Surgery is the main treatment for melanoma. For most patients, once the diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy, surgical treatment is indicated. During surgery, the doctor strives to remove all tumor tissue from the patient's body to prevent recurrence in the future.
They resort to different types of surgical intervention, depending on the stage, size and location of melanoma.
Risks of occurrence
Predisposing factors play one of the key roles in the development of skin cancer. Among them are:
- prolonged exposure to the sun and frequent sunburn;
- hereditary predisposition. If there have been cases of tumor formations on the skin in the family, this increases the risk of their development in subsequent generations;
- fair skin with a lot of moles and freckles, red hair color. This dermis is characterized by a low content of melanin in the cells;
- elderly age. It is believed that with age, the chance of developing skin tumors increases. Despite this, oncologists note an increase in the detection of pathology among young people;
- occupational hazards. Some professions involve constant contact with carcinogenic substances. Prolonged interaction of toxins with the skin increases the risk of tumor development.
The presence of at least one of the listed risk factors requires regular visits to the doctor for preventive examinations.
Causes
The exact causes of this type of cancer are unknown. The study of melanoma is also complicated by the fact that it is usually asymptomatic, especially in the early stages. It attracts attention after a mole changes color to a darker color or due to tumor growth. Malignancy of moles and birthmarks occurs due to the following factors:
- excessive ultraviolet irradiation - sunburn, trips to the solarium - all this negatively affects not only the general condition of the skin, but also increases the risk of malignancy of moles;
- congenital nevi;
- hereditary predisposition (cases of melanoma in the family);
- thyroid diseases;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- injury to the skin, birthmarks and moles;
- increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation;
- skin cancer (even in remission);
- age factor;
- Skin phenotypes 1 and 2 – people with fair skin, blond or red hair, blue or gray eyes and freckles are most susceptible to melanoma due to genetic predisposition.
It is important to understand that if you have at least 3 risk factors listed above, you should undergo regular examinations with a dermatologist, checking all newly formed moles and freckles. Timely removal of malignant tumors increases the chances of stable long-term remission and relieves the patient from secondary complications.
Expert opinion
Author:
Milana Khanlarovna Mustafaeva
Head of the oncology department, oncologist, chemotherapist
It has been clinically proven that melanoma is the most aggressive type of malignant neoplasm. In the mortality structure, skin cancer accounts for 40% of cases. Each year, an increase in the onset of the disease is determined. Failure to seek medical help in a timely manner leads to the development of severe forms of the disease. As a result, diagnosis is carried out at stages 3–4, when treatment is ineffective.
At the Yusupov Hospital, oncologists pay special attention to the diagnosis and treatment of skin melanoma. If suspicious lesions appear on the skin, you should consult a doctor. This will allow cancer to be diagnosed in the early stages, when the prognosis for recovery is considered favorable.
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors conduct a full course of examination, which is necessary to determine the stage of development of skin cancer and all related criteria. For this purpose, a CT scan with the possible use of a contrast agent, dermatoscopy, and biopsy are prescribed. The laboratory determines cancer markers in a blood test. After diagnosis, oncologists develop an individual treatment plan. The drugs are selected according to the latest European recommendations for the treatment of skin tumors.
Patient reviews
Boris Grachev: For three years now I have been treated with Keytruda for metastatic melanoma. And all these years with Dr. Aronov at Medis. Previously, I had it operated on by a surgeon I knew, but it soon metastasized. If it weren't for this medicine, I would no longer exist. And for this medicine, for the protocol from Professor Schechter, I express my gratitude to all the staff of the clinic. The clinic’s logical and quick actions have always been effective. I am being treated in the only possible way in the world. There is remission. I am staying on these medications.
Anatoly Solntsev: When I realized that I had an abnormal mole, I went to a dermatologist in a private clinic. He said it was melanoma and suggested removing it with a laser. I turned the entire Internet to understand the situation as soon as I found out how deadly this disease is. As a result, I went to Medis and was operated on by a surgeon who did it surgically, removing everything deep down. It certainly cost more, but I didn’t see any other alternative.
