your own.
If you know for sure that you could not be bitten by any insect or you have not eaten anything that could cause an allergy,
Is it okay to scratch blisters?
If you want to scratch an itchy blister, it is worth remembering that such a mechanical effect on the blister can lead to its rupture. In this case, a scar may remain after healing, and in the worst case, an infection can be introduced into the resulting wound or the process of suppuration can begin.
What to do if you find a blister on your ear
The first step is to contact a qualified dermatologist to find out the causes of the formation and prescribe treatment. Self-medication, especially when it comes to a child, is not recommended.
If you cannot go to the doctor, and the pain from the blister does not give you peace, you can alleviate the condition by following these steps:
- Wash the affected area of skin with warm water and soap.
- Disinfect the area with the blister with alcohol or iodine.
- Using a sterilized needle, make punctures along the edges of the bladder and thus open it.
- Completely remove fluid from the blister.
- Apply a bandage with antibacterial ointment.
What not to do with blisters on and behind the ear
Whatever the root cause of the blister, it should never be:
- press;
- rub;
- allow moisture (sweat) to accumulate behind the ear, thereby creating favorable conditions there for the development of pathogenic bacteria.
Prevention is the best cure
To avoid the recurrence of blisters on the ear, you must:
- watch your diet;
- maintain a healthy lifestyle;
- observe the temperature regime (do not overheat or overcool);
- avoid unprotected sex (in case of herpes);
- promptly and completely treat viral diseases.
This video will tell you how to get rid of fungus without causing blisters:
And do not forget about observing the rules of personal hygiene
- wash your ears every day;
- When taking a shower or washing your hair, do not forget to rinse your ears, the area behind the ears;
- get rid of the habit of picking your ears with dirty hands and objects not intended for this (matches, hairpins, pins);
- When using cotton swabs to clean the ear, be careful not to damage the eardrum and ear walls.
Of course, maintaining hygiene will not prevent the appearance of blisters, which are symptoms of allergies or viral and infectious diseases, such as chicken pox, erysipelas, shingles or herpes and others
Hygiene is quite capable of preventing the appearance of acne on the auricles, in the ears and behind them.
Symptoms of herpes on the oral mucosa
Symptoms of herpes are individual, have varying degrees of manifestation, and can occur in different parts of the oral cavity. For most cases, there are a number of signs that indicate the occurrence of herpes:
- Regular headache;
- Fever;
- A person gets tired quickly;
- Discomfort when eating and drinking;
- The appearance of water bubbles filled with transparent white or yellowish exudate, up to 3 mm in diameter;
- The appearance of ulcers at the site of burst blisters;
- Inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, redness, itching, burning, swelling of the lesion.
According to clinical studies, blisters in the mouth can form in different areas: on the palate, on the inside of the cheeks, on the tongue, on the gums, on the tonsils.
Symptoms of purulent otitis media
A distinctive sign of the disease, which distinguishes it from non-purulent otitis media in adults and children, is discharge of purulent exudate from the ear. This sign is not always present. Suppuration is possible only when pus ruptures the eardrum. If the eardrum has not ruptured, the purulent accumulations cannot leave their location, which can lead to possible complications.
Another sign of suppurative otitis media is ear pain. It can be either tolerable and non-intense, or simply unbearable.
During the period of inflammation, body temperature may rise, although this is not a mandatory sign.
Patients also note hearing loss, ear congestion and headaches.
It is more difficult to understand that a child has developed otitis media, since children cannot clearly explain what and how it hurts. In infants, diagnosis is even more difficult. But based on his behavior, one can suspect ear inflammation: the baby is capricious, has become whiny, and refuses milk.
The disease occurs in stages: inflammation goes through several stages. These stages of otitis differ from each other in symptoms.
Stages of development of herpes in the oral cavity
The disease develops sequentially, including passing through several distinct stages:
- At first, the patient may experience drowsiness, malaise, and tingling or itching of the mucous membrane. Sometimes body temperature rises slightly;
- Next comes redness and swelling of the lesion, minor pain occurs due to the appearance of herpes on the tongue or lip;
- Blisters appear in the oral cavity, filled with transparent contents. During this period, the patient is most contagious, blood counts change;
- The blisters become cloudy and open, and yellowish, shallow, painful ulcers form in their place;
- A hard, fragmented crust forms on the ulcers, damage to which causes bleeding. After a few days, the crusts disappear.
