Human papillomavirus is one of the most common sexually transmitted infectious diseases. A certain percentage of people live with a virus that does not manifest itself in any way in a latent state, without even knowing about its presence in the body. But in some cases, HPV causes inconvenience. For example, the manifestation of a virus in the form of warts or genital warts on the genitals is perceived as an aesthetic defect. But this is not even the true threat of the disease. At first glance, a harmless papilloma on the genitals can degenerate and take on a malignant form. In this case, the diagnosis is oncology. Is it possible to prevent such risks?
Important: The International Agency for Research on Cancer identifies 1.5 dozen strains of papillomavirus that lead to the development of cancer. The most dangerous (up to 90% of cancer cases) are the 16th and 18th types of the virus.
Specialists at the Lasersvit Mole Diagnostic Center talk about the causes of papillomas on the genitals, the threats and effective methods of combating them. The leading specialized clinic in Kharkov offers services for the diagnosis and treatment of HPV on the genitals. You can make an appointment and consultation with a dermatologist by phone. In the meantime, doctors at the medical institution are answering the most frequently asked questions related to genital HPV.
Papillomatosis in men
The chance of contracting viral papillomatosis is higher for men.
Because a woman may not know that she has HPV on her cervix.
With each episode of unprotected sex, her sexual partner will be at risk of acquiring papillomaviruses without knowing it.
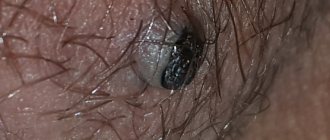
In men, the typical localization of papillomatosis is the penis: its frenulum, coronary groove, internal layers of the foreskin.
The reason is simple: these places are most easily injured during sex and it is easiest for viruses to gain a foothold here.
Less commonly, papillomas appear on the head itself, in the area of the external opening of the urethra.
Sometimes they develop inside the urethra, in the navicular fossa at the external opening and then complicate urination and ejaculation.
Penile papillomatosis in men is visually diagnosed quite easily.
The process has its own characteristics depending on the location.
Typical papillomas form on the shaft of the penis, the skin of the groin and the outer layer of the foreskin.
Condylomas appear on the head, coronary sulcus and perianal area.
How to get rid of genital papillomas?
Despite the scale of research and understanding of the problem by the medical scientific community, it has not been possible to develop specific drugs for the treatment of HPV, as already mentioned. Some countries offer vaccination against the virus at an early age. However, high positive results cannot be achieved with this measure. After all, the vaccine is effective for a fairly short time, but the risk of infection is present throughout life.
Important: The HPV vaccine can only protect up to a certain point. For example, young people who have not reached puberty and have no history of sexual contact are offered to use this type of protection against the virus. After all, it is during adolescence, when the first sexual experience is acquired, that the greatest change of sexual partners is noted, weakened immunity is diagnosed, and infection most often occurs.
But if you couldn’t protect yourself from the virus, you can fight it. An integrated approach to treatment includes:
- measures to strengthen the immune system, because the body’s internal defenses can suppress the activity of the virus;
- taking antiviral drugs that chemically inhibit the spread of the virus;
- removal of papillomas on the genitals, oral cavity and other parts of the body.
Important: If HPV is detected in one partner in a couple, treatment is carried out on both of them, because the risk that both are infected is more than 80%. An adequate, gentle treatment program is developed for an individual patient or couple, taking into account the manifestations of the disease and the type of virus identified through laboratory tests.
There is a chance of self-healing, but it is quite low. And not in a couple where there will be constant relapses. At the same time, a well-chosen treatment tactic by a doctor allows you to get rid of the pathology quite quickly.
Important: It is strictly not recommended to remove papillomas at home, since the use of aggressive media based on vinegar and iodine is dangerous to health. An extensive tissue burn may form at the site of exposure. In this case, self-medication will not bring the desired result. After all, the skin tumor must be removed completely “at the root.” Only in this case it will not grow again.
Do not try to remove warts at home or in a beauty salon. Such treatment does not provide a complete picture of a person’s health status. The type of virus is not determined, and antiviral therapy is not carried out. This means that the symptoms are only muted, and the problem gets worse.
Medical methods for treating genital and other types of papillomas are:
- Radio wave method.
- Laser method.
- Use of liquid nitrogen.
The best of them today is burning out tumors with a laser. A safe, bloodless and painless method has virtually no contraindications. One or two warts are removed in 5 minutes. Hospitalization of the patient is not required, as the procedure is performed on an outpatient basis. Immediately after micro-surgery, a person can return to his usual lifestyle.
The laser burns out pathological tissue completely and without a trace. There are no scars or scars left on the skin. Papilloma on the genitals or in the perineum is removed forever. It is enough to look at the photos of the skin before and after the procedure to be convinced of this.
You can learn more about laser removal of warts at the Lasersvit clinic at your appointment. You can sign up for a consultation right now at a time convenient for you.
How are papillomas on the genitals in men removed?
