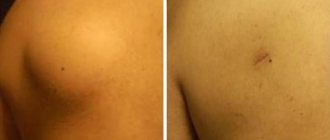
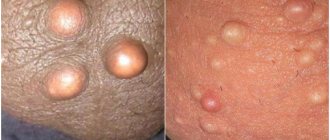
Atopic dermatitis (AD) in children is one of the most common diseases of young children. This disease is an allergic inflammation of the skin, which is characterized by itching, as well as frequent relapses and age-related characteristics of the skin rash. As a rule, dermatitis appears at an early age; if left untreated, it continues to progress into older age, which significantly worsens the quality of life of patients and their families.
For the development of this pathology, a hereditary predisposition to the development of allergies is of great importance. Therefore, this disease is often combined with other forms of allergies, for example, bronchial asthma, allergic conjunctivitis and rhinitis, food allergies. There is such a thing as “atopic march” . Atopic march is a natural progression of allergic diseases. As a rule, it all starts with a food allergy, which often gives impetus to the development of atopic dermatitis. In the absence of adequate treatment, the march progresses. Over time, the child develops allergic rhinitis. Over time, a more dangerous, in some cases, life-threatening condition arises - bronchial asthma.
What are the varieties?
Dermatitis has a complex classification. Depending on the nature of the skin disease, there are:
Simple contact
Occurs with direct physical irritation. Factors that provoke the occurrence of dermatitis are skin friction, pressure, temperature effects, alkalis, acids, poisonous plants. Surely, many have encountered this type of skin irritation. Yes, yes, we are talking about burns, frostbite, chafing, and rashes from detergent.
Contact
Symptoms appear almost immediately after contact, the area of skin damage corresponds to the area of contact with the irritant. With minor exposure, dermatitis manifests itself as mild redness and itching; acute cases may be accompanied by the appearance of blisters filled with liquid and swelling of the skin.
Allergic
This is a hyperreaction of the body to contact with certain substances. Allergic dermatitis, like all forms of allergies, manifests itself in individuals predisposed to it.
Causes of allergic type development
Unlike simple contact, allergic does not develop immediately, but after several contacts with the allergen. An allergic reaction must form; several weeks may pass from the moment of the first interaction.
Manifestation of allergic dermatitis
With the allergic type, the area of the affected skin area may be larger than the immediate site of contact with the irritant. As the disease worsens, the skin becomes bright red with pronounced swelling, weeping blisters appear, which open and erosion develops in their place. As the inflammation heals, scales and crusts form - these may be symptoms of incipient eczema.
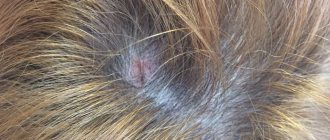
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp
Irritation appears in the area of greatest accumulation of sebaceous glands - in the scalp, on the ears, and less often on the face (on the wings of the nose). Often the initial form of the disease is dandruff in the hair.
The cause is the Malassezia fungus, which is present on the skin of most people. But its excessive reproduction leads to increased peeling, and as a result, seborrhea develops.
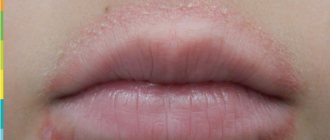
One form of the disease is perioral cutaneous dermatitis - irritation appears near the mouth.
Allergic contact dermatitis: basic approaches to diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Allergic contact dermatitis is a classic form of delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction mediated by sensitized lymphocytes. According to a number of authors, this pathology affects 1% to 2% of the population in various regions. The prevalence of the disease is higher in industrialized countries. It is increasing as more and more new chemical substances are introduced into use in medicines, cosmetic products, medical implants, household chemicals, and industrial reagents.
Unlike simple contact dermatitis, in which an irritant causes inflammation in all people when exposed to the skin, allergic dermatitis occurs only in sensitized individuals, that is, in people who have immune cells specific to this substance - T-lymphocytes. Contact dermatitis is often caused by harmless chemicals that, under normal conditions, do not cause any clinical symptoms in healthy people. But allergic dermatitis is also known when in contact with aggressive agents - components of hair dyes, hair growth products, dyes for fabrics, fur and leather, detergents, medications, juice of poisonous plants.
A classic example of allergic contact dermatitis is dermatitis caused by plants of the genus sumac (in particular, poisonous sumac - Rhus toxicodendron), in which the rashes often have a linear shape and are located on exposed areas of the body.
The pathogenesis of allergic contact dermatitis is based on a tuberculin-like delayed (cellular) hypersensitivity reaction, the inductive phase of which begins with local exposure to the skin of low molecular weight chemicals of organic or inorganic nature. Their sensitizing (allergenic) properties depend on their ability to penetrate the skin and form stable covalent bonds with the proteins of the host organism. Thus, dinitrochlorobenzene forms complexes in the epidermis with proteins containing a lot of lysine and cysteine. Skin lipids can also serve as an adjuvant.
In the formation of hypersensitivity, the leading role is played by professional macrophages of the epidermis - multi-processed Langerhans cells. The resulting delayed hypersensitivity is directed not only to the chemical itself, but also to the carrier protein.
Typically, at least 10–14 days pass from the moment of skin contact with the allergen until the development of the first clinical manifestations. The duration of the sensitization period is usually shorter for aggressive chemicals. Thus, according to our observations, drug allergens when applied to the skin can cause manifestations of contact dermatitis as early as 7–8 days. The most common allergenic medications are local forms of antibacterial drugs; contact allergic reactions to local anesthetics, antiseptics and latex are less common.
