Furunculosis is one of the most unpleasant skin diseases: in addition to cosmetic problems, it can lead to the development of severe purulent complications - meningitis, sepsis, phlegmon. Many people who are sick with boils (boils) wonder which antibiotics are best to take. Regardless of the cause, the treatment of furunculosis is based on antibacterial therapy designed to suppress the growth of bacteria.
Furunculosis - what is it?
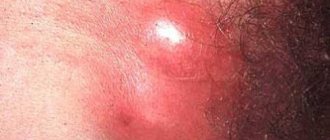
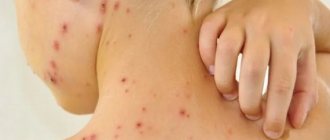
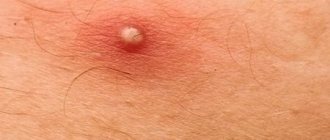
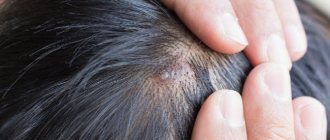
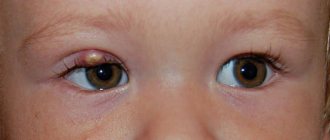
Furunculosis is an infectious skin disease accompanied by the appearance of abscesses and nodules on the skin. The infection can be chronic or short-term. If two or more boils form at once in one place, then doctors call this phenomenon carbunculosis. In addition to the skin, the infectious process can affect the skeleton and internal organs.
Reasons for appearance
The main cause of boils is a staphylococcus infection, which, when infected, develops a purulent process in the human body. There are several causative factors for the development of the disease. The most common of them include:
- decreased protective functions;
- diabetes;
- the course of chronic infections;
- skin damage.
Even minor skin injuries can trigger the appearance of boils, so all wounds that appear must be immediately treated with medications. First of all, this concerns teenagers, because they most often receive similar injuries due to their increased activity.
How does the pathology manifest itself?
The main cause that provokes furunculosis is staphylococcus. It usually penetrates through an injury to the skin in any area of the body. This injury is not always a cut - sometimes it is abrasion, the result of hypothermia or intoxication.
- Inflammation develops at the initial stage of the disease; pus may appear near the follicle. All of it is involved in the purulent process only after a few days. The surrounding tissue is swollen, painful, and inflamed.
- Inflammation also spreads to the sebaceous gland. Visually, it looks like a bump rising above the surface. If you palpate the site of the lesion, a cone-shaped stagnant node is determined. After a short period of time, palpation will be accompanied by acute pain. It is sometimes felt even without touching, but has a tugging, aching character.
- Severe swelling develops when a boil appears on the face or neck. The infiltrate accumulates for about 4 days, and then, when pressed, pus will separate from the upper part of the boil (fluctuation zone). The tissue at the site of the follicle melts and a fistula forms.
- The separation of pus begins at the stage of opening the boil. As a rule, a small amount comes out, but even after squeezing it out, a purulent core can be detected - a distinctive feature of this skin disease. Its rejection will occur only after a few days, and at the same time blood and pus are also released.
- After removing the rod, all symptoms begin to subside. A deep injury will remain in place, in which necrotic masses or pus may still remain. It is very important at this stage to use high-quality ointments for treatment, otherwise furunculosis will progress to the chronic stage.
There may be no symptoms at all if there is only one boil. You feel much worse if there are several lesions, because in this case it even affects your performance. If the boil is localized on the face, then additional pain is felt during facial movements.
Factors provoking the disease
The main causes of the disease are the presence of staphylococcus in humans. On healthy skin, the infection does not manifest itself, but when the epidermis is injured (for example, a cut or abrasion), good conditions are created for the inflammation process to begin. Provoking factors for the development of the disease can be:
- Chronic infections of the body.
- Intoxication.
- Failure to maintain body cleanliness.
- Hormonal disorders (diabetes mellitus, overactive adrenal glands)
- Excess weight.
- Some medicines.
- Weak immunity (decreased immunity occurs due to various diseases, hypothermia or overheating of the body, poor nutrition).
- Increased sweating when the protective functions of the skin are impaired.
- Exhaustion of the body.
- Diseases of the intestines, teeth, tonsils.
- Low iron levels in the body.
- Pathologies of the urinary system.
- The causes of furunculosis are determined by a number of the above factors with a simultaneous violation of the protective function of the skin.
The degree of infectiousness of bacteria (their virulence) affects the development and course of the disease. It can affect both previously healthy skin and skin affected by staphyloderma. To identify the cause in each specific case, it is necessary to conduct a full examination of the body: blood tests, urine, stool, throat culture for flora, determination of the level of sex hormones, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, electrocardiogram and other procedures at the discretion of the attending physician.
