Any dermatitis is a reaction to some external or internal factors. In the case of seborrheic dermatitis, skin manifestations are a response to excessive activity of a yeast-like fungus caused by improper functioning of the sebaceous glands. The causes of malfunction of the sebaceous glands are different, but among them are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as unhealthy diet. Seborrhea is treated with medications and cosmetics. But the condition is also greatly influenced by diet as a type of rational nutrition with the exclusion of allergens and substances that cause excessive sebum secretion.
The diet for dermatitis has two goals:
- exclusion of foods that cause the onset or exacerbation of the disease;
- formation of proper nutrition, which helps the patient cope with the disease, and the skin to recover and be protected from the development of the disease.
When the first symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis appear, you should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and selection of drug therapy, if required. It is also necessary to choose skin care cosmetics. For treatment to be effective, you need to follow a diet. The menu can be compiled by a nutritionist in a specialized center. But you can simply follow the general recommendations that are suitable for everyone suffering from dermatitis.
Necessity of diet
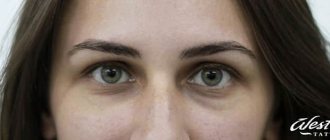
The appearance of crusts and scales on the scalp and face in children and adults is associated with disruption of the sebaceous glands. Their functioning directly depends on the food eaten by a person. All substances entering the body are carried in small particles into various systems and then absorbed by cells.
Food can affect the composition of sweat and sebaceous secretions. When you eat unhealthy foods, they can become thick and sticky, clogging the glands that remove them. In addition, some products can be an excellent assistant in the proliferation of harmful microorganisms and fungi.
Crusts on the scalp and face can appear as a result of consuming products with a high content of dyes, chemical preservatives, and emulsifiers. In this case, the immune system may give the wrong reaction. It can be expressed in the form of seborrheic dermatitis.
That is why doctors say that proper nutrition is necessary during the treatment of the disease. A diet for seborrheic dermatitis allows you to restore balance in the body and improve immunity. With this effect, crusts on the scalp and face will appear much less frequently, and then disappear completely.
A diet for seborrheic dermatitis will help normalize the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Briefly about the disease
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp is a common phenomenon. The causes of this disease may be hormonal imbalances, genetic predisposition, stress, metabolic disorders and general weakening of the body.
The main culprits in the development of seborrheic dermatitis are considered to be Malassezia (Malassezia), these are yeast-like fungi. Their activity leads to some changes, in particular, accelerated division of cells in the upper layer of skin.
These processes lead to the formation of dandruff. The increased activity of these microorganisms also affects the production of sebum, as a result the patient’s hair quickly becomes oily.
for seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp :
- the appearance of dandruff, which is accompanied by itching;
- curls quickly become oily;
- There is profuse hair loss.
In total, there are 3 types of disease: dry, oily or mixed seborrhea. With dry seborrheic dermatitis, the hair becomes brittle, dry, and small white flakes (dandruff) appear. With oily seborrhea, on the contrary, patients note excessive oiliness of the hair and the appearance of an oily sheen (gloss). The mixed type combines the symptoms of dry and oily seborrhea.
Attention! Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the head is carried out simultaneously in two directions: special medications and normalization of internal processes through proper nutrition (diet).
Nutritional Features
When scales and crusts appear on the scalp, a person needs to reconsider not only the composition of products, but also their diet. You need to eat in small portions, increasing the number of meals to 6 times a day and eliminating allergenic foods. It is allowed to eat only hypoallergenic foods that will soothe the gastrointestinal tract.
After the signs of dermatitis on the head decrease, you can try introducing new products. It is imperative to monitor the body’s reaction to notice negative or positive changes. If itching, peeling and rash on the scalp or face area intensify, you should urgently stop using the administered product.
If there is dermatitis on the head of a baby who is breastfed, the nursing woman should review her own diet. She should observe the reaction of the child’s body, noting the decrease and increase in symptoms.
For children
Treatment of children with atopic dermatitis involves the elimination of causally significant food/non-food allergens, the role of which in exacerbating the disease has already been proven. The basis for exclusion from a child’s diet is the establishment of a connection between the disease and exposure to a causally significant allergen and sensitization to it identified according to the results of an allergological examination (positive skin testing or detection of specific immunoglobulins E ).
When in doubt, as well as in the presence of multiple food sensitization, provocative tests are performed with food products - suspected allergens - to confirm hypersensitivity. It is important to achieve complete exclusion of the allergen from the diet, taking into account its possible hidden presence in other foods and taking into account potential cross-reactivity.
