Causes of the disease
The pathological process occurs as a result of colonization of the upper layers of the skin by microorganisms of the genus Trichophyton (T. rubrum, T. tonsurans, T. mentagrophytes, T. violaceum). Less common pathogens are candida and molds (including Scytalidium hyalinum and S. dimidiatum).
The development of the disease is facilitated by factors that reduce the human body’s resistance to the influence of specific agents. Among them:
- the presence of chronic abnormalities (diabetes mellitus, varicose veins, autoimmune conditions, malfunctions of the endocrine system);
- HIV;
- injuries, cracked heels;
- flat feet;
- taking immunosuppressive drugs (corticosteroids, cytostatics);
- surgical manipulations in the lower extremities;
- wearing orthoses, plaster casts;
- maceration of the epidermis (including with increased sweating);
- frequent hypothermia.
Additional reasons for the appearance of pathology include: the use of uncomfortable, tight, non-absorbent shoes, daily prolonged standing, and failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
Moisture and heat are the 2 main circumstances that provoke the development of foot fungus.
Why can skin and nail fungus be dangerous?
Fungus of the skin and nails can occur either as an independent disease or as a consequence of existing ones. For example, frequent fungal infections may indicate problems such as:
- presence of viral hepatitis;
- HIV infection;
- a general decrease in immunity, which can cause the development of very serious diseases.
In addition, the development of fungus can cause serious harm to health and reduce the quality of life. With endless itching, it is impossible to concentrate on daily activities, and sores on exposed parts of the body can be a deterrent for many.
Moreover, the fungus is easily transmitted to other people, and being a source of infection is unpleasant, to say the least. By the way, if you notice symptoms of fungus, you should not visit public places with conditions favorable for its development: saunas, swimming pools, cosmetology and beauty salons.
Routes of infection
The main mechanism of transmission of the causative agent of mycosis is contact (household).
Infection occurs at home (if there is a sick person in the family), in public places. The anomaly is often diagnosed in people who go to swimming pools, saunas or baths, pedicure salons, sports or gyms.
The risk of developing the disease increases significantly when wearing someone else's shoes and hosiery, or using another person's bath accessories, bed linen, and manicure tools.
Many shopping center visitors are interested in the question of why they can’t try on shoes on bare feet. The answer is simple - a similar method of choosing new clothes is on the list of indirect routes of transmission of microorganisms from a person suffering from a disease to a healthy one.
Causes of fungal diseases of the skin and nails
Here are just the most basic reasons for the appearance of fungus on the skin or nails:
1. Lack of hygiene.
You don't have to go weeks without showering to get fungus. Sometimes it’s enough to not wash your feet once after a hard day at work. Especially if your feet sweat in shoes, as happens, for example, in winter boots.
2. Dirty floor at home.
In our standard apartments, the hallway is a transit area where people walk around both wearing shoes and barefoot. Dirt brought from the street can contain absolutely any microorganisms, and not everyone is ready to wash the floor every evening. Therefore, it is best to wear slippers at home.
3. Public saunas and swimming pools.
There is no need to refuse to visit the pool or sauna: their benefits for the body have long been proven by hundreds of studies. But it’s definitely not worth walking there barefoot or sitting on surfaces without a towel.
4. Contact with animals.
You shouldn’t be afraid to touch your cat or dog, but it’s better not to let them play with stray animals and always wash their paws after walks. And if you pet an unfamiliar pet on the street, be sure to immediately wash your hands with soap or use an antiseptic: fortunately, today its presence is a new form of etiquette.
5. Contact with soil or sand.
Walking barefoot on the hot sand on the seashore or on the warm earth by a cool river is something worth waiting for summer for or going to warm countries for. But this pleasure can easily turn into a trip to the dermatologist: public beaches are almost the main breeding grounds for fungus. If the surfaces in the pool are washed and treated, then this is definitely not done with sand or earth. We advise you to buy beautiful slates and not worry about your health.
