Fungal diseases develop very quickly and cause inconvenience. It is not always easy to fight them on your own and it is best to carry out prevention.
However, if you are still affected by mycosis, you should immediately contact an appropriate specialist and begin treatment.
Often, complete restoration of the skin and nails can take about a year. To make the process go faster, patients simultaneously use folk remedies against toenail fungus and fingernail fungus. The components that are popularly used for treatment are available to anyone.
They not only prevent the fungus from developing further, but also help painful areas gain a healthy appearance.
What does fungus in the body or mycosis mean?
Everyone knows about fungal diseases in humans, from newborn thrush to nail damage and hair loss. Less common are fungal infections of internal organs - the respiratory and digestive systems, when the fungus penetrates through the skin and mucous membranes deep into the body. As a result, mycosis develops, often in a severe and difficult to treat form.
About 500 species of fungi live in the human body, being conditionally pathogenic. This means that they may not cause disease if they are in bacteriological balance with other microflora and with a strong immune system. As soon as these parameters are violated, the fungi are activated, acquire pathogenic properties, and visceral mycosis develops.
Effective prevention
The most important thing when preventing fungus is to remember to take precautions. Nobody canceled hygiene after visiting public places. When returning from the pool or sauna, do not be lazy and use folk remedies.
Take a bath with baking soda or tea tree oil. Relax and be sure that treatment for nail fungus on your toes or hands will not affect you. Strengthen your overall health through nutrition, exercise and quality rest.
By preventing the body from lowering its immunity and weakening, you reduce the risk of fungal diseases.
Reasons leading to the development of mycosis of internal organs
The following factors can lead to activation and increased reproduction of fungi that previously peacefully coexisted in the body:
- Long-term use of antibiotics, especially modern, broad-spectrum ones. They kill not only pathogenic, but also beneficial microbes that inhibit the development of fungi. And the fungi themselves are very resistant to antibiotic therapy.
- Taking chemotherapy drugs in cancer patients, which suppress both the immune system and the protective microflora in the body.
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs - corticosteroids, which reduce immunity.
- Immunosuppressive drugs used in people with organ transplants to suppress the immune system and prevent rejection.
- Ionizing radiation is radiation treatment or increased background radiation that sharply suppresses the immune system.
- Blood diseases - anemia, leukemia.
- Immunodeficiency - after serious illnesses, with HIV infection, chronic intoxication in those who abuse alcohol, drugs, and smoking.
- Chronic diseases with circulatory and metabolic disorders: diabetes mellitus, hypofunction of the thyroid gland, liver and kidney failure, dysbacteriosis, systemic diseases, severe forms of allergies.
- Age-related immunity deficiency - in infants and the elderly.
- Sedentary lifestyle, overweight.
- Stressful situations that reduce the body's protective properties.
- Failure to comply with sanitary and hygienic rules.
- Surgical operations, the presence of wounds, abrasions, abrasions, ulcers, rashes on the skin and mucous membranes.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
Often these provoking factors are combined. For example, unprofessional antibiotic treatment of pneumonia in infants without the use of antifungal agents.
Herbal mixtures against fungus
With the combined use of antifungal herbs, you can achieve good results in killing fungi. Parasites cannot tolerate an acidic environment, so it is possible to select preparations whose use would maximize the effect of treatment. You can use the following recipe: take burdock root, yarrow leaves, wormwood stem, dry the ingredients, chop and mix. 2 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the mixture and leave in a thermos for 12 hours. Drink the resulting tincture a day. Treatment lasts 1-1.5 months.
Routes of transmission of the fungus and symptoms
Visceral mycosis in humans is caused by 3 types of fungi: candida, coccidoid and histoplasma, and, accordingly, diseases develop - candidiasis, coccidomycosis and histoplasmosis. They affect the respiratory, digestive and genitourinary systems, parasitizing the mucous membranes, in severe cases they enter the bloodstream, developing fungal sepsis and damage to all organs.
Transmission of the infection occurs through contact through damaged skin and mucous membranes, by airborne droplets and oral routes, through sexual contact, and possible activation of conditionally pathogenic fungi living in the body.
Symptoms of visceromycosis depend on which organ is affected, these may be:
- cough with phlegm;
- dyspnea;
- increased body temperature;
- frequent loose stools;
- painful urination;
- general weakness, lethargy, poor appetite;
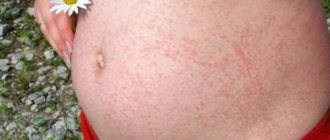
- the appearance of a rash all over the body;
- areas of subcutaneous hemorrhage.
