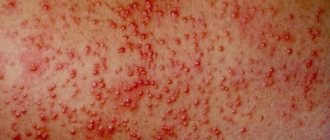
Acne or acne is a disease of the sebaceous glands, a fairly common dermatosis. Despite the fact that this disease is not life-threatening for patients, it is significant for children and adolescents because it reduces the quality of life and affects their social activity. In addition, acne can be a marker of immunodeficiency conditions and serious diseases of the endocrine system. Therefore, determining the causes, diagnosing diseases, and starting acne treatment should be carried out in order to diagnose the pathology as early as possible, shorten the period of acute rashes and prevent the occurrence of complications.
Sebaceous glands and causes of pathological changes in children
Sebaceous glands are appendages of the skin (like nails, hair, sweat glands), which are microscopic exocrine organs that secrete sebum, located in the skin (with the exception of the feet and palms).
In total, on the surface of the human skin there are approximately 80-100 thousand sebaceous glands, which in different anatomical areas differ significantly in size and density of location.
The largest sebaceous glands are located on the nose, chin and forehead, on the scalp, as well as on the chest, around the navel and on the genitals.
The areas of the skin that are richest in sebaceous glands are called seborrheic zones or areas.
The sebaceous glands are located in the upper layers of the dermis. The overwhelming majority of them open into the hair follicles, forming piloseboceous complexes with the hair. Several ducts from two to four glands open into the upper part of the hair follicle, sebum is distributed along the surface of the hair shaft.
Sebocytes in children who have not reached puberty and in adolescents with hypofunction of the gonads are similar in structure to the cells of adults, but are much smaller in size. Considering that the maximum activity of the sebaceous glands during life is observed in newborns, and the largest glands are localized on the head, face and upper shoulder girdle, it has been suggested that the main purpose of the sebaceous glands is to produce a secretion that protects the child from the negative consequences of exposure to amniotic fluid. water and for a less traumatic passage through the mother’s birth canal.
In the fetus, sebaceous glands begin to develop at 13-16 weeks of embryonic development and are defined as superficial tubercles on the developing hair follicles. The sebaceous glands begin to function almost immediately from the moment they appear. Sebum is the first substance secreted by the fetus.
The development and function of glands in the embryonic and neonatal periods is regulated by maternal androgens and the synthesis of intrinsic steroids, as well as possibly by other morphogens, including growth factors, cell adhesion molecules, intracellular signaling molecules (catenin and LEF-1), other hormones, cytokines, enzymes and retinoids.
Age-related cycles of sebaceous gland activity
A marked increase in sebum excretion is observed during the first hours after birth. At this time, the first physiological peak of sebaceous gland activity is noted. Hypersecretion increases during the 1st week of a child’s life and slowly fades away throughout the entire infancy. Minimal sebum production is observed in children aged 2 to 6 years.
The second physiological peak of sebaceous gland activity coincides with adrenarche and occurs at approximately 7-9 years of age, lasting on average up to 17 years.
A high level of sebum secretion persists during the second or third decade of life, but there is a pronounced tendency towards its decrease. It was found that after 20 years, in each subsequent decade of life, sebum production decreases by 23% in men and by 32% in women. During menopause, women experience a significant decrease in its production.
Functions of the sebaceous glands
The main function of the sebaceous glands is the production of sebum, which serves as a lubricant for the human skin and hair. Sebum (the first protective barrier) provides natural skin care, without which it would become dry, less elastic, and prone to damage.
Most skin surface lipids (about 90%) come from the secretions of the sebaceous glands. Sebum lipids, together with the secretion of apocrine sweat glands, are components of the water-lipid mantle and have an occlusive effect, preventing transepidermal water loss. Also, sebum has antimicrobial, photoprotective and antioxidant activity.
Atopic dermatitis51
This is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease, which is characterized by itching, relapses, age-related features of the location and morphology of the affected areas. In the pathogenesis of the disease, a special place is occupied by hereditary determination, due to which the following occurs:
- the skin barrier is broken;
- immune system defects occur;
- hypersensitivity to allergens appears;
- pathogenic microflora develops;
- the functioning of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted, resulting in an increase in the synthesis of inflammatory mediators.
Acne on a child's body associated with the manifestation of atopic dermatitis occurs in 20% of children.
