In Europe alone, the number of detected cases of syphilis has almost doubled over the past 10 years. Moreover, 85% of the sick are men!
In Russia, according to experts, the overall situation with syphilis is stable. According to the Ministry of Health in Russia, in 2022 the incidence rate in our country was 16.5 cases per 100 thousand people, which is 10 times lower than in 2000.
The leaders in the incidence of syphilis are the regions of Eastern Siberia and Primorsky Krai. In the European part of Russia, amur disease was most often recorded in the Kaluga and Saratov regions.
Causes of syphilis in men
There are three main reasons:
- unprotected sexual intercourse - in 90% of cases of infection, this is the route of transmission of the infection;
- blood transfusion - from an infected donor or through shared syringes and utensils for drug preparation;
- household infection - when using the patient’s personal belongings that came into contact with his blood or mucous membranes, for example, a toothbrush with drops of blood, but this route of transmission of infection is rarely observed.
The most dangerous are people with early forms of syphilis, especially those who have weeping rashes on the skin and mucous membranes (erosions, ulcers, etc.). Most often, the rashes are located on the external genitalia, in the perineum, on the oral mucosa and on the lips.
To the point
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): what is important to know
Symptoms of syphilis
Depends on the stage of the disease. In rare cases, syphilis in men can go unnoticed, but in others it is so pronounced that it is impossible not to notice it.
Primary stage. Its symptoms are:
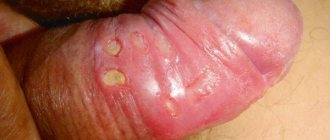
- chancre - deep, often painless ulcers with smooth sides, bottom and edges, regular round shape; sometimes chancre can be multiple and affects the hands, mouth, scrotum, lips, abdomen, etc.;
- enlargement of local lymph nodes;
- temperature increase;
- joint pain.
Secondary syphilis. It appears as follows:
- multiple spots, plaques and papules on the body;
- focal hair loss.
Chancre
A chancre visually represents a small ulcer, often located in the genital area.
Hard chancre appears in places where the pathogen enters the human body:
- on the head of the penis;
- on the scrotum;
- on the bridle.
The formation of hard chancre occurs within 7-21 days after treponema enters the body.
Visually, chancre may have atypical manifestations:
- Felon. Education hurts. There is a necrotic plaque on the surface. Later, erosions form.
- Induactive edema. The formation takes on a bluish tint and is accompanied by increased swelling.
Treatment of syphilis in men
The first medicine to treat a terrible disease was invented by Paracelsus. The greatest physician of the Middle Ages did not know that treponema pallidum was sensitive to compounds of mercury, arsenic, bismuth and iodine, but he noticed that the mercury ointment, which he rubbed into the legs of patients, slowed down the course of the disease. Those infected in the USSR were treated with mercury preparations until 1963. However, the effectiveness of this technique left much to be desired. The toxicity caused patients to lose hair and develop serious complications. Since 1943, doctors began to introduce effective and non-toxic penicillin drugs into clinical practice.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of syphilis is made after a careful study of the clinical picture and is confirmed in the laboratory. To do this, blood tests and sometimes cerebrospinal fluid tests are taken. Today, the following methods are used to diagnose syphilis:
- serodiagnosis and PCR;
- Wasserman reaction (obsolete);
- linked immunosorbent assay.
You can test for syphilis at home. The tests are sold in regular pharmacies.
Today, syphilis is diagnosed relatively rarely: the vicious circle of infection interrupts people's awareness and choice of safe sex. Photo: Pixabay
Modern methods of treating syphilis
Treponema pallidum has maintained sensitivity to penicillin and drugs based on it for centuries. Therefore, antibiotics are the only effective way to treat patients.
If syphilis is detected, all sexual partners of the infected person are also treated.
“Of course, today this disease is diagnosed less frequently,” says dermatovenerologist Azamat Kintaev . – Venereologists themselves explain this by the uncontrolled use of antibiotics in the treatment of other diseases, which muffles the manifestation of syphilis, but aggravates its latent forms. In this case, syphilis can be determined only by a blood test, without any clinical manifestations of the disease. The increase in incidence is also reduced by people's increased awareness of the need for safe sex, in particular using condoms, which prevents infection with many dangerous sexually transmitted infections, including syphilis.
Preventing syphilis at home
These tips may have set your teeth on edge by now, but they work:
- avoid casual sex;
- use a condom (does not protect 100% as foci of infection may be on the oral mucosa or other uncovered areas of the body).
The causative agent of syphilis is very sensitive to traditional antiseptics and soaps. Therefore, if a “casual relationship” does take place, the following procedures will help reduce the risk of infection:
- urinate;
- wash your hands and external genitalia with soap;
- treat the genitals, pubis and thighs with miramistine or chlorhexidine or betadine.
Important! The described measures are effective no later than 2 hours after sexual intercourse!
