The scrotum is located in the perineum between the penis and the anus and is considered the most delicate and painful organ in the male body. For some reason, men protect this place only from blows, forgetting about dangerous urological pathologies that can cause many painful minutes, even if the organ was not injured. Among them, it is worth highlighting scrotal atheromas - cystic formations in the hairline area.
What is atheroma and atheromatosis
The content of the article
The scrotum is a male reproductive organ, which is a skin-muscular sac in which the testicles are located. The peculiarity of the organ is that it is covered with hair.
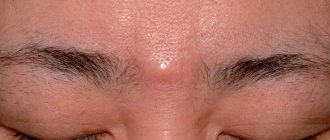
Atheroma is a common subcutaneous formation that is formed as a result of blockage of the sebaceous gland duct located in the hair follicle. The secretion (discharge) of the sebaceous gland accumulates in the pouch, causing stretching of the walls, which visually manifests itself in the form of a dense round formation that can be movable when pressed. If the mouth of the duct is not completely closed, the atheroma may look like a large blackhead.
Such formations most often occur in the area of dense hair, including in women, but in men atheromas are often observed in the scrotum area. This is due to the large number of sweat glands located in this area and poor air access due to tight clothing.
Being benign cystic neoplasms, atheromas often appear in the form of multiple structures, which in medicine is called atheromatosis.
Causes of papillomas
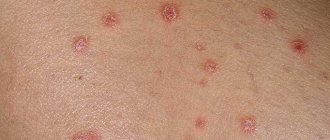
The cause of the appearance of papillomas in intimate places is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which circulates in the blood of almost every man and woman, starting from adolescence.
According to WHO, 80-90% of the population is infected with HPV. Most often, papillomas occur in young people who have a large number of sexual partners. Genital-anal papillomas are typical manifestations of human papillomavirus infection. In 90% of cases they are caused by the sixth and eleventh types of HPV.
In the daily life of every person, the following exposures increase the risk of infection:
- smoking;
- stress;
- using other people's hygiene products;
- visiting baths, saunas;
- shaking hands with carriers at the acute stage;
- decreased immunity.
Globally, the spread of HPV is influenced by many factors, including socioeconomic, medical, hygienic and geographic. The virus can stay in the body for years without showing itself. Its activation is provoked by a weakening of the protective forces of the immune system, which entails the appearance of papillomas in intimate places, both in women and men.
Pregnancy, hormonal imbalances, metabolic disorders, acute viral infections, long-term chronic diseases, poor nutrition and lack of sleep can also trigger the growth of papillomas in intimate places.
Reasons for the formation of atheroma of the scrotum
Statistics say that about 20% of the stronger sex face the problem of atheromatosis of the scrotum, which is explained by the high content of the hormone testosterone in the male body, which is responsible for the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
In addition to the hormonal factor, there are several other reasons that cause the appearance of such an unpleasant neoplasm as atheroma. Most often, a cyst is formed due to:
- mechanical injury to the tissues of the scrotum or excessive friction of too tight underwear;
- inflammation in the area of the hair follicle;
- failure to comply with general hygiene rules;
- increased sweating in the scrotum area;
- spending a long time in trousers while sitting, especially if the room is hot or the car uses heated seats.
Pathology is diagnosed most often in young patients whose age does not exceed 35 years.
Pimples on the penis in a child
This alarming symptom in a child may indicate simple heat rash. During the hot season, due to increased sweating, children's delicate skin becomes irritated, causing small pimples to appear.
A more dangerous cause is intestinal mycosis. This manifestation is also characteristic of a very contagious disease - frequency. Only a doctor can identify the specific cause, so first of all the child must be shown to a specialist.
Symptoms of atheroma of the scrotum
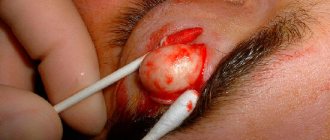
Initially, atheroma of the scrotum is defined as a small compaction in this area, which may be accompanied by minor pain. In the absence of rational treatment, the risk of formation of adjacent atheromas increases significantly, which ultimately leads to the formation of multiple cysts.
The consistency of the neoplasm is characterized as dense or jelly-like. Quite often, a pigmented point in the center of the compaction becomes a typical symptom of atheroma of the scrotum. As for mobility, an atheromatous neoplasm can be either fixed (linked to epidermal (skin) structures) or freely mobile.
The danger of scrotal atheroma lies in the likelihood of severe inflammation and infection in the area of stagnation of the sebaceous secretion of the gland. As a result, suppuration may develop, which is manifested by redness and intense pain. One of the unfavorable consequences of atheroma is scrotal abscess. This condition requires immediate surgery. If an abscess ruptures, you can lose your testicles.
Causes of white plaque
The causes of white plaque on the penis are classified into three groups:
- physiological. Associated with the peculiarities of the secretion of tyson glands located under the foreskin. The problem is aggravated by the lack of proper hygienic care of the genitals;
- non-infectious (endogenous). Caused by disruption of internal organs. Whitish accumulations on the penis are a concomitant symptom of chronic diseases or a sign of activation of opportunistic microorganisms that are part of the natural microflora of the body;
- infectious (exogenous). These are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
In the first case, it is enough for a man to get medical advice. To eliminate other causes, proper treatment is required.