In different age periods, the manifestations of atopic dermatitis differ:
- Infant. It appears in the first 3 months of a baby’s life. The clinical picture is dominated by erythematous spots, vesicles, papules located on the forehead, cheeks, and scalp. There is severe itching, weeping, and swelling. The location of the disease is the extensor and flexion surfaces of the limbs.
- Children's. This period is characterized by a rash represented by papules, papulovesicles, erythematous-squamous formations located on the arms (elbows, wrists, forearms), legs (feet, knees, ankles).
- Teenage and adult. Rashes on the child’s body are concentrated on the flexor surfaces of the arms and legs, on the back of the neck, and in the behind-the-ear areas. The disease is characterized by the appearance of erythema, peeling, papules, cracks, and infiltration.
Hormonal regulation of sebaceous glands
Differentiation, proliferation of sebocytes, and lipid synthesis are controlled by complex endocrinological mechanisms.
Androgens and growth hormones promote differentiation and hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands, while estrogens and retinoids, such as 13-cis-retinoic acid, inhibit the activity of the sebaceous glands.
Androgens
Testosterone is the main male sex hormone. It is secreted by Leydig cells in the testes in men, in small quantities by the ovaries in women, and also by the adrenal cortex in both men and women. The hormone circulates mainly in the blood in a bound inactive state (about 40% with albumin and about 60% with sex hormone-binding globulin). Only unbound testosterone molecules have potential activity (about 2%).
Androgenic activity of testosterone manifests itself during the period of intrauterine development of the embryo (starting from the 13th week of gestation). During the prepubertal period, through a negative feedback mechanism, androgens suppress the secretion of gonadotropin. By the onset of puberty, pituitary cells become less sensitive to the inhibitory effects of circulating androgens.
The adrenal cortex plays an important role in the synthesis of hormones, including androgens. All adrenal steroid hormones are synthesized from cholesterol. The synthesis of glucocorticoids and androgens is regulated by adrenocorticotropic hormone. The main androgens of the adrenal cortex are dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and androstenedione, which are weak androgens in their activity. Testosterone is 20 and 10 times more active than them, respectively.
DHEA and androstenedione are the main androgens in the body in women, from which more than 2/3 of circulating testosterone is formed. The concentration of DHEA and its sulfate form increases significantly during puberty, which corresponds to the period of adrenarche. The maximum concentration of DHEA in the blood is present at the age of 20-30 years, and then it decreases by 20% over each subsequent 10 years. In women under the age of 35, the normal concentration of the hormone is 2660-11200 nmol/l, and in men - 5700-11 500 nmol/l.
Androgen synthesis
The pathway of androgen biosynthesis in various endocrine organs is the same.
The precursor of androgens, like other steroid hormones, is cholesterol, which either comes from the plasma as part of low-density lipoproteins, or is synthesized in the glands themselves from acetyl-coenzyme A. The main difference is that the formation of pregnenolone from cholesterol in the adrenal glands is stimulated by adrenocorticotropic hormone , and in the testicles - luteinizing hormone.
Treatment of pimples on a child’s body
If a child has pimples on his body, he should consult a dermatologist. Only a doctor can accurately determine their cause and prescribe the correct treatment. One of the groups of drugs that can be prescribed by a dermatologist for acne are topical antibiotics18. Please note that they have age restrictions. For example, Clindovit® gel is not recommended for use under 12 years of age6.
Clindovit® is a gel that helps fight acne. The main active ingredient in its composition is the antibiotic lincosamide clindamycin6. The drug exhibits antibacterial activity against a large number of strains of propionibacteria6. Clindovit® helps reduce the level of free fatty acids on the skin6. To reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance, it is recommended to combine the use of the drug with the use of azelaic acid (for example, Azelik® gel) or benzoyl peroxide28.
The influence of androgens on the functioning of the sebaceous glands
The level of influence of androgens on the proliferation and differentiation of sebocytes depends on the location of the sebaceous glands.
The sebaceous glands located on the skin of the face are most sensitive to male sex hormones.
Androgens regulate the function of the human sebaceous glands by binding to nuclear androgen receptors.
An increase in the level of testosterone and other androgens, especially in girls, provokes the appearance of active acne on the face, décolleté, shoulders, and back.
Female sex hormones (estrogens) have an inhibitory (inhibiting) effect when the sebaceous glands are overactive. This regulatory effect may be explained by suppression of gonadotropin secretion or an increase in the binding of testosterone to a special globulin.