The location and configuration of the lesion is determined by the causative factor. The most common form of the disease is eczematous dermatitis. The disease is easy to diagnose and, as a rule, is characterized by a favorable course. The rash disappears when exposure to the pathogenic factor ceases. To accelerate the regression of clinical manifestations, local anti-inflammatory drugs, mainly topical glucocorticosteroids, can be used.
Etiology
According to our observations, the most common cause of allergic contact dermatitis is stainless metal alloys from which household products are made - kitchen utensils, jewelry, watches, denim rivets, zippers, keys, as well as medical supplies - dental crowns, braces , devices for focal and extrafocal osteosynthesis. Thus, having analyzed 208 cases of allergic contact dermatitis that we encountered in practice in the period from 1999 to 2009, we came to the conclusion that the metals nickel, cobalt and chromium, which are part of stainless alloys, were the cause of inflammation in 184 (88.5% ) patients.
A list of the most common, according to our data, causes of allergic contact dermatitis is given in
.
Pathogenesis
Allergic contact dermatitis is a delayed-type allergic reaction. An allergen that gets on the skin binds to tissue proteins, forming a compound that can cause an allergy - an antigen. Langerhans cells absorb antigen in the membrane molecules of the major histocompatibility complex class 2 by T lymphocytes. Activated T lymphocytes and Langerhans cells produce gamma interferon, interleukins 1 and 2, which enhance the immune response and inflammatory response. Activated T lymphocytes migrate through the lymphatic vessels to the paracortical zone of the regional lymph nodes. In the lymph nodes they undergo antigen-dependent proliferation and differentiation. Some of the “specialized” T-lymphocytes take part in the immune response, while the rest turn into memory cells. They cause the appearance of a rapid, pronounced response after repeated contact with the allergen. After the first contact with the allergen, T-lymphocytes recognizing it accumulate, which usually lasts 10–14 days. After this, T-lymphocytes leave the regional lymph nodes into the blood and populate all peripheral organs of the immune system. Upon repeated contact with the allergen, memory cells are activated and rapid accumulation of delayed-type allergic reaction effector cells—macrophages and lymphocytes—occurs.
Histological picture
The histological picture of allergic contact dermatitis is characterized by infiltration of the dermis with mononuclear cells, primarily near blood vessels and sweat glands. The epidermis is hyperplastic and also infiltrated with mononuclear cells. Typically, the formation of vesicles in the epidermis combines with the formation of bullae. The serous fluid filling them contains granulocytes and mononuclear cells.
Clinical manifestations
The disease, according to our data, is more common in young and middle-aged people. However, exceptions are possible. Thus, of the people we examined, the youngest was a one-and-a-half-year-old girl with an allergy to cobalt, and the oldest patient was an eighty-year-old man, sensitized to chromium and nickel.
In the clinic, allergic contact dermatitis is distinguished into acute, subacute and chronic forms, as well as mild, moderate and severe.
The interval from the initial exposure to the allergen to the formation of skin hypersensitivity can vary: from relatively short (2–3 days when exposed to a strong sensitizer, for example, urushiol from the juice of plants of the genus sumac) to very long (several months or years in the case of a weak sensitizer, for example, chromic acid salts or chloromethylisothiazolinone). As a rule, in an already sensitized organism, the disease develops acutely 12–72 hours after exposure to the allergen and is manifested by itching, bright hyperemia and swelling of the skin at the site of contact, against which papules, small blisters or blisters are visible, opening and leaving weeping erosions (wetting) . Sometimes skin necrosis occurs.
The subsiding inflammation leaves crusts and scales. In a chronic course, peeling and lichenification appear.
Acute allergic contact dermatitis is characterized by the following stages of development of rashes: erythema => papules => vesicles => erosions => crusts => peeling. For a chronic course: papules => desquamation => lichenification => excoriation.
In severe allergic contact dermatitis (for example, caused by sumac poison), the patient may experience symptoms of intoxication - headache, chills, weakness and fever.
The localization of dermatitis can be any and depends on the place of contact with the allergen. Thus, occupational allergens more often form foci of inflammation on the palmar and lateral surfaces of the hands and fingers, forearms, and metal allergens sensitize the skin and mucous membranes at points of contact with rings, bracelets, zippers, and denim rivets (“jean rivet disease”). , metal dental crowns.
Different areas of the skin are characterized by varying susceptibility to allergic dermatitis. Inflamed and infected tissues become sensitized more often. Friction, squeezing, maceration and increased sweating contribute to the formation of allergies. In this regard, the skin of the eyelids, neck, perineum, and anterior abdominal wall in the area of contact with fasteners and buckles is often sensitized. Often patients do not realize that they suffer from allergies, believing that they simply “rubbed” the skin in the area of inflammation.
Allergic contact dermatitis always begins at the site of exposure to the allergen. Therefore, at the beginning of the disease, the lesion is clearly demarcated, although it often extends beyond the area of skin in contact with the allergen. In sensitized patients, the lesion may spread to other areas of the body or become generalized.
With a single contact, the disease lasts several days or weeks. With frequent and regular contacts - months and years.
Diagnostics
Based on the location of skin lesions, as a rule, possible causative allergens can be assumed. In the future, their role in the pathological process is determined when performing skin patch tests. To conduct a patch test, the test material is applied to the skin for 48–72 hours, and then the size of the reaction caused by the allergen is assessed.
