A pressing problem in modern gynecology that many girls and young women face is papillomas on the labia. In these intimate areas on the mucous membrane from some types of HPV, the so-called appear. "genital warts". If a wart on the genital organs is detected or suspected, each patient should know how the disease manifests itself, what treatment should be carried out and what tests should be taken for diagnosis.
These formations are very common. Warts on the labia minora and majora in girls are mainly represented by genital warts, the causative agents of which are types 6 and 11 of the virus. These types of HPV are of low oncogenic risk, that is, the risk of their degeneration into a malignant tumor is low. Children, teenage girls and girls with virgin status cannot be excluded from possible risk groups for the presence of these formations, because sexual is not the only way of transmitting the virus (see more details).
What causes papillomas in intimate places?
Papillomas on the genitals are exclusively of viral origin and are associated with human infection with the “papilloma virus”. Absolutely anyone can become a carrier of this viral agent, even if they carefully monitor their own hygiene. The fact is that infection occurs through direct contact, by simply touching the skin of a virus carrier, as well as through the use of common household items.
The sexual mechanism of transmission of the virus is the most active and ensures 100% infection through unprotected sexual contact. Given that on average about 85% of the world's population suffers from the papilloma virus, infection becomes almost inevitable.
Despite this, not all carriers face the problem of developing tumors. The virus can remain latent for a long time without manifesting itself. At the same time, its active reproduction occurs in the basal layer of the epidermis, which ultimately causes hyperplasia. For the development of skin manifestations of genital papillomas, the creation of certain conditions is required:
- Weakening of the immune system;
- Injuries and damage to the mucous membrane of the genital organs;
- Hormonal imbalance or chronic diseases associated with endocrine disorders;
- Having bad habits;
- Stress, overwork, nervous-emotional tension;
- Severe infectious or inflammatory process.
What papillomas can be removed at home?
The intimate zone is a complex system of internal and external genital organs. Despite the wide range of remedies available in pharmacies for papillomas, not all growths can be treated on your own.
Common types of papillomas that can occur in the genital area are:
- filamentous - small formations with an elongated shape and a thin base;
- flat papillomas - formations do not rise above the skin, externally resemble plaques;
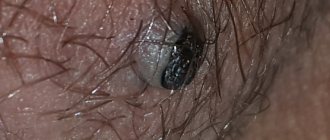
- genital warts - warts with pointed ends that look like a rooster's comb;
- giant condyloma Buschke Lowenshtein is an abnormal growth that reaches a size of 10-20 cm.
You can remove small growths that are located on the external genitalia yourself.
Trying to remove formations in the vagina or anus is dangerous.
Can lead to severe tissue burns, aggravating the existing situation.
When processing at home, it is important to follow safety rules:
- you need to act exclusively on papillomas, avoiding contact with healthy areas of the skin;
- special gentle agents should be used.
A mandatory step before self-treatment at home is a preliminary consultation with a specialized doctor (gynecologist, urologist, proctologist).
Based on examination and testing, the doctor will approve or prohibit the use of such removal methods.
Types and danger of papillomas on the genitals
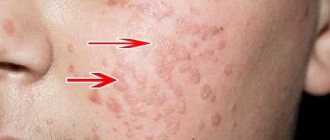
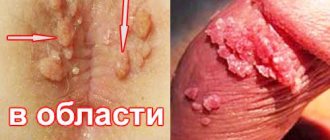
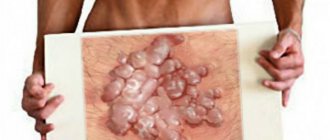
Most papillomas in the intimate area have the appearance of pointed papillae, which can merge to form lobular structures resembling cauliflower. Moreover, the color of such neoplasms ranges from light pink to bright red. In medicine, such epithelial growths are also called genital warts. The localization of condylomas in representatives of different sexes is somewhat different.
Papillomas in intimate places in men:
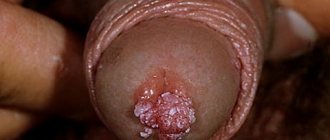
- Papillomas on the head of the penis;
- Papillomas on the penis (directly on the body of the organ);
- Papillomas on the surface of the scrotum;
- Papillomas in the anal area.
Papillomas in intimate places in women:
- Papillomas on the labia;
- Papillomas in the vagina;
- Cervical papillomas;
- Papillomas in the uterus;
- Papillomas in the anal area.
The formation of genital warts in the intimate area carries several dangers, the main one of which is malignant degeneration. The fact is that some types of virus are oncogenic, integrating into the genome of the carrier. Such a process can lead to a precancerous condition or progressive oncology. This is especially true for cervical papillomas, which cause cancer in 50% of cases.
Many countries have introduced a vaccination system for the fair sex, which helps to significantly reduce risks, but preventing this phenomenon is made difficult by the fact that symptoms of papilloma in women on the internal genital organs may not appear for a long time. As a result, a neoplasm is usually discovered during a gynecological examination.
Vaginal papillomas make themselves felt by insignificant bleeding and discomfort during sexual intercourse, which reduces the quality of the patient’s sexual life. In addition, this phenomenon may be characterized by a burning sensation and pain during urination, as well as heavy vaginal discharge.