Diagnosis and treatment of atheroma of the scrotum
Diagnosis of atheroma is usually limited to visual and physical (palpation) examination, while treatment of atheroma requires mandatory removal of the cystic neoplasm.
In medical practice, several methods are used to eliminate atheroma of the scrotum:
- surgical opening and cleaning;
- electrocoagulation using an electric loop;
- laser destruction (destruction);
- Radio wave excision is the latest method using a radio wave knife.
Laser and radio wave treatment make it possible to remove atheroma very quickly without affecting healthy tissue. In addition, after using these devices there is no bleeding, since both the laser and radio waves seal the vessels. There is no residue left after removal of tumors or scars—everything heals very quickly. Since the urologist applies anesthesia, the patient does not feel anything.
What does a white spot on the penis look like?
For different diseases, white spots on the penis look different:
- vitiligo - spots of different sizes with clear boundaries, irregular shape, can merge, are multiple, do not rise above the skin level
- Setton's nevus - looks the same as vitiligo, only there is a mole in the center (sometimes the mole disappears, but the depigmented spot remains)
- psoriasis – silvery, dense plaques with small scales
- scars - may be denser than the surrounding skin, rise above it or fall below the level
- lichen sclerosus - multiple small (no more than 1.5 cm) white papules rising above the skin level (can merge into irregularly shaped plaques)
Relapse Prevention
To prevent the problem from recurring, you need to get tested for hormones - it is especially important to measure testosterone and undergo treatment to normalize hormonal levels. You also need to constantly take care of the cleanliness of your genitals and wear loose cotton underwear. This is enough to avoid relapse and another operation on the scrotum.
The choice of the optimal technique, as well as the appropriateness of a particular method of pain relief, is determined by the doctor. Medical offers the services of a highly qualified specialist in the field of urology and andrology. Urologists will perform a full diagnosis and treatment of atheroma of the scrotum. Removal of any tumors is carried out with a laser or radio knife.
Treatment
To the question of how to treat papillomas in intimate places , modern medicine gives a clear answer: they need to be removed. Destruction of benign neoplasms can be carried out using various methods:
- electrocoagulation – exposure to high frequency current;
- cryodestruction - removal using cold treatment;
- laser removal – layer-by-layer treatment with laser radiation;
- chemical destruction - using special chemical solutions.
Classic surgical removal is also an option.
A specific scheme for how to completely and safely remove papillomas in intimate places is prescribed by a specialist in accordance with the localization of the process, the severity of the course, and concomitant diseases.
An important aspect of treating papillomas in intimate places is changing lifestyle and strengthening the immune system. An integrated approach avoids the emergence of new formations.
How is inflammatory diseases of the scrotum organs diagnosed?
The basis for diagnosing diseases of the testicle, its epididymis and spermatic cord is a physical examination (primarily palpation or palpation). The leading auxiliary methods are diaphanoscopy and ultrasound examination of the scrotum. All of these methods are completely painless, and their correct use and proper interpretation allow an accurate diagnosis to be made in the vast majority of cases. In recent years, ultrasound of the scrotum, as a much more informative and accurate method, has practically replaced diaphanoscopy.
To establish the causes of epididymitis, orchitis and orchiepididymitis, a general analysis and culture of urine for microflora are required, and sometimes sperm (ejaculate) is analyzed for the presence of various infections. Tests are performed for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases. If there is suspicion, an examination is carried out for the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the urine and/or ejaculate. If a testicular tumor is suspected, blood tests are performed for the appropriate tumor markers. Only a correctly constructed set of diagnostic measures makes it possible to establish an accurate diagnosis and carry out the most effective treatment. Be sure to contact a urologist!
Diagnosis of testicular cyst in men
It is not possible to diagnose a testicular cyst based on the patient’s complaints. At the appointment, the urologist palpates the scrotum and, if there is a mass formation, prescribes an ultrasound examination. During an ultrasound, the doctor who conducts the examination specifies the type of mass formation, location and size of the cyst.
Simple cysts have several characteristic ultrasound signs:
- No long-range gain effect;
- They are anechoic structures with thin-walled membranes;
- They have good echo conductivity.
With color Doppler ultrasound, there is no blood flow in them. The cyst and spermatocele do not have distinctive features on ultrasound examination. Some cysts are septated or multi-chambered. Sometimes functional diagnostic doctors find bilateral cystic lesions of the epididymis during ultrasonographic examination.
Sometimes difficulties arise when examining small cysts. In such situations, the sonologist palpates the cyst with one hand, and visualizes the cystic formation with a sensor with the other. When assessing ultrasound data, doctors sometimes encounter situations, the incorrect interpretation of which leads to an unjustified expansion of indications for surgical treatment. Thus, with anomalies in the development of the epididymis (retracted epididymis), ligamentous apparatus or sinuses of the epididymis, the fluid normally contained in the scrotal cavity can simulate a cyst.