Since allergies are always a systemic process, the skin and mucous membranes of the entire body are sensitized. Consequently, inflammation develops when an allergen is applied to any area of the skin. However, it is technically more convenient to carry out patch skin tests in the interscapular region, the outer surface of the shoulder and the inner surface of the forearm, when fixing the material on which the patient feels most comfortable during the study.
The test materials are applied to dry skin treated with alcohol, covered with pieces of gauze and then attached with adhesive tape (that’s why the test is called “plaster”). It is convenient to use a standard test system with standardized allergens already applied to the adhesive base. Thus, the Allertest system for diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis to 24 reagents has been registered in Russia. It is sold in a pharmacy and allows you to diagnose contact allergies to nickel sulfate, lanolin, neomycin sulfate, potassium dichromate, a mixture of local anesthetics - caine derivatives, a mixture of flavoring substances, rosin, epoxy resin, a mixture of quinolines, Peruvian balsam, ethylenediamine dihydrochloride, cobalt chloride, p-tert-butylphenol formaldehyde, parabens, carbamate mixtures, black rubber mixtures, chloromethylisothiazolinone, quaternium 15, mercaptobenzothiazole, paraphenylenediamine, formaldehyde, mixtures of mercaptans, thiomersal and mixtures of thiuram derivatives. This is a simple and ready-to-use patch skin testing system. Allergens are included in a hydrophilic gel, from which the allergen is then released when soaked. "Allertest" contains two plates that are adhesive to the skin, each of which contains 12 allergens. All 24 antigens can be tested simultaneously, or the desired allergen can be cut from the plate with scissors and applied independently.
After 48–72 hours from the start of placement, the flaps are removed, wait 20–30 minutes for the nonspecific mechanical irritation to subside and take into account the severity of the reaction. Changes at the site of skin contact with the allergen are taken into account quantitatively. The gradation of a positive result is carried out as follows: (+) - erythema; (++) - erythema and papules; (+++) - erythema, papules, blisters; (++++) - erythema, papules, blisters and severe swelling.
A true allergic reaction lasts 3-7 days, while a reaction caused by skin irritation disappears within a few hours. Therefore, in doubtful cases, the severity of the reaction should be re-evaluated the next day.
H1 blockers do not affect the results of application tests. Topical use of corticosteroids on the skin area selected for testing should be discontinued at least one week before the test. Taking systemic corticosteroids in a daily dose exceeding 15 mg of prednisolone can suppress even sharply positive reactions, therefore skin patch tests are carried out no earlier than 7 days after the cessation of immunosuppressive therapy. In rare cases, skin tests are performed in patients chronically taking corticosteroids if the dose of prednisolone does not exceed 15 mg/day. However, it should be borne in mind that in this case there is a risk of obtaining false negative test results.
When performing a patch test, it should be remembered that the procedure itself may cause sensitization in the patient. Among the substances that have the ability to cause sensitization even at the first contact, it is worth noting plant resins, paraphenylenediamine, and methyl salicylate. Therefore, the application test must be justified. In addition, when conducting the test, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of nonspecific inflammation - primary irritation of the skin by the tested substances. To do this, the test materials, if they are not included in the standard test system, must be used in concentrations that do not cause irritation in the majority of healthy people (in the control group). The test should not be performed in cases of acute or extensive contact dermatitis, as increased skin reactivity may lead to a false positive result. In addition, testing with the causative allergen can cause a sharp exacerbation of the skin process. Therefore, before conducting the study, the patient must be instructed in detail, drawing his attention to the fact that if severe irritation occurs, he must remove the bandage with the allergen and contact the doctor.
When receiving a positive result from a skin patch test, it must be remembered that it only indicates sensitization to the test substance, but is not absolute proof that this particular allergen caused the dermatitis, because the possibility of long-term and polyvalent sensitization always remains. In other words, another antigen that you have not tested may also be the cause of your allergy. Therefore, when making a diagnosis, it is also necessary to take into account the history and physical examination.
Differential diagnosis
Allergic contact dermatitis must be differentiated from simple contact dermatitis, seborrheic and atopic dermatitis.
Simple contact dermatitis can develop due to damage to the epidermis by irritating chemicals (croton oil, kerosene, phenol, organic solvents, detergents, caustic soda, lime, acids, etc.) or physical impact (overheating, squeezing, compression). There is no primary sensitizing effect. Symptoms of inflammation occur immediately after exposure to the irritant, rather than 12 to 48 hours later, as with allergic contact dermatitis. The presence of papules in acute contact dermatitis indicates its allergic nature. Occupational simple contact dermatitis is similar in appearance to allergic dermatitis. The patch test allows you to differentiate these conditions.
The distinctive signs of seborrheic dermatitis include oily skin, as well as other signs of seborrhea and typical localization - the scalp and nasolabial folds. The affected areas are covered with greasy crusts and peel off profusely; Itching is usually not typical.
Atopic dermatitis usually begins in early childhood. The skin is dry. Itching is characteristic that appears before the rash, and not after it, as with allergic contact dermatitis. The flexor surfaces are most often symmetrically affected. The edges of the affected areas are indistinct; There is no consistent development of the elements of the rash: erythema => papule => vesicle.
In our practice, we encountered combined skin lesions when allergic contact dermatitis developed in response to ointments and other topical dosage forms for the treatment of dermatoses. Thus, in a 45-year-old woman suffering from microbial eczema, aggravated by the use of Zinerit (erythromycin, zinc acetate), we identified sensitization to erythromycin, an antibiotic from the macrolide group. 3 days after stopping this medication, the symptoms of exacerbation disappeared.
