Causes of roughness on the face and head
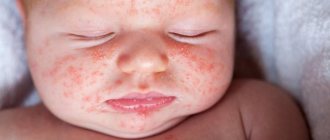
On the skin of children's faces, more often on the cheeks, rashes and roughness are caused by allergens of household origin, that is, food products. The reason for this manifestation is the products consumed by the nursing mother or those introduced into complementary foods. The baby’s digestive tract is not yet able to cope with the latter, for example:
- Whole cow's milk.
- Chicken eggs.
- Citrus fruits and nuts.
A rash appears in the form of red or pink spots that are flaky and very itchy. Redness behind the ears of newborns may appear due to the frequent flow of formula or breast milk into this area, the excess of which is not eliminated by parents in a timely manner.
A dry spot on the fontanelle or forehead is observed in almost all newborns. If parents do not take measures to combat this, after some time the dry scales will spread throughout the head and will not allow the hair follicle to develop. You can eliminate roughness on your head with the help of special baby oils and a soft brush; with their help, you need to remove dry scales every day and very carefully to prevent them from spreading.
The pediatrician will give a more detailed recommendation for eliminating rough skin on the face and head after examining the baby, and will also recommend a nutritious diet after allergies.
Rough and dry skin on a baby's belly most often occurs due to the following reasons.
Walks in the open air
If peeling appears on the skin, walks are not canceled. They must be daily. You should not keep a newborn with dry skin in direct sunlight for a long time.
Children with skin problems are protected from direct sunlight
If it's hot outside, use UV creams for protection. At any age, children benefit from regular air baths, as well as short light massages.
You should not keep a newborn with dry skin in direct sunlight for a long time.
Features of children's skin
A baby's skin is significantly different from the skin of its parents. She is more vulnerable, gentle. Sweat glands are not sufficiently developed in the first year of life, and therefore the baby has to transfer excess heat through pulmonary breathing. If at the same time the baby has to breathe too dry air, or he lives in a room where, thanks to the efforts of his mother and grandmother, it is hot all the time, then the load on the immature sweat glands increases and the skin deteriorates.
The stratum corneum (the uppermost layer) of children's skin is well supplied with blood, so any scratches on a baby heal faster than on an adult. However, the stratum corneum, which is thin and loosely connected to other skin layers, creates favorable conditions for irritation and injury.
Initially, dry skin in babies practically never occurs due to the saturation of lipids - an innate feature of all toddlers. But these fats perfectly dissolve most of the chemicals that are contained in washing powder, soap, and urine, and therefore inflammation of the skin in children is common. Dry skin can also become due to health problems.
The most common cause of dryness, in which the skin becomes somewhat rough to the touch, is contact dermatitis, says Evgeny Komarovsky.
Features and functions of baby skin
Newborns have very thin, easily vulnerable skin, which loses heat very quickly. It also has an insufficient pH level up to a certain point, which causes various microbial diseases.
In addition, infants have a very low concentration of melanin, a pigment that protects against ultraviolet rays.
The thickness of children's skin becomes close to adult parameters only by the age of 7 years.
The epidermis is the most important part of the human body and performs the following functions:
- Protective. In newborns, this quality is poorly expressed, so their skin is often inflamed and damaged.
- Respiratory. The skin absorbs oxygen and evacuates carbon dioxide. The intensity of skin respiration in infants is much stronger than in adults.
- Sensitive. Receptors that perceive irritation are localized in the skin. In infants, the most sensitive parts of the body are the hands, face and soles of the feet.
- Thermoregulatory. The epidermis gives off heat and evaporates sweat. In babies, thermoregulation is imperfect, so they quickly overheat and become hypothermic.
- Immune. The skin contains cells that carry out many immune responses.
The epidermis is the place of formation of biologically active substances, enzymes and vitamins. This is why it is so important to keep your skin healthy.
Dry skin in a newborn is a natural phenomenon caused by a change in microclimate.
Diathesis (exudative and allergic) in a child
In newborns and infants, flaky areas of skin on the face, tummy, butt, back, arms and legs often appear due to diathesis. Contrary to popular misconception, this phenomenon does not apply to diseases. This is nothing less than a constitutional anomaly. In pediatrics, this term refers to the hereditary predisposition of the body to the appearance of certain pathological reactions or diseases. The table shows the characteristics of the types of this phenomenon.
Bathing helps keep your baby clean and also promotes better blood circulation.