In the best case, the disease resolves naturally within two weeks and without treatment. All wounds heal quickly and without scars.
But there are also complications that lead to infection of internal organs. Suppuration occurs at the site of the wounds, the temperature rises to 40 C. Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the jaw and neck may begin.
How to treat if the appearance of a blister still cannot be avoided
To properly treat a blister, you need to know its origin. Therefore, if the cause of the formation is unknown, it is more appropriate to talk about pain relief, itching and swelling.
Modern pharmaceuticals and traditional medicine recipes come to the aid of the sick.
Medicines to combat illness
Broad-spectrum antimicrobial ointments such as Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Levomekol ointment, the root cause of the appearance of a blister is unknown, because they act on almost any group of bacteria.
Furacilin solution will help disinfect the surface of the skin.
Treatment of blisters caused by the herpes virus
Antiviral ointments are used to treat blisters caused by the herpes virus. They act precisely, reach the source of inflammation faster, and many of them have healing properties.
The most commonly prescribed are Oxolinic ointment, Viferon, Zovirax, Cycloferon.
Treatment of blisters - signs of allergies
In case of an allergic reaction, it is possible to use Suprastin, Zodak tablets and other antihistamines. For topical use, Fenistil gel is usually prescribed; herbal-based Gistan cream is also suitable.
Help with blisters formed at the site of a burn
Panthenol foam cream has proven itself to be effective in the treatment of blisters from burns; it has a light texture that allows you to apply the product without increased friction of damaged skin.
The well-known balm Rescuer, made from natural ingredients, helps to accelerate the restoration of the protective properties of the burned area of the skin.
OzhogovNet and Appolo gels are also effective; they not only have antiseptic properties, but also have a wound-healing and analgesic effect.
How to properly care for your ears, watch this video:
Treatment of blisters - symptoms of fungal ear disease
To get rid of a blister formed due to ear fungus, you must first cure the fungus itself. If the fungus is caused by taking antibiotics or hormonal drugs, you should stop using them.
Vitamin therapy will help boost immunity, a decrease in which could also lead to the formation of ear fungus and, as a result, a blister.
Antifungal agents should be prescribed by an ENT specialist depending on the type of fungus (yeast-like, mold, especially pathogenic). Nitrofungin and Econazole are usually prescribed.
The very prescription of antibiotic drugs for internal use in the treatment of any ailment is strictly prohibited. Remember, only your doctor can prescribe antibiotics. By self-medicating, you can cause serious harm to your health.
Traditional medicine comes to the rescue
If you don’t want to poison your body with medications, you can turn to traditional medicine. There are many recipes to get rid of various types of blisters.
Chereda is a natural antihistamine
The series has excellent antibacterial and wound-healing properties. In addition, this plant has long been known as a natural antihistamine.
To relieve itching and swelling from the blister, you need to gently wipe the affected area several times during the day with a cotton pad soaked in the infusion of the string. Lotions made from a concentrated infusion of herbs are also effective.
If you have allergies, you can also take the series orally. Brew 1 tablespoon of dried herb per glass of boiling water, leave for 20 minutes and drink warm. But this infusion should not be consumed more than 2-3 times a day.
Chamomile is an excellent anti-inflammatory agent
Truly a wonderful flower with a whole range of beneficial properties. Chamomile infusion has anti-inflammatory, antiviral and antimicrobial effects.
It is useful to use chamomile infusion lotions for blisters on the ears. This lotion will also relieve pain due to the soothing properties of chamomile. A crushed aloe vera leaf applied to the blister will have the same effect.
Apple Cider Vinegar - An Inexpensive Refrigerator Remedy
An antibacterial agent available to everyone. Using a cotton swab dipped in an aqueous solution of apple cider vinegar (1:1), you need to wipe the area of skin affected by the blister.
It is also useful for burns: diluted with cold water, vinegar will remove heat from the burn, thereby relieving pain and burning.