Three of the patients we examined, who received topical Celestoderm-B with garamycin for a long time, complained of the lack of therapeutic effect from the use of this medication. That is, despite the use of an anti-inflammatory drug, the itching and intensity of the rash not only did not decrease, but sometimes intensified some time after applying the medicine. During an allergological examination using the patch testing method, sensitization was established - a drug allergy to the antibiotic gentamicin (Garamycin), which is part of the drug. Replacing the drug with the topical glucocorticosteroid Elocom after a few days led to complete regression of dermatitis symptoms in all three patients.
When carrying out differential diagnosis, it is also necessary to remember about photocontact, phototoxic and true photoallergic dermatitis.
Photocontact dermatitis is caused by the interaction of a chemical and ultraviolet light in the skin. With it, rashes appear only on open, insolated areas of the body. The sensitizing agent is most often drugs (tetracyclines, sulfo compounds, griseofulfin, hormonal contraceptives) or locally applied resinous extracts. In phototoxic dermatitis, skin damage is caused by the action of substances (for example, hogweed juice) that acquire toxic local irritating properties under the influence of ultraviolet rays. In true photoallergic dermatitis, the sensitizing allergen undergoes chemical changes under the influence of ultraviolet rays. In the absence of insolation, it is harmless to the patient's body.
One of the rare variants of contact allergies is contact urticaria. Depending on the pathogenesis, allergic, non-immune and combined forms of this disease are distinguished. The non-immune form develops due to direct exposure of the skin or mucous membranes to an agent, most often nettle, leading to the release of mediators from mast cells. Allergic contact urticaria is caused by the production of specific IgE antibodies and, according to the mechanism of development, is classified as type 1 hypersensitivity. Most often it is caused by food products (fish, milk, peanuts, etc.), pet allergens (saliva, fur, epithelium) and penicillin antibiotics. Little is known about the combined form of contact urticaria, caused by the influence of both immune and nonspecific factors. It is believed that ammonium persulfate, an oxidizing substance found in hair bleach, often causes this type of reaction.
Treatment
The treatment of allergic contact dermatitis is based on eliminating contact of the body with the allergen that caused the disease. In the acute stage, with swelling and oozing, wet-dry dressings are indicated, followed by topical application of glucocorticoids. If the rashes are represented by large blisters, then they are punctured, allowing the liquid to drain; the bladder cover is not removed; every 2–3 hours, change bandages moistened with Burov's liquid. In severe cases, systemic corticosteroids are prescribed.
Prevention and treatment of staphylococcal and streptococcal skin infections play an important role.
Allergic contact dermatitis generally has a favorable prognosis. With timely identification of the causative allergen and elimination of contact with it, the symptoms of the disease completely regress within 1–3 weeks, and sufficient patient awareness of the nature and causative factors of the disease significantly reduces the possibility of chronicity and recurrence of dermatitis.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of allergic contact dermatitis, the local use of medications with a high sensitizing ability, primarily beta-lactam antibiotics, furatsilin, antihistamines, sulfonamides and local anesthetics, should be avoided.
In case of frequent and professional contact with low-molecular compounds, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment for the skin, mucous membranes and respiratory tract - special protective clothing, gloves, and protective creams.
Once the cause of allergic contact dermatitis has been identified, the patient must be carefully instructed and all possible sources of the allergen discussed with him, drawing his attention to the need to stop contact with this reagent and cross-reacting substances (the most common allergens, their sources and cross-reactive substances are listed in
). For example, patients with nickel allergies are not recommended to wear stainless steel jewelry or use nickel-plated cookware. For such patients, implants containing nickel are contraindicated, including dental crowns and white metal braces, and steel structures for osteosynthesis. It is also recommended that steel rivets and fasteners on jeans or other underwear be sealed on the inside with adhesive tape or cloth to prevent their contact with the skin.
If dermatitis is caused by rubber gloves, they can be replaced with vinyl ones. It is also necessary to remember that rubber drains and other medical supplies should not be used in such patients. The use of latex condoms is contraindicated for them.
If you are allergic to formaldehyde, the patient should not use certain medications and cosmetics containing this preservative. The patient should be explained that before using medications and cosmetics, it is necessary to familiarize themselves with their composition indicated on the packaging.
In the case of occupational dermatitis, it is necessary to recommend acceptable types of work to the person.
Literature
- Harrison T.R. Internal diseases. Ed. E. Fauci, J. Braunwald and others. In two volumes. Per. from English M., Practice - McGraw-Hill (joint ed.), 2002.
- Patterson R., Grammer L.K., Greenberger P.A. Allergic diseases: diagnosis and treatment. Per. from English edited by A. G. Chuchalina. M., GEOTAR MEDICINE, 2000.
- Popov N. N., Lavrov V. F., Soloshenko E. N. Clinical immunology and allergology. M., REINFOR, 2004.
- Luss L.V., Erokhina S.M., Uspenskaya K.S. New possibilities for diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis // Russian Journal of Allergology. 2008. No. 2.
- Fitzpatrick T., Johnson R., Wolfe K. et al. Dermatology. Atlas-directory. Per. from English edited by E. R. Timofeeva. M., Praktika, 1999.
E. V. Stepanova , Candidate of Medical Sciences, Research Institute of Vaccines and Serums named after. I. I. Mechnikova RAMS, Moscow
Key words: allergic contact dermatitis, patch skin tests, preventive dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, drug allergens, occupational allergens, contact allergens, metal allergy, contact dermatitis, metal dermatitis, contact urticaria.