First symptoms and signs
Among the main clinical signs of skin cancer are:
- pain syndrome. The degree of its severity depends on the stage of development of melanoma. This may include tingling, burning, itching. The symptom is caused by rapid cell division within the tumor;
- alopecia in the area of tumor growth. As melanoma grows, the hair follicle is damaged. As a result, hair falls out;
- change in the color and contours of the mole. After trauma, the nevus may darken or lighten. The color depends on the degree of melanocyte damage;
- rapid growth of the tumor. Melanoma is characterized by rapid growth. This is due to the high aggressiveness of the tumor;
- changes in the skin in the area of cancer formation. This symptom is characteristic of the later stages of melanoma development. The skin becomes deformed due to damage to healthy cells;
- hyperemia of the tumor contours. The symptom is caused by an inflammatory process. The appearance of this symptom indicates an immune response to the changes taking place;
- damage to neighboring organs. Melanoma metastasizes early. Depending on their location, certain symptoms appear. The liver, bones, brain, lungs and gastrointestinal organs are most often affected;
- lymphadenopathy. As the tumor process grows, nearby lymph nodes are affected;
- lack of appetite. The result is sudden weight loss. As the tumor process spreads, cachexia develops;
- intoxication syndrome. It is characterized by weakness, a sharp loss of strength, fluctuations in body temperature, headache and dizziness.
How does the procedure work?
No preliminary preparation or equipment is required. The doctor performs an examination and clarifies the diagnosis, after which the patient receives local anesthesia. Treatment lasts no more than five minutes in an outpatient setting.
After using the laser, it is important that no water gets on the wound (at least three weeks). The skin of adults and especially children should be protected from exposure to direct rays of the sun, i.e. Always use sunscreen with a high SPF filter. The results will be visible within a couple of weeks.
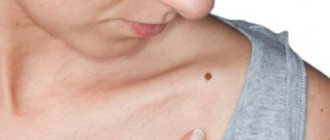
Differences between melanoma and mole
There are a number of characteristic signs of melanoma that are characteristic of a malignant tumor. During degeneration, the mole changes its shape and loses its symmetry. To check whether melanoma can be benign, draw a conditional line in the middle of the nevus. Benign tumors are completely symmetrical.
The difference between a mole and melanoma is that healthy nevi have clear, even edges. This is due to the local location of melanocytes. If the process of transformation of a mole into melanoma begins, melanocytes begin to spread into neighboring tissues. This leads to a kind of “blurring” of the contour.
Normally, the nevus is uniformly colored with pigment. Birthmarks may contain areas of different shades of the same color, but this is the exception rather than the rule. Usually, due to the uniform distribution of melanocytes in the neoplasm tissue, nevi are colored evenly over the entire area. During degeneration, the cells begin to be distributed unevenly. This leads to the appearance of areas with different colors.
Regular moles do not increase in size. Slight growth may occur during puberty and between the ages of 20 and 30. If a mole begins to grow rapidly, this is an alarming symptom that may appear as it degenerates into melanoma. If you have a mole with a diameter greater than 6 mm, you should immediately undergo examination by a dermatologist.
Our doctors
In another case, recognized “Western” experts, including from Israel, will take part in your treatment, specifically on these types of oncological pathologies. Until recently, this level and quality of services were available exclusively abroad, but now you can be treated with the same effect and using the same protocols in Russia. Doctors invited by Dr. Aronov to treat oncodermatology problems at Medis in Moscow:
- Professor Yakov Schechter is the best expert on melanoma in the world, co-author of the drug Keytruda;
- Professor Chaim Gutman is a famous surgeon who periodically comes to Moscow;
- Dr. Alexander Aronov - a famous Israeli doctor in Moscow, diagnostics and immunotherapy;
- Doctors Elmira Gesheva and Marina Biksel are surgeons with “Western” experience in Moscow.
Diagnostics
Among the main methods for studying skin melanoma are:
- Collecting anamnesis of illness and life. The doctor finds out the time of appearance of the pathological formation and accompanying symptoms. Presumable causes and predisposing factors are determined. The presence or absence of a hereditary predisposition to tumor diseases is clarified.
- Skin examination. The doctor conducts an objective examination of the tumor. Experts identify the so-called alphabet of melanoma. It is designed specifically to characterize pathological formations:
- A (asymmetry) - asymmetry of the shape of the mole;
- B (border irregularity) - uneven borders of the nevus;
- C (color) - change in pigmentation of the mole;
- D (diameter) — increase in nevus diameter;
- E (evolving) - a combination of the above changes.
Dermatoscopy. It is carried out using a dermatoscope. Thanks to it, it is possible to increase the size of the pathological formation several times. This allows you to examine the structure of the tumor in detail.
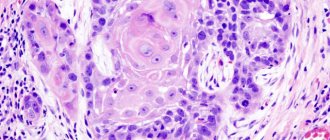
Biopsy. The most reliable way to confirm skin cancer. The material selected during diagnosis is sent for histological examination. The danger of manipulation is that additional damage to melanoma can provoke an acceleration of the growth of the tumor process. Therefore, it is important to contact experienced doctors.
