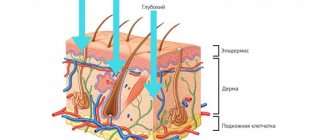
The Eustachian tube is a canal in the human middle ear that connects the nasopharynx and the tympanic cavity. Normally he:
- drains mucous membranes, removing exudate and transudate;
- provides air exchange between the cavity and the nasopharynx, expanding when swallowing;
- produces a bactericidal secretion.
If one or all functions are disrupted, eustachitis occurs (other names are tubotympanitis, tubootitis, salpingootitis) - an inflammatory process that affects the mucous membrane of the auditory canal and often develops into otitis media.
Causes
Unilateral or bilateral eustachitis is a consequence of low air exchange in the tympanic cavity caused by certain factors. This:
Complications after:
- ARVI;
- measles, whooping cough, influenza;
- tonsillitis;
- sinusitis.
Structural pathologies, neoplasms:
- overgrowth of adenoids;
- nasopharyngeal polyps;
- irregular shape of the nasal septum;
- enlargement of the posterior ends of the inferior turbinates (hypertrophy).
Medical procedures:
- nasal tamponade in the treatment of bleeding;
- condition after operations on ENT organs.
Sudden changes in pressure:
- in divers, divers during a rapid dive or ascent (mareotite);
- on an airplane during climb and landing (aerootitis).
Allergic reactions with constant inflammation of the mucous membranes (allergic eustacheitis becomes a consequence of vasomotor rhinitis).
Regardless of the cause, the mechanism of occurrence of the disease is the same:
- the tympanic cavity is not sufficiently ventilated;
- the mucous membrane of the Eustachian tube absorbs air;
- pressure in the middle ear decreases;
- transudate (fluid) is formed, inflammation of the auditory tube develops, then otitis media occurs.
How long does it take to treat eustachitis? The process often occurs in an acute form and goes away within a week, but without proper attention it can become chronic. In order to cope with the disease as soon as possible, it is important to contact an otolaryngologist in time for diagnosis and treatment.
Prevention of ear diseases
It's no secret that any disease is easier to prevent than to treat, including ear diseases. To minimize risks, parents need to follow a few simple recommendations:
- Proper ear hygiene (once a month).
- Treat ENT diseases in a timely manner and only under the supervision of a doctor.
- Monitor the sound level, as loud sounds over 80 decibels kill your hearing.
- Do not allow your child to become hypothermic, dress him according to the weather, and avoid drafts.
- Visit your otolaryngologist every six months for a preventive examination.
Kaliningrad residents can make an appointment with an otolaryngologist for their child by filling out an online form on our website or calling one of the numbers: +7 (4012) 357-773 or +7 (4012) 973-100.
In children
The disease usually results from acute respiratory viral infections and upper respiratory tract infections. The younger the child, the more often bilateral eustachitis is diagnosed. Older children suffer from unilateral damage to the auditory tube. Without treatment, painful otitis media can quickly develop. The temperature is normal or slightly elevated, but the child gets tired quickly and eats poorly.
With inflammation of the Eustachian tube, children complain of:
- slight periodic congestion in one or both ears;
- mild pain;
- nausea, dizziness, noise;
- balance disorders;
- the feeling of an “echo” of your own voice in your head, its unusual volume;
- feeling as if water is pouring in the ear or ears.
Infants react to poor health with low-grade fever, tearfulness, refusal to eat, lethargy, poor sleep at night, and regurgitation.
Glomus tumor of the middle ear
Tympanic paraganglioma (glomus tumor of the middle ear) develops from glomus bodies, which are located on the medial wall or roof of the tympanic cavity, jugular - on the bulb of the jugular vein. Paraganglioma is a benign neoplasm, but mature forms of the tumor have infiltrating and locally destructive growth.
Due to the impossibility of total removal, a glomus tumor of the middle ear can pathologically spread to vital structures of the body (brain stem, internal carotid artery).
Patients complain of a “pulsating” noise in the ear. During an objective examination behind the eardrum, the doctor sees a pulsating red mass. As the tumor grows, the following symptoms occur:
- Hearing impairment;
- Facial asymmetry;
- Dysphonia (speech disorder);
- Dysphagia (swallowing disorder).
If the glomus tumor of the middle ear is widespread, angiography is mandatory. The study is necessary to confirm the vascular nature of the neoplasm, determine its size, location and sources of blood supply.
This plays a role in the possibility of embolization, a minimally invasive procedure that is an alternative to surgery. The procedure is aimed at preventing blood supply to the damaged area, which helps to reduce the size of the tumor and achieve a good effect with further surgical removal of the identified tumor.
