Additional and dangerous symptoms
Most often, a moving lump under the jaw indicates inflammation of the lymph node.
Often, a neoplasm on or under the jaw is accompanied by unpleasant sensations, pain and itching. Some symptoms should prompt you to see a doctor:
- increased temperature against the background of other unpleasant sensations;
- intensive growth of the cone or its larger size - from 2-3 cm;
- noticeable accumulation of pus;
- the skin above the tumor has changed color and darkened;
- the neoplasm arose without previous viral or infectious pathologies;
- the affected area is very painful and has become sensitive.
Many of the symptoms indicate a malignant lump under the jaw on the right or left, or intense inflammation in the lymphatic system.
Ignoring a set of symptoms can lead to the rapid development of dangerous pathologies. After detecting a lump, you need to see a doctor and undergo instrumental diagnostics.
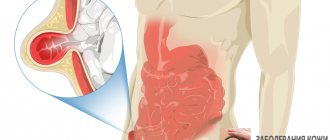
Lymph nodes: what role do they play in the body?
The submandibular lymph nodes are responsible for the safety of the nose, throat, ears, and teeth. They act as a kind of filter in the body. It is through them that lymphatic fluid flows - the basis of the immune system.
When the activity of harmful bacteria increases, the filters react instantly: they release lymphocytes to destroy the pathogenic flora.
Experts have found that the adult body contains about two liters of lymph and more than four hundred nodes. Most of them are found under the arms, on the neck, head and groin. Each is responsible for a nearby organ or tissue cells that are located nearby.
Causes of lump formation in the jaw area
All reasons for the formation of a ball in front of the jaw or under it can be divided into several groups: pathologies of the oral cavity and teeth, disorders in the lymphatic system, various neoplasms and infections. In rare cases, other pathologies are added.
Diseases of the mouth and jaw
On the lower jaw, a hard lump can be palpated with a long-term course of such pathologies:
- alveolitis – inflammation of the socket after tooth extraction;
- pulpitis – inflammation of nervous tissue due to staphylococcal or streptococcal infection;
- stomatitis is an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane that can take severe forms;
- abscess – purulent inflammation of the roots of a tooth;
- periodontitis is damage to the soft tissue around the roots, accompanied by severe pain and swelling of the cheek.
If left untreated, many diseases of the oral cavity and jaw cause lymphadenitis - inflammation of the lymph nodes. As well as bone damage and osteomyelitis.
Another reason is a cyst of the tooth or jaw. The condition becomes a consequence of injuries, improperly treated teeth and ENT diseases. The first symptoms occur when the cyst reaches an impressive size.
Periostitis of the jaw, or gumboil, also develops in response to the lack of treatment of teeth damaged by caries or other diseases. It can become a complication of influenza, sore throat or acute respiratory viral infection if there was a previous jaw injury. With periostitis, a purulent process occurs that affects the periosteum.
Tumor processes
Lipoma is a mobile benign tumor.
Often a lump on the cheekbone turns out to be a symptom of very dangerous conditions. Even benign tumors should not be ignored.
- Phlegmon. Inflammatory complication of cysts and dental diseases. Accompanied by the accumulation of pus. Recurs when immunity decreases. Symptoms include: pain when swallowing, limited jaw mobility. Requires hospital treatment. If treated incorrectly, it can lead to sepsis, facial deformation, and death.
- Lymphoma. A malignant tumor on the left or right, affecting the lymphatic system. It grows quickly and is accompanied by darkening of the skin, swelling, redness and severe pain. Over time, common symptoms of cancer appear: sudden weight loss, fever, lack of strength.
- Lipoma. Benign neoplasm, or wen. The seal is motionless, does not hurt, and is soft. Requires removal as it continues to grow and can reach 10 cm in diameter. This will lead to compression of blood vessels and nerve endings. It can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
- Atheroma of the sebaceous gland. Occurs with prolonged accumulation of fat in the sebaceous glands. It is also called a cyst. A soft, mobile and painless lump that slowly increases in size. One of the common complications is suppuration. Therefore, atheroma requires medical intervention and removal.
