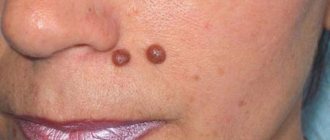
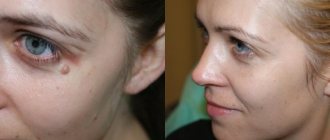
Warts on the hands are a benign viral disease in which single or multiple rounded protruding papules of various sizes appear on the skin - from 1 mm to 1.5 cm (sometimes more), gray or flesh-colored. In addition to the skin of the hands, warts can appear on other parts of the body (face, anogenital area, soles of the feet, etc.), as well as on mucous membranes.
The formations tend to spread, merge into large conglomerates, rapidly grow, bleed when injured, and relapse. Self-treatment using questionable methods leads to the appearance of scars, and malignant degeneration is possible on the mucous membranes. Therefore, the problem cannot be ignored.
Sometimes warts can disappear without treatment within 2 years. However, you should not rely on this, since the pathogen still remains in the body and, against the background of a weakened immune system, the formations will make themselves felt again. And over time, they may become less sensitive to therapeutic effects. Therefore, it is important to remove them and, in some cases, undergo antiviral therapy and immunocorrection.
What does a wart on your hand look like?
Warts are quite difficult to confuse with any other skin defects, since the emerging epidermal growth is not accompanied by itching, pain or discomfort. Most often, vulgar neoplasms that affect the skin of the hands are almost identical in color to healthy skin or have a mild reddish tint. The surface of the wart is initially smooth and even, but over time it undergoes pronounced keratinization. The skin pattern at the site of the defect disappears, replaced by an oval or round seal.
The danger of such benign neoplasms lies in the high risk of injury to these epidermal structures. Which can lead to the following unpleasant consequences:
- Heavy bleeding;
- Infection of the wound surface;
- Formation of a scar or scar;
- Autoinoculation of the papilloma virus onto healthy tissue, which leads to the spread of warts.
In addition, many people are wondering how to cure warts on their hands, guided by the aesthetic side of the issue.
Removal of plantar warts
It is worth treating a plantar wart if:
- There are painful sensations.
- The wart is bleeding.
- There were spots on it.
- The wart quickly increases in size.
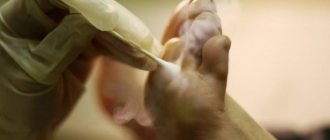
There are many treatment methods. One of them is cryodestruction. The meaning of the method is that the wart is exposed to liquid nitrogen at a temperature of minus 196 degrees. The virus-affected area is frozen and the wart is removed.
The usual and aggressive method of exposure is used. With the aggressive method, nitrogen is applied for a few seconds longer, but this method is more painful. It is important to note that if a wart appears and exists for more than six months, then the effectiveness of cryodestruction is greatly reduced, and the meaning of such an operation, accordingly, also disappears.
After removing a plantar wart using liquid nitrogen, you should follow some recommendations:
- the blister remaining at the site of the wart cannot be opened;
- to avoid mechanical damage, use a sterile bandage rather than a plaster;
- Treat the affected area with salicylic alcohol 2% twice a day;
- try to prevent water from entering the affected area.
Another method is laser coagulation. This is one of the most common methods for removing warts. Most laser systems are equipped with a special cooling system. Thus, the procedure takes place with minimal discomfort and does not allow inflammation, since the laser has antiseptic properties. Moreover, this is a non-contact method.
There are several ways:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. Treatment in this case occurs using infrared light. The method is 70% effective, but the downside is that healthy tissue can also be damaged.
- Erbium laser. This treatment method uses a shorter wavelength, which reduces the likelihood of scarring after surgery. Efficiency is typically 75%.
- Pulsed dye laser. With this method of exposure, the primary destruction of dilated capillaries in the wart and stimulation of the immune system, which contributes to effective healing. The effectiveness of treatment is about 95%.
After laser treatment, a crust forms on the affected area, which disappears on its own within seven to ten days. The recommendations for this method of treatment are the same as after exposure to nitrogen - avoid mechanical damage and ingress of water.