Many men are embarrassed by warts on the penis and try to remove them at home using various aggressive media. This is a harmful practice that carries a high risk of complications. A secondary infection may be added to a skin burn. In this case, the treatment will be long. At the same time, it is not difficult to get rid of penile HPV if you go to a specialized medical institution.
Our clinic employs qualified dermatologists who clearly know how to treat papillomavirus on the penis. Rest assured, in a fairly short period of time there will be no trace of the pathology left.
We use a laser method that allows us to target the overgrown tissue of the epidermis. Adjacent tissues are not damaged. And since the capillaries are immediately cauterized, no bleeding occurs.
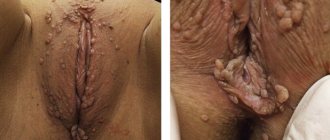
How are papillomas on the genitals of women removed?
Due to the structural features of the female genital organs, removal of papillomas in women is somewhat more difficult. The papillomavirus on the genitals of women often spreads not only to the external genitalia, but also to the vagina and cervix. Therefore, the removal of warts after a thorough examination, taking tissue samples, in case of external manifestations is carried out by a dermatologist, and in case of internal manifestations, it is carried out by a gynecologist. Any independent attempts to get rid of papillomas are unacceptable and dangerous.
Papillomatosis in children
Infection with viral papillomatosis in childhood occurs during childbirth through the mother's birth canal infected with HPV.
Or when using shared towels or washcloths.
Because of these features, in infancy and early childhood, papillomas are more often found on the epithelium of the larynx and ENT organs (respiratory forms).
Older children in organized groups are already more prone to the appearance of papillomatosis of the skin of the torso, face and extremities.
Clinical manifestations are normal, the appearance of the neoplasms is the same as those described above.
Recommendations for the patient after cryodestruction of genital warts
After removing condylomas with nitrogen, it is important:
- To prevent relapses, examination and treatment of the sexual partner is necessary.
- Limit intimacy until complete sanitation and restoration of the skin after removal of condylomas.
- Change your underwear daily and monitor the hygiene of your intimate areas. If a “wound” forms at the site of condyloma rejection, it is necessary to treat the skin defect with antiseptic agents (a solution of chlorhexidine, miramistin, aniline dyes, manganese).
- Replace household items (washcloths and razors) with new ones or thoroughly disinfect them. It is enough to wash towels and bed linen at maximum temperature and iron them with a hot iron.
- Refuse to visit swimming pools, baths and public bodies of water for a period of 1 month after cryodestruction.
Even if there are no complaints, you need to come for a follow-up examination to the doctor within the recommended time frame.
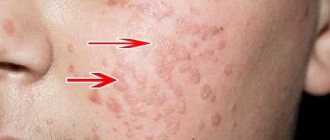
Papillomatosis on the face and neck
This form of pathology also very often has a viral basis.
With such localization of the process, HPV is usually transmitted through personal hygiene items - towels, cosmetics.
This happens at an early age, in children's groups.
A small percentage of papillomatosis of the face and neck occurs in cases of autoinoculation.
When a person himself brings HPV there from other places in his own body, for example, from the groin area.
When several papillomas appear on the face and neck, this initially causes a minor cosmetic defect.
Over time, as the number and size of formations increase, discomfort increases.
From cosmetic it turns into completely organic:
- men find it difficult to shave, papillomas become injured and painful, and there is a risk of infection
- women find it difficult to use cosmetics
- people of both sexes do not like it at all when the neck and face are strewn with papillomas
- when localized on the inner surface of the eyelids, papillomas lead to the sensation of a foreign body in the eye, irritate the conjunctiva and cornea
A typical complication for such processes is the addition of an infection.
Lipomas
Lipomas are formations in the subcutaneous fat layer. Their origin is still not fully understood. There is a possibility of a genetic, hereditary predisposition, but this process cannot be predicted. The size of lipomas ranges from 1 to 15 cm. They do not cause any unpleasant sensations: itching, pain, but they cause inconvenience and cosmetic negatives. They pose a threat to health only if they are damaged by clothing or other mechanical means, which will lead to inflammation.
When treating lipomas up to 3 cm, drug therapy is provided. For larger sizes, lipomas are removed surgically using a radio knife.
Atypical variants of papillomatosis
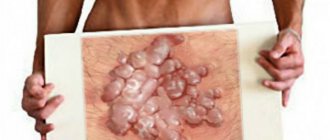
Viral papillomatosis sometimes leads to the fusion of neoplasms and the formation of a huge Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma.
This, although benign, is quite a serious process.
The base of the condyloma is wide and penetrates deep into the epithelium.
Due to this endophytic growth, it destroys the tissues of the organs on which it grows.
Buschke-Levenshtein condylomas occur on the genitals of men (more often) and women (less often).
They reach large sizes and, without treatment, always cause severe damage to the genital organs.
A number of researchers believe that giant condylomas lead to skin cancer.
Sometimes patients with fungal infections come to dermatologists.
For example, chromomycosis, which manifests itself as typical papillomatous growths.
It is also capable of forming condylomatous formations with a characteristic “cauliflower” appearance.
