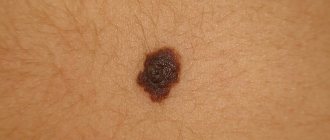
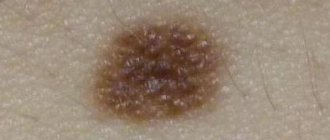
Symptoms of blue nevus
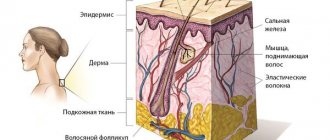
Blue nevus can appear in people of any age group, but most often it is first discovered in middle age. It usually does not cause patients any particular discomfort (except for a cosmetic defect when it is localized on the face and is large in size). Blue nevus has the following clinical characteristics:
- intradermal nodule;
- round, spindle-shaped or elliptical shape;
- light gray, dark blue, blue-black or blue color;
- uneven color;
- clear contours;
- smooth, hairless surface;
- the size rarely exceeds a centimeter (although there are blue nevi larger than 3 cm);
- protrudes slightly above the skin or does not rise above it at all;
- the consistency is elastic and dense;
- most often localized on the buttocks and limbs;
- can form on the mucous membranes of the mouth, vagina, and cervix.
Signs and symptoms
This benign patch appears on the skin at birth or in early childhood. For most people it is under 10 years of age. to size. If there is doubt about the diagnosis, rubbing the area causes the skin around the lesion to become red, while the lesion itself does not change color.[3] Often the spots are difficult to see against the patient's skin color, but if a sunburn develops, then the white area will stand out noticeably.[4] The affected area is lighter than normal skin, not due to loss of pigment, but due to narrowing of the blood vessels causing the area to become permanently pale. This blanching is a functional rather than a structural abnormality, which is thought to be caused by hypersensitivity to catecholamines.[5] Although the cutaneous vasculature appears normal histologically, the blood vessels in the nevus do not respond to the injection of vasodilators. It has been suggested that persistent pallor may represent a persistent localized adrenergic effect. vasoconstriction.[6] The results of a skin biopsy will be interpreted as normal, and only physiological examination can reveal a nevus as opposed to normal skin. Stroking the spot does not cause red highlights. Only normal skin will react with the characteristic erythematous response. Examination under a wooden lamp may also reveal a patch of anemic nevus, which would not stand out as a vitiligo patch.[7]
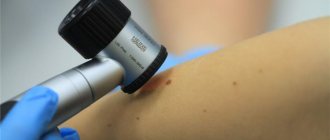
Diagnosis of blue nevus
In most cases, one visual examination by a dermatologist is sufficient to accurately verify the diagnosis. In unclear and controversial clinical cases, the following examination is recommended:
- dermatoscopy (under magnification, the boundaries, depth and structure of pigment formation are studied more carefully);
- siascopy (assessment of the structure and distribution of melanin);
- ultrasonography of the nevus (to exclude infiltrative growth of a malignant nevus);
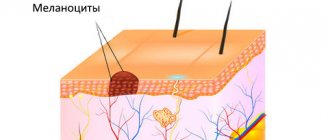
- histological examination of biopsy specimens (rarely) or surgical material (detects characteristic accumulations of melanocytes in the deep layers of the dermis; with a simple blue nevus, the cells are rich in melanin, and with a cellular nevus, islands of large cells with a small amount of pigment are observed);
- determination of tumor markers SU100 and TA90 (to exclude the development of melanoma).
Reasons for appearance
By its origin, this type of vascular nevus is congenital. Despite this nature of the etiology, in newborns this simple nevus is almost invisible and is better visualized at school age. Appears as a result of disturbances in the development and nervous innervation of blood vessels. The reasons that can lead to this condition are still completely unknown, but scientists and doctors identify a series of factors that can contribute to the appearance of this formation:
- genetic disorders and pathologies;
- the influence of various types of radiation on the body of a pregnant woman;
- effect on a pregnant woman of toxic substances (chemicals, nicotine, alcohol);
- infections of the genitourinary system in a pregnant woman;
- hormonal imbalances during pregnancy.
Treatment of blue nevus
As a rule, doctors choose a wait-and-see approach. Patients only need to visit a dermatologist or oncologist regularly for examination. Removal of a blue nevus is necessary only if localization is unsuccessful, causing permanent injury to the formation, and if a number of alarming signs appear:
- a significant increase in its value;
- color change;
- blurred contours;
- the appearance of itching or pain.
To remove a blue nevus use:
- electrocoagulation
- cryodestruction;
- laser;
- radio wave method;
- traditional surgical excision (the nevus is removed along with 5–8 mm of intact skin surrounding it and subcutaneous fat).
Helpful information
INFANTILE (INFANT) HEMANGIOMA
Infantile hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor that develops from endothelial tissue. It is characterized by the following periods of development:
- proliferation (growth) up to 6-8 months. child's age
- stabilization 8 – 12 months
- involution (regression) up to 5 – 10 years.
