What properties does azelaine peeling have?
Rye, wheat and barley contain azelaic acid. In the human body it is synthesized during lipid metabolism; industrial production is based on the oxidation of oleic or linoleic acid. Pharmacists and cosmetologists use potassium azeloyl diglycinate. This water-soluble compound, being an acid derivative, is chemically inert and has a strong brightening effect.
Azelaic acid is less active as an exfoliating agent compared to other organic acids, but it has a number of useful characteristics:
- powerful antimicrobial effect not only on surface pathogens, but also on microbes located in the hair follicles;
- highly effective against Staphylococcus epidermidis and propionic bacteria, which contribute to acne;
- a course of azeloin peels will significantly reduce the number of microbes that cause inflammatory processes;
- the anti-inflammatory effect extends to the deeper layers of the skin;
- good antioxidant properties;
- inhibition of increased activity of the sebaceous glands;
- preventing increased pigmentation by blocking the growth of melanocytes;
- normalization of keratinization of the epidermis.
Acne is one of the most common skin diseases in daily dermatological practice. Acne accounts for 22-32% of all cases of dermatological pathology [1]. The progressive course of acne, tolerance to therapy, and cosmetic imperfections sharply reduce the quality of life of patients, causing significant discomfort and psycho-emotional disorders [2].
Pathogenesis
Many dermatologists consider acne to be a disease of “transitional” age - these are the so-called “physiological acne”, which resolve spontaneously. Indeed, about 60% of acne resolves on its own or requires minor intervention. The consequences of resolved acne can be expressed in the form of scars and persistent hyperpigmentation, which are difficult to treat. Early treatment of acne prevents scarring and reduces emotional stress. In 40% of cases, acne can last for years, especially in women, causing significant discomfort, scarring, and psychological breakdowns. Thus, it has been shown that in the USA, 50% of women suffer from acne at the age of 29, 35% at the age of 30, 26% at the age of 40 and 15% at the age of 50 [3]. The long course of the disease leads to depression, which is especially pronounced in women [4]. In this regard, the international association of doctors, Global Alliance to Improve Outcomes in Acne, currently proposes to consider acne as a chronic disease [2].
The causes of chronic acne have been studied by many groups. It is believed that the chronic release of androgens by the adrenal glands, a decrease in local immunity, leading to colonization of the skin by the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes
, certain forms of acne (conglobate, keloid or inverse acne, pustules, scalp folliculitis, abscessive and erosive folliculitis and Hoffmann's perefolliculitis) predispose to a chronic course of the disease. Analysis of factors predisposing to the development of acne showed that the most significant parameters are: the presence of the disease in the family (complicated medical history), obesity or overweight, and early sexual development [5-8]. No associations of other parameters (age, gender, skin color, environmental factors, age of the first episode of the disease, genetic mutations, atypical and usual localization of lesions, relationship with the menstrual cycle, seasonal variability, smoking, diet) with the severity of acne have been identified [5-8 ]. With inverse acne, 93% of patients have a history of smoking and 77% are obese [4].
A 2014 expansion study in the UK compared the genomes of 1,900 patients with severe acne with the genomes of 5,100 healthy people. As a result, three loci were identified (11q13.1, 5q11.2 and 1q41) associated with acne [9]. All three loci contain the genes for the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling pathway proteins OVOL1, FST and TGFB2. Patients have reduced transcription of these genes. TGF-β is one of the main agents that suppress the hyperactivation of cells of the immune system and endothelium. In addition, TGF-β controls sebocyte differentiation. A high level of TGF-β ensures the maintenance of sebocytes in an undifferentiated state. A low level of the factor leads to differentiation of sebocytes, increased expression of the FADS2 and PPARγ genes, which are responsible for the synthesis of characteristic lipids of sebocytes and lipid accumulation, which in turn contributes to the development of acne [10, 11].
TGF-β is one of the regulators of the expression of endothelial ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase (NTPDase), which regulates the local response of Langerhans cells to pathogens ( P. acnes
) through the hydrolysis of adenosine tri- and diphosphate to adenosine [12]. Adenosine, in turn, is a suppressor factor that inhibits the activity of any cells. Thus, in mice with the NTPDase (CD39) gene deleted on Langerhans cells, irritants caused severe inflammation [13]. In addition, limited studies [14] have shown a possible association of acne with interleukin-10 (IL-10) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) gene polymorphisms. IL-10 also has a suppressive effect on Langerhans cells, and TNF-α is an inducer of CD39 expression [12].
