Lip cancer is a malignant neoplasm that consists of elements of the integumentary epithelium of the red border of the lips. A tumor on the upper lip appears rarely. Over time, lip cancer spreads to the bones of the lower jaw. Atypical cells are transported with lymph to the lymph nodes, resulting in the appearance of new malignant foci.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital carry out early diagnosis of lip cancer using modern research methods. Oncologists provide radiation therapy and perform gentle surgical interventions. In the later stages of lip cancer, complex therapy is used. Early diagnosis of a malignant lip tumor and adequate therapy can not only save the patient’s life, but also avoid cosmetic defects after surgery.
Lip cancer - what is it?
Depending on the type of tumor growth, the following forms of lip cancer are distinguished:
- Papillary;
- warty;
- Ulcerative;
- Ulcerative-infiltrative.
A malignant tumor of the lip in 95% of cases is represented by keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. In 5% of cases, histologists have squamous cell non-keratinizing cancer of the lip mucosa. A tumor of the lip, which from the inside, on the mucous membrane, is characterized by a malignant course (infiltrative growth and early metastasis to regional lymph nodes).
A tumor of the lower lip most often affects the border of the lower lip. A crack, ulcer or swelling forms on it, which looks like a wart. The disease is predominantly diagnosed in people over 60 years of age.
Cancer of the upper lip occurs less frequently than the lower lip, but the tumor is more aggressive. Upper lip cancer has a high risk of metastasis and spreads quickly. This is explained by the fact that the malignant tumor is located close to the nasal cavity, where the blood supply system is developed. A tumor on the inside of the lip is dangerous because it quickly grows into the soft tissue.
Melanoma on the lip is 10 times less common than squamous cell carcinoma of the lip, but is characterized by a high degree of malignancy. Basically, the tumor is located on the red border of the lower lip. It penetrates deeply into tissues, quickly transfers to nearby tissues and gives metastases.
At the Yusupov Hospital, oncologists make a diagnosis of lip cancer using the following methods:
- Examination with the naked eye and using stomatoscopy;
- Cytological examination of impression smears from a tumor ulcer;
- Histological examination of lymph node punctate.
After establishing the primary diagnosis, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out.
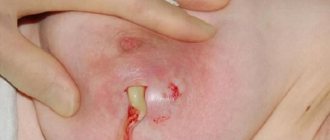
Venous lake removal
Removal of a venous lake can be carried out in several ways:
- Removing a venous lake with a scalpel threatens bleeding during the procedure;
- Cryosurgery and excision of the venous lake with an electrocoagulator are highly traumatic and have a high probability of destruction of adjacent healthy tissue;
- Laser removal of venous lake should be considered the most effective.
Rice. 3. Stages of laser removal of venous lake on the lip
Causes of lip cancer
Lip cancer develops for many reasons:
- From smoking;
- After a long stay in the sun;
- As a result of inflammatory processes of an infectious and non-infectious nature;
- Under the influence of high temperatures;
- In the presence of microtraumas;
- Due to prolonged exposure to chemicals.
Lip cancer often develops from smoking. Men get lip cancer much more often than women. Currently, the trend is changing, because many women suffer from tobacco addiction. Doctors believe that lip cancer develops due to smoking strong cigarettes for a long time.
The average smoker smokes at least ten cigarettes a day. In this case, the paper surface is constantly in contact with the lips. The skin here is especially delicate and sensitive. Microcracks appear on its surface. They are invisible to others and do not cause problems for the smoker. Damaged areas of the epithelium are affected by tobacco smoke. It contains a lot of harmful substances. Skin cells begin to degenerate.
The cause of mechanical trauma that causes lip cancer can be improperly made dentures, the habit of holding various objects with the lips (nails, the mouthpiece of a smoking pipe), or biting the lower lip. The mechanism of development of lip cancer is as follows: a long-term non-healing crack, wound, inflammation on the lip, papilloma develops into leukoplakia, Manganotti cheilitis, keratoacanthoma, warty form of dyskeratosis or other precancerous diseases. Against this background, lip cancer occurs.
Causes and risk factors
Any disease has causes; you should include a list of factors that can provoke the formation of a cancerous tumor of the lip:
- Bad habits: alcohol, nicotine.
- Infectious diseases of soft tissues.
- Metabolic disorders in the body.
- Exposure to the sun's rays.
- Mechanical injuries to the skin of the lips.
- Surgical interventions in this area.