Typical localization of neoplasms is the feet and palms.
Papillomas grow slowly, over the years, and do not merge.
They are often covered with horny scales, after which they turn into ulcers and scar.
Another option is Gottron's carcinoid papillomatosis.
It is a fairly rare pathology: as of 2014, about 60 cases have been described in the medical literature.
The discoverer simply called the disease: skin papillomatosis.
It is now known that the development of the process is not associated with infections, and most likely has an autoimmune origin.
Externally, this is an extensive area of flaking (the size of a palm), similar to skin carcinoma, which is where the name of the disease comes from.
But Gottron's carcinoid papillomatosis itself is benign.
But it’s not easy to understand the diagnosis; a biopsy and histological examination are needed.
Contraindications for cryodestruction of condylomas
Contraindications for removing condylomas with liquid nitrogen:
- The presence of other sexually transmitted infections (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, urogenital mycoplasmosis, syphilis, genital herpes). Before cryodestruction of condylomas in these cases, preliminary sanitation of these infections is required.
- The presence of individual intolerance to cold. This may be indicated by the appearance of any itchy rash when exposed to cold (usually like urticaria). To perform a cold test, applying an ice cube to the skin can be used, followed by assessing the patient's condition.
- Feverish conditions accompanying ARVI, exacerbations of chronic diseases.
- Decompensation of diabetes mellitus, cardiac activity.
Methods to combat papillomatosis
The first thing people do when they notice papillomatosis in themselves or their child is to turn to folk remedies.
These conspiracies, the red thread and all sorts of rituals sometimes really give results: the placebo effect is well known to doctors.
But most patients are not successful.
Moreover: the process progresses, the number of papillomas and their size increase, the quality of life decreases.
Complications often occur in the form of secondary infections, the appearance of ulcers and scars.
And then people do what should have been done right away: they come to see a dermatologist.
What do condylomas look like?
The formation of growths in the intimate area is a common reason for girls to make an appointment with a gynecologist. Papillomas on the labia are small white growths. Vaginal papillomas can be of 2 types: exophytic and endophytic. The former are characterized by a papillary surface and a pointed shape; they are localized in the superficial layer. As a rule, they are provoked by HPV with a fairly low level of oncogenic activity. The latter are flat, they usually grow deep into the epithelial tissue and can cause pathologies in healthy tissue.
If such condylomas are not treated in time, the risk of developing cancer increases.
Examination for papillomatosis
The first thing to do with any type of papillomatosis is to establish its nature.
To do this, doctors analyze the clinical picture (features of the course) of the disease.
The most important stage of diagnosis is analysis: biopsy and histological examination of a tissue sample.
This is the only way to ensure that the process is truly benign.
Considering the prevalence of HPV, papilloma tissue is analyzed to determine the type of pathogen using PCR.
If it turns out to be HPV of high oncogenicity (type 6, 11, 16,18), then treatment must be taken with the utmost seriousness.
Especially for women with cervical papillomatosis.
Treatment of human papillomavirus
After the operation, the removed tissue is sent for analysis to determine the type of virus, and based on the results, antiviral therapy is prescribed. The doctor prescribes medications to reduce the concentration of the papilloma virus in the blood and boost immunity. There is now a large selection of antiviral drugs that can effectively combat HPV. Simple removal of skin papillomas, unfortunately, does not completely rid the patient of the virus. Without undergoing comprehensive treatment, papillomatosis cannot be eradicated.
Removal of papillomas
Basic techniques:
- cryodestruction is optimal for small papillomas in small quantities;
- electrocoagulation is effective for small and numerous formations; it is widely used for papillomatosis of the neck and face;
- laser vaporization is more suitable for less common processes;
- the scalpel is an ideal tool in the fight against large papillomatoses, such as Gottron's carcinoid or Buschke-Levenshtein's condyloma.
Recovery is individual.
The earlier the removal is carried out, the less damage to the skin and the faster healing occurs after any manipulation.
The larger the papillomas and the more extensive the process, the longer everything will take to heal.
Papillomas on the genitals: causes of pathology development
The most common route of infection is direct contact, in which the skin and mucous membranes of the virus carrier and a healthy person come into contact. As a rule, this is sexual contact. Although there is a risk of infection of the child from the mother, the household method is through personal hygiene items. You can also become infected with HPV in common areas – swimming pools, showers.
Important: With each new sexual partner, the risk of infection for a healthy person increases by 20%. Unfortunately, standard protective equipment used during sexual intercourse does not protect against HPV, since latex products do not protect all parts of the genital organs from contact.
The causes of infection are not as important as methods of combating it. After all, the risk of direct or household infection is very high. The main thing is to start treatment on time to avoid complications. It is noteworthy that Western scientists understand the importance of the problem. Up to 6 billion dollars a year are allocated for HPV research and the development of new treatment protocols in the USA alone. But a medicine that will cure the virus once and for all has not been found. However, today’s methods of combating pathology are quite effective with timely access to a specialized medical institution.