Furunculosis occurs more often in adults than in children. Men suffer from the disease more than women. In the spring and autumn, outbreaks of the disease become more frequent. Increased nervousness, irritability and anger lead to the constant release of stress hormones, which depletes the adrenal glands and reduces immunity.
Stages of furunculosis
After contracting an infection, the process of development of a boil can be divided into three stages, the duration of each of which is approximately 8-10 days.
- First stage
. Along with the resulting boil, an inflammatory process develops, against which characteristic signs appear. The skin begins to turn red, and the red spot of the infectious process does not have clear boundaries. The patient experiences pain. - Second stage
. The size of the skin formation gradually increases, reaching up to 2-3 cm in diameter. A small purulent core appears approximately in the center of the boil. Gradually, the inflammatory process spreads to neighboring tissues. - Third stage
. After opening the abscess, a small depression (crater) appears in its place, from which purulent fluid will be released. After a few days, with proper treatment, this crater becomes scarred. As a result, practically no traces remain on the patient’s body. But if you had a large boil, then even after complete healing there remains a visible mark.
Not in all cases, the development of a boil occurs according to the scheme described above. Sometimes skin formations occur without purulent cores, which greatly simplifies the scenario. But in some cases, the appearance of a boil is accompanied by an acute aerobic purulent infection.
Diagnostic measures
Clinical manifestations, the presence of a fluctuation zone, and the presence of signs of an infectious process allow a diagnosis to be made. In a clinical blood test, there is a noticeable increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left and pronounced leukocytosis. Cultural diagnostics confirms the staphylococcal nature of the disease. Together with cultural diagnostics, the sensitivity of the microorganism to antibiotics is determined. Accurate identification of the pathogen also helps to identify the source of infection; for example, nosocomial infection often manifests itself in the form of pyoderma and furunculosis.
Features of therapy
Self-medication for furunculosis can lead to undesirable consequences, so opening or squeezing out skin formations on your own is strictly not recommended. During the treatment process, if the lesion is small, the patient must strictly follow the rules of hygiene, regularly change bed linen and reduce the number of water treatments. In parallel with this, doctors prescribe drug therapy, including antibiotics, antiseptics and other types of drugs.
If the course of furunculosis is abscessive in nature, then doctors may prescribe surgical intervention, during which the boils are surgically opened. Antibacterial treatment can be supplemented with UHF therapy, which is equally effective at all stages of treatment of the disease.
Furuncle in the ear
A boil in the ear receives therapeutic treatment with minor differences. The opening and rejection of necrotic masses may be accompanied by their flow into the middle ear, which is very unfavorable and dangerous for the hearing organ, therefore the use of dry heat, which can also contribute to the occurrence of sepsis, is not recommended. It is recommended that the patient sleep on the affected side to prevent swelling. Be sure to contact an otolaryngologist. The specialist manages the patient conservatively throughout the entire period and only if necessary can perform minor surgery. Under no circumstances should you attempt to clean your ears at this time, squeeze out the boil, or carry out any other activities. The vascular network on the head is very well developed, so in this location it is necessary to approach treatment methods very carefully so as not to cause life-threatening complications. In addition to the local reaction, severe headache, loss of appetite, fever, and irritability often occur. When such a clinic develops, symptomatic additional treatment is prescribed: antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, analgesics.
Antibiotics for furunculosis
Antibiotics in purulent surgery have long become a necessary and main means of treatment. The ways of introducing them into the body are varied. There are products for topical use in the form of ointments, gels, solutions, there are capsules and tablets, you can administer them intramuscularly, intravenously and even in suppositories.
Antibiotics for boils and boils (which are the same thing) can be in any of these groups - it all depends on the stage and severity of the process, the age of the patient, and concomitant pathology. Every patient with furunculosis wants to use an antibiotic that “definitely helps.” Obviously, a doctor will help you choose which antibiotics to take for boils.
Patients, with their careless attitude towards these powerful pharmacological agents, unauthorized use due to their availability in pharmacies, and non-compliance with treatment courses over a long period of time, have led to resistance of microbes to treatment on the one hand and sensitization of the human body on the other.
Despite this, the doctor has a way to select an effective antibiotic for boils on the body and face. To do this, it is necessary to culture the purulent discharge and determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to a whole range of antibiotics.