- Poor heredity, predisposition to cancer diseases.
- Poisoning with chemical reagents, which is systematic.
- Contact with carcinogenic substances.
The risk of developing the disease increases if a person has ulcers and erosions of the skin of the lips. When damage does not heal over a long period of time, the risk of secondary infection increases. As a result, the risk of developing atypical cells in the tissues of the lips increases several times.
The seal, consisting of connective tissue, can “degenerate”. A similar thing happens with formations (papillomas, warts, creatures).
Effect of smoking
Addiction to tobacco has been linked to various forms of cancer. Including malignant formations of the lip. With systematic contact with tobacco smoke, the human body is “saturated” with carcinogens (combustion products). As a result, the risk of developing cancer diseases increases significantly.
What happens to lip tissue with systematic tobacco use:
- contact with cigarettes thins the skin;
- microcracks and erosions form on the lips, invisible to the human eye;
- tobacco smoke successfully penetrates microcracks, leading to the development of a malignant process in tissues.
If a person has a cracked lip, wound or damage to the tissue in this area, the risk of developing cancer increases.
But not only cigarettes are dangerous for humans; smoking a pipe, chewing tobacco leaves and using nasvay can also have a detrimental effect on a person’s health.
The appearance of infectious processes on the lips, cracks, the development of inflammation in the tissues - all this is regarded as a precancerous condition. Although there may not be any atypical cells in the affected area. But only diagnostic measures can refute or confirm this fact.
Precancerous diseases of the lips
Lip cancer does not occur on healthy mucous membranes. Malignant neoplasms develop against the background of obligate or facultative precancerous diseases. Obligate precancerous diseases include:
- Abrasive precancerous cheilitis Manganotti;
- Warty precancer of the red border;
- Limited precancerous hyperkeratosis of the red border.
Facultative precancerous diseases with greater potential for malignancy are:
- Erosive and verrucous leukoplakia of the lip;
- Papilloma;
- Keratoacanthoma;
- Cutaneous horn.
Malignant neoplasms of the lip can develop against the background of optional precancerous diseases with less potential malignancy:
- Flat leukoplakia of the lip;
- Chronic ulcers;
- Ulcerative and hyperkeratotic forms of lupus erythematosus and lichen planus;
- Chronic cracked lips;
- Post-X-ray cheilitis;
- Meteorological and actinic cheilitis.
Background conditions that are precursors to lip cancer include scars after burns, trauma, surgery, and benign neoplasms.
Heilith Manganotti
Abrasive precancerous Manganotti cheilitis occurs in older people. Small, round erosions appear on the lips, which do not heal for a long time. They have a smooth surface of yellow-red or bright red color. In some cases, a bloody or serous crust appears on the surfaces of erosions. If you remove it, the opened wound bleeds a little. Touching erosions does not cause pain. Once erosion appears, it does not heal for several weeks or months. After disappearing, soon enough new erosions appear in their place or nearby.
Manganotti cheilitis is diagnosed by external examination and questioning of the patient. This disease has symptoms similar to those of herpes, leukoplakia, lichen planus or lupus erythematosus. For differential diagnosis, oncologists scrape the affected area of the lip and send it for a thorough histological examination. This scraping makes it possible to detect emerging cancer cells in a timely manner and prevent the development of a malignant neoplasm of the lip.
Leukoplakia and lip hyperkeratosis
Leukoplakia of the lip is a lesion of the mucous membranes with keratinization of the epithelial tissues. Unfavorable factors that contribute to the development of leukoplakia may be alcohol abuse, smoking and eating very spicy foods. Leukoplakias of the lower lip most often develop in the mucous membranes at the corners of the mouth.
Hyperkeratosis of the lips appears as a limited area from 0.2 to 1 cm in diameter. Its surface is smooth, covered with thin, tightly packed grayish-white scales. Scraping cannot remove them.
If the ball in your mouth does not cause discomfort
The color of the bubble will help the doctor make a diagnosis. A white lump on the gum indicates the presence of exostosis or purulent exudate. A red or bloody ball indicates the development of inflammation. If the growth matches the shade of the tissue, it is the initial stage of epulis, flux, or a malignant tumor. When the tumor does not hurt, this indicates the presence of one of the pathologies:
A fistula is a white ball on soft tissues that appears under or on a tooth. There is a hole on the surface for the release of pus. If, when pressed, suppuration flows out of the bladder, the patient does not feel pain. If the hole is closed with pus or bloody clots, the patient will experience discomfort with any impact.