Causes of oral herpes infection
Herpes that affects the oral cavity develops when infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1, which not only provokes the appearance of a blistering rash, but can also cause complications in 10% of cases. The second type of herpes virus (genital) also causes a rash in the mouth, but does not cause serious disruption to the body and differs in its mode of transmission (through sexual contact).
Most often, primary infection with a herpes virus occurs in childhood, after which it is introduced into the genome and remains in an inactive form for life.
The main routes of infection with a viral agent are close conversation, skin-to-skin contact, kissing, and the use of shared hygiene products or utensils. However, the entry of viral particles into the body does not guarantee that the disease will develop, since the immune system can suppress the action of the pathogen. In this case, situations that worsen the overall health of the body, on the contrary, provoke a clear manifestation of infection:
- surgical interventions;
- emotional and physical stress;
- lack of sleep, overwork;
- colds;
- chronic pathologies;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- periods of menstruation, pregnancy or lactation;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- AIDS;
- abuse of nicotine or alcohol;
- the appearance of microtraumas from excessive exposure to the sun or frost.
2. Reasons
Abscess suppuration in the area of the outer ear is an infectious pathology. In the vast majority of cases, the pathogen is bacterial cultures, most often pyogenic (pyogenic) staphylococci.
The most significant risk factors include:
- incorrect treatment and insufficient sanitary care of the ear canal for purulent otitis;
- sharing linen (towels, pillows, etc.) with a family member suffering from pyoderma in one form or another;
- scratching, using objects not intended for this purpose (and non-sterile), such as matches, hairpins, etc., to clean the ear canal;
- metabolic disorders, in particular carbohydrate metabolism (for example, with diabetes mellitus);
- weakened immune system;
- hypovitaminosis (especially A, B and C);
- ototrauma.
Visit our Otolaryngology (ENT) page
Diagnosis and treatment of herpes infection
It is better to start treatment of herpes in the mouth at earlier stages of development to reduce the risk of complications and reduce the likelihood of infecting other people. In order to identify the disease, specialists carry out diagnostic measures:
- collect anamnesis;
- conduct an examination, determine the location of the rash and its nature;
- take a smear to identify the herpes virus and determine its type;
- laboratory tests are prescribed.
Modern methods for identifying the pathogen are a patient’s blood test to detect antibodies to the pathogen and a PCR study of tissues aimed at searching for the DNA of the viral particle. Differential diagnosis is of great importance, since herpetic infection must be distinguished from other similar diseases: stomatitis (not herpetic), tonsillitis, etc.
How to treat herpes on the lip, tongue or gum? Herpes therapy is based on an integrated approach that combines:
- The use of local antiviral agents to stop the process of reproduction and spread of the pathogen;
- Prescribing antiviral medications for internal use (usually indicated for those whose symptoms occur frequently and acutely, or who are immunosuppressed);
- The use of antiseptic drugs for treating blisters and ulcers, rinsing;
- Use of topical anesthetic gels;
- Prescribing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to alleviate general well-being;
- Strengthening the immune system by taking vitamins and immunomodulators.
To eliminate symptoms, advanced technologies such as laser radiation are also used. The technique allows you to quickly and painlessly destroy viral particles without harming mucosal cells and effectively healing damaged tissue. In most cases, several short procedures are sufficient for complete disappearance of symptoms in 2-4 days.
Complications of acute purulent otitis
If the disease is treated late or incorrectly, acute inflammation can become chronic.
Chronic purulent otitis is the most common complication of the acute form. There are two forms of chronic suppurative otitis media – mesotympanitis and epitympanitis. The disease can also lead to:
- labyrinthitis - inflammation of the inner ear;
- to the spread of purulent inflammation to the membranes of the brain (meningitis, brain abscess);
- sepsis;
- paresis of the facial nerve, when the face becomes asymmetrical and the affected side loses its mobility;
- mastoiditis – inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone;
- hearing loss or complete hearing loss.
Treatment of otitis media
If you have otitis media, treatment can only be prescribed by an otolaryngologist. Treatment of otitis media depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s condition.
In acute eustachitis, treatment of otitis media is aimed at restoring the functions of the auditory tube. Sanitation of the paranasal sinuses, nose and nasopharynx is carried out in order to eliminate infection - rhinitis, sinuitis, etc.).