Choice of drug
Modern medicine provides several types of antibiotics for the treatment of furunculosis. Treatment of furunculosis. They all come in different forms, but the most commonly used are ointments, injections, or tablets. The most common types of antibacterial drugs include the penicillin series, but if the bacteria are resistant to penicillin, doctors use anthraglycosides, tetracyclines or cephalosporins. Now let's look at the most common groups of antibiotics that are actively used in the treatment of furunculosis. All of them are potent drugs, so they can only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
How will the pills help?
Medications in this form are needed in severe cases of the disease. Tablets for furunculosis, the duration of therapy is prescribed by the doctor. The course should not exceed 14 days. Antibiotics have a bad effect on the mucous membranes of the stomach, intestines and oral cavity, causing dysbacteriosis and stomatitis. It is important to simultaneously take probiotics, which restore the body's microflora.
Amoxicillin
. An inexpensive antibiotic destroys the walls of bacteria and quickly copes with furunculosis. Amoxicillin is prescribed for the treatment of children and adults. Contraindications are taken into account: sensitivity to penicillins, renal failure, lactation, pregnancy.
Tsiprolet
. One of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics for furunculosis stops the growth and reproduction of bacteria. The boil goes away quickly; the pathogens are not resistant to Tsiprolet. The medicine lasts 12 hours and does not affect the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract. It is contraindicated for use in children under 18 years of age, pregnant women and nursing mothers, and patients with liver and kidney diseases.
Sumamed
. Tablets are prescribed to adults and children over the age of three for abscesses on the face, soft tissues, and with a high risk of septic shock and death of the patient. Sumamed is drunk five times a day. The antibiotic is contraindicated for use by pregnant women, nursing mothers, and patients with kidney and liver failure. Possible side effects - skin rash, headache, diarrhea. Price Sumamed, 125 mg 280 rub. for 6 tablets. A cheap analogue of the drug is Azithromycin. Its price for a dosage of 500 mg is 65 rubles. for 3 tablets.
Ointments
As soon as the boil breaks out, a bandage treated with ointment must be applied to the resulting wound. For this purpose, various antibacterial drugs are used in the form of ointments. Below are the most effective ones.
Table. Antibiotics for boils in ointment form.
| Name of the drug, photo | Description |
| An effective remedy that perfectly fights many types of pathogenic microorganisms. When boils appear, the ointment must be applied several times a day. | |
| The active component is chloramphenicol, a medicinal substance that has a detrimental effect on various bacteria. Treat the affected skin every day until complete recovery. | |
| Another antibacterial agent in the form of an ointment, successfully used in medicine in the treatment of furunculosis. The drug should be applied to the affected areas of the skin 2-3 times a day. Mupirocin ointment is also effective for secondary bacterial infections. | |
| The drug has anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties. Used to treat boils on the neck, face or groin area. To treat furunculosis, it is recommended to apply the ointment to the skin twice a day. | |
| For furunculosis, Ichthyol ointment is also used, which must be applied to a gauze bandage or bandage and then applied to the boil. It is recommended to perform the procedure 2 times a day. It is strictly not recommended to apply the drug to a broken boil. |
This is not the entire list of drugs used for furunculosis. But only a doctor can prescribe a remedy, so you cannot self-medicate.
Injections
Treatment with antibiotics for furunculosis can also be carried out in the form of injections. Injections are given if therapy with other forms of drugs does not give a positive result. The most effective drugs in this form of release:
- Amoxicillin
. Popusynthetic antibiotic of the penicillin series. For furunculosis, it is administered intravenously by stream and drip. The dosage is prescribed by the doctor individually. The average course of treatment is 7-10 days. During therapy, undesirable reactions of the body may occur: tachycardia, irritability, headaches, dysbacteriosis, dyspepsia. - Levomycetin
. Powder for injection with the active ingredient antibiotic chloramphenicol. For furunculosis, adults are prescribed intravenously or intramuscularly. The daily dose is 1-3 g. The drug is administered at a dose of 0.5-1 g 2-3 times a day for 5-15 days. Adverse reactions may occur in the lymphatic system, digestive tract, peripheral and central nervous systems.
It should be remembered that antibiotics have many contraindications and adverse reactions that can even cause death. For this reason, it is strictly forbidden to prescribe them yourself. Antibiotics for furunculosis are prescribed by the doctor, based on the stage of the disease, the patient’s history of chronic diseases and other reasons.