A fistula is often formed due to advanced periodontitis, accompanied by periodontal hyperplasia. Overgrown tissue is good soil for the proliferation of microorganisms. In this case, the patient urgently needs treatment for periodontitis.
In the absence of therapy, the fistula enters a chronic stage, which can only be eliminated through surgical treatment. The progression of the disease must not be allowed, otherwise you may lose healthy molars.
Hematoma is a round lump on the inner surface of the cheek. Sometimes it occurs in the form of a dark bluish swelling on top of the gums. Blood accumulates in or around the root of the molar. The mucous membrane grows, the patient experiences discomfort and cannot completely close the jaw. The main reasons: consequences of filling or tooth extraction, gum damage, poor blood clotting.
Hematomas are generally not dangerous. Processes take place in the body through which soft tissues are cleared of bloody clots. After some time, the bubble disappears, but if the seal remains, you need to visit a dental clinic.
Exostosis is a hard blister that is an abnormality in which the bones protrude and protrude from the jaw. Gradually, the lump increases in volume, which causes discomfort and pain. Exostosis can be provoked by various reasons:
- jaw damage;
- heredity;
- congenital disorders;
- tissue diseases after molar removal.
An examination by a dentist or an x-ray will help detect the disease. The formation will need to be removed if the development of a malignant tumor is suspected.
Epulis is a pedunculated bubble in the form of a mushroom-shaped growth on the periodontium. The tumor may be the same color as the gums or red. The reasons causing the development of pathology include:
- improper filling of the molar or too large a filling;
- dental plaque, stone;
- jaw damage;
- malocclusion;
- hormonal imbalance;
- poor prosthetic material or incorrect prosthetics.
The symptoms of epulis resemble gingivitis; for diagnosis, the dentist prescribes radiography and histology to the patient. With their help, the degree of destruction of bone tissue at the site of the epulis lesion is determined. Mostly, pathology occurs in children during the growth of primary molars and in women.
Papilloma or fibroma is a bubble on the gum, sometimes a benign formation that does not pose a threat to the health or life of the patient. They are formed in people of different genders and ages. Predisposing factors to the appearance of a lump can be: damage to the mucosa, stress, systemic pathologies, heredity.
Papilloma is an enlargement of the papillary layer of skin. The bubble grows gradually, but with reduced immunity, systemic pathology, or stress, growth accelerates, but without turning into a malignant tumor. A papilloma neoplasm looks like a smooth, soft lump on the mucous membrane of a white or pink shade on a thin stalk.
Papilloma often does not create any discomfort. But after some time it may increase in size. You should consult a dentist and get tested.
Symptoms of lip cancer
There are local and general signs of lip cancer. Local symptoms of a malignant neoplasm can often be seen on the lower lip. When the pathological process is located on the mucous membrane of the lips, facing the vestibule of the mouth, the tumor has a pronounced malignancy. General signs of lip cancer can develop if the tumor is not detected in a timely manner and treated inadequately in the later stages of cancer.
First symptoms
The first signs of lip cancer usually go unnoticed. First, you can determine the enlargement of the mental lymph nodes. You can notice this by feeling the lower jaw. The next early sign of lip cancer is a swelling of a dense consistency. Itching occurs in it. This neoplasm is usually mistaken for a herpetic rash.
A small ulcer with a crust forms in the center of the swelling, which does not cause pain. If it is removed, the patient feels quite severe pain, and upon closer inspection, he may find a bleeding base, which is formed by tubercles.
Local signs of tumor
Symptoms of lip cancer are:
- Dyskeratosis of the lips;
- Papilloma;
- Erosion;
- Cheilitis.
In most cases, dyskateriosis looks like cracks and ulcers. The erosions are covered with a crust and resemble herpes in appearance, but, unlike it, they do not heal after a certain period of time. Some patients have no ulcers or erosions. Instead, a small compaction appears, which over time grows and becomes covered with a crust.
On the red border of the lower lip, away from the midline, a patch or formation may appear that protrudes above the surface. An erosion or ulcer with a granular surface and a roll-like edge forms in the center of the tumor. The formation has a dense consistency and gradually increases in size, eventually acquiring an irregular shape. Its boundaries are unclear.
Exophytic lip cancer predominantly develops from a warty form of productive diffuse dyskeratosis of papilloma. With exophytic growth, the tumor has a dense consistency, often covered with flat scales. Endophytic growth of a cancerous tumor is characterized by the formation of an ulcer with uneven, dense edges. It often appears against the background of destructive dyskeratosis, quickly infiltrates the soft tissues of the lip and is prone to metastasis.