- Other benign tumors. Among the least common pathologies is ameloblastoma, which affects the lower jaw and grows into the soft tissue. Leads to tooth displacement and jaw deformation. Also distinguished are bone osteoma, fibroma and cementoma. The last two arise from the connective tissue and root of the tooth.
Malignant tumors such as carcinoma and sarcoma that affect the oral cavity are practically not diagnosed.
Sialadenitis
Siloadenitis is a blockage of the salivary gland in the ear area under the jaw.
A rare salivary stone disease that appears when the salivary glands are blocked. The tumors are located under the jaws and near the ears. Over time it causes swelling and pain. Characterized by a relapsing course.
Submandibular lymphadenitis
Inflammation of the nodes under the jaw most often occurs in response to other diseases, but in rare cases it can be an independent disease. Lymphadenitis is characterized by weakness, pain when swallowing and high body temperature. If left untreated, it becomes complicated by a purulent process.
Mumps or mumps
The disease, caused by an infection, occurs mainly in boys and young adults. Women suffer from the virus very rarely. Lack of proper therapy leads to male infertility.
Other pathologies and problems
Acne or boils under the jaw can cause severe pain.
A complicated course of furunculosis or acne can cause a lump. Sometimes subcutaneous pimples are painful and reach a size of 1-2 cm. If squeezed, the infection can damage the circulatory system.
The following causes of lumps under the jaw are also distinguished:
- inflammation of the lymph nodes in response to hypothermia;
- a consequence of otitis and other ear diseases;
- hormonal and immune pathologies;
- the presence of herpes in the body;
- acute infection in the body.
If the lump does not go away within a week or longer or often recurs, complicated by additional symptoms, you should not ignore visiting a doctor.
A lump on the gum after dentures - is it dangerous or not?
A crown or denture is a common cause of gum swelling. A lump can occur both at the stage of preparation for the installation of a prosthesis, and some time after wearing artificial teeth.
If swelling occurs before the installation of dentures, the reason may be a violation of the depulpation procedure or poor-quality filling of the canals. Penetration of infection into the pulp provokes an inflammatory process that occurs in periodontitis.
Most often, after prosthetics, bumps appear on the gums due to poor quality of the prosthesis, discrepancy in the size of the crowns and errors when installing artificial teeth. The mucous membrane can be injured by the prosthesis. Even through small wounds, an infection penetrates, which leads to inflammation, or under constant exposure, a disruption occurs in the cells of the gum tissue, which begin to pathologically increase, forming a growth.
Methods for diagnosing a neoplasm
To diagnose a tumor, an ultrasound of the jaw and surrounding tissues is performed.
If a lump appears on the jaw under the skin, is small in size and does not hurt, it still needs to be carefully examined. A simple examination must be supplemented with instrumental techniques and tests:
- Ultrasound as the main starting method for differentiating oncological and other pathologies.
- If cancer is suspected, a biopsy is performed and tissue is taken for histological examination.
- X-rays will help identify some pathologies of bones and teeth.
- An MRI or CT scan will establish a more precise cause of soft or hard tissue diseases.
- If there are diseases of the skin and sebaceous glands, a dermatologist is involved in the work and tests of scrapings are prescribed.
Before contacting a doctor, it is strictly forbidden to apply hot or cold compresses. Doctors also do not recommend taking medications. For severe pain, you can take 1 tablet of a suitable NSAID, but do not abuse them. It is also prohibited to try to squeeze out or otherwise influence the tumor.
Why do the lymph nodes under the jaw hurt?
The patient himself can, with the help of simple palpation, determine whether the lymph node under the jaw has enlarged or not. After all, inflammation does not always occur with pronounced symptoms. Much depends on the type and severity of the infection in the body.
After detecting a compacted, enlarged node, you must visit a doctor. Before going to the clinic, you need to prepare answers to the questions that the specialist will ask in order to conduct a competent diagnosis:
- Remember if there were any injuries in the near future in the area where the neck was swollen, or if you received blows in this place. If it is a bruise, then the injury will resolve in the near future.