Atopic dermatitis
Serious chronic disease. It is of an allergic nature: irritation occurs to substances that can penetrate both through contact and through the lungs and stomach. The atopic type often develops in childhood and often remains with a person for life, turning into a chronic form.
Due to the fact that dermatitis is a general name for skin diseases, symptoms and external manifestations of the disease are of great importance in diagnosis.
How it works?
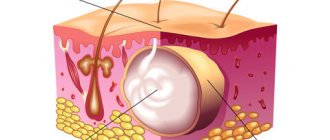
Human skin consists of 3 layers - epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous fat. A special role in the development of atopic dermatitis belongs to the so-called “dermal response” gene. This means that the basis of the pathology is hereditarily caused increased inflammatory activity of the dermal layer. The pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis is caused by three types of skin defects:
- Violation of the barrier functions of the epidermal layer, which increases the possibility of penetration of allergens and promotes rapid loss of moisture. The resulting dryness of the skin is enhanced by a significant decrease in the synthesis of lipids - a kind of “cement” for the structure of the skin.
- Congenital defects of the immune system (reduced synthesis of antimicrobial peptides and sensitivity of skin receptors) in combination with defects in barrier functions, which leads to recurrent processes of skin infections.
- Violation of immune physiological regulation. The basis of the pathological process is a violation of the ratios of various subpopulations of phagocytic immune cells and increased secretion of a protein that stimulates the synthesis of Ig E (immunoglobulin). The interaction of the allergen with Ig E causes the release of histamine and other biological compounds into the intercellular space, provoking the development of a local inflammatory reaction and itching. An increased concentration of Ig E is a diagnostic sign of atopic dermatitis in children.
Many factors can provoke diseases.
Products
Despite the established opinion, food allergies are diagnosed in only 30% of infants and 4% of older children who suffer from severe dermatitis. Sugar in its pure form is not a food allergen and there is no need to exclude it from the diet of sick children.
Meals are selected according to the age of the children. The best option for up to one year is breast milk. There are practically no allergies to it. But if there is an error in the nutrition of nursing mothers, the food antigen with milk can enter the child’s body and provoke the development of the disease.
If symptoms of the disease appear with the introduction of mixtures and complementary foods, the provoking product must be excluded. This could be cow's milk, eggs or fish, grains, red or orange vegetables and fruits. It is important to know about cross-allergic reactions - if an allergy is caused by eggs, the same reaction can be caused by the eggs of other birds, chicken and duck meat, feather pillows, some medications and vaccines. With age, the leading role of food allergies is lost.
Background pathologies
Chronic foci of infection (including parasitic infestation), bronchopulmonary diseases, gastrointestinal pathologies.
Psycho-emotional stress
There are many nerve receptors in human skin. When it is damaged, the excitation signal is transmitted to the central nervous system, forming a kind of feedback: a severe course of the disease supports a neurotic disorder, and neurotic disorders worsen the clinical picture of the disease. Neuropsychiatric abnormalities are observed in more than 80% of children with atopic dermatitis.
To eliminate such deviations, it is necessary to provide the child with a restful night and daytime sleep, take him for walks more often, create the right psycho-emotional background in the environment, undergo a course of medication and physical therapy on the recommendations of a neurologist, and, if necessary, involve a psychologist.
</3>Contact allergens
Preservatives in hygiene products, metals in children's accessories and clothing, components of rubber, glue and dyes in children's toys or household items.
Aeroallergens
Mold, pet hair, house dust, grass and tree pollen.
Exposure to irritants
Synthetic or woolen clothing, disinfectants, chemical reagents, increased sweating (as an irritant).
Climate
The influence of sharp fluctuations in temperature, air humidity and other natural factors.
Ecology
The child’s residence near enterprises and highways, his prolonged or constant presence among smokers.
Itchy skin dermatitis
Chronic inflammation of the skin, which is characterized by inflammation, itching, burning. Itchy skin is the body's reaction to irritation of nerve endings, accompanied by scratching of the skin and general increased nervousness.
Itchy dermatitis can spread throughout the body (atopic and allergic dermatitis, allergies to animal hair, pollen, etc.) and be localized - on moving parts of the body, on open areas of the skin.
Infectious dermatitis
The main causes of this disease are infections in non-healing wounds on the skin. The infectious type develops in patients with chickenpox, atopic dermatitis, or another disease if the infection gets into the rash that accompanies these diseases (often by scratching). Also, skin irritation may appear after operations and injuries due to infection with staphylococcus, streptococcus, etc.
The course of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of pustules without clear boundaries on the surface of the skin or purulent inflammation under the skin.
What is seborrhea?
Seborrheic dermatitis, or seborrhea, is a chronic disorder of the skin epithelium and sebaceous glands, which causes inflammation, pain, itching and flaking of the skin. The disease can develop in different parts of the body, most often on the scalp and face.
Upon examination, areas of inflammation and peeling are observed on the skin. If seborrheic dermatitis is left untreated, the skin and hair follicles suffer, and foci of inflammation with clear boundaries form. The disease leads to excessive hair loss.
Red dermatitis, also known as lichen planus
This is a chronic itchy skin disease, which is accompanied by the appearance of pink-red-violet rashes, merging into large plaques, up to 10 cm in size, with the formation of garlands and rings.
Locations: the lateral part of the body, the inner surface of the arms in places of flexion, mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals.
There are several forms of damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Manifestations of the disease are very diverse: papules, spots, erosions, blisters, etc.
Maintaining personal hygiene
Patients with seborrheic dermatitis are recommended to injure the inflammation as little as possible. Personal hygiene rules include cleansing the skin twice a day using special products with a low pH. To cleanse the skin, it is prohibited to use aggressive agents such as laundry or tar soap.