Papilloma on the labia often gives rise to complexes and self-doubt, which is associated with the aesthetic component of the genitals. It should also be understood that even benign neoplasms in intimate places can be injured during sexual contact, urination or active movement. The danger of mechanical damage to genital papillomas lies in the likelihood of severe bleeding and infection. In addition, a humid environment creates conditions that prevent the rapid healing of the wound surface.
Intimate warts: how to treat and who to contact?
To properly treat the infection and its consequences, you need to consult a dermatologist-venereologist.
A specialist will be able to accurately determine the course of the disease and select the optimal treatment.
If consultations with other specialists are necessary, they will be prescribed by the attending physician.
The compulsory health insurance system allows you to seek help from state medical institutions.
You can wait several weeks for an appointment at such institutions.
Paid services are available to the patient much faster and allow you to choose a convenient time to visit the doctor.
Forms of existence of HPV in the body
Once in the female body, the virus penetrates the epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes, where it can exist in two forms.
| Form of existence of HPV | Characteristic |
| Episomal | The inactive stage of virus development, which is considered benign. Viral particles are located outside the cell's chromosomes. Observed in asymptomatic carriers of the virus. It is observed in patients with good general body resistance. |
| Introsomal | The active stage of HPV development is regarded as a malignant form of parasitism of viral particles in the body. The virus integrates into the genome of epithelial cells and begins to control the cellular genetic material for the reproduction of HPV-encoded proteins, which leads to the appearance of clinical symptoms. |
Methods for excision of papilloma in the intimate area
In modern clinical medicine, there are several effective ways to treat genital warts in the intimate area:
- Cryodestruction (removal of genital papillomas with liquid nitrogen);
- Cauterization of genital warts with radio waves;
- Electrocoagulation (burning out papilloma with electric current);
- Surgical excision of condylomas;
- Removal of genital papillomas with laser.
Each method has its own characteristics, limitations, advantages and disadvantages, which should be taken into account when choosing the most suitable method for treating warts in a delicate area. Regardless of what method of papilloma removal is used, the patient is advised to use antiviral, restorative and immunostimulating drugs. This will prevent infection and inflammation of the postoperative wound, as well as increase the body's defenses and strengthen the immune system.
Is itchy papillomas dangerous?
To understand whether danger exists in each specific case, you should understand what factors provoked this sensation.
In the presence of external provoking factors, after they are eliminated, the feeling of discomfort disappears, and the condition of the growth returns to normal.
Papilloma can begin to itch if there are serious problems with the body or cause their formation.
When scratching, there is a risk of damaging the growth, and this can happen accidentally.
Then, in addition to itching, other symptoms will appear:
- the appearance of redness around the tumor.
- painful sensations.
- growth tear.
- discoloration, including black.
- increase in the size of papilloma, intensive growth.
- loss of shape.
- bleeding of the growth.
- the appearance of cracks on the surface of the neoplasm.
If the cause of the itching is not identified in time, the risk of developing negative consequences increases.
There is a risk of the following complications:
- infection by pathogenic microorganisms;
- development of papillomatosis;
- suppuration of the affected area;
- development of sepsis;
- tissue necrosis.
One of the most dangerous complications is the possibility of papilloma degenerating into melanoma.
Melanoma takes about two months to form, after which the person is diagnosed with cancer.
Melanoma is one of the most terrible complications, since the development of this form of cancer cannot be stopped.
She is not amenable to chemotherapy and other procedures.
Therefore, if discomfort appears in the area where skin tumors are localized, you should immediately seek advice from the appropriate medical institution.
Timely measures taken will save health, and in some cases, life.
Treatment methods
When unpleasant neoplasms appear on the skin, almost everyone is interested in the question of how to treat papillomas in intimate places. It is important to know that effective removal of growths is possible only with complex therapy, including the use of local agents that help eliminate external manifestations of infection, as well as immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs that help suppress the activity of pathogenic flora.
It is strictly not recommended to remove growths on your own, without first consulting a specialist.
Self-medication of intimate tumors is associated with the risk of bleeding, infections, and a number of other problems. Additionally, home remedies may not be effective.
Removal of genital papillomas by cryodestruction
Cryodestruction (cryotherapy) of condylomas is one of the most common and effective methods of combating genital warts. Cryotherapy is a procedure for hardware or manual cauterization of condyloma with liquid nitrogen, which leads to the destruction and destruction of pathologically altered tissues. Before cryodestruction, the doctor determines the required intensity and depth of exposure by assessing the size, location and number of condylomas. An insufficient level of exposure can provoke incomplete destruction of the wart, which will lead to recurrence of the tumor. For excision of small and single condylomas, one session is sufficient. Cauterization of multiple and large genital warts may require multiple procedures.
A few hours after the procedure, a bubble forms at the site of exposure to liquid nitrogen, which can cause significant discomfort. Damage to it is fraught with infection and inflammation of the postoperative wound, so the blister should be protected from various types of mechanical influences and not pierced. If the blister strongly tightens the skin, limits the patient’s movements and interferes with wearing underwear, a specialist can puncture it in a clinic and apply a sterile bandage.