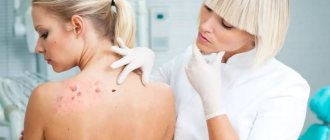
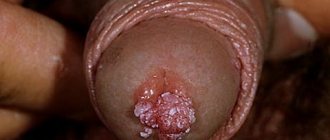
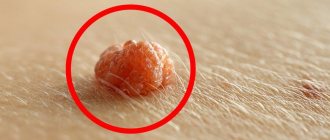
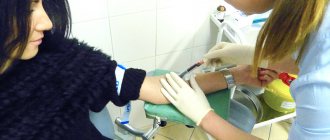
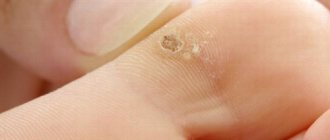
Papillomas are a widespread phenomenon in modern society. According to medical statistics, they are observed in one form or another in 80% of people and are benign small tumor-like formations on the skin and mucous membranes of different parts of the body. They are only one of the manifestations of infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), of which there are more than 190 types. Among them, viruses with high, medium and low oncogenic risk are distinguished. Therefore, in addition to an aesthetic drawback, papillomas can pose a serious danger to human life and health, since some of them can transform into malignant tumors.
Why do they appear?
Like warts, papillomas are not dangerous
.
Their appearance is associated with the human papillomavirus (HPV),
which is transmitted through contact with a carrier. It is also possible to transmit HPV from an affected area of skin to a healthy one in one person. High humidity and microcracks in the skin increase susceptibility to viral particles. In this regard, you should always use personal hygiene items when visiting swimming pools, saunas and showers.
Important:
a large number of papillomas may indicate problems with the immune system.
For women in such cases, it is necessary to take a smear for HPV, since some of its types can cause cervical cancer
Possible methods of infection with HPV
The virus remains viable in the environment. Transmission of infection occurs from a carrier to a healthy person in the following ways:
- during sexual intercourse;
- through household means (through personal hygiene items);
- in bathhouses, saunas, gyms when common items are infected;
- from mother to child during childbirth;
- self-infection - during hygiene procedures or in places of friction.
The risk of infection and degeneration of papillomas into malignant formations increases with decreased immunity. Factors that increase the risk of infection are:
- early onset of sexual activity, different partners;
- the presence of urogenital infections (chlamydia, trichomoniasis, bacterial vaginosis, HIV, etc.);
- local irritating mucous discharge in the genital area;
- dysbiotic conditions;
- bad habits.
Depending on the type of virus and the state of immunity, the rate of spread of infection varies. Some types of papillomas may not manifest themselves for years. It is better to remove condylomas immediately - they almost always degenerate into malignant formations.
What is the best way to treat?
A large number of papillomas certainly causes inconvenience and does not look aesthetically pleasing. However, this is not a reason to use old-fashioned methods for removal with thread, pliers or a blowtorch.
For single small (1x1 mm) formations, celandine juice
- a proven folk remedy.
When there are many papillomas or they are large, this method is not suitable
, as it can last for months and lead to severe inflammation.
Removal using radio wave surgery is much more convenient and effective
The operation does not require special preparation, is practically painless, and after it you can drive a car.
Once I had the opportunity to remove about 70 papillomas from one patient at once. It is difficult to convey all the joy of a person who got rid of them, whom they tormented for several years.
Treatment and removal of papillomas
Treatment of human papillomavirus infection is always complex. Of course, you can simply remove the disturbing papilloma, but in this case there is a high risk that a new one or even several will soon form in its place. Since the main reason for the formation of papillomas is a decrease in the body’s own defenses, which allows HPV dormant in the body to become more active, patients with papillomatosis are first prescribed drug therapy. It includes taking immunomodulators and antiviral drugs. For extensive lesions of the skin and mucous membranes by papillomas, cytotoxic drugs can also be prescribed. But their use is carried out under the supervision of a doctor, since they can provoke serious side effects.
If a patient is diagnosed with concomitant infections or diseases, he must be prescribed treatment appropriate to the situation, and sometimes it is additionally necessary to obtain advice from a specialized specialist and undergo therapy under his supervision.