Diagnosis of infantile hemangiomas:
- Superficial infantile hemangiomas do not require special diagnostic measures, since they are diagnosed according to a specific clinical picture, however, to diagnose complex forms of hemangiomas (subcutaneous, combined, segmental), additional ultrasound examination with Dopplerography may be required to determine the nature of the blood flow, the volume of the subcutaneous part of the hemangioma and the presence feeding vessel(s). In some cases, an MRI or CT scan with contrast may be required (a CT scan without contrast is not informative)
Treatment of hemangiomas in children:
- conservative treatment: systemic therapy with beta-blockers, local lotions - the most modern, gentle method with a minimal likelihood of side effects, provided that parents strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations
- wait-and-see tactics
- cryodestruction – performed according to indications for small hemangiomas
- sclerotherapy – most effective against vascular and lymphatic malformations
- laser treatment – cosmetic removal of residual elements, telangiectasias.
- Close-focus X-ray therapy is one of the most outdated methods and is not recommended due to the large number of serious, irreversible side effects
- surgical treatment - indicated in the case of complex forms of large hemangiomas when drug treatment is ineffective
- steroid hormones – has a large number of side effects, can be used extremely rarely if other treatment methods are ineffective
- vincristine for kaposiform hemendothelioma, Kasabach-Merritt syndrome - segmental infantile hemangioma in combination with thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy
Treatment of infantile hemangioma with beta blockers:
- In 2008, the French doctor Lehaute-Labrese discovered the effect of propranolol on infant hemangiomas. Given the low risk of side effects and high effectiveness of treatment, beta-blocker therapy has become the “first line” in the treatment of IH. The exact mechanism of action of beta-blockers on IH is still unknown. The proposed mechanism is vasoconstriction, inhibition of angiogenesis, and stimulation of apoptosis.
- Therapy with beta-blockers can be carried out both locally, in the form of lotions, and systemically.
The treatment method is selected taking into account each specific clinical case, the type of hemangioma and its location, and the wishes of the parents are also taken into account.
PYOGENIC GRANULOMA
The formation, consisting of vascular tissue, is not of true bacterial origin and is not a true granuloma. Granuloma develops rapidly, often at the site of a recent injury (although the patient may not remember the injury), is usually less than 2 cm in diameter and may be a vascular or fibrotic reaction to injury. Education occurs with equal frequency in men and women of different ages.
The epidermis covering the formation is thin, and the formation is fragile, bleeds easily and does not fade when pressed. The base may be pedunculated and may be surrounded by a rim of epidermis.
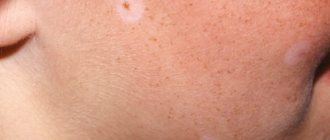
NEVUS OF UNNA
Nevus of Unna is a red birthmark on the skin of the face, back of the head and neck in newborns. Causes: expansion of capillaries on the scalp. Do not confuse nevus of Unna and hemangioma.
Symptoms:
- A pink or red spot on the skin of the nose, bridge of the nose, forehead, eyelids, neck and back of the head
- The spot is flat, does not rise above the skin, when pressed with a finger, the spot turns pale, parents note that when the child is restless and crying, the spot becomes brighter
- Treatment is not required, it goes away on its own by the age of 1-2 years, if with age, after 3-5 years, residual elements remain, laser correction with a vascular laser is possible.
When is it best to treat this pathology?
Since such a disease does not cause discomfort, does not progress and is not complicated in any way, but is simply a cosmetic defect, you can refrain from treatment. If the location of the nevus causes significant discomfort, for example, the presence of a spot on the face, you can resort to special methods of therapy. You can start treatment at any age, you just need to remember that in children tissue regenerates faster than in adults. Therefore, by starting treatment at an early age, the patient will recover faster and will be protected from possible psychological discomfort in the future.
Therapy methods
The only treatment for such a nevus is surgery. After using surgical methods, the resulting tissues are sent for histological examination to exclude the malignant nature of the formation. Among the treatment methods for this pathology are the following:
Treatment of anemic nevus is possible with various safe methods.
- Radiosurgery - tissue in the area of the spot is removed using radio waves. The appearance of postoperative scars with this method of treatment is quite rare.
- Laser surgery - used to treat small nevi. When using this technique, adjacent areas of the skin are not damaged and no traces of intervention remain.
- Cryodestruction involves the action of cold and “freezing” of the affected area.
- Electrocoagulation is the use of low frequency currents to remove a stain. After applying this treatment method, a small scar may remain at the site of the removed spot.
In addition, it is recommended to use cosmetic and pharmaceutical concealers. These are foundation creams, manganese peroxide, nut butter.
Traditional treatment methods
Traditional recipes do not get rid of the existing pathology, but they affect the color of the spot, making it much darker, bringing the shade of the spot closer to the color of the skin. For this, fresh rhubarb juice is used: it is applied to the affected area twice a day. Oil infusion of St. John's wort, alcohol tincture of walnut leaves and walnut shells also darken the skin. It is recommended to combine the use of oil infusion with sunbathing. The course of treatment is usually 20 days. In addition, anise oil helps darken stains.