Symptoms of the disease should be a signal to immediately contact oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital. Lip cancer, treatment of which is started on time, is completely cured in 90% of cases.
When should a malignant process be suspected?
A long-term pathological process on the skin of the lip without a tendency to cure with active therapeutic measures should always raise suspicion that it is of poor quality. If the “spot” does not respond to local treatment and increases in size, you should immediately consult an oncologist.
The appearance of ulcerations and bleeding, or any thickening where there used to be soft skin, should be alarming. These symptoms can be either single or in combination, but even with a single symptom, the lack of treatment result within 3 weeks can be regarded as a bad sign, which can only be “clarified” by a biopsy of the skin defect. And the sooner it is done, the better.
Stages
Currently, the generally accepted classification of lip cancer is TNM (T-size of the tumor, N-damage to the lymph nodes, M-metastases). Based on the size of the tumor, there are 4 stages of lip cancer.
Table 1. Stages of lip cancer
| Stage | Tumor size |
| T1 | Less than or equal to 2cm |
| T2 | More than 2-4cm |
| T3 | More than 4cm |
| T4a | The tumor grows into the cortical layer of the bone, tongue muscles, maxillary sinus and skin |
| Т4в | The tumor grows in the bed of the masseter muscle, the pterygoid process, the internal carotid artery and the base of the skull |
If on the affected side there are single enlarged lymph nodes, the size of which is less than 3 cm, this is stage N1 lip cancer. At stage N2, enlarged lymph nodes are detected on the affected side, the diameter of which is more than 3 cm. If the patient has single enlarged lymph nodes on the affected side measuring 3-6 cm in size, this is stage N2a of lip cancer. At stage N2, oncologists determine multiple metastases to the lymph nodes. Their size is equal to or greater than 6cm. In the presence of bilateral metastases in the lymph nodes measuring 6 centimeters, they speak of the N2c stage of lip cancer. If the diameter of the lymph nodes exceeds 6 cm, this is stage N3 of the disease.
In the absence of distant metastases, oncologists determine stage M0 of lip cancer, if there are distant metastases - M1, in the case of distant metastases that cannot be assessed - MX. The diagnosis of “early stage lip cancer” is made in the presence of a tumor less than or equal to 2 cm, the presence of single enlarged lymph nodes less than 3 cm on the affected side and the absence of distant metastases. This is T1 N1 M0.
Prognosis and survival
It is difficult to make a prognosis for oncology, but as for lip tumors, the prognosis is conditionally considered favorable.
| If the pathological process is at the initial stage of development (stage 1-2): | The survival rate for patients is good and ranges from 97-100%. |
| If cancer develops and metastases appear: | The survival rate decreases and is about 85% if the tumor can be surgically removed. |
| In severe condition, when the cancer reaches stage 4: | The survival rate of patients decreases and amounts to 55%. |
Much depends on the individual characteristics of the body. But lip tumors develop slowly, and the survival rate decreases when metastases appear. They destroy lymph nodes and jaw bones.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, such complications can be avoided.
Diagnosis of a tumor by a doctor in a hospital
What does lip cancer look like? It could be a small ulcer or a widespread tumor. Doctors at the Oncology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital make a diagnosis of lip cancer based on the patient’s complaints, the results of an external examination and additional studies. The oncologist carefully examines and palpates the lips, cheeks, gums and regional lymph nodes. When examining the red border of the lips, skin and mucous membrane, use a magnifying glass.
How to identify lip cancer? Further examination is carried out using instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound examination;
- X-rays of the lower jaw;
- Panoramic tomography;
- Cytological examination of material obtained by taking fingerprint smears from the surface of the ulcer or histological examination of tissue obtained during a biopsy.
For lip cancer with lymphatic metastasis, a biopsy of the lymph nodes is performed. To exclude hematogenous metastases, chest X-ray and ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs are used. When the diagnosis of lip cancer is confirmed, an X-ray examination of the chest organs, general clinical and laboratory examination (electrocardiography, blood and urine tests) are performed.
A PET-CT study (positron emission computed tomography) is prescribed for the following purposes:
- Determining the stage of lip cancer;
- Assessment of response to treatment;
- Detection of disease relapse during the observation period.