Condylomas of all types are subject to mandatory removal, as well as papillomas, which are often injured and inflamed. In other cases, removal is carried out at the request of the patient. But it is possible to begin eliminating visible manifestations of HPV infection only after completing treatment for concomitant diseases, if any have been identified, and while antiviral therapy is continued.
In general, all modern methods of destruction or removal of papillomas can be divided into 2 large groups:
- chemical - involve the use of various chemical compounds to remove papillomas, including trichloroacetic acid, Solcoderm, Ferezol, Collomak, etc.;
- physical - involve the removal of papillomas surgically, using electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser, radio wave or plasma coagulation.
After removing the papilloma by one method or another, it is important to use topical products prescribed by your doctor to speed up healing and eliminate the risk of infection.
The success of treatment and especially the removal of papillomas depends on the strength of the immune system. In its normal state, in 90% of cases, within 2 years from the moment of infection, HPV is suppressed or even completely destroyed. But this does not guarantee that there is no risk of re-infection or the formation of new papillomas. If immunity is reduced due to certain factors, papillomatosis becomes chronic, periodically relapses and can lead to serious complications.
In order to prevent infection with dangerous strains of HPV and the development of severe complications, it is recommended, especially for girls, to be vaccinated with Gardasil or Cervarix vaccines between the ages of 9 and 25.
Surgical removal of papillomas
The essence of the method is to remove the tumor using a scalpel, which is associated with the formation of scars and an increase in healing time. Therefore, it is used only when it is necessary to remove a large papilloma or in cases where it is necessary to conduct a histological examination, since the formation of malignant cells is expected in it.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, which ensures its painlessness. The doctor uses a scalpel to remove the tumor itself, including surrounding healthy tissue. This is necessary to eliminate the risk of re-formation of papilloma in the same place. If it has a pedicle, it is cut with surgical scissors, and the blood vessel that fed the neoplasm is “sealed” using an electrocoagulator. The remaining wound is sutured, treated with an antiseptic and covered with a sterile bandage.
Today, surgical removal of papillomas is mainly carried out if there is suspicion of the formation of cancer cells.
Cryodestruction
The method involves the use of low temperatures to destroy papilloma cells. This is achieved through the use of liquid nitrogen, the temperature of which is -196° C. The essence of the procedure is to use a special attachment or touch the papilloma with a cotton swab dipped in liquid nitrogen. Under its action, the water contained in the cells instantly turns into ice crystals, which destroy them from the inside. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia or without it, since the exposure time to liquid nitrogen does not exceed 5-20 seconds.
The complexity of the method lies in choosing the correct duration of exposure in order to remove the papilloma to its full depth and not harm healthy tissues, which will lead to scar formation.
Immediately after treatment with liquid nitrogen, a white spot forms at the site of the papilloma. Subsequently, a small blister with clear or pinkish liquid contents forms on it, and the surrounding skin turns red and may swell slightly. This may be accompanied by minor discomfort such as a burning or tingling sensation.
After 3-4 days, the blister bursts, and in its place a crust forms, which itself falls off after a few days, revealing healthy young skin. Under no circumstances should you pierce the bubble yourself or injure it or the crust in any other way.
Cauterization of papillomas with liquid nitrogen is possible only in cases where the possibility of the formation of malignant cells in it is completely excluded. This method is most often used to remove papillomas and condylomas on:
- centuries;
- face;
- small joints;
- genitals.
Laser removal of papillomas
The use of a laser to remove papillomas is also possible only in cases where their malignancy is completely excluded. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia and consists of evaporating moisture in papilloma cells using thermal laser energy. Thus, a focused laser beam is directed at the tumor. The duration of exposure does not exceed 1 minute.
As a result, a crust forms at the site of the papilloma, and the surrounding skin turns red and swells. The crust will come off on its own within a week. It should not be wetted and steamed for 3 days, nor should it be torn off or injured, as this can lead to the formation of scars. In addition, for 2 weeks after removal of the papilloma, you should protect the treatment area from sunlight. Otherwise, there is a high probability of hyperpigmentation of this area.
When removing papillomas on the face with a laser, decorative cosmetics should not be applied to the affected area until complete healing.
