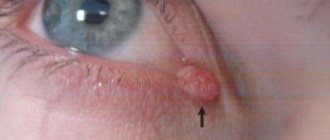
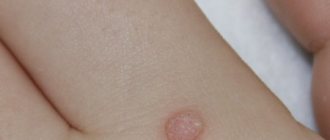
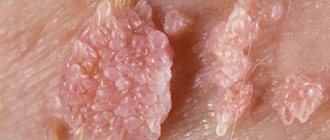
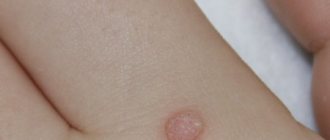
To get rid of papillomas, people resort to various methods of removing them. One of these methods is wormwood for papillomas. All parts of the medicinal plant are very successfully used in folk medicine. Wormwood is used to treat warty growths of viral origin, allowing the skin formation to be eliminated in a short time without leaving scars on the surface of the dermis.
Wormwood is a medicinal plant that is useful in the treatment of human papillomavirus (warts).
Composition and beneficial properties
Wormwood is a medicinal plant that contains the following substances beneficial to the human body:
- resins;
- potassium salts;
- phytoncides;
- essential oils;
- tannins;
- vitamins A and B;
- organic acids and other natural compounds.
Useful properties of wormwood:
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkiller;
- healing.
The herb is used to treat various inflammatory processes and dermatitis, and is used in the fight against helminthic infestation. The plant is effectively used as a remedy that normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, a sedative for the nerves, etc. In the treatment of HPV (human papillomavirus), all parts of the plant are used in the form of tinctures, decoctions, powders and medicinal baths. Wormwood removes warts absolutely painlessly; it has a gentle effect on the skin when used externally, and on the stomach (when taken internally).
Ogulov's technique
A. T. Ogulov is a doctor of traditional medicine, professor. His method of treating the papilloma virus using wormwood is popular not only in our country, but also abroad. In particular, Ogulov claims that this medicinal plant is capable of completely expelling the HPV virus from the body. To achieve this effect you need:
- Grind the dried wormwood leaves to a powder.
- In the first three days, take the resulting product a quarter of a teaspoon (five grams) at intervals of two and a half hours.
- For the rest of the treatment period (until the end of the week), drink the powder in the same volume, but at intervals of four hours.
The professor allows the use of wormwood powder in parallel with the local use of products based on this plant.
Wormwood tincture against papilloma
Wormwood tincture for the papilloma virus should be taken no more than 6 drops per day.
Traditional therapy with the help of the plant continues for a long time. For medicinal purposes, medicinal tinctures are prepared: alcohol, cognac and oil. A tincture prepared on the basis of wormwood eliminates papillomas in various parts of the body and normalizes metabolic processes in the human body. Do not forget that the plant contains toxic substances, so you need to take the tincture strictly according to the instructions, without exceeding the therapeutic dosage (daily dose - no more than 6 drops).
Oil tincture
An oily tincture of wormwood for papillomas is easy to prepare and very simple to use. Recipe for preparation and use:
- take 1 tbsp. l. plant seeds;
- grind them to a powdery state;
- mix with half a glass of olive or refined vegetable oil;
- leave the solution for 2 days in a cool, dark place;
- take 2 drops of tincture orally 3 times a day before meals;
- The treatment course will be at least one and a half months.
Alcohol tincture
Alcohol tincture is used to treat warts only in adults; use is contraindicated for children. Preparation and use of tincture for medicinal purposes:
Drinking an alcoholic tincture of wormwood for a month will help you recover from the human papillomavirus.
- take 1 tbsp. l. wormwood seeds;
- chop in the same way;
- pour alcohol or vodka (500 ml);
- infuse the product longer, for 2 weeks;
- strain and drink 2 drops 3 times a day, adding to tea or coffee;
- store the alcohol infusion in the refrigerator;
- therapeutic course 1 month.
On cognac
Tincture of wormwood in cognac is an equally popular folk remedy for getting rid of the papilloma virus. Cooking at home does not take much time and effort. Folk remedy recipe:
- take 1 liter of cognac and 2 tbsp. l. crushed wormwood roots;
- mix the ingredients;
- pour into a jar or bottle;
- seal and leave for 10 days;
- strain and drink at the same dosage as the alcohol infusion;
- therapeutic course 1 month.