General recommendations for maintaining personal hygiene:
- the use of washcloths or sponges with hard fibers is excluded;
- For a while, you should avoid cleansing your skin with scrubs and peels containing abrasive particles and aggressive chemical compounds;
- During water procedures, it is recommended to use dechlorinated water; for this purpose, it is recommended to first settle or filter it;
- the duration of water procedures should be reduced to 10-15 minutes;
- when choosing shower products, choose products without dyes and fragrances, with a low pH;
- use towels with soft bristles, and it is better to blot your skin with them rather than rub them;
- to reduce the likelihood of skin injury when combing, try to cut your nails as short as possible;
- Avoid using other people's personal hygiene items.
How to distinguish psoriasis from seborrheic dermatitis?
Diseases are often confused. Although both diseases share common features, they also have many differences. Common characteristics include a chronic type of disease and an undulating course, the presence of rashes, itching, and peeling of the skin. What is the difference between psoriasis and dermatitis?
- Prerequisites for development. If psoriasis appears under the influence of autoimmune, endocrine, and genetic disorders, then seborrheic dermatitis is caused by increased activity of the sebaceous glands and yeast-like fungi.
- Symptoms. Despite the fact that in both cases the skin is covered with scales, their structure and appearance are different. When oily yellow crusts appear, we are talking about seborrheic dermatitis, and when dry gray, white or silvery scales form, psoriasis can be diagnosed.
- Localization. Psoriasis can affect almost all areas of the skin, and seborrheic dermatitis is localized mainly on the scalp, neck and face.
If you experience skin rashes that could be a sign of both dermatitis and psoriasis, be sure to consult a dermatologist. Usually, a qualified doctor can determine what it is by the external manifestations of the disease. If mixed symptoms occur, the dermatologist will write a referral for additional examinations.
How dangerous is psoriasis and does it need to be treated?
Advanced stage
The danger is that psoriasis can take a widespread, severe form, with rashes occupying more than 10% of the skin. This stage of the disease is severe, recurs, the elements of the rash become injured and become wet, and infection often occurs. Only timely treatment for psoriasis can stop the process of its spread.
Sometimes the disease is complicated by inflammation in the joints with the formation of psoriatic polyarthritis, against which the function of the joints can be significantly impaired.
Against the background of a systemic autoimmune process, which has a significant impact on the patient’s condition, other autoimmune diseases often develop (rheumatoid arthritis, some types of arthrosis, Crohn’s disease, etc.), as well as severe cardiovascular pathology, diseases of the digestive system, and neurological reactions.
If treatment for psoriasis is not started on time, the patient’s condition will become more complicated and lead to disability.
There is also a complication such as psoriatic erythroderma, which develops with improper or insufficient treatment of psoriasis, as well as with exposure to various irritating factors on the inflamed skin. The skin acquires a bright pink color with a clear demarcation of the affected areas from healthy ones, small and large lamellar peeling. This patient requires emergency medical care.
Is there a cure for psoriasis?
Yes, and quite successfully, but complete recovery cannot be guaranteed.
Find out how to get rid of psoriasis in a course of therapy of 10 sessions
Reasons for appearance
The main factors that can trigger the appearance of one or another form of dermatitis have already been listed. All inflammation and irritation of skin diseases are the result of remote or provoked causes.
- Remote ones include genetic predisposition or acquired individual predisposition. The latter occurs, for example, due to allergies or a previous infectious disease.
Related causes that trigger the development of dermatitis are various conditions to which the body reacts with skin irritation. These include stress, contact with chemicals, reaction to climate, and hormonal changes in the body.
Regardless of what resulted from the onset of the disease, remember: dermatitis must be treated immediately before it becomes protracted and chronic.
Will they be drafted into the army with psoriasis?
Do they take you into the army with psoriasis? This question interests many conscripts. Widespread, progressive and severe forms of this autoimmune disease are grounds for exemption from service, regardless of whether psoriasis is contagious or not to others. They can join the army if psoriasis first started and it was stopped. But more often, such conscripts are given a “Partially fit” conclusion and sent to the reserves. A Partially Unfit determination means that a person can only be called up for service if hostilities break out.
Dermatitis on the skin of the body
A dermatologist can diagnose the disease. Contact him if you notice the first symptoms.
Symptoms
Typical manifestations of skin disease:
- redness
- itching
- combs
- pustules
- peeling skin
Allergic dermatitis can be accompanied by a prolonged runny nose, paroxysmal cough, nasal congestion and sneezing. Acute dermatitis is usually characterized by the formation of subcutaneous blisters filled with colorless liquid. With wet dermatitis, redness and deep cracks form on the skin, from which pus or lymph oozes. Dry dermatitis is characterized by flaking and a feeling of tightness of the skin. Since it is possible to cure your skin, you should never give up, no matter what the symptoms of the disease are!
Clinical signs
Throughout the childhood period, the clinical picture of dermatitis in children can change many times, not only regarding the type of rash itself, but also regarding the location of the lesions.
Signs of the infant form
They manifest themselves as the formation of red spots, skin swelling, and blistering rash. The opening of the bubbles forms pockets of weeping, which, when dry, become covered with yellow-brown crusts. The skin of the cheeks, forehead, scalp, buttocks and extensor joint surfaces is affected. The whole process is accompanied by severe itching, disturbing the child’s peace of mind.