Symptoms
When the pathogen gets on smooth, intact surfaces, mycosis does not appear immediately. The manifestation of the disease is caused by the penetration of pathogens into the epidermis through macerations, abrasions, and deep abrasions. The photo below will help you find out what fungus on your heels looks like.
There are 4 forms in the development of the disease;
the symptoms of each are different.
- The most common type of anomaly - erased - is accompanied by slight itching, mild burning and floury peeling of the skin.
- With the squamous-hyperkeratotic type of the disease, thickening, tightness, dryness of the epidermis, cracks and white plaque appear on the heels. There may be no constant unpleasant sensation of irritation of the skin.
- Characteristic signs of the intertriginous form include hyperemia of the back of the foot. The patient complains of burning and itching, peeling of the skin. This type of mycosis of the heels may be accompanied by a bacterial infection.
- The dyshidrotic type of abnormal condition is characterized by the development of vesicular rashes - hollow formations containing exudate. The merging of the formations with each other leads to the appearance of multi-chamber bubbles. After opening the latter, extensive erosions appear on the skin. With blisters on the heels, there is severe discomfort, itching, and an unpleasant odor from the feet.
How does the disease progress?
The first manifestations of the disease begin in the spaces between the fingers, especially between 4 and 5, since there is the smallest distance between them. A slight itching begins, and over time a strip of thickened and slightly flaky cuticle appears on the finger fold.
After 2-3 days, a small crack forms, from which serous fluid is released, which acts as an excellent medium for the successful proliferation of the fungus. The tough layer of epidermis may fall away, revealing a dark pink area underneath. The progression of the disease leads to its spread over all the toes and the adjacent side of the foot.
Through damaged areas of the upper part of the skin, the fungus can penetrate into the deeper layers behind the epidermis. The disease is accompanied by an eczematous reaction. Fluid-filled blisters form on the skin, which are very itchy. Over time, they can coalesce and erode, resulting in wet spots.
Reference! When studying skin affected by fungus, it was found that the “bare” wet surface that appears under the blisters does not contain the pathogens themselves, but is only a consequence of their activity.
Without proper timely treatment, the fungus affects the entire surface of the foot and toes, sometimes extending to the area above the heel. There is instability in the course - the disease either slows down or intensifies again.
Without treatment, the disease can drag on for many years. In this case, there is a high risk of complications from pathogenic streptococcus: the fluid in the blisters begins to fester, foci of inflammation spread beyond the initial boundaries, and the foot swells greatly. It becomes difficult for a person to move due to painful sensations in the legs. In addition, complications may arise in the form of problems with the lymph nodes.
The development of athlete's foot usually occurs in the summer months. At this time, sweating increases, fingers often become wet, and increased humidity in the interdigital areas creates favorable conditions for the introduction of fungus and its active reproduction.
Mycosis usually appears on the 1st and 5th fingers, spreading from the free side. The nail gradually thickens, acquires a yellowish tint and an uneven sharp edge. Over time, pronounced subungual hyperkeratosis of varying degrees appears.
Treatment at different stages
Detection of the first signs of the disease signals the need to visit a medical clinic. Adequate treatment regimens are developed by a dermatologist after receiving the results of a mycological study. Self-medication can lead to an increase in the area affected by the fungal infection.
The early stages of the disease are stopped by using liniments with an antimycotic effect. The development of advanced forms of the disease is suppressed with the help of systemic drugs. When identifying associated pathologies, antibacterial drugs are additionally used.
The use of alternative medicine recipes helps to consolidate the achieved effect.
To avoid re-infection, the recovered person must replace personal hygiene items, disinfect living quarters, shoes, manicure accessories and clothing.
The list of the most popular means that help destroy the pathogen:
- Terbinafine solution (1%).
- Chlorhequidine bigluconate in a similar concentration.
- Formalin (25%).
The listed drugs are used to treat insoles and inner surfaces of shoes. Items used are washed with a chloramine solution.