Treatment
Treatment of melanoma requires an integrated approach. For this purpose the following activities are prescribed:
1. Surgery.
It is the main treatment method for skin melanoma. Surgery becomes the only way to treat cancer if it is diagnosed at stages 1–2 of development. In order to reduce the risk of melanoma recurrence, surgery removes the tumor along with healthy cells.
2. Chemotherapy.
Prescribed to destroy rapidly growing cancer cells. Due to the aggressiveness of the tumor and the early appearance of metastases, unified chemotherapy regimens for melanoma have not yet been developed. Doctors select medications and their dosages individually depending on the stage of cancer development. When melanoma is detected in late stages, chemotherapy is palliative.
3. Radiation therapy.
High doses of radiation help destroy cancer cells. In this way, it is possible to improve the prognosis for further treatment and recovery. Radiation therapy may be given in combination with surgery and chemotherapy. For inoperable melanoma, radiation therapy is palliative.
4. Immunotherapy.
Drugs that enhance the body's protective functions are necessary to activate the antitumor immune response. As a result, the immune system begins to fight cancer cells on its own. Drugs used during immunotherapy include:
- interferon-alpha;
- interleukin-2;
- reaferon;
- ipilimumab.
Thanks to immunotherapy, it is possible to reduce the risk of relapse of the disease.
5. Diet food.
The diet prescribed as part of the complex treatment of melanoma requires the exclusion of the following products:
- canned food;
- spices;
- smoked products;
- spicy and fatty foods.
The daily menu should contain a sufficient amount of fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs, cereals, lean meats and fish, poultry, and dairy products. Thanks to such a diet, the body receives vitamins, minerals, micro- and macroelements. They are necessary during the period of treatment and recovery.
Stages and prognosis
Determining the stage of the tumor process is necessary to prescribe appropriate treatment. Depending on the stage at which skin cancer was diagnosed, the further prognosis is determined. The later the tumor is detected, the more unfavorable it is. In accordance with the size of the formation, its localization, the degree of germination into surrounding tissues and metastasis, the following stages of melanoma are distinguished:
- first. Characterized by shallow penetration into the thickness of the skin. At this stage, the thickness of melanoma does not exceed 1 mm. The pathological process does not spread to nearby lymph nodes. The tumor does not bleed or form ulcers;
- second. Accompanied by a more rapid spread of the tumor process. Cancer grows into the skin to a depth of 2 mm. The changes are characterized by a corresponding clinical picture. The tumor formation becomes covered with ulcers, bleeds and peels off. At the second stage of melanoma, regional lymph nodes are not affected;
- third. The tumor process spreads to nearby lymph nodes. This worsens the prognosis for further therapy and survival. At this stage, complex treatment is required, including surgery and chemotherapy;
- fourth. The last and most severe stage of melanoma. Characterized by the presence of multiple foci of metastases. They spread through the blood and lymph flow. Melanoma at this stage of development has an unfavorable prognosis in terms of recovery. Treatment may be ineffective. In some cases, only palliative therapy is prescribed.
Third stage of development
By the time the third stage is reached, melanoma has usually already spread to the lymph nodes. Surgical treatment requires wide excision of the primary tumor and lymph node dissection. Adjuvant interferon therapy allows many patients to delay the relapse of the melanoma process.
If there are several tumor foci, then all of them must be removed. If this is not possible, therapy is carried out, consisting of the introduction of biological vaccines directly into the tumor. If the tumor is located in an arm or leg, isolated limb perfusion may be an alternative.
In case of massive damage to the lymph nodes after surgery to remove them, in some cases radiation therapy is prescribed as an adjuvant. It is also possible to carry out immunotherapy with cytokines, chemotherapy or combination treatment.
Relapse and treatment tactics
The risk of relapse depends on the degree of tumor germination and the presence of metastases. Most often, recurrent melanoma is localized near the previous lesion. In order to reduce the risk of tumor recurrence, doctors recommend following the following preventive measures:
- limit the time spent under ultraviolet rays;
- Conduct regular self-examination of moles;
- use protective clothing when in contact with toxic substances;
- undergo a preventive examination by a dermatologist.
If you suspect the presence of skin tumors, we recommend that you contact the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital. The clinic’s specialists use modern equipment to diagnose diseases. Therapy is carried out in accordance with the latest global oncological recommendations. You can make an appointment by phone.