In addition to genetic predisposition, diet plays a big role in the formation of acne. The association of acne with excess body weight, early puberty, and high stature is known [5-8]. In a study by C. Berkey et al. [14] describe the results of the Growing Up Today Study, conducted with the participation of 13,000 English schoolchildren, which showed a high correlation of milk consumption with weight gain. Further observation of these children allowed us to establish a direct connection between milk consumption, increased body weight and the occurrence of acne [15, 16].
It is clear that the pathogenesis of acne is associated with increased sebum production and an imbalance of lipids in the secretion of the sebaceous glands. Colonization of P. acnes
may be a trigger of inflammation through activation of Toll-like and protease receptors on innate immune cells, which leads to the synthesis of antimicrobial peptides and interleukins. However, it is known that the formation of comedones and the development of inflammation can also occur under sterile conditions [17]. The inflammatory process in the area of the pilosebaceous follicle leads to the development of follicular hyperkeratosis and obstruction of the ducts of the sebaceous glands (microcomedone, comedo).
Summarizing the features of acne pathogenesis, we can distinguish two groups of factors that are involved in the development of the disease. In the first case, these are factors mediated to a greater extent by high levels of hormones, increased body weight, a dairy diet and, as a result, increased activity of the sebaceous glands; in the second, these are factors mediated primarily by genetic reasons. Lack of TGF-β production leads to sebocyte differentiation and increased lipid production, as well as decreased CD39 expression and decreased hydrolysis of the energy carriers ATP and ADP, which together create an energy-rich lipid depot.
Acne therapy
Microbiological and endocrinological examinations are not mandatory when making a diagnosis and choosing therapy [2]. The main pathogen most commonly cultured in acne is the gram-positive bacterium P. acnes
, which are a normal part of the skin flora.
In some patients, nodular and pustular elements are caused by various gram-negative microflora. In these cases, conventional antibacterial therapy for acne is ineffective, which may require microbiological studies to select therapy [18] (see figure)
.
Figure 1. Algorithm for diagnosing and treating acne.
It should be noted that most acne patients have normal hormone levels. Since sebum secretion is stimulated by androgens and correlates with serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA) levels, a relationship between these parameters can be assumed. However, even elevated androgen levels in severe acne are within the physiological norm, which casts doubt on the direct cause-and-effect relationship between hormone levels and the presence of acne [19]. It is highly likely that there is an unknown factor that plays a significant role in the initiation of acne against the background of increased androgen levels. At the moment, endocrinological testing is indicated only for patients with signs of androgen excess: menstrual irregularities, excess male pattern hair growth, androgenic alopecia, infertility, acanthosis nigricans, obesity [18].
Women with symptoms of hyperandrogenism may experience late-onset acne that is resistant to treatment. If hormonal testing is necessary, it is recommended to determine the hormonal spectrum of the blood: the level of 17-hydroxytestosterone, DHEA, luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones. In general, for women with signs of peripheral hyper- or hypoandrogenism, the use of combined oral contraceptives in combination with other acne treatments is an effective treatment method [20].
Therapeutic methods of combating acne consist of treating the affected areas, preventing complications (scars, dyschromia) and suppressing the emergence of new lesions. Treatment of acne is determined by the severity of the pathological process and the nature of its course. Topical therapy is the standard treatment for acne and is prescribed to patients regardless of the severity of the disease. External treatment includes the use of retinoids, benzoyl peroxide (BPO), topical antibiotics, combination drugs, azelaic acid (AA) [18].
AA is a dibasic saturated carboxylic acid, which is formed naturally on normal skin during lipid metabolism and is found in small quantities (4-90 ng/ml of blood) in the human body [19]. After application to the skin, AK preparations easily penetrate the epidermis and dermis. Up to 4% of the total dose enters the systemic circulation. AA has moderate anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial and antikeratinizing effects. Due to the presence of two carbon groups, AA is able to form complexes with divalent cations of calcium and magnesium, cofactors of enzymatic reactions, and also bind free radicals [19]. There is evidence that AK suppresses melanin synthesis by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which may be undesirable with long-term use of AK in patients with dark skin color due to the appearance of depigmentation [21]. On the other hand, for fair-skinned patients, the effect of AA tyrosinase inhibition is used to treat post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation [22]. AA also has an antiandrogenic effect, suppressing the synthesis of type I 5α-reductase, which leads to a decrease in the content of dehydrotestosterone in sebocytes, thereby normalizing the processes of keratinization and sebum secretion [23]. It has been shown that AA eliminates hyperkeratosis at the mouth of the sebaceous gland follicle, apparently reduces the thickness of the epidermis, and with long-term use leads to normalization of the differentiation process of epidermal cells [24].