The next way to remove warts is electrocoagulation. In this case, a high frequency current is applied to the wart. Treatment is carried out under local anesthesia. Exposure of a wart to high temperatures leads to the evaporation of cells affected by the papilloma virus. Another advantage of this method is that cauterization of blood vessels prevents bleeding. After surgery, a crust forms on the affected area of the skin, which disappears within 7 to 10 days.
A plantar wart can be treated with direct surgery. In this case, excision occurs under local anesthesia, then sutures are applied. After the operation, the doctor will prescribe certain recommendations. Thus, it is recommended to prevent water and soap from entering the affected area, not to tear off the resulting crust, and to treat the affected area with an antiseptic in the first 7-10 days.
For each type of operation there are certain contraindications. Thus, it will be impossible to perform the operation if the following occurs:
- pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- malignant tumors in the body;
- infection and inflammation around the wart;
- exacerbation of herpes;
- elevated temperature.
If your blood pressure is high, the procedure should also be postponed.
Causes and etiology of the appearance of warts on the fingers
Warts on the fingers and other parts of the body are exclusively viral in nature, which is associated with the penetration of the human papillomavirus into the patient’s blood. Based on this, treatment of warts on the fingers, palms and elbows should be aimed at eliminating the underlying cause. Unfortunately, today no medical technique is capable of completely freeing the patient’s blood from the virus, which explains rather the symptomatic therapy of neoplasms.
An important concomitant factor that provokes the appearance of warts on the hands is a decrease in the body’s immune response, which can occur against the background of overwork, poor nutrition or an infectious process. Considering the fact that HPV is able to penetrate into the blood through damage to the epidermis, it is worth noting the role of microtraumas, scratches and small wounds, which are not uncommon for the skin of the hands. Based on all of the above, you can once again appreciate the importance of maintaining personal hand hygiene.
Despite all of the above, HPV infection cannot be called something critical. Statistics show that about 90% of all people are carriers of the virus, which may not manifest itself for a long time, remaining latent in the blood.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- bumps grow on the joints of the fingers;
- difficulty bending the finger;
- Difficulty in straightening the finger;
- pain when moving;
- increase in leukocytes in the blood;
- redness and swelling in the area of the affected joint.
In the case when the results of a general blood test show low lymphocytes, this fact may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, including one that causes the formation of tubercles on the fingers. Lymphocytes are cells of the human immune system. They are responsible for creating antibodies to viruses, bacteria and other substances that are foreign to the body.
Symptoms that may accompany wart pain
Painful growth is generally not the only symptom of negative changes that a patient may complain about at an appointment with a dermatovenerologist.
Often an additional group of complaints is presented regarding the affected area of the skin.
These include:
- Inflammatory symptoms
Symptoms of inflammation most often include pain.
However, they are not limited to pain.
The patient may complain that the tumor has become red and very sensitive to touch.
In some cases, it may be noted that it has increased in size or the tissue around it has become swollen.
- Skin symptoms
Patients often feel that the wart is itchy and a pronounced burning sensation appears in the area.
These symptoms contribute to increased inflammation.
Especially if a person cannot restrain himself and combs the problem area.
- Blood discharge
Often, if the scratching is very strong, blood is released from the formation in small quantities.
If the growth is very severely injured, the bleeding may be noticeable, and sometimes medical assistance is required to stop it.
When should you see a doctor for flat warts?
In any case, we recommend making an appointment with a dermatologist. Yes, it is easy to diagnose growths. Flat warts have characteristic features and you can easily determine the type of tumor. However, there are also difficult cases.
Sometimes the growths don't look like typical flat warts. In such situations, you cannot do without the help of a doctor, because a dermatologist has a much better understanding of neoplasms. He can also perform a dermatoscopy. This is the name of the study of formation using a special apparatus - a dermatoscope.
So, the doctor helps with the diagnosis.
What about treating warts?
It is not necessary - in most patients the formations disappear on their own. Yes, not right away. Scientists conducted a study on this topic and found out the approximate lifespan of flat tumors. Up to 23% of warts disappear within two months. Up to 73% in two years. That is, in a couple of years, most of the formations will disappear.
When should flat warts be removed?
Treatment will be required if the growths:
- Bleeding
- Grow
- Change color
These are alarming signs in which it is best to go for an examination with a dermatologist. The doctor will determine the degree of danger of the formations. Sometimes they need to be removed. Usually no.