Dry skin on feet
As already mentioned, roughness and dry skin can appear in various parts of the body. Very often such lesions occur on the skin of the legs. Most often, rough skin on a child’s legs is observed in the summer, when high temperatures and wind dry the legs, it cracks and hurts due to loss of moisture. During this period, it is recommended to wear sandals or other shoes that allow your feet to have maximum air access.
- For better security, it is advisable for the child to wear socks - this will protect the feet and prevent dirt and dust from getting on them, especially if there are already cracks and wounds.
- Before putting your child to bed, it is imperative that you carefully care for his feet. Use baby soap for washing. After this procedure is completed, the feet should be wiped dry, and then a special fortified cream should be applied to soften the skin. It should be rubbed in, carefully massaging the area to be rubbed. This will eliminate roughness of the skin of the legs and reduce its sensitivity, as well as avoid complications.
- With all the well-known prickly heat, the appearance of diaper rash, as well as diaper dermatitis, parents also need to show care and concern. After all, they tend to spread quickly and even in some cases lead to the formation of a pustular rash. There may be no consequences if the child is shown to a doctor in a timely manner and treatment is started.
During this period, it is recommended to wear sandals or other shoes that allow your feet to have maximum air access.
Prevention of dry and flaky skin in children
Everyone is familiar with the well-known truth that it is always easier to prevent a disease than to undergo long and expensive treatment later.
Dry skin and the appearance of flaky spots are no exception, and you need to think about preventive measures in advance.
Use only high-quality mixtures from well-known manufacturers.
Prevention measures
To avoid dry skin, offer your child something to drink often. Make sure there are enough vitamins in his diet. Moisturize your baby's skin after bathing. In your care, use only hypoallergenic products tested by dermatologists.
The creams should include moisturizing and soothing components: panthenol, niacinamide, oils (shea, olive, wheat germ), zinc oxide, vitamins A, B, E, F, plant extracts (chamomile, calendula, string).
Exposure to cold and dry indoor air contributes to excessive dryness of the skin.
Worm infestation
The appearance of dry patches on parts of a child’s body sometimes indicates the presence of parasites in the child’s body. This reason is detected extremely rarely; experts generally associate changes in the condition of the skin with the above factors. Doctors consider dry skin as a reaction to toxins. With this diagnosis, the child will be prescribed antiparasitic treatment.
Treatment of dry skin in children.
Rough skin in a child: on the legs and arms. Why and what to do?
A child differs from adults in having healthy skin, since his body is not yet poisoned by toxins. But as soon as a parent begins to care for it incorrectly, irritation, redness and dryness may occur. And they mostly affect the limbs.
- Causes of rough skin in children
- Diseases
- Allergy
- What to do for rough skin
- How to properly moisturize rough skin on your hands and feet
In order not to get confused in such a situation, I suggest reading today’s article here on the website o-kozhe.ru, which will tell you why rough skin appears on a child’s legs and arms, and what to do about it.
A child differs from adults in having healthy skin, since his body is not yet poisoned by toxins.
Non-drug treatment
First of all, you need to adjust and normalize the baby’s nutrition. It is understood that it is necessary to exclude the food allergen; if the child is breastfed, then the mother should analyze her own menu and exclude from it foods that could theoretically trigger an allergy outbreak.
It is imperative to pay attention to the mother’s intestinal function. If she constantly suffers from constipation, then toxins resulting from stool retention are absorbed into the blood and passed on to the baby through the woman's milk. To combat constipation, the mother can use lactulose, suppositories with glycerin and increase the consumption of fermented milk products.
If the child is bottle-fed, you should seek help from a doctor - you may need to change the previously selected formula for feeding.
If dry and rough skin appears after introducing complementary foods, parents should stop giving the baby a new product and feed only familiar foods for two weeks. Parents must remember: each new product is introduced as complementary food separately, addiction should last at least 3 weeks, which will allow the true irritant to be identified with great accuracy.
If the child is over one year of age, then you need to keep a diary of observations of the body’s reaction to different foods. It is imperative to exclude fish, eggs, citrus fruits, cheeses and strawberries from your diet - foods that most likely cause allergies. Subsequently, they can be administered, but in minimal quantities.
In addition, you should remember the following recommendations from doctors:
- Sweets are strictly contraindicated for children with rough and dry skin (atopic dermatitis), as they increase fermentation in the intestines and improve the absorption of allergens. Consumption of honey, sweet drinks and jelly leads to deterioration of health.
- Preservatives, stabilizers, emulsifiers and flavor enhancers, and exotic fruits are prohibited for children with this phenomenon.
- The child needs to be provided with a full volume of fluids, since a lack of fluid in the body leads to constipation.