There is data on bactericidal action against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, including antibiotic-resistant strains [25]. In the literature of recent years, there is information on the antifungal effect of AK. in vitro experiments
It has been shown that 1% AA has an effect on fungi of the genus
Pityrosporum ovale and Candida albicans
, which are resistant to antibiotics, and resistance to AA itself does not develop in microorganisms even with prolonged exposure [26].
AA is widely used in the treatment of acne. According to clinical studies [2, 27], AK is effective both as monotherapy and in combination with antibiotics, retinoids and BPO. AK in the form of monotherapy can be recommended for maintenance therapy, for the treatment of comedonal acne, papulopustular acne of mild to moderate severity. Efficacy and favorable safety characteristics are important advantages of AKs in long-term treatment. When comparing the effectiveness of AK with BPO, local retinoids, also prescribed in the form of monotherapy, a similar therapeutic effect was shown. Thus, in the work of H. Gollnick et al. [28] presented data from 2 clinical studies examining the effectiveness of 15% AA gel compared with 5% BPO gel and 1% clindamycin gel, which included 351 and 229 acne patients. The authors showed that when using the drugs for 4 weeks, an effectiveness of 70% was achieved in reducing the number of inflammatory elements in all groups. Side effects in the form of local burning and irritation were more pronounced in the group of patients using BPO than in the group with AK. Minimal side effects were observed in the group of patients who used clindamycin gel for treatment. In a study by G. Stinco et al. [29] studied the sebostatic effect of AA, adapalene and BPO in the treatment of 65 patients with moderate acne. Using sebumetry, the level of sebum secretion in the facial area was assessed. All drugs used had a comparable therapeutic effect. The level of sebum in all areas of the face (forehead, chin, cheek) decreased more in patients who used AA (14, 14 and 15%, respectively). In the group of patients using BPO, there was also a decrease in sebum (10, 10 and 25%), while adapalene had no effect on the amount of sebum on the forehead (0.2%), on the cheeks it decreased by 7%, and on the chin increased by 6% [29]. Thus, this study showed that there is no correlation between clinical effectiveness and reduction in sebum levels in various areas of the face in patients with acne. The authors concluded that AK is an effective topical agent for the treatment of acne, which has a pronounced sebostatic effect. When studying the safety of topical medications, a trend toward better tolerability/safety of AA compared to topical retinoids and BPOs was noted.
AA is also used to treat rosacea. Two multicenter, double-blind, randomized studies involving 670 patients with papulopustular rosacea were conducted in 2003 to study the effectiveness of monotherapy with 15% AA gel. The gel was applied twice a day. Both studies showed a significant therapeutic effect of AC, expressed in a decrease in the number of inflamed elements (58% versus 40%), improvement in erythema (44% versus 29%), and improvement in the overall disease severity index (62% versus 40%) [30]. No significant side effects were observed during the studies.
An analysis of data from clinical studies and reviews, which included studies since 2004 collected in the Ovid, MEDLINE, and EMBASE databases, showed that BPO, topical antibiotics and retinoids in various combinations are effective and safe in the treatment of moderate to moderate acne [31]. There are practically no studies comparing the effectiveness of various combinations and the price/effectiveness balance. In addition to these drugs, drugs are used, which include topical dapsone, salicylic acid and AK, topical zinc preparations, the effectiveness of which has also been proven in clinical studies [31]. European acne treatment guidelines recommend a combination of adapalene and BPO; clindamycin and BPO; erythromycin and tretinoin; erythromycin and isotretinoin, erythromycin and zinc [32].
The European Guidelines for Acne Therapy draw the attention of clinicians conducting clinical trials to the criteria for assessing the best clinical effectiveness of a particular combination. One clinical study specifically examined the level of improvement that patients rate as a treatment effect and showed that patients considered treatment successful if the number of lesions decreased by 10-15% [33]. This limit can be used to compare the effects of therapy with different combinations: a drug is considered more effective if the number of lesions is reduced by more than 10% compared to monotherapy or other combinations [33]. In general, monotherapy with retinoids, AA or BPO is recommended for comedonal acne. For papulopustular acne, the treatment of choice is BPO in combination with adapalene or clindamycin [2, 32]. AC, BPO, topical retinoids as monotherapy or systemic antibiotics in combination with adapalene may also be recommended for the treatment of this form of acne [2]. For severe forms of pustular, nodular and conglobate acne, AK is used in combination with systemic antibiotics [2].