The duration of the elimination diet should be 6–12 months and is determined individually. After this period, a repeat allergological examination is carried out, which determines the possibility of using an allergen product in the child’s diet. However, at the same time, the diet must correspond to the age-related nutritional needs of children and be balanced in proteins, fats and carbohydrates .
When transferring a child under one year of age to artificial/mixed feeding, one should not include in the diet mixtures based on whole cow's milk, as well as milk from other animals (goat, sheep) and mixtures based on partial hydrolysis of cow's milk protein and soy protein. It is better to use mixtures based on a high degree of whey protein hydrolysis: Frisopep , Alfare , Nutrilon Pepti TSC , or casein hydrolysis: Frisopen AS , Pregestimil , Nutramigen .
If the effectiveness of diet therapy based on mixtures of highly hydrolyzed protein (after 2-4 weeks of use) and in severe forms of the disease is low, it is recommended to use mixtures based on amino acids ( Neokey ). A hypoallergenic diet for older children is based on similar principles, but you should not overuse the child on it for a long time, as this can cause a disruption in his physical development. A strictly restrictive diet is recommended to be used only during the period of exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, no more than 7-10 days, and after identifying and eliminating causative allergenic foods from the diet, it is necessary to transfer the child to an individual hypoallergenic diet.
Prohibited Products
When eating for seborrheic dermatitis, any foods that are irritants are prohibited. An exception is necessary to reduce the likelihood of an intensified allergic reaction. Common allergens are some of the most common factors influencing the appearance of seborrheic-type crusts and scales.
A person suffering from dermatitis should avoid using:
- honey and dishes based on it;
- citrus fruits;
- nuts;
- mushrooms;
- dairy products;
- caviar and seafood.
It is worth reducing the amount of carbohydrates that enter the body with food. This rule also applies to simple carbohydrates. To do this you will have to exclude:
- baked goods and baked goods;
- pasta;
- semolina porridge.
Only dishes made from durum wheat are allowed.
It is important for the patient to limit the consumption of fatty foods. The rule applies to both animal and vegetable fats. When they are introduced into the diet, the condition of the skin significantly worsens, and the course of the disease is also aggravated.
It is important for the patient to reduce the amount of:
- potatoes;
- strawberries;
- raspberries;
- sweets
Also, special attention should be paid to fish, shrimp, squid and other seafood. They often become sources of an allergic reaction.
It is strictly prohibited to include in the diet:
- fast food;
- smoked meats;
- pickling products;
- crackers, chips.
The list of drinks also needs to be reviewed. It is necessary to refuse:
- soda;
- alcohol;
- coffee;
- strong tea;
- tomato juice.
With seborrheic dermatitis, the consumption of most familiar foods will have to be reduced.
Allowed food
The list of permitted products is wide enough to ensure that the patient has a variety of food on his table. Even some prohibited foods can be eaten under certain conditions.
For example, you can cook porridge using an allergen product such as milk, diluting it with water (you need to take equal amounts of both).
Approved products for patients with seborrheic dermatitis:
- dairy - cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented baked milk, kefir, matsoni (they contain vitamin B, calcium, and other microelements necessary for the body);
- meat - chicken, veal, turkey, rabbit, lean pork and beef (provide the body with protein);
- sea fish and seafood, if a person does not have an individual intolerance to them - squid, mussels (fatty amino acids are needed to normalize the functions of the sebaceous glands), fish oil;
- vegetables - zucchini, different types of cabbage, including sea cabbage, pumpkin with light pulp; celery, green onions, cucumbers;
- fruits - pears, white cherries, apples (can be eaten fresh or in compote, excluding jam);
- from cereals and cereals - buckwheat, oatmeal, bran;
- from oils - olive, linseed, corn;
- jellied dishes using gelatin (accelerates skin regeneration);
- drinks - still mineral water, herbal tea (for example, chamomile), fruit juice, compote (you can use both fresh berries and dried fruits).
By the way, liquids occupy an important place in the menu of a patient with seborrheic dermatitis. In adults, the required minimum is 1.5 liters per day, and this figure can be exceeded.
Once in the stomach and intestines, water participates in the elimination of toxins. In addition, it is needed to normalize metabolism, to saturate the skin cells, which makes them elastic.
Vitamins are necessary to improve the health of the patient. If not enough of them enters the body with food, the doctor prescribes a vitamin complex to the patient.
Healthy foods
Some patients are afraid that if many foods are excluded, the diet will become meager. However, this is not the case. For seborrheic dermatitis, it is important to enrich your diet with healthy and tasty foods.
It is worth increasing the frequency of consumption of fermented milk products. They help eliminate digestive problems and also help saturate the body with useful microelements and nutrients. It is important that they are not too fatty and are also enriched with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Preference should be given to products without dyes and preservatives. Such products have a short shelf life.