So operations are often performed at the request of patients, and not due to medical necessity.
Types of flat warts
All juvenile warts are almost the same. They are flesh-colored or brown in color and are only slightly raised above the skin. Therefore, they are difficult to detect.
Based on location, growths are divided into:
- Flat plantar warts
- Flat warts on the face
- Flat warts on the body
The greatest problems are caused by neoplasms on the face. Yes, flesh-colored growths, even in large quantities, are almost invisible, but with a different color they stand out on the skin. Mostly, patients want to remove warts on the face.
The formations on the legs and arms are not so obvious. At the same time, growths on your hands increase the risk of infection to people you come into contact with.
Should they be removed?
Hard to tell. These warts are completely safe and never turn into malignant tumors. Yes, they are contagious. But there is no threat to health or life.
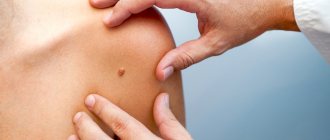
Diagnostics is everything
To identify the root cause of the disease and select an effective course of treatment, the doctor gives the patient appointments for ultrasound, X-ray, MRI, and urine testing. The study of uric acid salts will determine the presence of gout. An x-ray will reliably demonstrate the presence of osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. However, the results of a visual examination and verbal complaints from the patient are often sufficient to make a diagnosis.
Treatment of flat warts
Although these tumors disappear sooner or later, not all people are ready to wait for months for a joyful moment. They want to speed up this process.
For example, with the help of improvised means, salicylic acid is very popular, which gradually destroys the tissue of warts.
Unfortunately, this method has not been properly studied at this time. No studies have been conducted.
Doctors do not recommend using salicylic acid, as it can leave scars and burns on the skin. To treat flat warts, it is better to use proven methods. One option is for dermatologists to prescribe special creams that irritate the upper layer of growths. After treatment, the tumor is simply torn off.
Creams are not always effective. Sometimes get rid of flat warts only by surgical methods.
Pain when a wart is damaged
If the wart is inflamed and hurts, then first of all you should think about the fact that it has been damaged.
This happens most often if the formation is localized in some unfortunate place.
For example, this could be the armpit, the area under the breasts of the fair sex, etc.
The growth may be located in a seemingly problem-free place.
But at the same time, when wearing clothes, it can be influenced by friction that occurs upon contact with fabrics.
Damage to the formation is the most common cause of unpleasant symptoms.
Traumatization can be either quite pronounced, up to the appearance of blood, or weak, but systematic.
The second option is most often found during friction.
Doctors draw the attention of patients to the fact that problem areas should remove growths as early as possible.
This will help avoid their irritation and subsequent negative changes.
Also, all pathogenic growths, which are often rubbed with clothing, must be removed as early as possible.
Provided that a person does not have the opportunity to change style.
An option may be to change synthetic clothing to natural ones.
There is no guarantee that this approach will be an effective way to solve the problem.
Symptomatic means problematic
The growths are visible to the naked eye. The reason for their occurrence can be judged by their appearance.
Hard and dense lumps on the joints, covered with smooth skin, usually form in men over 40 years of age and indicate gout. They are usually called gouty tophi. They grow during periods of exacerbation of the disease. The patient becomes weaker and complains of malaise. The temperature in the area of the tophi rises, and the pain sometimes becomes unbearable.
If the skin on the lump is rough and red, and the growth itself is round and elastic, it is a hygroma. It usually forms in women 20-30 years old and can be single-chamber or multi-chamber. Hygromas differ from other types of growths in that their size gradually increases, and pain is felt when pressed.
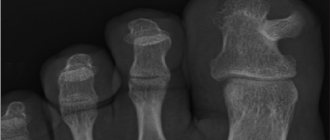
Formations on the interphalangeal joints that appear after 60 years are called Heberden's nodes. They are equally likely to be found on any phalanx and are signs of osteoarthritis. This disease leads to stiffness of the hands and deformation of the joints.
Nodules up to 2 cm in diameter, which form in 20% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, are rheumatoid nodules. They do not cause pain, but the course of the disease is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms: lethargy, fatigue, fever, and sometimes loss of body weight.