PET-CT is an innovative method that combines the capabilities of computer technology and radiology. At the Yusupov Hospital, it is used not only to diagnose lip cancer, but also to monitor tumor development and evaluate the outcome of treatment. Thanks to PET-CT, radiologists have the opportunity to very accurately carry out radiation treatment, significantly reduce the irradiation area, and minimize the impact on healthy organs and tissues.
In many cases, the use of PET-CT excludes a number of additional studies in the future. This allows patients of the Yusupov Hospital to save time and money. The issue of the need to use this method is decided individually for a specific patient at a meeting of the expert council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category. A comprehensive examination of patients using the latest diagnostic equipment, the use of modern methods of performing laboratory tests using high-quality reagents allows oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital to obtain reliable results and provide adequate therapy for lip cancer at an early stage.
Diagnostics
External signs of lip cancer, as a rule, are not enough to accurately determine the diagnosis, so the oncologist prescribes a series of laboratory and instrumental tests for the patient.
- A smear or scraping from the surface of the ulcer to perform a cytological analysis of cells and determine the type of cancer.
- Tissue biopsy followed by histological examination of the removed sample to confirm malignant changes.
- Ultrasound of the neck to identify affected lymph nodes.
- X-ray of the lower jaw, chest to identify metastases or ensure their absence.
- CT scan of the facial skeleton to detect metastases in them.
Attention!
You can receive free medical care at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) under the program of State guarantees of compulsory medical insurance (Compulsory health insurance) and high-tech medical care.
To find out more, please call +7, or you can read more details here...
Treatment of lip cancer
How to treat lip cancer? When treating the disease, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital take into account many different factors: the patient’s age, histological type of tumor, features of the spread of the tumor. Doctors at the Oncology Clinic provide multidisciplinary treatment for lip cancer:
- Surgical interventions;
- Radiotherapy;
- Chemotherapy.
Regardless of the chosen technique, they affect the lesion or tumor, areas of regional metastasis. For grades I and II of lip cancer, radiation treatment is performed, which includes external radiotherapy and surgery.
Treatment in the initial stages
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lower lip is a common complex tumor process. Its treatment consists of two stages: removal of the main focus and the fight against metastases that have spread to neighboring tissues and organs. Radiation treatment can suppress the development of a tumor focus. The radiologist selects the method of radiation therapy individually, depending on the size of the tumor, stage of the disease, and age of the patient.
Removal using the Krail method
In the initial stage of the tumor, surgeons perform a wedge-shaped excision of the entire thickness of the lip under local anesthesia. In order to remove a defect on the lip, plastic surgery is performed - skin flaps are transferred from the patient's cheek. Removal of the lesion is performed using the Krail technique. The operation is performed at the first and second stages of lip cancer, when the tumor has not spread to nearby tissues. Surgical excision of carcinoma makes sense in the absence of metastases.
The decision to remove a lymph node is made by an oncologist surgeon if the primary tumor process has already been cured or if the lymph node is removed along with the removal of the main lesion. In some cases, surgeons remove the primary cancerous tumor, the affected lymph nodes and the vessels that connect them. The scope of the operation is determined collectively by the clinic's oncologists.
Due to the fact that metastasis can occur in a cross way, the lymphatic apparatus of the suprahyoid region on the left and right is removed. If the oncologist sees that there are cancer metastases in certain lymph nodes, he decides to remove them, and those that are located along the lymph outflow.
Treatment tactics for lip cancer depend on the stage of the disease:
- Preventive surgery at stages I and II of lip cancer is carried out exclusively in cases where it is not possible to control the dynamics of the disease and there are unfavorable prognoses regarding the spread of cancer;
- At stage III, in the absence of metastases, treatment is carried out using a combined effect on the lesion and adjacent areas;
- In case of spread of cancer cells and the presence of single metastases in the lymph nodes, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform combined treatment of lip cancer with subsequent surgery, plastic surgery and surgical correction of the lips;
- In stage IVC, palliative chemoradiotherapy is performed.
Candidates and doctors of medical sciences use innovative methods of treating lip cancer. The presence of modern equipment and competent medical personnel who are attentive to all the wishes of patients allows us to achieve good results in the treatment of lip cancer for many years. Lip cancer, treated in the early stages, is cured in 97-100% of cases. At stage III, 67-80% of patients can be cured. In the fourth stage of cancer and repeated relapses, complete recovery occurs in 55% of cases.