What to do if there is a patient with syphilis at home:
- use separate utensils and personal hygiene products;
- Avoid kissing during the contagious stage.
It is generally accepted that the saliva of patients with syphilis is contagious only if they have rashes on the oral mucosa.
“If a person has become infected with syphilis, he must maintain strict hygiene: he must have separate dishes, a towel, manicure accessories, his toothbrush must be kept separately,” advises dermatovenerologist Azamat Kintaev .
Prevention
It is enough to see at least once what syphilis looks like to forever decide to give up promiscuous sexual intercourse. This is the most effective way to prevent this disease.
If a person has to live with a sick person, strict hygiene rules must be observed. Despite the fact that the risk of household transmission of infection is minimal, it still exists. Also, a person living with an infected person must periodically visit a doctor and undergo diagnostics to make sure that infection has not occurred.
If you have sexual contact with an infected person, it is recommended to immediately urinate, wash your genitals with laundry soap, and wipe your private parts with a disinfectant solution. This treatment is effective only in the first 48 hours after possible infection, since during this period of time the pathogen is still on the skin and mucous membrane. After more than 3 hours, such treatment is useless.
Syphilis is a dangerous disease that in the vast majority of cases is transmitted sexually. The disease is insidious in that even in the absence of symptoms, it can affect any organ of the human body and provoke various ailments. It is important to understand that cure for syphilis does not guarantee protection against re-infection. Immunity to Treponema pallidum is not developed. Therefore, you should always adhere to preventive measures, and at the first suspicion of a disease, immediately consult a doctor. With timely treatment, syphilis can be successfully treated. But untreated syphilis will destroy the body for years and can be fatal.
Popular questions and answers
We asked questions regarding modern methods of treating syphilis, its prevention and possible complications to the dermatovenerologist Azamat Kintaev .
Is it possible to become infected with syphilis at home?
Syphilis is a chronic systemic venereal disease, usually transmitted sexually, less often through blood, and even more rarely through contact. The disease can occur in closed and open forms. As a rule, first one or two hard ulcers (chancres) appear in the groin area of the body, then with the blood flow the infection begins to spread throughout the body, manifesting itself in the form of pustular rashes. When exposed to these rashes, for example while breastfeeding, a baby can easily become infected from an infected mother. You can become infected with syphilis through a kiss or a blood transfusion. This disease can also be acquired during dental or gynecological examinations if unsterile instruments were used.
What complications can there be with syphilis?
Syphilis is an insidious disease that causes infertility, affects the central nervous system, and can cause damage to internal organs and the cardiovascular system. As the infection spreads in the body, the disease attacks the brain, causing meningitis. Penetrating into the membrane of the eye, syphilis leads to atrophy of the optic nerve, the disease provokes encephalitis, affects the auditory nerve, and leads to deaf-muteness.
Diagnostics
Who to contact : a venereologist.
Testing for syphilis must be done on an empty stomach. Do not drink alcohol or fatty foods for 3 days.
Blood and syphilide secretions are taken as research material, and the contents of the lymph nodes are obtained using a puncture. To identify the causative agent of syphilis, the following methods are used:
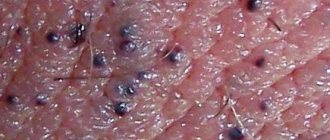
- Phase-contrast, dark-field and fluorescence microscopy (RIF). Used for primary syphilis. In addition to pathogenic Treponema pallidum, non-pathogenic types of infection refringens, balantidis, microdentium, and buccalis can be found on the genitals and mouth. They differ from Treponema pallidum in their structure. For diagnostic reliability, it is advisable to take the contents of enlarged lymph nodes for microscopic examination.
- PCR technique.
- Testing for antibodies using ELISA, RPHA, TPHA, TPPA, RSK (Wassermann reaction). The most accurate method is the RPR method. The test result will be ready in 8 minutes.
If the test results are positive, the reactivity of the treponeme is checked using the RPR/VDRL test. A titer greater than 16 means the active phase.
Treponema pallidum detected by RIF
Dark-field microscopy
Stained treponema in a smear
Tests RSKcard, VDRL, RPR, RMP - non-treponemal, or cardiolipin. They are carried out on the basis of antigens of non-treponemal origin. They are used for initial screening of syphilis and for monitoring treatment. May give false positive results in the following cases:
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Senile age.
- Injection drugs.
- Intake of alcohol and fatty foods.
- Hepatitis.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Oncology.
- Kidney diseases.
Tests based on antigens isolated from cultured Treponema pallidum are called specific. These include RIF, RPGA, RIBT, RIT, ELISA. They are performed in cases of positive non-treponemal tests for syphilis.
Test strip for performing a home test for syphilis
If there are neurological symptoms, MRI, CT, and cerebrospinal fluid analysis are used.
Summary table of diagnostic methods for syphilis
Decoding tests for syphilis
Diagnostic methods for identifying complications