Hunting for the papilloma virus
S. M. Andreev,
Candidate of Chemical Sciences
,
State Scientific Center Institute of Immunology of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia
“Chemistry and Life” No. 12, 2008
Just as hunters prepare for a hunt - they study the tracks, set up feeders, place beaters, place shooters in the line of fire, release dogs - in the same way, immunologists, in order to rid the body of the virus, step by step prepare and direct the process of activation of the immune system. The first step is to identify the target.
Target - virus protein
The papilloma virus, once in skin cells, manifests itself as a two-faced Janus. Its genome can be in two forms: either integrated into the cell chromosome, or existing as a free molecule - a DNA episome. If it is integrated into the cell chromosome, then in the presence of predisposing factors, the program of its genome is implemented and the virus begins to multiply. The affected area turns into a papilloma, or wart. Moreover, sometimes this happens not on an arm or leg, but on the mucous membrane in the most intimate places of the human body. And if the virus belongs to a special subtype, then in ten years the affected cells may transform into a cancerous tumor.
For its successful life, the virus must force the cell to synthesize several proteins that are useful to it. In particular, the papilloma virus needs the L1 protein, which is used to build the shell of new viral particles, as well as the E6 and E7 proteins - they make the infected cell immortal, these are oncogenic proteins.
There are several fundamentally different ways to fight the virus. The first is to prohibit it from contacting target cells, the second is to prevent it from multiplying in them, the third is to destroy diseased cells along with the virus. Since in the case of the papilloma virus, diseased cells do not contain it in the traditional sense - after all, after entering the cell, only DNA remains, which sets the synthesis of those very dangerous proteins - reproduction cannot be prohibited. Therefore, the first and third methods remain in the hands of doctors, that is, a preventive vaccine and a therapeutic one. Recently, another one has emerged - the use of short, so-called silent RNAs, which silence viral genes. But movement along this path is still at the very beginning.
The situation is complicated by the fact that each species of mammals has its own papilloma viruses, which do not live in the tissues of other species, and in cell culture the human virus multiplies extremely reluctantly. As a result, the search for a vaccine must be carried out on mice, and then hope that these results can be reproduced in trials involving volunteers.
A great success in the fight against the papilloma virus was the discovery in 1991 of an interesting phenomenon made by Zhou Jian and Ian Fraser, who worked at the Brisbane hospital. Princess Alexandra, Australia (Ian Fraser was awarded the Italian-Swiss Balzan Foundation Prize in the amount of 1 million Swiss francs for this work in November 2008. - Ed. note.
). They found that L1 proteins spontaneously assemble into virus-like particles (VLPs) even when there is no genetic material inside them. Such proteins can be synthesized very simply and in large quantities using yeast by inserting the desired gene into them. They emerge from yeast in the form of ready-made particles, and their immunogenic properties are the same as those of a real virus. If HPV is introduced into the body, it will begin to produce protective antibodies. In many experiments, such protection has proven its reliability, and eleven years after its discovery, a large experiment involving 1533 volunteers showed that a similar vaccine against human papillomavirus subtype 16 (HPV16), firstly, is completely safe, and secondly, provides complete body protection. This result is also important because it is subtypes 16, together with 18, 31 and 45, that account for 80% of all cases of tumor degeneration of virus-affected tissue, primarily cervical cancer. Thirteen other variants of this virus are responsible for the remaining 20%. Over the six years that have passed since the start of the experiment with the participation of volunteers, the effect of the vaccine has not weakened - not a single case of infection with the virus has been recorded among them.
In 2006, it was the first to receive permission to sell the preventive vaccine Gardasil
", which protects against human papillomavirus infection of subtypes 6, 11, 16, and 18. Doctors recommend vaccination for girls aged 9 to 26 years.
In 2007, it received approval for the Cervarix
, which protects against subtypes 16 and 18 of the papilloma virus.
Peptide bullets
However, these are all preventive vaccines, and it is not yet known how quickly the immune system will forget about the information it received at the time of vaccination. Therefore, there is great interest in a therapeutic vaccine that destroys already infected cells.
To create it, immunologists hope to use such a bright trace of the virus as those same two proteins, E6 and E7. They must be on the surface of diseased cells, and, therefore, the task is to teach killer cells to find these traces.
Many laboratories around the world compete in this field, because the price of victory is very high. To excite an immune response, E-proteins themselves, their peptide fragments (T-epitopes), and chimeric constructs of E- and L-proteins are used. (Recall that substances that stimulate an immune response are called antigens.) To enhance the response, cytokines, heat shock proteins and other stimulating elements are added to the vaccine.