After the crust falls off, healthy pink skin is exposed, which gradually acquires a normal shade. This is the main advantage of laser removal of papillomas, since it is not associated with the formation of scars. They can only form when large tumors are removed and the rules of care in the postoperative period are violated. Also, laser removal completely eliminates the risk of wound infection and is an absolutely bloodless method, since under the influence of thermal energy, instant coagulation of small blood vessels occurs.
Using a laser, papillomas are mainly removed on:
- hands;
- legs and feet;
- face;
- centuries;
- neck;
- genitals.
Laser is the only reliable way to remove plantar warts, as their roots can go 1 cm or more deep into the tissue.
Electrocoagulation of papillomas
The essence of the method is to use electric current to remove papillomas. Using a special device called an electrocoagulator, the doctor captures the papilloma and cuts it off within healthy tissue. In this case, bleeding is completely absent, since the thermal energy of the current is enough to coagulate small blood vessels. But the procedure can be painful, especially if it is necessary to remove a tumor in areas of the body with delicate skin.
After electrocoagulation, a crust also forms. And the entire recovery period takes 7-10 days. After the crust falls off, the skin underneath should be protected from damage and exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
The method is used to remove papillomas in different parts of the body. Moreover, electrocoagulation can also be used in cases where it is necessary to conduct a histological examination of the neoplasm and accurately determine its nature. But the result of the procedure completely depends on the qualifications and experience of the doctor, however, as in other cases, since if the removal is not deep enough, the papilloma can form again in the same area.
Radio wave surgery
This method is one of the most advanced in removing papillomas of any kind. It involves the use of a special Surgitron device. But at the same time, it has much in common with laser removal of papillomas. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia, and the actual removal occurs due to the effect of radio waves on the tumor. Thanks to them, it is possible to completely cut off papilloma of any size and location, and also avoid the formation of scars.
Chemical removal of papillomas
The method involves regularly applying special compounds to the papilloma that destroy their cells, which leads to the subsequent loss of the tumor. But when using such drugs, it is important to exercise maximum caution and not allow the substance to come into contact with healthy skin.
Most often, drugs such as:
- Condylim;
- Solcoderm;
- Solkovagin;
- Collomak;
- Feresol.
Thus, anyone can encounter the formation of papillomas. There is no effective prevention of HPV infection, and vaccines only protect against the most dangerous strains of the virus in terms of cancer risk. However, in most cases they do not cause significant inconvenience to a person, with the exception of condylomas in the genital area and anus, which must be removed. In any case, you can get rid of any papillomas quickly and effectively, but since it is impossible to completely destroy HPV in the body with medication, and there is always a risk of being infected again or with a different strain, there is a possibility that the problem will return again. The only reliable way to minimize the likelihood of papillomas formation is to strengthen the immune system. And if they do appear and represent a cosmetic defect or interfere with a person’s daily life, contact a dermatologist. The doctor will be able to accurately differentiate papillomas from other skin tumors and solve this problem in a matter of minutes.
Treatment results
The photo below shows the results of removal of neck papillomas using radio wave surgery
Rarely occur again. Reappearance of papillomas is possible with high virus activity in the body. In this situation, additional treatment with immunomodulators or consultation with an immunologist may be required.
Diagnosis: which doctor to contact
The examination is prescribed by a dermatovenerologist after a visual examination in a number of cases:
- the presence of papillomas on the skin or mucous membranes (or their presence in a sexual partner);
- pregnancy planning;
- infertility or unsuccessful pregnancies in the past.
The very fact of detecting a virus is not decisive - it is much more important to identify its type and degree of oncogenicity.
The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- colposcopic examination - examination using a special microscope of the cervix and vagina;
- cytological examination - taking a smear, has low accuracy; if the result is poor, additional analysis is carried out;
- histological examination of a biopsy specimen - sampling of a small fragment of tissue for analysis;
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) - the material for the study is a smear, urine or blood, the accuracy is close to 100%.
PCR is most often used in specialized clinics. The accuracy of the result depends on compliance with the research technique. Such analysis is best done in laboratories with strict compliance with standards.