- It is important not to overfeed your baby. For example, when artificial feeding, a small hole is made in the nipple so that the baby eats his portion of the mixture in 15 minutes - this way he will receive pleasure and a feeling of satiety.
- The first complementary food is vegetable puree. And the most hypoallergenic foods are cauliflower and zucchini.
- The air in the children's room should always be fresh, slightly cool and sufficiently humidified. Only in this case will it be possible to prevent sweating and dry skin.
- Children's clothes should be washed with hypoallergenic phosphate-free powder and rinsed at least 3 times in clean water. If dryness and roughness of the skin is in a progressive stage, complicated by a bacterial infection, then rinsing the laundry will need to be done in boiled water.
- Your child's dishes and toys should be washed regularly with hot water. This must be done without the use of chemical detergents/cleaners.
- The child should walk in the fresh air every day, for at least 3 hours and in any weather. If you have to go for a walk on frosty days, then the baby’s face must be lubricated with rich baby cream.
Atopic dermatitis occurs in waves - periods of exacerbation are followed by periods of remission. But even during periods of “calm”, parents must follow certain rules:
- When bathing a child, do not use a washcloth;
- shampoo and baby soap for bathing can be used no more than once a week;
- After bathing and drying, the skin should be moisturized with baby cream, milk or a special moisturizing lotion;
- You need to lubricate your child’s skin not only in areas of flaking and dryness, but throughout the entire body;
- You need to wash your child’s face and perineal area as often as possible, and you can use wet hypoallergenic wipes for this.
The use of sorbents Smecta, Enterosgel, Sorbogel, which help remove toxic substances from the body.
White
White spots on a child's feet are caused by vitiligo. This is a skin disease in which the production of melanin pigment, responsible for coloring, stops in certain areas. As a result, the skin in this area becomes milky white.
The spots can appear on any part of the skin, including the feet. At first they are small in size. If treatment is not started, they will gradually increase. The causes of vitiligo include genetic predisposition, weakened immunity, and autoimmune disorders.
Photos of what spots on a child’s foot with vitiligo look like, see below:
Features of vitiligo spots:
- does not differ from healthy skin to the touch;
- do not cause discomfort;
- hairs growing in the affected area also become discolored;
- do not sunbathe in the sun, do not get goosebumps.
Rough skin in infants: the main causes of pathology
Most mothers begin to panic when faced with a phenomenon such as rough skin on a baby, especially if this condition is pronounced.
The child's hands, head or feet may be rough.
Sometimes such symptoms are not dangerous, but in some cases they can pose a serious threat to the baby's health. Over time, this phenomenon can develop into a chronic form of the disease.
If roughness on the skin appears in a baby after 2 months, and this condition is protracted, then this may be a sign of atopic dermatitis.
Water treatments
Improper care of children's skin often provokes peeling. The most common mistake parents make is bathing their baby with a solution of potassium permanganate added. It dries out the children's epidermis even more, causing peeling.
It is best to bathe the baby for the first days in boiled, settled water without adding any decoctions or cosmetics. It is recommended to use simple baby soap no more than once a week.
Diaper dermatitis.
Walks in the open air
Walk with your baby in the fresh air as often as possible, protecting him from wind and drafts. During your walk, try to ventilate your child’s room. During the heating season, the air in the apartment becomes too dry; during this period it is recommended to use a humidifier to create a favorable microclimate.
Remember, caring for your baby’s health in the first years of his life will allow you to get rid of the body’s allergic reactions in the form of rough skin in the future.
Reds
Red spots on a child's foot are most common. The color ranges from pale pink to rich dark red. The main causes of occurrence: allergic reactions, infections, mechanical factors.
Allergy
With allergies, changes in the skin usually manifest as urticaria or contact dermatitis. With urticaria, the spots are red, slightly raised above the surface of the skin, and tend to merge with each other. With contact dermatitis, they are pink, cause severe itching, become wet, and peel. In children susceptible to allergies, rashes on the feet are provoked by eating highly allergenic foods, sweets, treating the skin with inappropriate baby cream, wearing shoes or socks made of non-natural materials, insect bites and other factors.
Foot skin fungus
Usually occurs in children under 10 years of age. The development of the disease is facilitated by unformed protective mechanisms and the thinness of the skin, through which infection easily penetrates. Children who visit the pool and like to walk barefoot are at risk.
When a fungal infection occurs, small cracks, pink, red or yellowish spots form on the skin, with an unpleasant odor, causing a burning sensation and severe itching. The skin in the affected area becomes very dry and begins to peel. For treatment, local antifungal agents are used, which should be prescribed by a doctor.
