Atheroma can occur for a variety of reasons. The radio wave method of removing atheroma is the fastest and most painless. If you need atheroma removal in St. Petersburg, feel free to contact us. Atheroma is a cyst that appears due to blockage of the sebaceous gland duct. It is completely painless, has a round shape and soft consistency. Atheroma can appear in a variety of places in the body, but today we will talk about atheroma of the ENT organs, which most often appears on the earlobe and behind the ears. If a person has a large number of such neoplasms, doctors diagnose atheromatosis. The main cause of atheroma is blockage of the sebaceous glands. These are exocrine glands, which are located in the upper layers of the skin. The sebaceous gland includes the acini, which has a large number of alveoli, as well as an excretory duct. There are sebaceous glands that do not communicate with the hair follicle; their excretory ducts are located on the surface of the skin. The walls of the alveoli are made of cells that contain a small amount of fat. These cells are regularly renewed, and dead cells are excreted during normal metabolism along with fat. If the excretory channel becomes clogged with dead particles, the sebaceous gland begins to enlarge, thereby forming atheroma. Atheromas never appear in places where there are no sebaceous glands, that is, on the palms and soles. In some cases, atheromas are congenital; this occurs due to disturbances in the functioning of the sebaceous glands during embryogenesis.
Main symptoms of atheroma
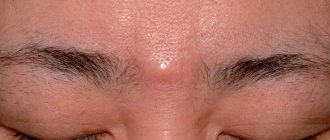
Atheroma is a rounded neoplasm that rises above the skin and is completely painless. It should feel soft to the touch or slightly compacted. Atheroma can vary in size from a few millimeters to ten centimeters. Over time, it can grow, due to the fact that the sebaceous gland continues to work and secretes secretions. So, the symptoms of atheroma:
- The appearance of a new formation on the surface of the skin.
- The texture of the tumor may be firm or elastic.
- The contours of the neoplasm should be clear.
- The subcutaneous capsule must be mobile.
- There may be a visible excretory duct in the middle.
Sometimes atheromas can burst open on their own, which is accompanied by the release of contents and an unpleasant odor. Due to the fact that the contents of the atheroma are a nutrient medium, bacteria can begin to multiply in it, which can lead to its suppuration. In this case, redness, swelling, and increased body temperature appear.
Causes of atheroma formation
Most often, atheroma appears as a result of poor personal hygiene. There may also be a hereditary predisposition to the appearance of atheromas, but this theory has not yet been proven, since scientists have not been able to find the gene that is responsible for their appearance. Atheroma of the earlobe can also occur due to an unsuccessful ear piercing, as a result of which the duct of the sebaceous gland is injured. The causes of atheroma can be very different:
- The presence of rare genetic diseases.
- Incorrect use of cosmetics.
- Damage to the skin during the removal of acne and pimples.
- Incorrectly performed facial cleansing.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Hyperhidrosis.
Possible complications
There are a number of consequences of atheroma:
- Risk of developing into phlegmon with an extensive abscess.
- Risk of relapse if opened independently.
- Risk of formation of suppuration and inflammation.
- The risk of postoperative scars that arise as a result of surgical removal of large atheroma.
- Inflammation of the scars may occur if the atheroma is removed in the clinic.
- As a result of incorrect diagnosis, a relapse may occur.
It is also worth noting that atheroma is a very rare disease; according to statistics, only 7-10% of the world's population gets sick with it. Atheroma is a benign neoplasm that never becomes malignant.
Postoperative period
In the first days after removal of the capsule, it is important to carefully monitor the condition of the wound. At first, the surgeon performs daily procedures, changing the drainage device and antiseptic dressings. The total duration of the postoperative period is 10-14 days. It takes place on an outpatient basis. Occasionally, complicated forms of atheroma are treated in a surgical hospital.
After the formation of connective tissue between the edges of the wound, the sutures are removed. This manipulation takes no more than 3-5 minutes and is usually painless.
Diagnosis of atheroma
Diagnosis of atheroma is not difficult. This is usually done through a routine skin examination. Atheroma does not pose a danger to life. If there is no suppuration, then you can limit yourself to ordinary observation without undertaking any treatment. There is a high probability that the atheroma will open on its own. But if it has reached a very large size and begins to ache, then it is better to remove it. If the contents of the atheroma break out on their own, the inflammation may subside. Further prospects: atheroma may disappear completely, or it may continue to fester periodically. Despite the fact that atheromas are benign tumors, if you discover a neoplasm, it is best to consult a doctor. Let the doctor tell you what kind of tumor it is and whether treatment is required.