How to get rid of HPV
So far, scientists have not been able to develop HPV treatment that would be aimed specifically at eliminating the papillomavirus infection. Official medical guidelines point to destructive methods of destroying external manifestations of the virus - cryodestruction, radiodestruction, electrocoagulation, laser destruction. If the disease is cyclical, it is necessary to repeat the destruction of genital warts, while simultaneously taking nonspecific antiviral drugs.
Chemical destructive methods involve the use of a 1.5% solution of zinc chloropropionate, a combination of several acids and a copper nitrate trihydrate solution, which is applied to the affected area.
In order to strengthen mucosal immunity, the patient takes immunomodulatory drugs.
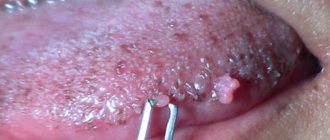
Are papilloma and condyloma the same thing?
Genital condylomas in the perineal area are sometimes single, and sometimes look like growths that resemble cauliflower in appearance. Sometimes these formations cause itching, irritation when touched, and sometimes they bleed. SM-Clinic doctors are often approached by patients who, having seen enough advertising, have been treated for years with “one pill” for supposed “exacerbations” of candidiasis (thrush). Upon examination, it turns out that the smear in such patients is normal, and the often recurring itching is actually caused by condylomas.
Indications for removal
The only way to treat already “formed” papillomas is to remove them. Indications for removal of tumors primarily include:
- Aesthetic problems. Papillomas are skin growths that are perceived as an aesthetic defect, especially when they are localized in open areas of the face and body.
- Papillomas can be constantly injured, cling to clothes, combs, etc. and due to this, quickly spread throughout the skin, soreness, inflammation, cracks and even bleeding may appear in the area of the tumors.
- Considering that some types of papillomaviruses have a high risk of oncogenicity, large papillomas (more than 6-10 mm) may be prone to degeneration, so timely removal of such tumors will prevent a serious illness in the patient.
Methods for removing formations
Depending on the diagnostic results, the doctor recommends one of the methods for removing papillomas:
- Laser is a minimally invasive technology using a laser beam: no pain and bleeding, quick recovery.
- Radio waves are a low-traumatic, non-contact method of removing tumors with an excellent cosmetic effect.
- Cryodestruction - to remove papillomas, liquid nitrogen is used, which cools and destroys tumors.
If you are faced with the need to remove papillomas, Harmony specialists will be happy to help. Our medical center employs leading doctors in the region and has modern professional equipment. Contact us if you want the treatment to be quick, painless and safe for your health.
Symptoms of papillomas
Most often the papilloma virus
in women and men it does not manifest itself at all; its diagnosis is possible only through a special analysis. Vivid signs of infection are observed only in a small number of infected people, and even these often disappear after a short time.
For a long time, the patient does not even suspect that he has become a carrier of the infection, contagious to others. The main symptom of infection - a skin neoplasm papilloma - appears when the virus is in full control of the body. In this case, papilloma can grow on any part of the body - on the skin and mucous membranes.
There are a huge number of photos on the Internet that clearly show what papilloma and its colony look like. This is a skin growth in the form of a dome-shaped compaction or papule on a thin stalk. The papule may also have a thickened base. The color of the papilloma is also ambiguous - for some it is a pale pink “wart”, and for others it is a dark brown growth. Some strains of papillomavirus form entire colonies of neoplasms, which gradually merge into one unpleasant-looking multi-headed wart, reminiscent of cauliflower.
Who is at risk of getting the papilloma virus?
Papillomas and condylomas can appear, disappear and appear again, because they are manifestations of a viral infection, and their presence depends on the state of the body’s defenses at the moment, that is, immunity. Infection is most likely among smokers and alcoholics, and among those who are indiscriminate in sexual relations.
Women who use oral contraceptives (COCs) for a long time are also at risk of contracting the virus. The carrier of the virus can be both old and young. It is enough for your body to experience internal stress of various origins: you have had the flu or ARVI, gastrointestinal problems have worsened, your body cannot cope with long-term medication use - and here you have a weakened immune system, and with it the papillomavirus.
It is enough to be in close contact or live next to a person carrying the virus, take a swim in a “dirty” pool or shower in a public bath, or just walk along the beach - and if your immune system fails, the virus will invade your life. The papillomavirus “loves” heat and high humidity, when your skin is not protected by clothing. He immediately finds refuge on your heated skin.