Important: at the first, even minor symptoms, especially in people of the listed risk groups, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Fungal skin diseases
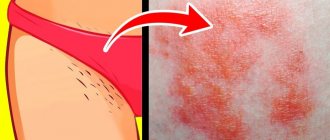
Fungal skin infections usually manifest as changes in skin color, the appearance of spots, itching and peeling. Of course, these symptoms in themselves are very unpleasant and are a reason for a visit to a dermatologist, but the main danger of the disease is that the waste products of fungi are serious toxins that literally poison the human body. As a result, not only the surface of the skin is deformed, but also chronic diseases worsen, intolerance to certain products or medications appears, and complications of a bacterial or viral nature arise. Therefore, fungal skin diseases should be taken very seriously and not delay visiting a doctor. Medical products (drugs, medicines, vitamins, medicines) are mentioned for informational purposes. We do not recommend using them without a doctor's prescription. We recommend reading: “Why can’t you take medications without a doctor’s prescription?” In order to choose the most effective treatment tactics, specialists must first determine what type of fungal skin infection they have encountered. To do this, a thorough examination is carried out: microscopic and/or cultural diagnostics. The microscopic method involves examining scrapings from the patient’s nails, skin flakes, or hair. In this way, the presence or absence of a fungal infection as such is revealed. In order to identify which fungal disease the patient is suffering from, the fungi are grown in a special nutrient medium, and then the grown colony is assessed and examined.
Types of fungal skin diseases
Today, there are several types of fungal skin diseases. All of them have their own clinical manifestations and require specific treatment:
- Keratomycosis is a disease in which the fungus affects only the top layer of the skin. One of the most common forms of keratomycosis is pityriasis versicolor, also called versicolor. It appears as slightly scaly patches of pinkish-brown color. As a rule, it appears on the chest, back, shoulders and neck. It is noteworthy that this disease does not cause any inflammatory reactions. Victims of tinea versicolor usually include teenagers and middle-aged people, and the peak incidence occurs in the spring.
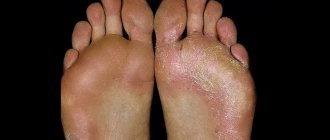
- Dermatomycosis is a disease in which the outer layer of the skin, dermis, as well as nails and scalp become “victims” of the fungus. It is this group that includes the most common fungal infections - mycoses of the hands and feet. The victims of the last of these diseases are usually people suffering from excessive sweating of the feet, as well as those who often visit public saunas or swimming pools. Endocrine problems and wearing rubber shoes also contribute to the development of fungal foot diseases. In mild forms of the disease, the skin only slightly peels, there is slight redness in the areas between the fingers, as well as itching, which intensifies after contact with water. If treatment is not started, the symptoms will intensify, calluses, erosions, swelling and hyperemia of the skin will appear.
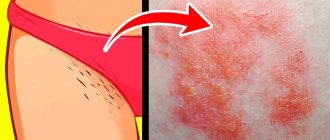
- Candidiasis is a disease that can affect the skin, intestines, mucous membranes, and genitals. The causative agent of this disease is the yeast-like fungus Candida, which begins to actively multiply as soon as the body’s resistance decreases. Therefore, those at risk are primarily children, the elderly, and those with significantly weakened immune systems. Candidiasis most often develops in skin folds. The skin turns red, and the inflamed area always has clear boundaries. The affected skin is moist and may be covered with a white coating.
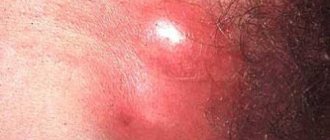
- Sporotrichosis. This fungus affects both the superficial and deep layers of the skin. Subcutaneous tissue, mucous membranes and internal organs are also affected. Most often, sporotrichosis nodules appear on the skin of the hands, legs and groin area.
- Deep coccidioidal mycosis is one of the most dangerous types of disease, since it affects not only the skin, but also the internal organs of a person. If medical care is not provided in a timely manner, the person may die.
Treatment methods for fungal skin diseases
To treat fungal skin lesions, three methods of therapy are usually used. The first of them involves the use of topical medications, the second - therapy with oral drugs, and, finally, the third - a combination of the first two options.
Local medications include a variety of ointments, gels, suspensions and other preparations. Their peculiarity is that they act exclusively on the site of the disease, without entering the bloodstream. As a rule, such products are used if a relatively small area of skin is affected by the fungus.