Increased prolactin levels
The clinical manifestation of hyperprolactinemia is severe seborrhea. The effect of prolactin on sebaceous cells is mediated by stimulation of androgen production by the adrenal cortex, rather than by direct action on prolactin receptors.
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and insulin in high concentrations are also important for regulating the function of the sebaceous glands, the interaction of which with the same receptors enhances the accumulation of lipids in sebocytes and promotes inflammation by stimulating the production of cytokines.
Hormones, diet, lifestyle, age and anthropometric characteristics influence IGF-1 concentrations. The effect is dose-dependent.
IGF-1 is a mediator that enhances the activity of other hormones (androgens, growth factor and insulin), and its concentration directly correlates with the amount of sebum and the severity of acne. IGF-1 polymorphisms have been noted to predispose to the development of acne. This fact has clinical significance in determining risk factors for the development of acne, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, polycystic ovary syndrome, and poor diet.
The acnegenic effect of dairy products and foods with a high glycemic index is also realized by increasing the concentration of IGF-1.
Preventive measures to prevent stomatitis in children
To minimize the risk of developing stomatitis you need to:
- wash the child’s toys, bottles and other things regularly, and do not forget to thoroughly wash the baby’s hands;
- strengthen the child’s immunity;
- do not let your child bite his nails;
- create a balanced menu containing all the necessary minerals and vitamins. The diet should be followed;
- promptly treat diseases such as tonsillitis, gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases. If you extinguish the outbreak in time, this will prevent stomatitis from developing;
- At least once a year, and preferably twice, visit the dentist for a detailed examination of the oral cavity.
All these simple recommendations will help avoid the occurrence of stomatitis, because any disease is much easier and cheaper to prevent than to treat it later. If it was not possible to avoid the disease, at the first signs of it, you must consult a doctor to prescribe effective treatment. If stomatitis appears again and again, a thorough immunological examination is required. The child should be examined by a pediatrician and an immunologist; it is also advisable to contact an endocrinologist and gastroenterologist (perhaps they will identify a chronic disease leading to relapse of the disease).
It is equally important to teach your child proper oral hygiene. If the teeth are affected by caries and covered with plaque, and there are fistulas on the gums, the fight against stomatitis will not be successful. A child must be taught how to properly brush his teeth and gums by buying him a brush and toothpaste appropriate for his age.
The influence of neural regulation on the development of acne
The nervous system modulates physiological and pathophysiological effects in the skin. Neuropsychic stress plays a special role in the pathogenesis of acne in adolescence, when the sebaceous glands are most active.
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system responds to the development of neuroendocrine reactions of the sebaceous glands to stress.
Also, pilosebocia complexes are an immunocompetent organ and their proper functioning of the innate immune system, which protects the sebaceous glands from pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria. Increased serum IGF-1 may suppress the transcription of antimicrobial peptides, thereby significantly reducing the innate immune response.
It is important to remember that severe acne in young children and especially in children from 1 to 7 years of age (baby acne) is almost always associated with pathology of the endocrine system.
Aphthous stomatitis in children
Manifests itself in the form of small individual ulcers on the lips and oral mucosa. Its appearance is provoked by:
- allergic reactions of various types (to food, medications, etc.);
- staphylococci (there are many of these bacteria in carious formations and dental plaque);
- immunity disorders;
- liver diseases.
Aphthous stomatitis in children: symptoms and treatment
Exacerbation occurs mainly in autumn and spring. Ulcerations most often form on the lips, tongue and inside the cheeks (in these places the mucous membrane comes into contact with food and can be injured by the teeth).
Sometimes weakness in the body and fever appear, but often the general condition of the body remains normal.
The size of the ulcers (ulcers) is 5-10 mm. They are covered with a grayish coating and are surrounded by a red, inflamed rim of mucous membrane. There is pain when touching them. It happens that only 1 ulcer forms.
Aphthous stomatitis in children: treatment
The causes of stomatitis in children will influence the nature of treatment. Immediately after the first symptoms appear, it is necessary to adjust the child’s menu, completely eliminating the main allergens (chocolate, honey, berries, citrus fruits, etc.). During illness, you should also not eat spicy foods with added spices.
Often, aphthous stomatitis becomes a reaction of the body to medications, so if a child is taking medications, it would be a good idea to consult a doctor.
Treatment methods:
- Antiallergic drugs. The most frequently prescribed are Suprastin, Diazolin and many others like them.
