General information
The term "pyoderma" from the ancient Greek language means "purulent skin."
This word fully characterizes the disease. Pustules appear on the skin, which merge to form weeping eczema. If the disease has developed for the first time and is active, we are talking about an acute form. When pathology appears periodically in a child, doctors talk about a chronic disease. There are also diffuse (2 or more parts of the body are affected) and localized (the rash is concentrated in a small area) forms. Depending on the depth of penetration of bacteria, superficial and deep pyoderma are distinguished. Each of these forms has its own symptoms.
Classification
The causative agent of the disease and the characteristics of the symptoms allow us to distinguish the following specific types of damage:
- staphyloderma (provoked by staphylococci): furunculosis, vesiculopustulosis, pemphigus of newborns, carbuncles, etc.;
- streptoderma: erosive-papular, intertriginous, erysipelas, paronychia, impetigo.
The course of the process can be acute or chronic, and the presence or absence of complications allows us to distinguish complicated and uncomplicated forms, respectively.
Symptoms of pyoderma in a child
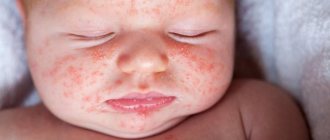
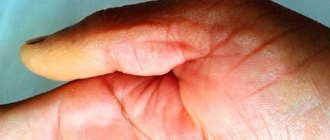
The external signs of infantile pyoderma can be deceptive because they are similar to the symptoms of many dermatological diseases.
It is even more difficult to identify the pathogen. It is difficult to determine the type of bacteria by the appearance of the rash: laboratory tests will be required. But parents should know what pyoderma looks like. This information will help you suspect the disease in time and consult a doctor. Distinctive features:
- a number of ulcers of different diameters form on the skin;
- the rash spreads throughout the body or remains in one area of the body;
- single rashes or groups of rashes that are weeping and damp;
- More often, pyoderma in children appears on the scalp.
Sometimes the appearance of the rash can suggest what pathogen caused it.
- Staphylococcus. Hair follicles remain the favorite place of these microorganisms. Staphylococcal infection is usually deep in nature.
- Streptococcus. It affects smooth skin and forms fluid-filled blisters. They are surrounded by an inflammatory border. The bubble bursts when touched, and a grayish crust forms in its place. It disappears painlessly, leaving no traces.
- Ringworm simplex. This is a chronic disease caused by streptococcus. When the form is spilled, the baby's temperature rises to 37.8 degrees. In newborns, lichen causes weakness, whims, and crying.
To confirm the assumption, laboratory diagnostics of skin samples are used.
What factors lead to diaper rash in the armpits of newborns?
- Temperature and humidity are too high;
- Clothes that are not selected for the weather or fit. Too hot, tight clothes do not allow air to pass through, and also rub the skin of the armpits.
- Incorrectly selected cosmetics for the skin of a newborn, as well as their excessive use. Such products disrupt the acid balance and increase skin sensitivity. This item also includes the use of irritant products for cleansing the skin in children, these include soaps, detergents, wet wipes with fragrance/alcohol;
- Lack or insufficient use of air baths;
- Rare bathing of the child, especially in the hot season;
- Skin injury: friction of diapers, excessive washing with intensive cleansing;
- Increased body temperature due to viral diseases.
Causes of pyoderma
The causative agents of the disease can be several types of bacteria.
These are mainly streptococci and staphylococci, but simultaneous infection with both types of microorganisms occurs. Pyoderma can occur on healthy skin. But this requires the presence of risk factors:
- overheating or hypothermia;
- skin damage (burns, wounds, cracks) through which infection penetrates;
- concomitant dermatological diseases (dermatitis, eczema);
- weakness of the immune system;
- diseases of the endocrine system, internal organs;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- tendency to allergies, in particular hypersensitivity to pyogenic bacteria and their metabolic products;
- hypovitaminosis, malnutrition;
- poor hygiene.
Infection occurs through contact with a sick person and his skin. Therefore, children attending kindergarten and school are at risk.
What is an abscess and the mechanism of development in a child
Inflammation is accompanied by a limited accumulation of exudate in tissues and organs. Ulcers occur in adults and children.
The reason for the appearance is pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate from other foci of infection or the external environment. The likelihood of an abscess in a child depends on the pathogenicity of the microorganism and immune resistance.
Human immunity is of primary importance in protecting against infections. Reducing it increases the risk of infectious diseases.
The invading microorganisms carry antigens, due to which interaction with the cells of the child’s immune system causes a cascade of biochemical reactions that provoke inflammation. The result is swelling, pain, and the skin becomes red and hot. Leukocytes, microphages, and other cells rush to the site of infection and destroy antigen carriers. The contents of the abscess are formed - a mixture of enzymes and bodies of microorganisms, immune cells, and dead tissue.
Under conditions of inflammation, reflex stasis and hypoxia, the formation of connective tissue begins - the pyogenic membrane, which separates pus from healthy tissue. Exudate continues to accumulate, and symptoms intensify. The child develops a high temperature, signs of intoxication, and the size of the formation increases.