At the initial stage of the disease, only the superficial layer of the skin is exposed to allergic inflammation. With timely elimination of the causative factor, the allergic process is easily amenable to involution. An attempt to stop the inflammatory reaction with medications or local preparations (creams, ointments) will not yield results. If the provoking allergen is not removed, the initial stage of atopic dermatitis will enter the phase of pronounced changes.
Manifestations of the child form
Vivid symptoms appear during periods of exacerbation. The localization of pathological foci is noted mainly in the folds of the skin in the area of flexion of the elbows, knees, feet, hands, on the neck and in the area behind the ears. The skin becomes dehydrated, peels off, and a pronounced, clear skin pattern appears (lichenification). The child’s face changes – the skin is dull, there is pronounced pigmentation around the eyes, and an additional fold of skin appears on the lower eyelid.
Even in the absence of exacerbation, intense itching is noted. The skin of the fingers and hands cracks due to severe dryness.
Symptoms of adolescent atopic dermatitis
They manifest themselves as widespread and permanent lesions of the skin. Localization of the pathological process - back, chest, face, neck, joint extension area.
Characterized by lichenification and dry skin, scratch marks, cracks on the feet and hands.
Treatment is real!
How to treat allergic dermatitis is an individual question. Sometimes it is enough to eliminate the irritating substance, sometimes drug therapy is necessary.
Treatment of any type of dermatitis, even such a complex form as chronic itching, begins with determining the source of such a reaction. Often you just need to stop contact with the irritating substance, and the reaction on the skin will gradually go away on its own. In more complex cases, therapy with antihistamines is necessary.
Treatment at home is only possible for mild skin lesions and a known cause. If you have any suspicions or doubts, you should contact a professional.
The answer to the question “How to cure dermatitis?” should be added a little: treatment of dermatitis should be accompanied by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. After all, irritation on the skin can occur with general weakening of the body. Therefore, it is necessary to switch to a diet of natural hypoallergenic products, maintain hygiene of the affected areas, and limit the use of decorative cosmetics that do not allow the skin to breathe.
An important aspect is the impact on the symptoms of the disease in order to relieve itching, eliminate the feeling of dryness and tightness of the skin - this is usually what worries patients the most, preventing them from leading a full lifestyle.
Diet for adults
If there is a food allergy confirmed by clinical diagnostic studies, the doctor prescribes a specialized diet, focusing on the patient’s medical history and individual characteristics. But there is also a non-specific hypoallergenic diet approved by Russian doctors.[1] It can be followed regardless of the nature of the allergen to reduce the load on the body and speed up recovery.
This diet is based on excluding any potentially allergenic foods from the daily menu, minimizing the risk of exacerbations. According to the degree of allergenicity, all products can be divided into:
- highly allergenic;
- moderately allergenic
- low-allergenic.
The ideal diet is one from which foods from the first two groups are completely excluded. If the diet consists primarily of low-allergenic foods, this can significantly improve the patient’s condition and help recovery. When prescribing therapeutic nutrition, the doctor focuses on the nutritional value of foods, so a person following a hypoallergenic diet will not overeat or starve. The specialist also gives recommendations regarding thermal processing of products in order to preserve nutrients as much as possible.
Ointment "La-Cri" - a reliable assistant
To care for affected skin, either alone or in combination with ongoing therapy, we recommend using La Cree cream. This is a non-hormonal product that does not contain dyes or fragrances, and therefore is suitable even for newborns, nursing and pregnant women.
The natural composition of the cream is selected in such a way as to simultaneously solve all the problems of irritated skin. The product perfectly relieves redness and itching, promotes rapid regeneration of damaged skin, nourishes and softens even very dry and flaky skin.
As an auxiliary product, you can use the non-greasy emulsion “La-Cri”, which provides gentle care for the skin, moisturizing it and protecting it from drying out. Treatment of dermatitis on the face will be faster with La-Cri washing gel, which gently cleanses delicate skin without clogging pores.
Experts' opinion
The conducted clinical study proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products for daily skin care of children with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
The products are recommended by the St. Petersburg branch of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
It has been empirically proven that La Cree emulsion moisturizes and nourishes the skin, relieves itching and irritation, and also soothes and restores the skin.
Sanatorium treatment of psoriasis at sea
Sea bathing, sunbathing and mud have a positive effect on patients with psoriasis. With this effect, the skin is cleansed, it becomes smooth and healthy. Staying a patient with psoriasis in a sanatorium for a month can prevent relapses of the disease for six months.
Important: Treatment at sea is contraindicated in the acute stage of psoriasis
There are sanatoriums for psoriasis patients on the Black and Azov Seas. Spa treatment at the Dead Sea is considered more effective. The method is suitable for patients in stationary and regressing stages. An acute inflammatory process (progressive stage) is a contraindication for such treatment, as progression may intensify. There are also patients for whom seaside resorts are contraindicated, as they contribute to the development of exacerbations.
How to care for skin with dermatitis?
Helping herbs
Many plants have an amazing property - when absorbed into the skin, they reduce inflammation and normalize its structure. Therefore, a common remedy for the treatment of dermatitis is herbal compresses, wraps, and herbal ointments for dermatitis.
You can use a single plant or herbal mixtures that contain several herbs.
- Grind the celandine and squeeze the juice out of the resulting mass. Dilute the juice with boiled water in a ratio of 1 to 2. Use the solution for compresses: soak gauze in it and apply to the affected skin for 10-15 minutes.