- Treatment of ulcerations. At the initial stage of the disease, “Miramistin” (they are recommended to spray the aphras using a special sprayer that comes with the drug) and “Cholisal” (ulcers are treated with gel at least 3 times a day) perform well. When the acute symptoms of the disease pass, you can use Solcoseryl, a gel that accelerates the healing of mucosal defects and has an analgesic effect.
- Exposure to UV rays in a physiotherapy room.
- Use of immunomodulators. Firstly, it is worth purchasing a special toothpaste based on lactoferrin, and secondly, you can take a course of Imudon.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity. Since one of the causes of stomatitis is microorganisms, all carious formations must be cured and plaque removed.
Acne in children
The cause of childhood acne is endocrinopathies. In addition to the premature onset of adrenarche, which is a benign condition, in these patients it is necessary to exclude more severe pathologies:
- congenital adrenal hyperplasia;
- malignant tumors of the adrenal glands and testicles;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome;
- early puberty of central origin;
- exogenous intake of androgenic drugs into the child’s body.
Consultation with a pediatric endocrinologist is mandatory.
Examination of a child with childhood acne includes assessing the child’s weight and height and comparing them with age norms, as well as determining bone age. Bone age characterizes the biological maturity of the body. The main indicators of age-related differentiation of skeletal bones are ossification nuclei and the formation of synostoses. Bone age is determined using x-rays of the bones of the child’s left wrist.
It is also necessary to conduct a hormonal profile study:
- testosterone (total and free);
- DHES, 17α-hydroxyprogesterone;
- prolactin;
- cortisol;
- luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones.
High concentrations of free testosterone and DHES are observed in cancer of the endocrine glands and polycystic ovary syndrome. An increase in the concentration of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone is characteristic of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Causes of stomatitis in a child
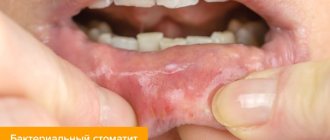
In childhood stomatitis, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is affected: small pimples of white or yellowish color, filled with liquid, appear on its surface. In some cases, ulcers form.
Stomatitis is predominantly a childhood disease, although it can also occur in adults. The rash affects the inner surface of the cheeks, tongue and gums. The disease causes a lot of inconvenience: pimples hurt and itch, their appearance is accompanied by a burning sensation in the mouth.
Among the main reasons for the development of stomatitis are:
- poor oral hygiene;
- injury to the mucous membrane;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- oral burn;
- pathogenic bacteria that enter the oral cavity from dirty hands, toys, etc.
Acne in children over 7 years of age and adolescents
In children after 8-9 years of age - prepubertal and adolescent periods - the first signs of puberty, ahead of the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics, hair growth in the axillary and pubic areas. Acne in girls during the premenarche period is noted in 61-71.3% of cases.
Most often, prepubertal acne is localized on the face in the central part of the forehead. Rashes are also found on the chin, nose and cheeks. In most cases, this type of acne is characterized by a mild course. For minor rashes in children, the diagnosis is not always made by pediatric dermatologists. What distinguishes prepubertal acne from vulgar acne is the absence of rashes on the back and chest.
The appearance of acne in girls and boys after 7-8 years is directly related to an increase in the blood concentration of androgens of adrenal, ovarian and testicular origin.
At the age of 7-11 years, the body experiences adrenarche, clinically characterized by the maturation of the adrenal glands and their production of androgens, and a later process of gonadarche - the maturation of the gonads: ovaries and testes.
Prepubertal acne is largely a consequence of normal adrenarche, which develops depending on the maturation of the adrenal glands.
In patients with prepubertal acne, genetic predisposition (family history) plays an important role.
A predisposing factor in the development of this dermatosis is the child’s low birth weight. Researchers have suggested that low birth weight may be directly related to insulin resistance and genetically determined polycystic ovary syndrome - diseases that play a large role in the development of acne.
When examining children with prepubertal acne, one should take into account the fact that these rashes can be a symptom of severe endocrinopathies: diseases of the adrenal glands and adrenal glands.
Premature and excessive secretion of adrenal androgens can be observed in congenital adrenal hyperplasia, Cushing's disease, 21-hydroxylase enzyme deficiency, and other androgen-secreting tumors.
In addition, an increase in androgen concentrations can be observed against the background of early maturation of the reproductive homeostasis system (gonadarche), which is stimulated by the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system.