The duration of treatment varies. It can range from a week to several months if therapy was not started immediately after the disease was diagnosed. Apply external agents several times a day.
Oral medications affect not only the affected area, but the entire body. As a rule, they have a wide range of side effects, and therefore most often the course of treatment is not too long. These drugs are used for large areas of damage, as well as for advanced forms of the disease.
Combination therapy is often used. External medications reduce the intensity of symptoms and speed up healing, while tablets eliminate the causative agent of the disease.
One more nuance is extremely important: no matter what type of therapy is used, you cannot interrupt the course on your own. The regimen according to which the drugs will be used, as well as the duration of treatment, is determined by the doctor, based on the symptoms and type of fungal infection:
- An indispensable condition for successful treatment of keratomycosis is careful hygiene and reduction of sweating. Antifungal and antibacterial drugs are used, both externally and internally. The affected areas of the skin are carefully treated with solutions of sodium hyposulfite and salicylic acid.
- For dermatomycosis, you should follow a diet with a minimum presence of sweet and salty foods in the diet. Antihistamines are prescribed to relieve itching, as well as vitamins. Local manifestations can be relieved by rubbing and lotions based on solutions of salicylic acid and iodine, as well as tar ointment. Fungal infections of the feet require careful hygiene and temporary refusal to visit the beach and pool. Antifungal ointments, lotions with a cooling effect, antimycotic and corticosteroid drugs are used.
- For skin candidiasis, systemic antibacterial drugs are completely discontinued. Antifungal therapy is carried out with ointments and creams, the lesions are treated with antiseptics. It is imperative to take medications that will help restore intestinal microflora. Baked goods, sweet foods, and foods containing simple carbohydrates are excluded from the diet.
- To treat skin manifestations of sporotrichosis, the latest generation antifungal drugs, as well as potassium iodide, are used.
- Treatment of deep coccidioidal mycosis involves the use of modern antimycotic drugs. It should be borne in mind that most of them are extremely toxic and therefore cannot be used to treat patients suffering from liver or kidney failure.
Treatment of skin fungus with folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers a huge number of recipes for the treatment of fungal skin diseases. Many of them are quite effective, however, before using herbal decoctions and tinctures, you must consult a doctor.
- Grind peppermint leaves and add a little salt to them. Grind thoroughly, the finished mass can be applied to the affected areas when treating foot fungus.
- Pour 10 g of lilac flowers into 120 g of alcohol. The product should be infused in a dry and dark place for two weeks. After this, strain and wipe the affected areas.
- Wipe areas of fungal infection with juice from cocklebur leaves.
- Mix oak bark, verbena officinalis, blue blackberry fruits, calendula inflorescences and horsetail in a ratio of 3:2:2:2:2. Pour three tablespoons of the collection into a glass of boiled water and boil over very low heat for a quarter of an hour. After cooling, use the decoction for lotions.
- In case of fungal infection of the nails, attach a pre-crushed fresh Kalanchoe leaf to the nail plate with a plaster.
Treatment of fungus in the body
The problem of getting rid of fungus is very complex and requires complex and long-term treatment. Special antibiotics with targeted antifungal action are used: clotrimazole, nystatin, lamisil, nizoral, ketoconazole and other representatives of this group. Their selection is carried out individually for each patient after microbiological examination, isolation of the type of fungus and determination of its sensitivity to a particular drug. Fukortsin also deserves attention.
The treatment complex also includes immunostimulating agents, vitamins and detoxifying drugs. Diet plays a big role. You should exclude flour, butter and sweet foods and drinks, alcohol, as well as yeast bread. You need to introduce more seafood, fiber and vitamins in the form of cereals, vegetables and fruits into your diet.
Fungal diseases of ENT organs
According to statistics, every fourth patient who has been diagnosed with chronic ENT diseases suffers from a fungal infection.
At the same time, diseases of the ears, nose and throat are caused not only by pathogenic fungi, but also by those that are present in a healthy body - for example, yeast-like candida fungi.
As soon as the microbial balance in the body is disturbed, increased proliferation of the fungus begins.
Fungal diseases of the throat are called pharyngomycosis, fungal diseases of the ears are called otomycosis. Rhinomycosis is a fungal infection of the paranasal sinuses and nasal mucosa, and laryngomycosis is a chronic laryngitis provoked by fungi.
Causes of fungal diseases of the ENT organs
The causes of fungal infections of the ENT organs vary. The development of mycoses can be provoked by both internal and external factors.