Dangerous signs of complications after surgery
- Addition of inflammation after removal of an uncomplicated form of the cyst, appearance of pus;
- An increase in temperature indicates tissue infection; normally, hyperthermia disappears within 2-3 days;
- Dehiscence of wound edges – discovered during dressing;
- Leakage of blood through the bandage - increased bleeding is diagnosed in hepatitis, hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, enlarged spleen, as well as in patients using anticoagulants (Aspirin, Cardiomagnyl, Heparin, Thromboass).
The appearance of any of the above signs is a reason to consult a doctor, who will assess the risk of complications and carry out therapeutic measures.
Who treats atheroma of the ENT organs
If atheroma appears on the ears, then you should seek help from an ENT doctor
. This specialist specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the ear, nose and throat. The study of these organs is united within the framework of the science of otorhinolaryngology. You should contact an ENT doctor if you or your family are concerned about diseases of the upper respiratory tract, runny nose, tumors in the ear area, pain when swallowing and breathing, as well as enlarged parotid lymph nodes. All these symptoms are known to many other doctors, but only an experienced otolaryngologist can prescribe the most effective treatment for you. Timely detection and treatment of diseases of the ENT organs will save you from complications that can spread to other organs.
Treatment of atheroma
An ENT doctor can offer the following treatment methods for atheromas:
- Medication.
- Surgical intervention.
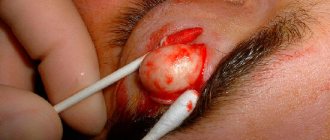
If atheroma occurs behind the ear, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary treatment for atheroma. The most effective way to treat this disease is surgery. And if the doctor directs you to undergo surgery, then you should not refuse; this operation is very easy to tolerate and is performed under local anesthesia. After the surgeon has completed his work, you will be able to forget about this disease forever. A good surgeon, when cutting the skin, acts as carefully as possible, without damaging the atheroma capsule. Then the capsule is removed from under the skin, and the cavity in which it was located is thoroughly disinfected with antiseptics. It will be much harder for those who waited until the inflammatory process appeared. If an atheroma tumor is detected, surgery is not performed. First, you will need to remove the inflammatory process so that the operation can be performed. Surgical intervention does not require an inpatient stay, but is performed on an outpatient basis. If the tumor is small in size, no sutures are applied. But if the atheroma has reached a large size, then there is a chance that you will have stitches, which will be processed once every 2 days. Recently, in surgery, instead of surgical intervention, laser and radio wave removal of atheroma have begun to be widely used. In this case, the contents of the atheroma are simply burned out or evaporated. As a rule, these methods are used in the early stages of atheroma development.
Clinical picture
When consulting a dermatologist, the patient undergoes a standard examination. Visually, the doctor determines the presence of a neoplasm with high mobility and absence of painful sensations during pressing. In the absence of complications, the skin over the cyst remains unchanged; sometimes an enlarged sebaceous duct is clearly visible in this area of the dermis.
If atheroma is characterized by rapid development, then small ulcerations may appear on the dermis. When an infection occurs and the subsequent development of the inflammatory process, the skin becomes red.
Atheroma without inflammation and secondary complications does not affect the life and health of the patient. Most patients seek professional help for aesthetic purposes. In other cases, surgical intervention becomes a necessary measure to stop developing inflammatory processes with the accumulation of purulent contents.
Radio wave removal of atheroma
Radio wave removal of atheroma is considered the most effective and safe method. The procedure is carried out using special equipment that converts radio wave radiation into energy. Exposure to energy destroys the contents of atheroma without causing damage to healthy tissues. Today, such removal of atheroma is a very common and popular method. This type of atheroma removal has a large number of advantages, including:
- Completely eliminating the risk of relapse.
- Removal of atheroma is carried out without suturing.
- An almost completely painless procedure.
- Excellent cosmetic effect.
- Possibility to return to work immediately after surgery.