An indispensable component of the vaccine is a vector that ensures the delivery of antigens - E-proteins or their peptide fragments - to special cells of the immune system (macrophages, dendritic cells), after which they begin to produce special cytokine proteins and give instructions to killer cells, what they, in fact, , must be destroyed. The vectors for papillomavirus antigens in different experiments were vaccinia virus, adenovirus, alphavirus, and bacteria. It should be noted that dendritic cells are the most active partners for initiating a strong immune response, so it is desirable that the antigens reach them.
That is why much attention is paid to chimeric constructs based on heat shock proteins, that is, containing both the E protein and the immune response enhancer protein. Heat shock protein has an affinity for dendritic cells. It was with this method that in model experiments it was possible to record a decrease in tumor size even with a single immunization. Several therapeutic vaccine candidates are currently in various stages of testing, but unlike preventive vaccines, none have yet achieved acceptable efficacy. The idea arises that success can be achieved by improving all parts of the vaccine: peptide fragments that most correctly repeat the T-epitopes of the E-protein, a vector for targeted delivery of the vaccine into a dendritic cell, a stimulator of the immune response, as well as the vaccine carrier on which all this rests .
We began work on the implementation of the “Combined vaccine for HPV 16, 18 and 31” program, which was led by teams of two institutes - the Institute of Immunology and the State Research Institute of Genetics - under the leadership of Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M. R. Khaitov - with computer calculations. To conduct such a study, you need to have good tools - a set of specific antibodies to various types of viruses, reference drugs (viral proteins), so that you have something to compare the resulting products with. It was impossible to buy any of this in Russia, and even in the USA it was impossible to buy antibodies to some L1 proteins - not a single company made them for sale. And here Professor Neil Christensen from the Milton Hershey Medical Center in Pennsylvania helped us a lot by providing microsamples of some recombinant proteins and monoclones. But we had to synthesize a lot ourselves, including antibodies to three types of L1 and E7 proteins and to their various sections, which were calculated using computer algorithms. All peptides were synthesized chemically using the solid-phase method; there were about 20 of them. Such peptides are safe for the body, and it is not difficult to synthesize them, but the immune system does not react actively enough to them - pure peptides almost do not induce antibodies. Therefore, we have to combine them, firstly, with a carrier, and secondly, add substances that stimulate the immune system. Hemocyanin (a huge protein from snail) “polyoxidonium” was used as carriers, on the basis of which the “Grippol” vaccine was previously created (see “Chemistry and Life”, 2005, No. 5. - Ed. note.
), and some other stimulants.
In parallel, GOSNIIGenetiki established the synthesis of three types of L1 proteins in yeast (there was a problem with one of them), which assembled into correct virus-like particles and reacted correctly with antipeptide antibodies and reference monoclonal antibodies.
Responses to different peptides varied widely, and these experiments identified the most effective fragments of both the L1 and E7 proteins. The final test showed that if snail hemocyanin or a special immunostimulant PM is used as an adjuvant carrier for these peptides, the immune system response will be the strongest. Most importantly, this produces a strong immune response to L1, and also activates populations of specific killer cells, the so-called cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. They are the ones who must destroy infected cells. In fact, the data obtained give reason to believe that we have succeeded in creating individual components of a prototype of a combined preventive and therapeutic vaccine. While this is not yet a vaccine, the drug must be tested in an acceptable biological model, for example, in mice with a transplantable tumor caused by the oncogenic E7 protein. Moreover, the resulting vaccine preparations are more likely focused on prevention, since it has already been proven that the L1 protein generates a strong protective response even in the absence of an adjuvant.
Peptides are weak immunogens, we were convinced of this by making a conjugate of one peptide from the E7 protein with standard Freund’s adjuvant. Activating T cells this way is not easy, and tactics may need to change. First of all, this requires targeted delivery of peptide antigens from the E protein to dendritic cells in order to achieve specific and strong activation of killer CD8+ lymphocytes.
And then we decided to take a new approach: use fullerenes, whose high cell-penetrating ability is well known, as a delivery enhancer, and add a vector that would direct them into dendritic cells. To do this, we had to do work that was not directly related to the creation of a vaccine: to determine the immunogenicity of fullerenes and their derivatives with amino acids and peptides, as well as their ability to penetrate inside cells. And here we got very interesting results.