How to treat
Recommendations for the treatment of lip cancer are based not on clinical studies, as is customary for the vast majority of malignant tumors, but on decades of practical experience. It so happens that, due to the rarity of the disease, no randomized clinical trials have been conducted anywhere in the world. The choice of treatment is determined by the size of the primary tumor and, of course, the expected cosmetic defect. Even a small lip tumor changes a person’s quality of life much more than all other cancers. It is too noticeable, as is the scar that remains after its removal.
When treating cancer, it is important that there are no malignant cells in the surgical wound, so the tumor must be retreated in all directions. The lip itself is small, so even with a tumor measuring 5 mm, a postoperative scar of several centimeters will remain. Only after treatment of very small and superficial tumors do minor defects remain. Unfortunately, it is impossible to treat the patient in such a way that there are no defects left at all, therefore, when choosing a treatment method, they are guided by the least functional deformation and the minimum undesirable aesthetic result.
In this situation, the determining factor will be the decision of the patient who chooses the treatment option that will result in the least severe psychological consequences for him. Surgical treatment is preferable based on results, but radiation therapy, if possible, will leave fewer “traces.” With a large and superficial tumor of the lower lip, for example, a good result is likely after radiation therapy, which cannot be achieved if the cancer grows in the jaw bone. In this situation, the treatment option would be surgery.
Squamous cell skin cancer is very responsive to chemotherapy, but how lip cancer will react to cytostatics in each specific case can only be assumed, since serious and reliable studies of the effectiveness of drug therapy in this localization have not been conducted. However, for large inoperable tumors and relapses after excision, combined chemoradiation treatment has a good effect. If there are metastases to the nearest lymph nodes, the question of radical removal of regional lymphatic collectors with subcutaneous fat is raised.
Treatment of cancer in this location is purely individual, because the reconstructive possibilities of restoring lost lip volume and microsurgical leveling of the postoperative defect tend to zero. However, in most cases the patient has every chance of recovery. In case of lip cancer, it is very important to get to a good oncologist surgeon in time.
Other materials:
Alternative medicine in cancer treatment
Cancer recurrence
New perspectives for personalized cancer therapy
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Prevention
There are primary and secondary prevention of lip cancer. Oncologists recommend:
- Take precautions when exposed to the sun (wear a wide-brimmed hat);
- Stop smoking pipes and cigarettes;
- Maintain oral hygiene;
- Change working conditions;
- Do not drink strong alcoholic drinks.
For persons prone to dyskeratosis of the lips and cheilitis, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct an annual preventive examination. Secondary prevention of lip cancer consists of regular dental treatment at the dentist, surgical intervention in the presence of dyskeratosis and cheilitis.
Causes of hematoma formation on the oral mucosa
The general scheme of hematoma formation is as follows: a rupture of a vessel causes the leakage of a certain amount of blood, followed by its compaction and the appearance of a blood clot. A bubble forms, noticeable on the smooth surface of the mucosa due to its dark coloring and relief. Often a similar picture can be observed during teething, when the gums bleed and become inflamed. The formation of multiple small hematomas, covering the entire surface of the mucous membrane in the mouth with unattractive dark spots, looks very unpleasant for the patient. But don’t panic if you suspect you have a serious illness. As practice shows, most of these phenomena occur due to mechanical trauma to the mucous membrane. But there are exceptions when the symptom indicates:
- allergic reaction;
- chronic injury;
- consequences of stressful situations;
- burns or cuts to the mucous membrane.
There have also been cases when multiple hematomas in the oral cavity are signs of:
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypertension;
- renal failure;
- complex types of stomatitis;
- blood diseases;
- vitamin deficiency, which causes fragility of blood vessels.
The exact cause and stage of formation of the pathology can only be determined after a thorough examination and diagnosis. For this reason, you should not self-medicate, so as not to further injure damaged tissues.
Lip cancer: treatment at Yusupov Hospital
Effective treatment of lip cancer in Moscow is carried out by doctors from the oncology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital. Oncologists have many years of experience in treating malignant neoplasms of the lip. Surgeons are fluent in surgical techniques. The cost of surgery is lower than in other oncology clinics in Moscow, despite the high level of qualifications of doctors and modern equipment.
Radiotherapy is carried out using modern radiation installations from leading European and American manufacturers. In order to undergo a course of effective treatment for lip cancer at an affordable price, call the Yusupov Hospital. After the operation, surgeons at the Oncology Clinic perform lip plastic surgery using innovative surgical techniques.