- 1 tbsp. Pour 100 ml of boiling water over a spoonful of dry crushed string and leave until a dark brown solution is obtained. Moisten gauze or bandage in the prepared concentrate and apply it to the irritated skin until completely dry (not with weeping dermatitis, otherwise the bandage may dry to the skin). The procedure can be carried out 3 times a day.
Recipe with tar soap
The healing properties of tar have been known for a very long time. This thick oily liquid has a positive effect on the condition of the skin. Birch tar has an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect, improves blood circulation and stimulates skin regeneration.
You can find tar soap on sale and use it to wash skin affected by dermatitis, or prepare soap according to a folk recipe.
- Mix 100 g of crushed and melted baby soap with 2 tbsp. spoons of any oil, add 2 tbsp. fly in the ointment and 100 ml of water. Mix the resulting mixture until smooth.
Preparations for external use
Dermatitis on the hands is often accompanied by itching, which gets worse at night. Many patients complain of waking up in the middle of the night and being unable to fall back to sleep. In such cases, it is recommended to wear cotton gloves before going to bed and take a light herbal sleeping pill.
Acute inflammatory process is relieved with glucocorticoid ointments or creams. Depending on the severity of the lesion, the use of drugs of weak or moderate effect is prescribed. If skin lesions spread and affect not only the skin of the hands, but also other parts of the body, the use of strong hormonal drugs is necessary. Since dermatitis on the hands is accompanied by swelling and burning, patients are often prescribed creams. Due to their structure, they have a cooling effect, which helps reduce swelling, and a rapid antipruritic effect. Weak hormones include hydrocortisone, and moderate hormones include prednisolone, fluocortolone, and prednicarbate. Glucocorticoid creams are used for a limited amount of time, usually no longer than a week.
Relieving acute inflammation is only the first step of therapy. The chronic stage is also characterized by itching (albeit not as intense) and, most importantly, dry skin. Dryness provokes peeling and cracks that interfere with the healing of the skin. To normalize metabolic processes in the skin, including water balance, it is necessary to resort to additional hydration. The greatest effect comes from applying creams after hygiene procedures. Under the influence of warm (but not hot) water, the epidermis softens, and the crusts dissolve and come off.
However, it is worth noting that washing your hands with soap will most likely lead to a negative result, since alkali dries out the skin and, once it gets into the wounds, causes tingling and exudate. Delicate care is provided by special medicinal and cosmetic care products for inflamed skin. Thus, “Losterin” body gel, which can also be used as hand soap, does not contain surfactants, fragrances or dyes. And 4 types of vegetable oils in its composition, deresined naphthalan and Japanese sophora extract provide both cleansing, bactericidal effect, and moisturizing of the skin. In the acute period, it is recommended to cleanse the skin of the hands with micellar water and clean soft wipes.
After water procedures, the skin is carefully blotted (do not wipe!) with a towel and moisturizer is applied. For hand skin dermatitis, creams containing vegetable oils and panthenol are useful, which create a thin fatty film on the surface of the skin and do not allow the liquid to evaporate. Vegetable oils can be applied to the skin in the form of lotions, or they can be included in creams. Traditionally, olive, flaxseed, sea buckthorn, sunflower oil, avocado and jojoba oils are used in dermatology. In addition, products with the addition of plant extracts and vitamins are needed. These components provide nutrition to skin cells and accelerate regeneration. Preparations containing tar, naphthalan, salicylic acid, and zinc help relieve skin itching.
The restoration of epithelial cells is facilitated by preparations with propolis. This natural remedy has desensitizing, anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties due to its composition. Propolis contains flavonoids, aromatic and fatty acids, free amino acids, proteins, alcohols, minerals, sugars, vitamins, steroids, and many microelements. However, ointments, sprays and creams with propolis can be prescribed only to those people who are not allergic to honey and pollen. In other cases, the product may cause a severe allergic reaction.
In most cases, chronic dermatitis on the hands can be treated with external herbal medicine. It can be combined with hygienic procedures. For example, after an evening shower, it is useful to take hand baths with extracts or infusions of pine needles, chamomile flowers, oak bark, calendula, birch buds, string, burdock root, plantain leaves, poplar buds, and lungwort. After a 10-minute bath, the skin of the hands is also dried with a towel and moisturizer is applied.
Chatterbox
Prepare a semi-alcohol solution: to do this, dilute 40 ml of alcohol with the same volume of water. Add 2 ml of 2% lidocaine or novocaine to the resulting solution - this will help relieve the painful symptom.
Add 30 g of dry white clay and the same amount of powdered zinc. Mix thoroughly until smooth.
The finished mash is applied to the affected skin, previously cleaned with an antiseptic, in a thin layer, the mixture is left on the skin for 20 minutes. There is no need to apply a bandage on top; excess talker can be carefully removed, and the remaining part on the skin forms a protective film.
Remember! Do not self-medicate, consult a doctor!
Cutaneous dermatitis is a general name for skin disorders caused by various irritants. All irritants can be divided into 2 large groups: those that cause irritation upon direct contact and those that affect the body when they get inside.
Sources:
- Molochkova Yulia Vladimirovna, Dermatology. Brief reference book, publishing house: GEOTAR-Media, 2017
- Baumann Leslie, Cosmetic Dermatology. Principles and practice, publishing house: MEDpress-inform, 2016
- Ratner Desiri, Avram M.R., Avram M.M., Procedures in Dermatology. Clinical cosmetology, Publishing house: GEOTAR-Media, 2019
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Clinical dermatology. A short guide to the diagnosis and treatment of dermatoses, publishing house: Notabene, 2017
Photos of dermatitis
Photo album on the disease