Treatment consists of surgical removal of the glomus tumor of the middle ear. Total surgery is performed in the presence of a glomus tumor that does not spread beyond the middle ear. For subtotal (incomplete) removal of the tumor, and depending on the patient’s age, radiation therapy or stereotactic radiotherapy (gamma knife) is used.
In adults
Adult patients are characterized by left- or right-sided eustachitis affecting one side without fever, but with a complex of unpleasant symptoms. Patients suffer from:
- congestion in the ears, decreased hearing (low frequencies are almost not perceived);
- autophony (loud distorted perception of one’s own voice in the form of an echo);
- sensation of fluid in the ear;
- headaches or earaches.
Improvement occurs briefly when chewing or after swallowing saliva, food, or when tilting the head due to a short-term opening of the Eustachian tube and a change in fluid level.
Lipoma and atheroma behind the ear
The area of skin around the ear contains a huge number of sebaceous glands. For this reason, lipomas and atheromas often form behind the ear. Lipomas that form behind the ear grow slowly and are often not cancerous. They are a soft-elastic formation with a smooth surface, surrounded by a capsule. The lipoma in the photo looks like a wen.
Atheroma is a cavity formation filled with sebum. Formed due to blockage of the sebaceous glands. Atheromas occur for the following reasons:
- Disorders of fat or carbohydrate metabolism;
- Genetic predisposition to increased oily skin;
- Hormonal imbalances and diseases of the endocrine system;
- Hyperhidrosis is a disease associated with excessive sweating;
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
Atheroma is a rounded formation protruding above the surface of the skin, which can reach up to 4.5 cm in diameter. When the tumor becomes infected or inflammatory reactions occur, the following symptoms occur:
- Pain behind the ear;
- Redness of the skin;
- Burning and itching;
- Fluctuation is a symptom that indicates the presence of fluid in a cavity formation.
When pressure is applied to the walls of the atheroma or they are damaged, the viscous mass contained inside comes out to the surface of the skin. It has a white color and an unpleasant odor. When atheroma suppurates, the contents have a green-yellow tint. Lipomas and atheromas behind the ear are removed surgically. Modern treatment methods are used - laser or radio wave removal.
Salivary gland adenoma is a benign formation that appears in the glandular epithelium of the salivary glands. The salivary glands are parotid, submandibular, and sublingual. The most common occurrence of tumors is on the parotid gland. If the components of such a tumor are benign, then it is an adenoma of the parotid salivary gland.
Diagnostics
Since the symptoms of the disease are sometimes disguised as other ailments, a doctor is needed for an accurate diagnosis. Treatment of eustachitis in adults and children should be carried out exclusively by specialists after the diagnosis has been clarified.
To confirm the disease the following are used:
1. Otoscopy.
The doctor uses an otoscope to examine the outer ear, ear canal, and eardrum. The examination reveals characteristic signs of tubootitis:
- the eardrum is cloudy and retracted;
- the location of structural components is disrupted;
- the auditory canal is narrowed.
2. Audiometry.
Measuring hearing parameters with an electroacoustic audiometer and speech tests. With tubo-otitis, a decrease in perception of up to 20-35 dB is detected.
3. Laboratory examination of discharge (smear).
It is done to determine the causative agents of infection or the allergic nature of the disease.
What might the nature of the discharge indicate?
Very often, the color of the fluid discharged from the ear indicates a problem. We are talking about the following signs:
- Yellow purulent discharge clearly indicates the presence of inflammation in the ear. In addition, the cause of exudation may be a burst boil or cholesteatoma,
- An admixture of blood indicates mechanical damage that occurred previously, for example, injury to the ear canal due to improper hygienic cleaning.
- Clear exudate may indicate allergic otitis media.
- White or gray curdled discharge suggests a fungal infection.
- The brown-colored substance is earwax accumulation, which initially does not cause problems for the child. However, when it accumulates, a cerumen plug can form, which will cause discomfort, blocking the ear canal.
Acute eustachitis
An acute form of inflammation is a common complication of viruses and infections of the nasopharynx. With insufficient treatment, inflammation continues in the auditory tube. Children often experience pain in both ears; adolescents and adults suffer from unilateral manifestations. When asked how long it takes to treat eustachitis, doctors answer: adequate measures can get rid of it in 5-7 days. If:
- no treatment;
- therapy is insufficient or prescribed incorrectly;
- the course is not completed;
- there are pathologies in the nasopharynx or nasal cavities;
- there is constant allergic inflammation of the mucous membrane
there is a high probability of a prolonged course of tubo-otitis and its chronicity.
Inflammation
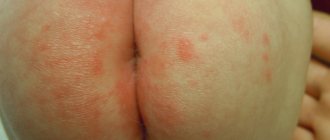
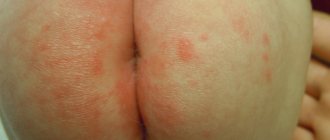
During the inflammatory process, primary elements appear and then secondary ones, aggravating the disease itself and reflecting the general symptoms. For example, eczema is considered a chronic inflammatory skin disease that causes rash and other erythematous signs. Its main cause is considered to be an immune reaction to various irritants.