Diaphanoscopy is a method of diagnosing a cyst using a special flashlight. The cyst has a pink color when illuminated, which is a pathognomonic diagnostic sign. Diaphanoscopy allows you to differentiate the cyst from other testicular formations and assess the amount of fluid in its cavity.
In diagnostically difficult cases, magnetic resonance imaging is performed. This research method provides a layer-by-layer analysis of testicular tissue. Used for differential diagnosis of testicular cysts and malignant neoplasms of the male reproductive gland. After receiving the examination results, urologists at the Yusupov Hospital collectively determine the patient’s treatment tactics.
What is the prevention of inflammatory diseases of the scrotal organs and their complications?
To prevent the diseases described above and their complications, you should, first of all, avoid contracting sexually transmitted infections and treat them in a timely manner, not be exposed to sudden hypothermia, and protect the scrotum from injury. You should give preference to tight-fitting panties and dress warmly in winter. If you have the above-described signs of epididymitis, orchitis and orchiepididymitis, you should urgently consult a urologist!
| Hello. Six months ago, a nagging pain arose in the scrotum. I did an ultrasound and discovered a varicocele on the left, the veins were dilated to 3.9 mm and a fluid formation of the appendage on the right was 4.2 mm. I did a prostate ultrasound - dilatation of the veins of the paroprastotic plexus on the left by 3.5 mm. The pain does not go away what should I do thanks in advance Look at other questions or ask your own on the topic: Pain in the scrotum |
What is the treatment for inflammatory diseases of the scrotum?
Treatment of epididymitis, orchitis, orchiepididymitis and deferentitis is carried out primarily with antibiotics, since their main cause is various infections. The choice of antibiotic for an acute inflammatory process is carried out empirically, taking into account the known age-related characteristics of the causative infections. Upon receipt of the results of microbiological studies and analysis of the sensitivity of the isolated microflora to antibiotics, it is possible to adjust antibiotic therapy, change its duration, dosages of drugs, and sometimes the drugs themselves and their combinations.
Along with antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin, diclofenac, Celebrex, etc.) are prescribed in order to reduce inflammatory swelling, pain and quickly reverse the development of inflammatory changes. For severe pain, a blockade of the spermatic cord with a local anesthetic (lidocaine, prilocaine, marcaine) is used, which significantly reduces pain. All patients are recommended to wear tight panties (swimming trunks) that tighten the scrotum during treatment. This promotes better blood and lymph flow in the scrotum and accelerates the reverse development of inflammation.
In the presence of ulcers or abscesses of the testicle and its epididymis, as well as in chronic recurrent epididymitis, which is difficult to treat, in the case of testicular tuberculosis, surgical treatment is used. It may involve opening and draining abscesses, partial or complete removal of the testicle and/or its epididymis. The use of various methods of physiotherapy for inflammatory diseases of the scrotal organs has not proven its effectiveness in correctly conducted scientific studies and is not included in the international standards for the treatment of epididymitis, orchitis and orchiepididymitis. In this regard, we do not use physiotherapeutic methods for treating these diseases in our practice.
Treatment of testicular cysts in men
Treatment of testicular cysts in men is carried out in cases where the cystic formation increases to a size at which discomfort and symptoms of the disease appear. Conservative treatment of testicular cysts in men is ineffective. Urologists first perform a puncture of the cyst, followed by suction of fluid from the cystic cavity. The resulting contents are sent to a cytology laboratory for examination under a microscope.
Sclerotherapy is a procedure for enucleating a cyst with the introduction of a chemical substance into the cavity that “glues” the walls of the cavity. This method of treating testicular cysts in men can be complicated by impaired patency of the spermatic cord, which subsequently leads to infertility. Therefore, urologists at the Yusupov Hospital offer this method of treatment to patients who do not plan to have children in the future.
Consequences
If testicular cysts in men are not treated, the following complications may develop:
- A purulent inflammatory process - develops when the scrotum becomes overcooled or becomes infected. More often it is one-sided, so the man’s one half of the scrotum becomes enlarged, redness, severe pain, and swelling appear;
- Rupture of the spermatic cord cyst - the contents enter the scrotum, causing an inflammatory process;
- Infertility - as the size of the cyst increases, it compresses the vas deferens, disrupting the passage of sperm. Due to impaired microcirculation, spermatogenesis in the testicle may be disrupted;
- Decreased potency - when the cyst grows and reaches a size greater than 3 cm, blood vessels and nerves are compressed, which is accompanied by pain and erectile dysfunction.
In order to prevent the formation of testicular cysts in men, one should avoid trauma to the perineum, hypothermia or overheating of the genitourinary organs, and promptly treat inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system: urethritis, prostatitis, inflammation of the epididymis. Men should perform a self-examination, which includes examining and palpating the scrotum for masses. You need to visit a urologist once a year. diagnostics: examine the scrotum for neoplasms. Timely detection of a testicular cyst will allow it to be treated quickly and effectively, avoid complications and improve the prognosis after treatment.
For timely prevention of infertility, it is recommended to conduct an ultrasound examination of the organs located in the scrotum in boys. In order to avoid the unpleasant consequences of a cyst, if you experience any unpleasant sensations in the testicle, make an appointment by phone at the Yusupov Hospital.