Medicines
The main remedies used to treat heel fungus include 4 groups of medications:
- polyenes;
- azoles;
- allylamines;
- morpholines.
In some cases, other drugs are used, the chemical structure of which varies.
The choice of drugs is made taking into account the general condition of the patient, the form of the disease, and the sensitivity of the pathogen.
Systemic drugs for the treatment of fungus
The most popular oral medical products are:
- azole Fluconazole (course ranges from 2 to 6 weeks);
- allylamine Terbinafine (taken for at least 14 days);
- morpholine Amphotericin B (used for up to a month).
What is skin and nail fungus?
The term “fungus” refers to a whole complex of various diseases and pathogens. But usually we are talking about only some types of fungus:
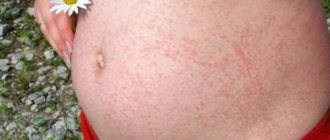
Dermatomycosis.
Caused by the fungi Trichophyton, Microsporum and Epidermophyton. Affects the skin and sometimes nails. At first it may not seem serious, because the first symptoms are:
- the appearance of pink or red spots on the body that have a clear shape and pigmentation around the perimeter;
- itching at the site of the spots, which does not always appear.
If you do not consult a doctor in time and do not prescribe the correct treatment, then the symptoms can become much more serious:
- the appearance of dandruff;
- baldness of affected areas;
- the occurrence of suppuration;
- uncontrolled increase in the area of affected areas.
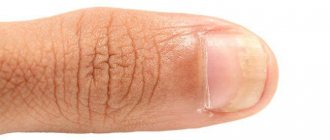
Onychomycosis.
Caused by the fungi Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton interdigitale, Trichophyton tonsurans. It affects the nails and is the most common type of fungal infection. It has the following symptoms that appear as the fungus develops:
- the nail begins to turn yellow;
- the nail becomes exfoliated and thickens;
- an unpleasant odor appears that cannot be eliminated by any means;
- the plate becomes deformed, irregularities and “waves” appear;
- the nail completely dies and “falls off” from the finger.
Prevention
Preventing the occurrence of mycosis is quite simple. The list of preventive measures:
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- use only personal bath accessories, shoes, items of clothing;
- regular disinfection of premises with chlorine-containing agents;
- careful foot care, application of preventive liniments;
- treating wounds with antiseptics;
- strengthening the immune system;
- wearing comfortable shoes;
- therapy for existing ailments;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Heel fungus is a pathology that is difficult to treat. The rapid suppression of the disease is facilitated by early detection and compliance with the recommendations of a dermatologist.
Treatment of foot fungus
For successful therapy, you need to pay a lot of attention to the treatment of lesions.
A person affected by fungus should take foot baths every day with potassium permanganate. It is necessary to get rid of the crusts, puncture the blisters and remove the “fringe” along the boundaries of the erosive areas and the covers of the festering blisters.
After the bath, you need to apply medicinal bandages soaked in an aqueous solution of copper sulfates (0.1%) and zinc (0.4%) or a 1% solution of resorcinol to the affected areas. After the weeping areas have begun to heal, dermozolon, mycozolon are used, and then alcohol solutions based on fungicide and fucorcin. If necessary, the kit is supplemented with fungicidal ointments.
Obtaining the desired result does not depend on the drugs used, but on the correct sequence of their use according to the current situation with inflammatory processes.
Additional treatment plays a huge role after the end of the fight against the lesions, because it helps prevent relapses. The skin of the feet is wiped with 2% salicylic alcohol or 1% thymol, and the use of 10% boron powder is also required. To get rid of and prevent the appearance of fungi in shoes, you need to wipe them from the inside with a formaldehyde solution, wrap them in thick fabric for a couple of days, and then dry them in the fresh air. For socks, tights and stockings everything is simpler - you just need to boil them in this solution for 10 minutes.
If a complication occurs with pyococci, then antibiotics are used - methicillin, cephaloridine and others. Bed rest is mandatory.