Let us highlight the main ones:
- Immunity disorders. The reason for the decrease in the body’s resistance can be not only diseases, but also the uncontrolled use of various drugs, primarily antibiotics and corticosteroids. The overuse of antiseptics can also provoke fungal infections of the throat, as a result of which the microflora of the mucous membrane suffers.
- Increased blood sugar due to diabetes.
- Changes in hormonal levels. This problem is faced mainly by older women. Dry mucous membranes is one of the factors in the development of fungal infection.
- Microtraumas of the mucous membrane. They are the ones that most often cause the development of otomycosis. Injured skin secretes intercellular fluid, which is an excellent breeding ground for the development of fungal infections. At the same time, the thickness of the skin of the outer ear is only half a millimeter, so it is easy to injure it. It is noteworthy that often we do not even notice this. Injury to the skin of the ear is possible even with an ordinary cotton swab, which many people use to remove earwax. Otomycosis can also develop due to water getting into the ear while swimming.
- Pharyngomycosis is often called a disease of removable dentures. If they were chosen incorrectly, fungal infection may develop.
- Another reason for fungal infections of the ENT organs is dental problems. Caries contributes to the development of fungal diseases of the paranasal sinuses. Often, fungal spores are introduced into this area after poor-quality treatment of the fourth, fifth and sixth teeth of the upper jaw - their roots either grow into the paranasal sinuses or are adjacent to their bottom. Therefore, you cannot delay dental treatment, and you should approach the choice of a dentist extremely responsibly.
- Fungal infections of the larynx, also known as laryngomycosis, often develop under the influence of harmful environmental factors. These diseases affect people who, due to their occupation, often inhale dust, fumes of acids or alkalis, as well as other chemicals. In addition, the delicate mucous membrane of the larynx can be damaged by too hot drinks or food and strong alcoholic drinks.
- The cause of laryngomycosis is often also GERD - gastroesophageal reflux disease. Fungal infection occurs due to the backflow of acidic contents from the stomach into the esophagus and larynx.
Symptoms of fungal diseases of the ENT organs
Fungal diseases of the ENT organs are often confused with manifestations of a cold or ARVI.
Indeed, the symptoms are somewhat similar:
- Pharyngomycosis is manifested by discomfort in the throat, burning, dryness and soreness. In this case, the unpleasant sensations are more pronounced than with a bacterial infection. The pain is classified as moderate, but increases with swallowing and when eating hot or spicy foods. Pain sensations can radiate to the submandibular area, as well as to the ear area. In addition, with pharyngomycosis, the mucous membrane of the throat swells and plaque forms on it. Patients complain of general symptoms of intoxication.
- Manifestations of otomycosis are hearing loss and discomfort in the ear. The external auditory canal may become red. Patients complain that the ear seems to be “bursting” from the inside, as if there is some kind of foreign body in it. There is also a thick discharge from the ear canal, which may be white, yellow or almost black.
- Rhinomycosis is manifested by frequent nosebleeds, increased dryness of the nasal mucosa, pain and “bloating” of the paranasal sinuses.
- Symptoms of laryngomycosis include a dry cough and a change in voice timbre. A “cheesy”, whitish coating appears on the tonsils. The cervical lymph nodes often become inflamed. Cracks may also occur in the corners of the lips, which do not heal for a long time and are very painful.
Treatment of fungal diseases of ENT organs
Fungal infections of the ENT organs are less treatable than bacterial ones. This is explained by the specific structure of the fungal cell membrane. Therefore, they are resistant to the action of even the most modern antimycotic drugs.
Before administering drug therapy, the doctor must conduct a laboratory test of a smear from the throat and ear. If a fungal infection of the sinuses is suspected, an x-ray or computed tomography is performed.
For the treatment of mycoses of the ENT organs, antimycotic drugs of external and internal action are used. The use of immunostimulating drugs is also recommended. To treat mycosis of the sinuses, surgery is often necessary.
How to fight fungus?
Let's find the herbs and herbal products that are sure to help.
For example, bedstraw will help heal from:
- tuberculosis, pneumonia;
- atherosclerosis, vascular and heart diseases:
- digestive and liver ailments;
- gynecological problems;
- inflammatory processes in the kidneys, bladder;
- wounds, ulcers, burns;
- oncology and fungus.
Bedstraw tincture: 1 tbsp. l. pour 200 ml of vodka over fresh chopped herbs, let stand in a dark place for 10 days, shaking from time to time. Then the liquid must be drained, the herb squeezed out, and the tincture strained. Drink 30 drops 3 times a day.