When comparing the effectiveness of various drugs for topical treatment of comedonal acne, the effectiveness of AK is at the level of drugs such as BPO, adapalene, isotretinoin and tretinoin [2].
The combination of drugs enhances the therapeutic effect, affects several stages of pathogenesis simultaneously, reduces resistance to antimicrobial agents and shortens treatment time. Many researchers note not only the possibility of combining AK with various drugs, but also show the greater effectiveness of combination therapy in the treatment of acne and rosacea.
The effectiveness of combinations of AA with retinoids, topical antibiotics and BPO was shown in a study in the treatment of mild to moderate papulopustular acne [34]. The same effect with combination therapy (AK with systemic antibiotics) is noted by researchers in the treatment of rosacea. Thus, a multicenter, two-phase study examined the effectiveness of combination therapy with 100 mg oral doxycycline and 15% AA gel in phase I, followed by maintenance therapy with AA alone in phase II for the treatment of patients with severe and moderate forms of papulopustular rosacea [35]. In phase I of the non-randomized study (n=172), the drugs were used twice a day for 12 weeks; phase II was conducted in a double-blind manner. The phase II study included patients who received phase I therapy for at least 4 weeks and achieved a reduction in the number of inflammatory lesions by more than 75% ( n
=136). Patients were divided into groups receiving AA or placebo for an additional 24 weeks. The number of inflammatory foci, the index of overall disease severity, the presence of erythema and spider veins were assessed. By 12 weeks of phase I therapy, 81% of patients achieved a 75% reduction in acne, and 64% of patients were cured. In phase II, AA therapy had a significantly better effect than placebo; 75% of patients remained in remission in the AC group during 6 months of maintenance therapy. There were no significant side effects in either group.
In a study by J. Del Rosso et al. [36] also demonstrated the effectiveness of this combination in the treatment of rosacea. Pilot comparative study ( n
=207) the effectiveness of 15% AA gel or 1% metronidazole gel in combination with the anti-inflammatory drug doxycycline at a dose of 40 mg daily for 12 weeks showed comparable effectiveness of both protocols.
The study of the effectiveness of combinations of AK with other topical agents in the treatment of acne has been shown in many domestic and foreign studies. In a multicenter, randomized, double-blind study conducted with the participation of 150 patients with moderate acne, the effect of 5% AA gel, 2% clindamycin gel, and their combination (clindamycin in the morning, AA in the evening) was assessed [37]. Treatment was carried out for 12 weeks, every 4 weeks the number of inflammatory and non-inflammatory elements, the severity index (ASI) was calculated, and the patients' assessment of the effectiveness of the therapy was recorded. It was shown that ASI significantly decreased in all three groups of patients. A decrease in ASI was observed in all study groups (48, 32 and 64% in the clindamycin, AA and concomitant therapy groups, respectively). However, in the group of combined therapy with AA and clindamycin, the effectiveness of treatment was more pronounced. Subjective patient assessment also correlated with ASI scores.
A similar study was conducted by the same group to evaluate the effectiveness of combination therapy for acne using a combination of 5% AA gel and 2% erythromycin gel [38]. The study included 147 patients with moderate acne; the duration of treatment was 12 weeks. In all three therapeutic groups (AK, erythromycin and combination therapy) the effect was significant. The combination of drugs was more effective compared to monotherapy. The result regarding the registration of side effects was quite unexpected: in the combination group, where patients received two drugs together, the proportion of side effects was lower compared to the erythromycin and AK monotherapy groups (27, 54 and 45%, respectively).
Currently, the management strategy for patients with acne includes not only active treatment methods, but also subsequent maintenance therapy using auxiliary treatments and/or cosmetics to maintain acne in remission. When choosing cosmetics to determine skin type, it is recommended to use non-invasive dermatological research methods - sebumetry, corneometry, pH-metry. This allows control over the prescription of optimal skin care products for patients with acne [39].