Furuncle during pregnancy
Treatment for boils during pregnancy is the most gentle. Everything is carried out within the framework of conservative therapy; if possible, it is recommended to use only local antibacterial agents. Any pathological process, as well as excessive use of medications, can significantly disrupt the development of the fetus. Systemic antibacterial drugs are prescribed only in extremely severe cases: multiple furunculosis, often recurrent, severe condition of the mother (fever, diffuse cellulitis, sepsis). In extremely severe cases, there may be a question of termination of pregnancy and appropriate therapy. To prevent such life-threatening conditions from arising, you should not touch the developing boil or try to cut or squeeze it out yourself. During pregnancy, if a woman experiences even a single boil, it is imperative to consult a doctor for advice and periodic monitoring of the development of the pathological process. A pregnant woman must follow a diet. If a boil occurs, it is worth reducing the proportion of carbohydrates. B vitamins have a beneficial effect on the skin and its immune processes. Complex vitamin complexes are prescribed. Biological food additives with vitamins, yeast. The diet should be varied, balanced and regular. Walking in the fresh air and doing gymnastics are very useful for stimulating the immune system.
Treatment of a boil of any location is aimed at preventing the development of complications. With a favorable course of the process, the necrotic core is independently rejected and a small ulcer is formed at the site of the boil, which often heals without leaving a trace.
Who should not take antibiotics?
Antibiotic therapy is contraindicated if:
- renal, liver failure;
- allergic reactions to the drug;
- fungal diseases of the skin.
Use with caution during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and childhood. Antibiotics for illness will bring the desired result when the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, does not exceed the dosage, and adheres to proper nutrition.
Treatment of furunculosis with antibiotics provides a quick recovery when the boil is on the cervical area or on the head. This placement of the abscess is dangerous because it leads to infection entering the brain. An abscess provokes complications, including death. Spreading quickly, Staphylococcus aureus provokes the appearance of new foci of inflammation.
Furuncle under armpit
When the boil is localized in the armpit, movements of the upper limb are significantly hampered due to the sharp pain of the formation. It is difficult to adduct or abduct the arm. This condition worsens the patient’s life and makes it impossible to perform usual actions. A developed vascular network can contribute to the spread of infection throughout the body. Regional lymph nodes often become inflamed in response to local inflammation, making movement even more difficult. Fever is typical. A boil under the armpit is treated mainly conservatively. During the period of illness, shaving the armpit and using deodorants are prohibited. It is recommended to thoroughly wash the skin and disinfect the skin with alcohol or iodine solution. In general, conservative measures are carried out, as with boils of other locations. After opening the formation, applications with saline solution and antibacterial ointments are applied. Antibiotics and, if necessary, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. With proper conservative treatment and avoidance of trauma to the pathological focus, surgical treatment is extremely rarely resorted to.
Prevention of furunculosis
There is no specific prevention of furunculosis. You can prevent the development of furunculosis using preventive measures:
- Strict adherence to personal hygiene.
- Thorough treatment of abrasions and scratches with antiseptics (chlorhexidine, alcohol, iodine, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green).
- Do not clean the ear canals with objects that can damage the skin and allow pathogens to penetrate into the hair follicle.
- Treat chronic diseases (anemia, diabetes, etc.) in a timely manner.
- Do not self-medicate the primary boil.
Why are boils dangerous?
Complications arise when the problem is ignored and treated incorrectly. Warming compresses, punctures, squeezing out the rod can provoke the development of an abscess or purulent-inflammatory process in the subcutaneous tissue. The most dangerous are pustular formations on the face. Any manipulations at home can lead to bacteria entering the blood vessels.
Boils on the lower extremities pose a great danger. Bacteria and toxins can enter the vein from inflamed tissue. If you consult a specialist in a timely manner and follow all prescriptions, single purulent lesions can be treated successfully. With a chronic course of the disease and frequent exacerbations, constant treatment is necessary, and the patient must be registered at a dispensary. Against the background of chronic furunculosis, a life-threatening complication may occur - septic endocarditis. The infection spreads through the blood into the heart and affects the inner lining.
Furuncle on the back
If you find a boil on your back, you should consult a doctor. This pathology can manifest itself either in a local clinic or in intense muscle pain. In case of complications and development of phlegmon (spread abscess), surgical intervention is necessary. The doctor carefully opens the cavity, cleans it of necrotic masses, and bluntly breaks off adhesions if they are present. The lesion is drained and a bandage with a hypertonic solution is applied (for better drainage of pus). A boil on the back is treated with local and systemic antibacterial therapy. If there is a fever and general weakness, antipyretic drugs are prescribed. Muscle pain is relieved with local and systemic analgesics. You should not try to remove a back boil yourself, comb it, or rip it off. Such actions can only lead to aggravation of the pathological process and the development of complications. Often with such localization there are not single, but multiple boils. A formation containing several necrotic rods is called a carbuncle. In case of multiple position of hair follicles, immunotherapy is recommended, and vitamin B complexes are also prescribed.