If a child has prepubertal acne, the possibility of developing pituitary adenomas, testicular tumors in boys, virilizing ovarian tumors (thecomas, granulosa cell tumors, Sertoli and Leydig cell tumors, etc.) and polycystic ovary syndrome in girls should be excluded.
The following algorithm for examining children is recommended:
- assessment of the child’s weight and height and comparison with age norms;
- determination of bone age;
- determination of the concentration of testosterone (total and free), DHES, 17α-hydroxyprogesterone;
- prolactin;
- cortisol;
- luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones (and their ratio).
If necessary, an ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the pelvic organs, ovaries, as well as an MRI of the brain should be performed.
If there are deviations, the child should be consulted by a pediatric endocrinologist.
Post Views: 3,347
Herpetic stomatitis in children
There are several types:
- sharp;
- chronic.
This type of damage to the oral mucosa occurs when the herpes virus first enters the human body. Acute stomatitis is typical only for young children. Herpetic stomatitis that occurs repeatedly is called chronic. Herpes stomatitis in an infant appears due to infection of the child by the mother or other people who kiss the baby out of excess of feelings or taste food with the spoon with which he is then fed.
Acute herpes-type stomatitis
The herpes virus enters the baby's body after he reaches the age of six months. At this time, the antibodies the child received from the mother gradually cease to act. In the vast majority of cases (about 90%), the symptoms of stomatitis at such an early age are mild, and only in 10% of children the disease is acute.
Stomatitis in children under one year of age, the treatment of which takes about 2 weeks, is accompanied by weakness in the body, general malaise and muscle pain, which is explained by poisoning of the body. In some cases, the temperature during the first two days of the disease may rise to 40 degrees or higher. The lymph nodes become inflamed, and touching them causes pain to the baby.
A distinctive sign of the disease are small bubbles that appear in groups on the lips, palate, and tongue. The oral mucosa takes on a bright red hue. The bubbles are filled with a clear liquid that gradually becomes cloudy. After about 3 days, the blisters burst, leaving behind erosions covered with a yellow or white fibrinous coating.
Sometimes the gums near the teeth may turn red, so the disease is often confused with gingivitis.
Chronic stomatitis
Once the herpes virus enters the human body, it remains there forever. Symptoms may occur when:
- cold;
- lack of vitamins;
- stressful situations;
- exacerbation of sinusitis, tonsillitis and other chronic diseases;
- injury to the mucous membrane;
- gingivitis or caries;
- habit of breathing through the mouth (lips become dry, causing the skin in the corners of the mouth to crack).
Chronic stomatitis develops in exactly the same way as acute stomatitis, with the exception that the disease does not affect the general condition of the body, because intoxication is minimal.
Herpetic stomatitis in children: how to treat
Types of treatment:
- Use of antiviral agents. Ointments and gels, which are often used to treat herpes on the lip, should not be applied to the oral mucosa. Treatment is possible with suppositories or tablets. The most effective drugs include two drugs. The first of them is “Viferon”, which contains interferons that have an immunostimulating effect. Available in the form of suppositories and gel. There are no age restrictions on the use of the product. The gel should be applied directly to the affected mucous membrane, after drying it with a swab. The treatment period does not exceed one week, provided that the product is regularly applied three times a day. The second is the antiviral drug Acyclovir, which acts on the herpes virus itself, and does not simply increase immunity. The dosage regimen is the same for children over 2 years of age and twice.
- Rinse. It is necessary to use solutions whose action is aimed specifically at suppressing the herpes virus (such popular and cheap remedies as chlorhexidine and various herbal infusions are not suitable). The most effective drug is Miramistin, which should be rinsed three times a day. For greater results, you can apply Viferon a short period of time after rinsing.
- Use of symptomatic remedies. Antipyretic drugs are used when body temperature exceeds 38 degrees. At lower temperatures, such tablets will do more harm, since they will interfere with the formation of natural immunity and the production of interferons.
- Use of immunomodulators. If stomatitis in children, which was treated according to all the rules, makes itself felt again, you can resort to the use of immunomodulators, the most effective of which are:
- “Immunal” is a basic drug that increases immunity.
- “Imudon” stimulates the immunity of the oral mucosa. One course lasts 20 days (you need to take 6 tablets every day). 2 courses per year are recommended.
- Toothpastes with lactoferrin and lysozyme (these substances are contained in special Splat children's toothpastes).