The introduction of AA into the composition of products used to cleanse the skin can effectively suppress the formation of inflammatory foci. Thus, in a limited, randomized, double-blind, 8-week study involving 13 patients with acne, the effect of using skin cleansers that included the therapeutic drugs triclosan, salicylic acid and AA was studied [40]. For control, conventional skin cleansing preparations were used. The comparison was carried out by assessing the effectiveness of using these products 2 times a day on the left and right sides of the face. It turned out that both a conventional cleanser and a product with therapeutic agents, which included AA, reduced the number of lesions, but only the therapeutic agent reduced the number of inflammatory elements, which was confirmed by histological studies.
In cosmetology, AK is actively used as a peeling for problematic, porous skin and for the treatment of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
One study examined the effect of superficial AA peeling on sebum secretion in various areas of the face in 11 women aged 49-71 years. Peeling was done 5 times with an interval of 2 weeks. The sebum level was measured with a sebumeter. It was shown that AA increases the level of sebum in the U-zone, but does not increase it in the T-zone of the face [29]. As facial skin ages, an increase in the amount of sebum can have a cosmetic effect. AK is also used for pre-peeling preparation and post-peeling skin care in the complex treatment of mild to moderate acne and non-inflammatory post-acne. The use of peelings in combination with drug treatment of acne allows you to achieve a quick, lasting effect [41].
In the arsenal of a Russian doctor today there are several drugs containing AK, one of them is 15% Azelik
(Akrikhin).
Azelik
also contains squalane, which restores the barrier properties of the skin and improves the tolerability of the drug.
Squalane is a high-quality emollient that does not have comedogenic properties; it fills the spaces between the scales of the stratum corneum of the epidermis, softens and eliminates the feeling of tightness, and deeply moisturizes the skin. The effectiveness of the combination of AA with moisturizers was studied in a multicenter open study ( n
= 102) “Skin Condition Assessment” of patients with rosacea. The study compared the effect of applying a moisturizer after using 15% AK gel on one side of the face for 7 days. Assessment of the cumulative severity index showed a significant increase in effectiveness when using a combination of AA and a moisturizer in the treatment of rosacea [42].
Conclusion
AK is widely used in the practice of dermatologists and cosmetologists. Data from Russian and foreign studies allow us to conclude that AK is highly effective in the treatment of acne, rosacea and post-acne. A number of advantages, such as the presence of anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antikeratinizing, antiandrogenic and antityrosinase effects, allow us to consider AK as an optimal topical remedy for the treatment of acne and the elimination of cosmetic problems associated with this disease.
Advantages of azelaine peeling
1.
Since azelaic acid is natural to the human body, it does not cause allergic reactions and is almost always well tolerated.
2.
Repeated use does not reduce the effect of antibacterial therapy.
3.
Can be used at home, since the likelihood of negative consequences is extremely low.
4.
The product can be used by young and fairly old people, as well as dark-skinned people with post-acne.
5.
After use there are no comedones or formation of sebaceous plugs.
6.
A short rehabilitation period after the procedure (only a few hours). You can cleanse your skin at any time of the year if you use sunscreen on sunny days.
Reviews
ANASTASIA, 32 YEARS OLD:
“I make an appointment for peeling every 2 weeks.
My skin is oily, my pores get clogged quickly, so without professional facial cleansing, inflammation and acne quickly appear. I have already done peelings based on lactic, trichloroacetic, and salicylic acid. I decided to try azelaic one. Before carrying out azelaine peeling, I studied reviews from cosmetologists for a long time.
On the one hand, they say that the procedure is safe, but on the other hand, it is not effective enough. In general, I really liked the effect. I decided to buy myself an azelaine peel and carry out the procedure at home.”
ALENA, 29 YEARS OLD:
“Azelaine peeling has positive reviews, so I decided to undergo the procedure.
He dealt with my age spots after acne after 5 procedures. They have brightened and are now almost invisible. And the skin has become noticeably cleaner. I plan to repeat several more courses.”
IRINA, 36 YEARS OLD:
“I recently discovered how gentle azelaine peeling is on the face. It is gentle on my sensitive skin. The procedure does not cause any particular discomfort, and the recovery period is very short.”
Who can and who cannot undergo peeling with azelaic acid?
Azelaine peeling will help in the treatment of many dermatological diseases (consultation with a cosmetologist or dermatologist is required). When combined with other ingredients, the acid strengthens the walls of the capillaries, thereby preventing spider veins and reducing the existing consequences of vasodilation. For inflamed hair follicles and ingrown hairs, it is also recommended to take a course of azelaine peeling. This is a fairly effective remedy in the fight against photoaging; prescribed in preparation for laser resurfacing and deep facial cleansing. Depigmenting peels often contain nonandioic acid.