Fullerene and life
A lot has already been said about the toxicity of fullerenes, and there are two opposing points of view: “they are extremely harmful” and “they are very useful.” It is possible that the emergence of such different points of view is facilitated by the peculiarities of the physicochemical properties of fullerenes, namely the fact that, due to their hydrophobicity, they are insoluble in water. As a result, in order to prepare a drug and inject it, for example, into the blood of an experimental animal, the fullerene molecule must be somehow modified: hydrophilic groups must be added to it or surfactants added to the solution that can suppress the hydrophobicity of fullerenes. These components may have specific chemical activity; they themselves turn out to be toxic, which may well lead to the conclusion that fullerene itself is toxic. And such cases are widely known. For example, one of the very authoritative specialists in the study of the biological effects of fullerenes, G.V. Andrievsky from the Institute of Therapy of the Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine, proved that the data given in the most frequently cited article on the toxicity of fullerenes are associated precisely with an artifact: toxic substances were present in the fullerene-containing liquid being studied. substance - tetrahydrofuran. G.V. Andrievsky himself is known for having managed to create a method for obtaining a fairly concentrated solution (nanosuspension) of fullerene in water.
The problem of the toxicity of fullerenes and other nanoparticles has long become very relevant. Immediately after the discovery of fullerenes, the idea spread among scientists that these molecules could be useful as a means of transporting drugs. Hundreds of fullerene compounds have now been synthesized, many of them exhibit biological activity, but it has not yet reached the point of creating commercial drugs. Perhaps because they do not have any special advantages over non-fullerene analogs, or perhaps because there is insufficient understanding of the mechanisms of fullerene metabolism and their interaction with living cells.
However, due to the development of nanotechnology, conditions almost inevitably arise for environmental pollution by these very persistent compounds, the scale of production of which is increasing. It's time to resolve the issue of the danger or safety of fullerenes, including immunological safety. First of all, we are talking about the ability of fullerenes to cause an immune response, such as an allergy.
Indifferent fullerene
In our experiments, we used crystalline fullerene, called fullerite, a nanosuspension of Andrievsky’s hydrated fullerene, as well as fullerene compounds with all kinds of amino acids, peptides and proteins. In this case, the amino acids were attached directly to the fullerene ball. A method for obtaining such derivatives was developed back in 1994 at the Institute of Ecological Ecology of the Russian Academy of Sciences. A. N. Nesmeyanova. There, in collaboration with the Institute of Chemical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, another functional fullerene was created, which very quickly attaches to peptides and proteins containing the amino acid cysteine. Why was it necessary to obtain such complex compounds?
The fact is that 12 years ago we already tried to induce a specific immune response in mice to pure fullerenes and their amino acid derivatives and were not at all successful in this matter. However, in 1998, information appeared that one American group had managed to achieve an immune response to fullerene in the presence of a strong immunostimulant. In our experiments, we just wanted to check this result, and we took known allergens like egg and serum albumin as immunostimulants. However, the result was the same: no specific response to the fullerene itself was noticed. But we found a well-expressed reaction to amino acids attached to fullerene. (The response to pure amino acids does not develop at all; the body is tolerant to them.)
The lack of an immune response to fullerene can be explained as follows. Theoretically, in an aqueous environment, hydrophobic fullerene molecules cannot exist in a single state, but are collected into clusters of tens or even hundreds of molecules. Once in a living organism, these clusters must interact with hydrophobic components of the environment and electron-donating molecules - proteins, fats or amines. As a result, the carbon sphere can be completely closed by these molecules, and then it is not able to bind to the B-lymphocyte receptor, which gives a signal for the development of an immune response. However, the mere presence of a specific receptor for fullerene in B cells raises serious doubts. Fullerenes as artificial molecules were obtained quite recently, in 1991, and in the process of evolution organisms could not come into contact with them, therefore, it is unlikely that there are cell clones that recognize such molecules. As work on the creation of carbon endoprostheses showed back in 1979, it is impossible to obtain antibodies to other forms of carbon - graphite and diamond. Although such an enzyme as HIV protease is known, whose active center has a hydrophobic cavity: fullerene (with a hydrophilic suspension) fills it well and thereby blocks the activity of the virus. But the receptors on the B-lymphocyte for capturing foreigners are located outside, that is, facing the aquatic environment, have a hydrophilic nature and are unlikely to capture fullerene.