Vivid manifestations in a child or adult are characteristic of a superficial location. If the abscess is localized deep in the tissues, the symptoms may be smoothed out.
READ ALSO: Types of oral leukoplakia: symptoms and treatment methods
Treatment of pyoderma
Conservative treatment
The basis of therapy for pyoderma is antibiotics.
Their selection is carried out individually based on the results of bacteriological culture. Broad-spectrum antibacterial medications are usually recommended. If pyoderma is superficial and does not pose a danger to the child, topical antibacterial ointments are recommended. Oral antibiotics are taken for severe forms of the disease. Antibacterial therapy continues for a week, less often - 14 days, if symptoms do not disappear. Treatment of infants and children under 3 years of age with deep or complicated forms of pyoderma is carried out in a hospital under the supervision of doctors. Children are given antibiotic injections. Other drugs are also prescribed in parallel:
- metabolic agents
- hepatoprotectors to protect the liver;
- vitamin complexes;
- antiseptic solutions (fucorcin, dioxidine, chlorhexidine, boric acid) for local treatment of inflammatory lesions.
It is not recommended to wipe the affected areas with alcohol solutions, since these drugs do not destroy pathogens, but at the same time irritate the skin. Washing with a washcloth is not allowed, so as not to spread the infection throughout the body.
During therapy, the child is prescribed a diet that excludes sweet, fatty, and salty foods. You need to eat more vegetables and fruits.
Surgery
In severe forms of pyoderma, boils and carbuncles form from ulcers. These formations can only be treated surgically. First of all, they are opened and sanitized. After this, complex treatment is prescribed according to the above scheme.
How to treat a purulent pimple
A surgeon treats abscesses in children. The difficulty for a doctor is to find a common language with a small patient and attract his attention.
The first stage of treatment is diagnosis. You need to donate blood and urine for tests. Afterwards, taking into account the patient’s well-being, the operation begins.
If the abscess is located in an internal organ, abdominal surgery is required. Such an intervention is difficult for the body to tolerate. Other removal methods have been developed. Using ultrasound, a needle is inserted into the cavity and the pus is removed. Afterwards enzymes or antibiotics are administered. But such operations are rarely performed; the classic version gives better results.
READ ALSO: Is Roseola infantum contagious - 25 recommendations for
The safest method in terms of complications is excision within healthy tissue. There is no infected wound, the skin is treated with antiseptics, the abscess is cut out without opening the pyogenic membrane. Then stitches are applied. There is no risk of infection spreading, the wound heals faster, and the cosmetic defect is less noticeable. When cosmetic stitches are used, the scars are almost invisible.
The tissues of the child’s body are plastic, wounds heal faster.
After removing the pus, general therapy is carried out. Various groups of drugs are prescribed: antibiotics, vitamins, blood substitutes.
In the case of furunculosis, when multiple abscessed pimples form, immunostimulating therapy is recommended. This is what an immunologist does. Before treating abscesses, a study of the immune status of the child’s body is carried out.
Prognosis and prevention
If the disease proceeds without complications, it is completely cured if the parents follow the doctor’s recommendations. With extensive damage, the prognosis is worse.
Parents should be careful: at the first symptoms of a rash, you should consult a doctor.
Preventative measures will help reduce the risk of infection:
- treat wounds and abrasions on the baby’s skin with antiseptics;
- dress your child according to the weather;
- strengthen your immune system by hardening and physical exercise;
- walk outdoors more often;
- monitor your child’s nutrition;
- maintain hygiene.
It is important to remember: pyoderma is treatable and does not leave any trace if you consult a doctor in time. Experienced dermatologists conduct consultations at the SM-Doctor clinic. Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice any suspicious rashes on your child's skin.
Pustular infections in children
A serious attitude towards child hygiene is the key to avoiding many health problems. This also applies to skin diseases - dermatitis , which has a large number of varieties. The most common of them in children (especially newborns) are pyoderma. Pyoderma is a purulent skin lesion. It is a group of diseases that are caused by pyogenic microorganisms when they penetrate the skin. It is important for parents to know how pyoderma is transmitted: it occurs through direct contact with a sick person and contaminated objects.
The disease occurs most often in children (especially newborns) and has many varieties. It is believed that pyoderma occurs mainly due to poor nutrition and poor child care. However, this is not always the case. This skin disease is caused by various pathogens: streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, E. coli and others. Often, some microorganisms live peacefully in the human body and do not make themselves felt. But as soon as for some reason the body’s protective functions decrease and the gates to infection “open,” they begin to manifest their pathogenic properties.
Since it is newborns and infants who have the weakest protective mechanisms, pyoderma occurs in them quite often with a severe course, especially with untimely treatment and improper care. Children under 2 months are not able to produce antibodies on their own. Therefore, it is very important in the first days of a baby’s life to especially carefully monitor the care of the skin of the entire body. Ideal conditions for the development of pyoderma are fumes under oilcloth diapers, sweat, saliva, urine, nasal discharge, which are not cleaned out in a timely manner, because infants have a thin and loose stratum corneum of the skin, which is easy to infect with pathogens. Hypothermia and overheating of the body can also cause purulent skin disease. They provoke pyoderma and itchy dermatoses: eczema, urticaria, scabies, neurodermatitis, etc.