It also happens that the tendency to eczema can be inherited and expressed by special sensitivity to certain provoking factors. When eczema appears, certain pathologies in the nervous system and diseases associated with internal organs have a separate impact.
If the rash on the ears is small, it may soon disappear and after that itchy elements remain, secreting serous exudate. Weeping processes may appear on top of the skin surface, followed by the appearance of scabs that are yellow-brown in color.
Chronic diseases are accompanied by severe peeling, cracking, severe dryness and the fact that the skin becomes thicker. Eczema is localized not only in the lower leg area, but also on the ears.
Publication date: 2018-02-07
Methods for diagnosing skin diseases:
- Diagnosis of skin diseases
- Diagnosis of skin diseases at home
- Diagnosis of allergic skin diseases
- Diagnosis of bacterial skin diseases
- Diagnosis of viral skin diseases
- Diagnosis of hair diseases
- Diagnosis of nail diseases
- Diagnosis of skin tumors
- Skin scraping
- Blisters on the skin
- Dermatoscopy
- Demodex tests
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections
- Mushroom tests
- Skin scraping
Complications
Over time, untreated eustacheitis causes:
- acute otitis after ARVI;
- hearing impairment;
- unpleasant sensations of echo, congestion, fluid in the ear;
- problems with coordination;
- headache.
During flights or when diving, patients with chronic eustachitis experience severe discomfort.
It is important to diagnose inflammation of the auditory canals in a child in a timely manner, since without treatment, ARVI will be complicated by catarrhal otitis. Chronic eustachitis and the changes it causes in the middle ear gradually worsen hearing.
Osteoma in the ear
Osteoma in the ear (exostosis, osteophyte) develops mainly from the compact layer of the posterior wall of the bony part of the external auditory canal. Much less often, neoplasms are found on the lower and upper walls of this section. Endophytic osteomas penetrate into the mastoid process. Osteoma is a benign tumor that grows rather slowly.
Osteoma has the appearance of a round formation, which is covered with a skin layer, very dense when palpated with a Vojacek probe. It is treated surgically. The operation is performed after the tumor has grown to medium size. In this case, removing the tumor is technically as convenient as possible. If the tumor is small, there is a risk of not completely removing the pathological tissue. If the osteoma is large, it is possible to capture a significant part of the healthy bone tissue during surgery. This will cause a large bone defect.
Treatment of eustachitis
For the treatment of eustacheitis in adults and children in the acute period, the following can be used:
1. Medicines to destroy infection (antiseptics, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory), relieve swelling (vasoconstrictors, antihistamines).
2. Physiotherapy to shorten the duration of the disease. UV irradiation, sessions on UHF devices, and electrical stimulation are prescribed.
3. Therapeutic manipulations - blowing out the ear (Politzer method), introducing medications directly into the ear canal through a catheter.
To eliminate allergic eustacheitis, or tubootitis, caused by pathology of the ENT organs, you should work with the root causes of the disease - allergies, deviated nasal septum, adenoid growths, etc.
At the multidisciplinary clinic "K+31", treatment of eustachitis in adults and young patients is carried out in the otolaryngology department. Specialists perform diagnostics, develop an action plan, monitor the progress of therapy and strive to prevent relapses of the disease.
Among the advantages of the medical center:
- qualified patient care on an outpatient basis or in a day hospital;
- a full range of necessary laboratory and hardware tests for diagnostics;
- drawing up a treatment regimen using drugs and physiotherapy, innovative techniques;
- if necessary, attracting doctors of other profiles;
- results in the form of recovery or attenuation of the chronic process.
For accurate diagnostics, expert-level equipment is used:
- special installation MODULA EUROPA Paris (Duo) HEINEMANN. It helps make a diagnosis and works as a device for therapeutic manipulations;
- audiometer-impedance meter for analyzing the hearing of young and adult patients.
Thanks to the professionalism of doctors and modern equipment of the department, diagnostics are performed quickly and accurately. After the first visit, the course of treatment begins.
Adenoma behind the ear
A benign tumor, a parotid adenoma, often develops in the parotid region. The structure of the neoplasm resembles the salivary gland itself. The cause of the development of benign tumors of the salivary glands is the formation of altered glandular epithelium.
The neoplasm is enclosed in a capsule, has a soft-elastic consistency, and is not fused to the skin and surrounding tissues. The skin above the adenoma behind the ear is not changed. It is treated surgically. In order to undergo examination and treatment of benign tumors of the ear and parotid region, call the contact center of the Yusupov Hospital.