Like a knife through butter
If fullerene does not cause an immune response, can it somehow damage the cell? The answer to this question is given by a series of experiments we conducted with human erythrocytes, platelets and symbiosomes - products of symbiosis of legumes with nitrogen-fixing bacteria of the genus Rhizobium
. The fact that the fullerene has penetrated inside the symbiosome can be judged by the charge of its membrane. In the presence of ATP and magnesium ions, it is able to generate a positive charge on the inner side of its membrane. Fullerenes with attached amino acids proline or aminocaponic acid are negatively charged. Once inside the symbiosome, they neutralize the charge on the membrane, which can be detected by spectral methods using special probes. As it turned out, this process is very fast: when a solution with fullerene derivatives was added, the cell membrane instantly lost the potential it had accumulated.
Fullerene with another acid, arginine, on the contrary, acquires a positive charge, and therefore its effect on the symbiosome could not be noticed. But it appeared on erythrocytes, the membrane of which was negatively charged with the help of valinomycin (K+ leaves the cell): with the addition of C60-Arg, a rapid discharge of the potential occurred.
Changing the membrane potential was not the only effect. There is such a fluorescent dye - acridine orange. It changes its glow when the acidity of the environment changes. With its help, it was possible to further confirm that amino acid derivatives of fullerenes actually easily penetrate into cells and change the acidity of the environment.
We also confirmed that fullerenes easily penetrate different types of cells. For example, platelets contain a lot of calcium, so fullerene transport can be studied using another dye, chlortetracycline, the glow of which depends on the concentration of calcium ions: if fullerene interacts with it, it extinguishes this glow. And so it happened: when fullerenes, including Andrievsky’s fullerene, were added to platelets loaded with chlortetracycline, fluorescence quenching was observed. True, it turned out that Andrievsky’s fullerene enters the cell a hundred times slower than with amino acid derivatives.
So, it has been established that fullerene, due to its hydrophobicity, passes quite freely through the lipid membrane of the cell. This gives rise to an idea that has already been heard by many: a fullerene with an attached peptide can drag it inside the cell. This means: it can serve as an excellent means of delivering peptides to dendritic cells of the immune system.
To test this assumption, we firstly added to the fullerene the E7 protein peptides found at the previous stage, which cause the greatest immune response. Secondly, a vaccine carrier was synthesized based on a copolymer of vinylpyrrolidone and maleic anhydride, to which chains of fatty acids were attached. Fullerene molecules with peptides clung to these hydrophobic tails due to van der Waals bonds. The result turned out to be very good already in the first experiment. The drug actually behaved as befits a therapeutic vaccine, generating specific T cells and antibodies. But so far we have not been able to trace in detail the mechanism of its action. Unfortunately, due to the cessation of funding, this work had to be interrupted. Although we do not lose hope for a continuation, time has been lost, and foreign researchers do not stand still.
The work began on the initiative of Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences R.V. Petrov
Wormwood essential oil
It is recommended to treat papillomas with wormwood essential oil until they disappear.
Plant ether is successfully used for cosmetic and medicinal purposes. It has many useful properties: kills bacteria and fungi, relieves inflammation, disinfects. With its help, bypassing a medical facility, you can get rid of papillomas, problematic nevi and boils. The oil acts gently and painlessly, allowing papillomas to resolve in a short time, without leaving any marks on the surface of the skin.
Application of oil
Ether is used internally and externally against warty growths. Directions for external use:
- treat new growths with oil using a cotton swab or swab;
- the treated areas are sealed with a medical plaster;
- the procedure is carried out 3-4 times a day;
- After 4-5 days the growths will dry out and then fall off completely.
Internal reception procedure:
- take ½ tsp. 3 times a day;
- The treatment course will last for at least 1 month.
How to make your own butter?
You can also make your own oil from wormwood to eliminate the papilloma virus.
Wormwood essential oil for papillomas is sold in any pharmacy; you can purchase it without a doctor’s prescription. If a person does not trust pharmacy, you can prepare ether at home yourself. A homemade option for preparing wormwood oil is presented in the table:
| Ingredients | Preparation | Application |
|
| Used for external and internal use |
Effective recipes
Wormwood powder (treatment regimen)
Professor Alexander Ogulov has developed an effective method that allows you to cleanse the body of worms, fungi and viruses using wormwood. If the patient does not have allergies, wormwood is used for medicinal purposes in powder form. The powder is extracted from the seeds of the plant. Drug dosage regimen:
Taking wormwood powder for a week against the papilloma virus will relieve the disease within a month.
- 1st day. Take the powder in a minimal dose (at the tip of a knife). Drink half an hour before the main meal, with a small amount of water. The procedure is carried out 3 times a day.
- 2nd day. The dosage is increased by approximately 1 g. The dose is also taken three times a day before meals.
- Days 3 and 4. The dosage of the powder remains the same as on day 2.