When not to use azelaine peeling:
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- herpes in the acute stage;
- drug intolerance;
- skin damage;
- inflammatory processes (except for those indicated in the indications).
The skin reacts to acid peeling with redness, itching, mild burning and tingling, to the point of numbness. The redness disappears after 2–3 hours. If you experience an allergic reaction, excessive dryness, swelling or exacerbation of skin inflammation that persists for 2-4 weeks, you should visit a dermatologist.
Opinion of cosmetologists
Many cosmetologists use Cytolife peelings to prepare the skin for further cosmetic procedures. This increases their effectiveness, allowing you to get visible results.
Experts believe that one of the main advantages of the cosmetic line is its gentle, gentle effect on the skin. When used correctly, peelings do not leave burns or injure the skin.
Peels from the Cytolife laboratory are highly effective against acne and redness on the skin. After using them, the skin becomes clearer and its color becomes even.
What is the effect of peeling with azelaic acid?
In order for the result to be “obvious”, it is necessary to undergo a course of 3–10 procedures with a break between them of 7–14 days. After peeling, the skin color improves, it becomes clean and silky to the touch. Redness from rosacea and rosacea is significantly reduced. Oily shine disappears, signs of acne decrease or disappear.
When azelaic and lactic acid are used together, the tone is evened out and the water balance of the skin is restored. Turgor increases, peeling disappears. If you use glycolic acid together, wrinkles, stretch marks, and senile pigmentation are reduced - the skin is rejuvenated as a whole. The result is long-term, over 6 months, after which you can repeat the course.
What does acid treatment include?
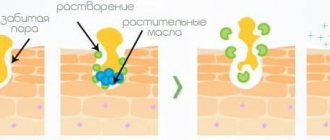
Acid treatments involve exfoliating the top layer of skin using chemicals called hydroacids. They irritate the skin and damage epidermal cells, enhancing their regeneration. Acid treatments are designed to improve skin condition and reduce signs of aging - wrinkles and discoloration, as well as treat acne scars.
Acid peeling was known already in ancient times. Women used lactic acid for the face (in the form of sour milk) and grape, lemon or apple cider vinegar. These at-home chemical peels, however, did not always produce good results - their incompetent use led to bacterial infections and scarring during healing.
In modern cosmetology, acid treatments are carried out using alpha and beta acids, which, at concentrations below 5%, do not irritate the skin and provide a slight exfoliation effect.
Treatment using hydroacids stimulates epidermal renewal processes and can be used for all skin types. However, people with sensitive skin should choose lower concentration hydroxy acids.
Fruit acids in lower concentrations affect the skin primarily by moisturizing and regenerating, while fruit acids in higher concentrations cause exfoliation of the epidermis and restoration of a new superficial layer of skin.
How to care for your skin before and after azelaine peeling?
A few days before the first procedure, it is necessary to test the skin for drug tolerance. The test is carried out on the bend of the elbow: the product is applied and the necessary time is allowed to take effect. Cosmetics used during the preparatory period must contain fruit and soft carboxylic acids and have protective properties against UV radiation from the sun.
After the session, you should strictly follow the recommendations on how to care for your skin. For half a month, use soothing and moisturizing products that accelerate skin restoration and prevent infection. You should also avoid solariums, baths and swimming pools. Use creams with sun protection factor SPF 30 or higher.
About company
Laboratory Cytolife is a modern Russian-Japanese company specializing in the production of innovative cosmetic products. The main office is located in Moscow. Cytolife skin care products can be purchased in online cosmetic stores or on the official website of the laboratory. Representatives of the official manufacturing company also distribute cosmetics. The cost varies between 3,000–10,000 rubles.
The founder of the company is Kirill Tokarczuk, a famous dermatocosmetologist who for many years has been developing cutting-edge hair care products for the skin of the hands, feet, face and body, as well as hair.
Attention! The drugs produced by Cytolife are recommended for use both at home and in beauty salons and beauty salons.
Benefits of using peeling for pigmentation
They accelerate the appearance of normally colored cells on the surface of the skin, thus speeding up the process of getting rid of pigmentation.
- Accelerates cellular renewal and exfoliation
- Allows you to quickly get rid of age spots
- The correct composition suppresses excess activity of melanocytes (lightens problem areas of the skin)
The leading advantage of peelings is that there is no need to apply an exfoliating composition every day; it is enough to visit a cosmetologist once every 2 weeks. If it is not possible to visit a cosmetologist, you need to use home peeling products.