Moreover, this method of removing atheroma makes it possible to reduce the risk of scar tissue, but this cannot be promised with the intervention of a surgeon. Radio wave removal of atheroma lasts for twenty minutes using local anesthesia. First, the tumor is processed and then exposed to radio waves through a special device. The radiation completely “burns out” the tumor and allows the atheroma to be removed along with the capsule, leaving behind a small depression. After this, the doctor will treat the damaged area of skin with iodine and apply a bandage. If a large tumor is removed, in some cases a hospital stay may be necessary.
What should I do?
If signs of inflammation appear, you should not hesitate - you must urgently go to the surgeon. But what you definitely can’t do is squeeze out or pick at the formation, trying to make a hole in it. If a breakthrough occurs and the pus is outside, the wound needs to be treated and wait until it heals. After this, the capsule and contents can be removed. The cyst should not be heated or steamed at any stage - this can cause infection.
At an emergency consultation with a surgeon, it may be recommended to relieve inflammation with levomekol or ichthyol ointment. The product is applied to a clean bandage and applied to the cyst, and then secured with a bandage. The compress is applied three times a day until the process subsides.
Recurrence of atheroma
During the operation, the atheroma is completely excised. Relapse can only occur if the sebaceous gland duct is poorly forgiven. The neoplasm must be removed completely, in some cases along with nearby tissues if the capsule has melted. The cause of relapse may also be the formation of a new cyst due to proximity to the postoperative scar. In some cases, relapse occurs due to incorrect diagnosis, when a lipoma or dermoid cyst is mistaken for atheroma. These tumors can also be treated surgically, but the operation is performed in a slightly different way. According to statistics, relapse of atheroma occurs in 15% of patients who have undergone surgery, and in 10% it is the result of opening an abscess cyst, when it is difficult to remove its contents due to purulent content. Such tumors must first be cured and removed after 2-3 weeks. It is recommended to remove atheromas in the winter season, when the cyst has just appeared and has not yet become inflamed. Relapse may also occur due to hyperhidrosis or a hereditary predisposition to obstruction of the sebaceous glands. In these cases, neoplasms appear not in the place where the operation was performed, but in the nearby excretory ducts of the gland.
Only radio wave removal of atheroma completely eliminates the risk of relapse. Before deciding on this procedure, try to find experienced surgeons to avoid possible unpleasant consequences due to an incorrectly performed operation. You can find out where to remove atheroma from reviews of people who have undergone this operation.
General information
Atheroma is also called a sebaceous cyst. Its appearance is typical for young people 20–30 years old. According to statistics, the problem is more often found in women.
The location is the zones that most actively produce sebaceous secretions and are prone to clogging pores. Cysts can be either single or multiple. They slowly increase in size over several years. Large atheromas can compress nearby tissues and blood vessels.
As a rule, cysts do not hurt, itch or fester. The formation itself does not pose a health hazard, but with prolonged existence, atheromas often become inflamed and suppurate, and can also become a chronic source of infection. This often occurs due to mechanical pressure or irritation, which facilitates the penetration of a bacterial infection. Timely qualified assistance will help avoid such complications.
Attempts to independently open the atheroma in the hope of squeezing out its contents do not lead to the expected effect. Self-medication can lead to infection and other unpredictable consequences. Even in the case of a favorable outcome, after an independent autopsy, in one hundred percent of cases there will be a scar. In addition, what you think is a cyst may turn out to be a formation of a completely different nature and even malignant.
A surgeon can correctly diagnose and safely remove a sebaceous gland tumor. Don't be afraid of going to the doctor. The procedure for removing atheroma is completely safe and painless. [3.5]
Advantages of visiting our clinic
If you need removal of atheroma using the radio wave method in a clinic in St. Petersburg, then you can safely contact us. Our clinic employs highly qualified specialists with extensive experience who can competently diagnose and prescribe effective treatment. During their work, our ENT doctors use the most modern equipment to treat atheroma. We try to find an individual approach to each patient in order to take into account the characteristics of his body as much as possible. Our center employs highly qualified surgeons who can successfully remove atheromas without the risk of relapse. So, by contacting us, you can enjoy the following benefits:
- Consultation with a doctor with extensive experience.
- Competent diagnostics.
- Correct prescription of treatment.
- Treatment of atheroma is carried out using the most advanced technologies and modern equipment.
- Individual approach to each client and polite treatment.
- Favorable prices.
In addition, our center also employs pediatric ENT doctors , during whose appointments your children will not be afraid. You can find out more detailed information about how atheroma is removed using the radio wave method, prices and much more by contacting our employees by phone.