- 5th and subsequent days. The regularity of taking the medicine is reduced to 1 time per day, the amount of the drug is increased to 1/3 tsp.
- The treatment course will be 7 days, a break of 3-4 days is taken, and a repeat course is carried out. Papillomas should disappear approximately 20 days after the start of therapy.
Infusion for lotions
Wormwood infusion is used to treat various types of papillomas on the human body. Its use can be both internal and external. It is too strong for internal use, so it must be diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio. If used externally in the form of lotions, the procedure is repeated 4 or even 5 times a day until the growth is completely absorbed. The preparation of the healing medicine itself:
- take 1 tbsp. l. dry leaves of the plant;
- pour a glass of boiling water;
- insist for 3 hours;
- used for medicinal purposes against papillomas.
Healing decoction
When warty growths form in the mouth and throat, a decoction of wormwood is prepared and used internally. Preparation procedure:
- take 1 tbsp. l. dried leaves or inflorescences of wormwood;
- pour 500 ml of boiling water;
- infuse for no more than 10 minutes;
- the solution is filtered;
- rinse the mouth 3-4 times a day;
- each procedure should last at least 5 minutes;
- The treatment course is about 10 days.
Symptoms of giardiasis
Giardia can number up to a million per square centimeter of intestinal wall. They mechanically damage blood cells (erythrocytes), cause irritation of nerve endings, and disrupt the absorption process. As a result, inflammation develops. Giardia waste products can cause allergic reactions.
Giardiasis can occur in acute or chronic form. Symptoms of acute giardiasis may appear 1-3 weeks after infection.
Giardiasis most often manifests itself as an intestinal disorder. In some cases, giardiasis can cause disruption of the gallbladder and stagnation of bile. In the case of long-term giardiasis (especially in children), neurotic symptoms may be observed.
Abdominal pain
With giardiasis, there is pain in the epigastric region and in the navel area. The pain is usually dull, but in some cases it can be sharp.
Flatulence
Increased gas formation (flatulence) is usually accompanied by a feeling of fullness in the stomach. Belching and heartburn are possible.
More about the symptom
Stool disorder
Possible diarrhea up to 3-5 times a day; The stool is initially watery or foamy, but may later become greasy. Diarrhea may give way to constipation.
Allergic manifestations
Possible allergic manifestations of giardiasis:
- hives;
- severe itching;
- atopic dermatitis;
- bronchial asthma;
- allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, blepharitis and some other manifestations.
Neurotic symptoms
With a long course of giardiasis (especially in children), the following neurotic symptoms may be observed: weakness, fatigue, irritability (tearfulness in young children), headaches, dizziness, cardialgia.
Contraindications
Before using a medicinal plant, you should consult a doctor, take into account contraindications and possible side effects. The most common contraindication for wormwood therapy is an allergy to the components in the plant. Some people cannot even stand its smell, starting to itch and sneeze. The herb is also contraindicated for people in the following cases:
- with gastritis with high acidity;
- stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- with anemia;
- during pregnancy and lactation;
- in children up to 12 years of age.
In the event that a person has no contraindications to wormwood, one must remember that the plant is poisonous and its correct use is required. In no case should you exceed the daily dosage of herbal medicine in pursuit of a quick result. Complications arise in the form of mental disorders, convulsions, dizziness and hallucinations. Therefore, it is important to adhere to the prescribed therapeutic course. Treatment with wormwood often gives good results, the main thing is regularity and the mindset to successfully get rid of papillomas.
Methods for diagnosing giardiasis
Giardiasis has no specific symptoms, and its manifestations are varied. Therefore, a typical situation is when a person is treated by different specialists for different symptoms, but giardiasis remains undetected.
You should definitely get tested for Giardia in the following cases:
- with a tendency to intestinal diseases, as well as with their chronic course;
- with eosinophilia (the presence of an increased number of eosinophils in the blood);
- for allergic manifestations;
- in case of intestinal disorder acquired while traveling abroad, especially to southern and exotic countries;
- in case of neurotic symptoms, especially against the background of intestinal disorders.
Giardiasis is diagnosed based on laboratory tests. To diagnose giardiasis, the following are usually used:
Microscopic examination
The feces are examined for the presence of Giardia cysts, and the intestinal contents are examined for the presence of vegetative forms.
Serological blood test
Using a serological analysis, the presence of antibodies to Giardia in the blood is determined.
More information about the diagnostic method
Stool examination
An immunological test can detect a specific Giardia antigen in the stool.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.