Vasoconstrictor nasal drops (otrivin, nazivin, etc.) are prescribed; in case of excessive mucous discharge from the nose, drugs with an astringent effect (collargol, protargol) are prescribed. Catheterization of the auditory tube is carried out using aqueous solutions of corticosteroids, and pneumomassage of the eardrums.
In the stage of acute catarrhal otitis media, catheterization of the auditory tube is carried out with the introduction of aqueous solutions of corticosteroids and antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins) into the cavity of the middle ear. Local anesthesia is prescribed (otipax drops, Anauran, Otinum). An intra-ear endaural microcompress according to Tsytovich is carried out: a cotton or gauze turunda soaked in a drug with an analgesic and dehydrating effect is inserted into the external auditory canal. Painkillers with an antipyretic effect (nurofen, solpadeine, etc.) are also prescribed. If there is no effect from symptomatic therapy, antibiotic therapy is prescribed within 48-72 hours.
Purulent otitis in the pre-perforated acute stage requires the same set of procedures as in the second stage, but supplemented with the following measures:
- prescription of penicillin antibiotics (amoxicillin, etc.), cephalosporins or macrolides;
- paracentesis (incision of the eardrum) when the eardrum appears to bulge.
It is important to prevent complications of the disease at this stage. After spontaneous opening of the eardrum or paracentesis, the disease progresses to the next stage.
The post-perforation stage of acute purulent otitis media involves the following treatment regimen:
- started antibacterial therapy continues;
- catheterization of the auditory tube is performed with the introduction of corticosteroids and antibiotics;
- a thorough toilet of the external auditory canal is carried out daily - cleaning it from purulent contents;
- transtympanic infusion of drops with an antibacterial and anti-edematous effect is prescribed (alcohol-based drops (otipax, 3% boric acid solution) are not used in this case).
In the scarring stage of AOM, spontaneous restoration of the integrity of the membrane occurs, and all functions of the ear are completely restored. However, this period requires mandatory observation by an otolaryngologist: there is a danger of chronic inflammation in the middle ear, its transition to a purulent form, or the development of an adhesive scar process in the tympanic cavity. It is also possible to develop mastoiditis.
1 Audiometry in MedicCity
2 Audiometry in MedicCity
3 Audiometry in MedicCity
In case of acute otitis media, timely contact with an otorhinolaryngologist is very important. The only measure to prevent complications is correct and timely diagnostic and treatment measures for otitis media. Sometimes the consequences of acute otitis media are adhesions in the tympanic cavity (adhesive otitis media), dry perforation in the eardrum (dry perforated otitis media), purulent perforation (chronic suppurative otitis media), etc. In addition, AOM can lead to such complications as such as mastoiditis, labyrinthitis, petrositis, meningitis, sepsis, venous sinus thrombosis, brain abscess and other life-threatening diseases of the patient.
What to do if it itches, scratch it or endure it?
No scratching, no matter how itchy the skin affected by the blister. A serious risk of infection arises due to the specific location of the irritation.
Constant friction with hair and hats contributes to the introduction of harmful bacteria into micro-wounds; even a tiny scratch heals here very slowly, and dermatitis will have to be treated for at least a week.
When affected by a fungus or infectious disease, the risk of spreading the disease with the liquid contained in the blister increases significantly, so herpes, fungus, and lichen can be “spread” throughout the body.
Physiotherapy for acute purulent otitis media
An important stage in the treatment of the disease, which enhances the effect of drug therapy and accelerates the recovery process, are physiotherapeutic procedures.
For acute purulent otitis, the following types of physiotherapy are effective:
- infrared laser therapy (reduces inflammation and relieves swelling of tissues);
- vibroacoustic therapy (improves blood and lymph flow, providing a good therapeutic effect for inflammation of the middle ear);
- ultraviolet irradiation (has a bactericidal effect);
- ultrasonic medicinal irrigation (has an anti-inflammatory effect);
- photodynamic therapy (helps relieve inflammation);
- ultrasound therapy (promotes deeper penetration of medicinal ointment, relieving inflammation and swelling of tissues);
- infrared laser exposure (stops the inflammatory process).
Which procedures should be used and how many sessions will be needed is determined by the ENT doctor, based on the patient’s condition.