Other causes of pyoderma include:
- insect bites;
- diseases of internal organs and nervous system disorders;
- immunodeficiency;
- lack of protein in the diet.
How to identify pyoderma?
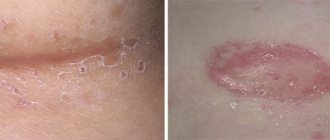
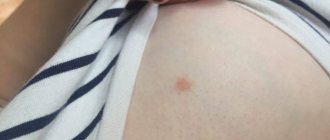
It is impossible not to notice it on a child’s skin. It all starts with small areas of redness, which over time become covered with small blisters filled with pus. After the bubbles “burst,” the contents flow out and in their place, on the skin, dry crusts form. Usually there are no traces of fallen crusts left. However, if the cause of the appearance of pustules is not eliminated and they are not treated, then boils may appear on the child’s body; in the worst case, an abscess and phlegmon may occur. As a result, a number of complications arise and the child’s general condition worsens. In extremely severe cases, sepsis can develop - a general infection of the body.
Pustular skin diseases manifest themselves in different ways. Everything depends on the pathogen, on the depth of the skin lesion, on the course of the disease itself, on the individual properties of the body, on the state of the immune system, and so on.
Forms of pyoderma that occur in childhood
Vesiculopustulosis (periporitis). Develops most often in infants. Periporitis is preceded by prickly heat, which is caused by overheating. Vesiculopustulosis is accompanied by multiple rashes (transparent blisters) on the body, in the folds, and on the scalp. With proper care, the rashes disappear after a few days. Vesiculopustulosis refers to staphylococcal pyoderma.
Streptococcal impetigo. Develops as a result of scratching with itchy rashes (insect bites, scabies, atopic dermatitis, purulent otitis media). It is characterized by the appearance on the face of pustules with purulent contents, which form into crusts and fall off, leaving unstable pink spots and small scars. Observed in children of the first year of life
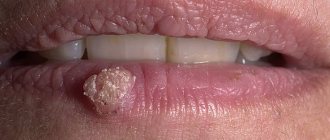
Slit-like impetigo. Bubbles form in the corners of the mouth, at the outer corners of the eyes, and at the wings of the nose. They open very quickly, leaving behind painful cracks. The disease is often chronic, especially in the presence of carious teeth, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, hypovitaminosis B2 and B6.
Pseudofurunculosis. The purulent process develops in the thickness of the skin, in the ducts of the eccrine sweat glands. Relapses are common. The rash appears in the form of small nodes with soft tissue swelling. This disease is accompanied by a disturbance in the general condition of the child: body temperature rises, appetite worsens, body weight decreases, and dyspepsia appears.
Pyococcal pemphigoid (epidemic pemphigus of newborns). Characterized by superficial purulent skin lesions. The rash appears in the form of small blisters, which do not form a crust after bursting. Appear on the abdomen and limbs, less often on the mucous membranes. Sometimes septicopyemia (sepsis) may subsequently develop.
Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis. This disease is considered a malignant type of pyococcal pemphigoid. It appears already in the first week of a child’s life and is the most severe disease caused by staphylococcus. The rashes that accompany the course of the disease resemble wounds from second-degree burns and affect the entire body of the child. The course of the disease has a number of complications, in 50% there is death. The disease is associated with the penetration of phage group 2 staphylococcus into the body of a newborn. This microorganism produces a special toxin, which provokes detachment of the epidermis.
This is not a complete list of forms of pyoderma in children. If you suspect this disease, you should immediately consult a doctor. Timely treatment can reduce a number of complications.
Treatment of pyoderma is carried out externally or systemically, depending on the form and type of the disease. However, it is important to adhere to 3 rules:
- Do not wet the affected areas of the skin.
- Trim hair in areas of rashes.
- Maintain child hygiene.
For pyoderma in newborns, treatment, on the contrary, involves regular baths with the addition of potassium permanganate. To detect the pathogen, a bacteriological culture is performed. If the area of the rash is small and the pustules are weakly expressed, antibacterial and antifungal ointments, creams, and antiseptic solutions (potassium permanganate, brilliant green) are used externally.
In case of extensive rashes and deterioration of the child’s well-being, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. To strengthen the immune system, multivitamins are prescribed.
Treatment with folk remedies in the form of compresses with aloe juices, potatoes, yarrow decoctions, burdock root, Vaseline ointment and crushed celery leaves is used for mild forms of pyoderma.
Lastly, always remember to take preventive measures. Careful care, good nutrition, adherence to personal hygiene rules, careful attention to the treatment of common diseases, immediate treatment of emerging microtraumas - this is what can protect your children from an unpleasant disease.
Deputy Chief Physician
in medicine Elena Ivanovna Rakovskaya