It is worth introducing vegetables and fruits, mostly green, into your diet. Any greens are also allowed (dill, parsley, cilantro, basil). They contain a large amount of vitamins and microelements that accelerate the process of skin tissue restoration. In addition, plant foods increase the body's immune defense, which is necessary to eliminate seborrheic dermatitis.
When the body is sick, it needs proteins. They must be of animal origin. The patient is allowed to use:
- lean meat;
- low fat fish;
- eggs (1–2 per day).
Sea kale is also rich in proteins. In addition, such food contains zinc, which normalizes the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Digestion is regulated by:
- bran;
- cereals;
- oatmeal and buckwheat.
Vegetable oils also affect the condition of the intestines and skin. They are rich in fatty acids and vitamins A and E. Do not overdo it with their consumption. You can add up to 2 tablespoons of flax, olive, and grape oil to your diet per day.
It is necessary to normalize the drinking regime. The amount of water you drink daily should be 2 liters. The patient is allowed to drink:
- unboiled purified water (maybe with lemon juice);
- fresh vegetables and fruits diluted with water;
- green tea;
- compote;
- rosehip decoction.
For seborrheic dermatitis, it is recommended to eat green fruits and vegetables.
Reviews and results
According to patient reviews, eliminating causally significant food allergens from the diet can reduce the clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis , and in chronic cases, lengthen periods of remission.
- “... Allergic diathesis in my daughter first appeared at the age of 6 months after the introduction of complementary foods based on cow's milk. I had to switch the child to special artificial formulas. However, diathesis appeared periodically for up to 2 years. Obviously, the child reacted to some other product, but we could not establish it for sure. After two years of diathesis, the rashes stopped on their own, but we, on the advice of the doctor, still adhere to a hypoallergenic diet”;
- “... My baby developed allergic dermatitis when complementary foods were introduced. We found out that this is a reaction to juices. The juices were stopped, and the condition immediately improved. At 6 months of age, I again tried to introduce various juices into the diet one by one and again had a negative reaction to almost all of them. It is a pity that the child is deprived of the opportunity to receive them. The doctor said that perhaps later the diathesis on juices will go away. We really hope so. I myself follow a hypoallergenic diet, and if I have a breakdown during the holidays, I drink sorbent and take a light antihistamine.”
How to cook the right food
The diet should become a way of life for patients with seborrhea; it is not enough to change the diet temporarily. The same rule applies to the method of cooking. Food for dermatitis is steamed, boiled or baked in the oven. Negative emotions can be softened by the beautiful presentation of dishes. There are general recommendations that need to be followed:
- You cannot eat fried foods. For the same reason, fast food is banned.
- Stop adding sour cream, butter, margarine and animal fat.
- When preparing porridge, milk should be diluted by half with water.
Many patients are cured by switching to a raw food diet. This type of diet involves eating only raw, uncooked foods. These include sprouted grains, fresh vegetables, and nuts. However, doctors do not recommend completely excluding meat and fish from your diet, because they contain proteins and iron that the skin needs.
Drinking regime
Regardless of the type of seborrhea, it is important to maintain water balance. It is necessary to drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day. Additionally, you can drink the following drinks:
- freshly squeezed juices from permitted fruits, vegetables, berries and herbs;
- herbal infusions and decoctions that do not cause allergies in the patient;
- fruit drink without artificial additives.
Even dry skin will become firmer if you drink enough water daily. A lack of fluid makes the epidermis wrinkled and sluggish, so you need to pay attention to drinking even after recovery.
Recipes
Even with a limited number of products you can experiment. This will make your diet tasty and varied.
Salad “Freshness of the morning”
Boil one chicken fillet until tender, cool and cut into cubes. Cut 2 small cucumbers into strips. Tear 3-4 lettuce leaves into a deep plate, add poultry and cucumber, add a little salt and season with sour cream.
Fish “Country style”
Peel 700 g of pollock, wash it, make cuts in the skin, add salt. Cut 1 small zucchini and 2 carrots into medium cubes. Divide 200 g of broccoli into florets. Place the vegetables on foil, place the fish on top and grease with 1 tbsp. l. sour cream. Cover everything with foil and bake for 20-30 minutes.
Cottage cheese casserole
Grind 400 g of low-fat cottage cheese until smooth. Pour boiling water over 100 g of raisins and dried apricots and leave for 10-15 minutes. Add raisins, dried apricots cut into strips, and 1 egg to the cottage cheese. 2 tbsp. l sour cream, 50 g whole grain semolina and salt.
Mix well, place in a pan greased with vegetable oil, level and bake for 20-25 minutes at 170-180 0C.