Infectious diseases
Red spots or a rash on a child’s feet can be symptoms of childhood viral infections: chickenpox, rubella, measles, erythema infectiosum, etc. Depending on the type of pathogen, the rash looks different, spreading throughout the body or in certain areas.
For example, when infected with Coxsackie enterovirus, the rash spreads only to the palms, soles and mouth. With infectious diseases in children, the temperature rises, there is weakness, lethargy, loss of appetite, and headache. They go away on their own. For treatment, only symptomatic medications are prescribed to reduce fever, relieve itching, and prevent bacterial complications.
Uncomfortable shoes
Red spots on the feet are often associated with improperly selected shoes. If certain areas experience pressure, friction or increased stress, the skin in that area will turn red. The reason may also be a violation of thermoregulation. For example, if your feet are too hot in your shoes and they constantly sweat.
You need to be especially careful when choosing shoes if your child has flat feet or other types of foot deformities. In this case, special orthopedic shoes are needed. The orthopedic surgeon decides which one is right for the child after an examination.
Ringworm in humans: types, symptoms
27.01.2021
Ringworm is a skin disease characterized by the appearance of patches that peel off. May occur at different ages. Most often it occurs in young people. The disease occurs in autumn and spring. Can be transmitted from a sick person or animal.
Causes:
- stress;
- reduced immunity ;
- hypothermia;
- heredity;
- overwork.
Symptoms: the disease begins with a single plaque. But it can increase to two or three pieces. The plaques can be from 3 to 5 cm in diameter. Within about a week, the rashes acquire a more characteristic type. There are more and more of them. They appear on the stomach and back and are accompanied by severe itching. If you have lichen on the scalp, your hair will fall out. The duration of the disease lasts from 1 to 2 months, after which they disappear on their own.
At risk are:
- Small children;
- pregnant women;
- people with weakened immune systems ;
- people who do not observe personal hygiene rules;
- those who have pets.
What can cause the disease?
Microscopic fungi can cause the disease; they live on the skin and fur of animals. In soil and on human skin.
Types of lichen
- Ringworm most often affects children . It is very easy to get sick from it, just touching the patient is enough. Appears on the face , neck , shoulders and head. Characterized by round, red and pink spots.
- Pityriasis versicolor or multicolored lichen - appears due to excessive sweating of the body, which leads to changes in the chemical composition of sweat. Excessive and prolonged exposure to the sun, use of fatty creams. The spots are located on the surface of the entire body, excluding the head and limbs. The first days the spots are greenish in color, but over time they become light brown.
- Shingles the nerve, appearing where the nerve passes. Most often in adults, but can also affect children. Occurs due to stress and hypothermia of the body. First, reddish bubbles filled with liquid appear. After a few days, the blisters burst and crusts appear in their place.
- Lichen planus is a chronic disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes. Appears between the ages of 35 and 65 years. The cause is unknown. But most often it occurs in people with diabetes and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Men get sick less than women. The patient's nails crumble, and red and purple nodules appear on the skin. On the skin of the abdomen , legs and chest .
- Solar lichen is characterized by the appearance of white spots on the skin of various shapes. There may not always be itching and burning. Inflammation occurs in winter. The spots reach a diameter of 4 cm.
- Squamous lichen - has a chronic form. Skin throughout the body may be affected. It may or may not be transmitted through casual contact.
- Ringworm ( eczema ) can be transmitted through household contact. It looks like a red spot that appears on the hands and face . Then bubbles appear, which then burst and release serous fluid. When they dry out, they become crusty.
Diagnostics
Examination by a dermatologist . They do an iodine test, and then wipe it with alcohol. Scraping Blood and urine analysis .
What complications can there be?
- Deterioration of vision
- Hearing impairment
- Nerve damage
- Inflammation of the heart muscle
Treatment
to treat lichen on your own . Different forms of lichen are treated differently. It is necessary to disinfect all things used by the patient. Wash your hands after contact with an infected person. On average, treatment takes 1-3 weeks, but if the disease is not advanced. It is necessary to limit water procedures. Do not apply cosmetics. Ointments, immunostimulating and antihistamines, multivitamins, antidepressants , and sedatives are prescribed.
Diet : exclude the consumption of alcohol, tea, coffee, eggs, chocolate, citrus fruits, canned and smoked foods.
Prevention
To prevent a disease such as lichen , you must adhere to a healthy lifestyle and eat well. Treat in a timely manner . And do not self-medicate.
Published in Dermatology Premium Clinic