- Remember what dosage forms you were treated with. Some drugs provoke this kind of inflammation. Such tablets include drugs that are prescribed to patients with epilepsy, vaccines against typhoid fever and some others.
When the lymph nodes under the jaw hurt when pressed, the cause of the phenomenon may lie in the fact that the patient has a serious pathology. If the node has increased in diameter by one and a half times, then the immune system itself is not able to cope with the inflammatory process
in the body - outside help is needed.
If a node is detected, which after some time becomes soft to the touch, the patient needs treatment with antibacterial drugs. This may indicate that the lymph node was unable to resist the inflammatory process and allowed the infection to spread further throughout the body.
Treatment options
In oncology, the tumor is removed, and neighboring tissues are irradiated.
Therapy consists of eliminating the cause that caused the discomfort. For this, different groups of medications, physiotherapy, and surgery are used.
- For dental diseases. Restore damaged areas, disinfect holes after removal. For long-term acute stomatitis, lidocaine-based rinses, antibiotics, and aloe juice are used. Anti-inflammatory pastes are also used for pulpitis and periodontitis. For severe pain, analgesics are prescribed.
- For autoimmune disorders. Pain is relieved with NSAIDs or glucocorticosteroids. Chondroprotectors are also used for diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. For other disorders, vitamin supplements and cytostatics are used.
- For complicated lymphadenitis. They are treated with antibiotics, and in case of purulent processes, tumors are removed surgically.
- For oncological pathologies. Complex therapy is required, including anti-cancer treatments: radiation and chemotherapy, surgery, and a restorative complex of vitamins.
Dermatological disorders are often treated with external remedies, including antibiotics.
The use of folk remedies is appropriate at the rehabilitation stage or as part of additional treatment methods. You need to select recipes together with your doctor to avoid allergies.
Hematoma
Description
If there is a swollen lump on the gum filled with blood, most likely it is a hematoma. This tumor occurs as a result of an incorrectly removed tooth or injury. Such a lump on the gum above the tooth, as a rule, does not hurt.
Treatment
Dissolves on its own. But if the lump hurts, consult your dentist for advice. The doctor will prescribe painkillers.
Preventive actions
If your immunity is low, it is recommended to take complex vitamin supplements.
Since the range of reasons why a lump may appear under the jaw on the left or right is wide, it is difficult to name exact ways to prevent the symptom.
Some basic actions reduce the risk of diseases and their complications:
- It is important to treat viruses and infections in a timely manner so that they do not worsen the condition of the circulatory, lymphatic and immune systems.
- You need to give up bad habits, including overeating and abuse of fatty foods.
- It is important to maintain a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, lean meats and grains.
- An active lifestyle and sports will strengthen the body's protective functions.
- Separate mention should be made of diseases of the oral cavity and teeth - their long-term course very often leads to dangerous consequences.
If a lump appears under the jaw, you should not treat it yourself, pierce it, or wipe it with herbal decoctions. Only after diagnosis and identification of the cause can you begin therapy prescribed by the doctor.
Sialadenitis
Salivary stone disease, or sialadenitis, appears due to blockage and inflammation of the salivary glands. The disease most often occurs in the submandibular and parotid areas1. Pathology develops mainly on one side of the jaw. Patients who consult a doctor with this problem complain of swelling under the jaw, chin, or near the ears. In the initial stages, the cheek and neck swell; in later stages, pain occurs when opening the mouth, talking, chewing and swallowing food.
The cause of the lump may be salivary stone disease
Sialadenitis can worsen and recur from 2 to 6 times a year. Dysfunction of the salivary glands and hyposalivation (lack of saliva) contribute to various infectious processes in the oral cavity. The most common is generalized periodontitis, due to which you can lose all your teeth.
“The other day, quite unexpectedly, a lumpy lump appeared under my chin, I went for an ultrasound, and there I was stunned by the news that these were stones in the salivary ducts. There were no other symptoms before. As treatment, they prescribed all sorts of pills and physical procedures, massage, but if it didn’t help, they said that they would put them in surgery and cut them up...”
Flo, review from 32top.ru