Hirsutism
Hirsutism is the appearance of excessive body hair in women. Dark, strong hair grows on the chin, cheeks, neck, abdomen, lumbar region, and sometimes also on the lower limbs and feet.
Hirsutism
Hirsutism is a symptom of androgen excess. Less commonly, this indicates excessive sensitivity of the hair follicles to the action of androgens. The condition can also be caused by taking certain medications and stimulants.
Melatonin
Melatonin, known as the sleep hormone, affects many other functions of the body. It is involved in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine and immune systems, and is responsible for the normal functioning of brain cells and protection against free radicals. Yes, melatonin is a powerful antioxidant, the level of which affects how the skin and other organs can independently resist free radicals that destroy cells. And that is not all. “The action of melatonin affects fat burning during sleep,” says Elena Shatkar. – The hormone is produced during sleep in its deepest phase – from about 12 o’clock at night to 4 o’clock in the morning. The main essential condition for its development is that a person must sleep in a dark room. The criterion of darkness can be the fact that it is impossible to see your outstretched hand. Any light is the enemy of melatonin, including the dial of an electronic alarm clock, not to mention the screen of a smartphone, computer, TV or street lamp. A decrease in melatonin levels is a signal to other organs and glands that it is time to rest. Women's ovaries stop working, estrogen levels drop significantly, and menopause occurs. In men, the amount of testosterone hormone decreases significantly.” Thus, a nocturnal lifestyle is directly related not only to the deterioration of the functioning of the entire body, but also to excess weight and rapid aging of the skin.
Beauty of the figure
The pleasant roundness of the figure that men like so much is formed under the influence of the hormone estrogen. In addition to the production of estrogen hormones by the gonads, they can be synthesized in fat deposits. Therefore, the balance of hormones with significant weight loss or weight gain can change noticeably.
Hormonal weight gain, which often occurs in women, occurs under the influence of excess progesterone. Weight loss under the influence of endocrine substances is also possible. This ability has been demonstrated by dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), which helps the body cope with fat deposits.
Diabetic dermatopathy
Diabetic dermopathy (called diabetic shin spots) are painless, non-pruritic, light brown maculopapular lesions. Over time, they disappear, leaving brownish discolorations and atrophic scars.
Skin problems as a symptom of diabetes include:
- dryness;
- itching;
- recurrent mycoses;
- delayed healing of even small wounds;
- may be the first symptom of diabetes.
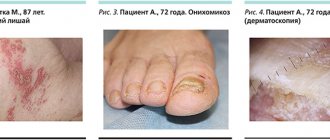
Mycosis
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism – triiodothyronine, thyroxine and calcitonin
Other hormones that have a tremendous impact on the condition of the skin are triiodothyronine, thyroxine and calcitonin. A lack of these hormones leads to hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism usually manifests itself with symptoms such as:
- dry, scaly skin on knees and elbows;
- decreased tolerance to cold;
- fragility and hair loss.
An overactive thyroid gland, on the other hand, produces more hormones than needed. In this case, hyperthyroidism begins.
In turn, hyperthyroidism can manifest itself as:
- increased sweating;
- dermographism;
- redness of the skin of the face and neck.
What hormones need to be checked?
As we found out, a whole complex of biologically active substances is responsible for attractiveness and femininity. To assess the state of a woman’s hormonal levels, it is necessary to measure the following indicators in the blood:
- estradiol (E2) is the main hormone from the estrogen group;
- testosterone (total);
- LH (luteinizing hormone);
- FSH (follicle stimulating hormone);
- progesterone;
- prolactin;
- SHBG is a protein responsible for the transport of sex hormones to receptors distributed throughout the body;
- DHEA-S (dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate).
When should you check your hormone levels?
The following situations may be the reason for taking a blood test to assess hormonal levels:
- increased hair loss;
- acne on the face, décolleté or back, which is difficult to treat or reappears periodically;
- excess pigmentation on the skin;
- excess weight, which is difficult to correct with diets.
In addition, hormonal levels should be monitored if you notice the following manifestations:
- menstrual irregularities, too heavy or long menstrual bleeding or, conversely, very scanty;
- too vivid manifestations of premenstrual or menopausal syndrome (irritability, anxiety, insomnia, hot flashes, etc.);
- decreased libido.
As mentioned above, assessing the hormonal balance is very important during age-related changes in a woman’s body. An analysis of the level of hormones in the blood is required when:
- menopause;
- postmenopausal period.
How to find out your balance of female beauty hormones?
Proper maintenance of the balance of sex hormones allows you to maintain female beauty and health. Modern medicine has gained such a unique opportunity thanks to laboratory diagnostics.
The levels of all important hormones are determined using venous blood tests. A comprehensive analysis of sex hormones helps solve many problems in the field of dermatology and trichology (medical disciplines dealing with diseases of the skin and hair), gynecology, reproductive medicine and sexology, which were previously considered insoluble.
Using laboratory tests you can evaluate:
- hormone concentration in the blood;
- there is a connection between problems with appearance or health and hormonal levels;
- changes in the content of one or another hormone over time, fluctuations over a certain period of time (days, weeks, months);
- the effectiveness of the treatment.
Cortisol
Cortisol is commonly called the stress hormone, but it is involved in all metabolic processes - in case of stress, it is responsible for the instant mobilization of the body. If cortisol is in excess, it has a truly destructive effect on us. For example, carbohydrate metabolism and insulin production depend on its level, and its excess can lead to a typical redistribution of fat in the body. At the same time, the face, neck, and upper shoulder girdle become very plump, and the legs and pelvis lose weight disproportionately.
When cortisol levels increase, acne and flaking appear, the skin becomes oily and thin, and the risk of hyperpigmentation increases. Damage takes longer to heal and leaves behind scars and age spots. In addition, cortisol causes swelling, makes hair brittle, and can lead to seborrhea and even hair loss.
Cushing's syndrome
Primary hyperactivity of the adrenal cortex, Cushing's syndrome, is caused by excess cortisol. The most common symptoms are:
- abdominal obesity;
- stretch marks;
- redness of the facial skin;
- acne;
- hirsutism;
- tendency to bruise;
- swelling;
- muscle atrophy (especially in the limbs).
Excess cortisol, resulting from an overactive anterior pituitary gland, causes similar symptoms.