Composition of Terbinafine ointment
The main component is terbinafine hydrochloride. In one tube it is contained in the amount of 1g per 100g of composition. As additional substances, it contains rare cross-linked polyacrylic acid in the amount of 1.5 g, as well as 10 g of propylene glycol, 5 g of petroleum jelly, 0.4 g of sodium hydroxide. A large share of the volume is purified water - here it is 81g.
Terbinafine is available both as an ointment and as a gel or cream. The product for topical use is packaged in aluminum tubes, which are placed in cardboard packages, 1 piece each.
Components of Terbinafine
The instructions indicate the following ingredients of the medication:
- Tablets - presented with terbinafine hydrochloride, lactose monohydrate, potato starch, talc, aerosil, magnesium stearate, MCC;
- Ointment - terbinafine hydrochloride, carbomer, vaseline oil, polysorbate, sodium hydroxide, water, propylene glycol, methyl parahydroxybenzoate.
Terbinafine is produced not only in ointments and tablets, but also in cream and spray. The choice of the appropriate form to combat fungal infection is the responsibility of the attending physician. External forms are used for mild lesions, oral forms for systemic infection.
pharmachologic effect
Terbinafine has a pronounced antifungal effect. The ointment is intended for topical use. It is effective in combating dermatophytes, varieties of molds and dimorphic fungi. When applying a small amount of the product, it is possible to achieve a fungicidal effect.
In relation to yeast fungi, Terbinafine can have both fungicidal and fungistatic effects. Its activity is mainly manifested in the treatment of skin lesions by representatives of the genus Candida albicans. The ointment affects biosynthesis processes during the early stage of sterol formation, namely, a deficiency of ergosterol is formed and a simultaneous increase in squalene content. This imbalance of chemical bonds leads to the death of fungal cells. The ointment is safe in relation to the cell membrane of the human body. It does not have any effect on the production of hormones, the functioning of internal organs and the effect of other medications. No more than 5% of the drug is absorbed into the bloodstream if a dense layer is applied. The systemic effect in this case is insignificant.
Lipophilic yeast-like fungi of the genus Malassezia
are representatives of the normal microflora of human skin.
At the same time, they can cause the development of lichen versicolor, Malassezia-folliculitis in persons predisposed to these diseases, as well as with the development of immunodeficiency states and severe endocrine diseases. The leading role of Malassezia
spp. has been confirmed. in the development of seborrheic dermatitis, the influence on the characteristics of the course of atopic dermatitis and seborrheic psoriasis has been proven [1-6].
In recent years, the genus Malassezia has expanded. It includes 11 species: M. globosa, M. sympodialis, M. furfur, M. obtusa, M. dermatis, M. restricta, M. slooffiae, M. pachydermatis, M. japonica, M. yamatoonsin
[1—7].
The causative agents of pityriasis versicolor can be M. globosa, M. sympodialis
, which, according to Russian and foreign authors, are more often isolated from patients in European countries, as well as
M. furfur, M. obtusa
, which more often cause the development of pityriasis versicolor in people living in hot and humid climates (Thailand, Malaysia, Iran etc.) [1—6, 8].
Over the past 10 years, the pharmaceutical market has offered a wide selection of antimycotic agents for external use. More than 200 different drugs have already been developed. The most promising of them are drugs that have fungistatic and fungicidal effects simultaneously [1-3, 7-9]. terbinafine (Termikon) meets these requirements.
, belonging to the class of allylamines.
In therapeutic concentrations, it has a fungicidal effect against dermatophytes, molds and some dimorphic fungi. The activity of terbinafine (Termikon)
against yeast-like fungi, depending on their type, can be fungicidal and fungistatic.
Purpose of the study: to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of using Thermikon spray
(
terbinafine
) in the treatment of patients with pityriasis versicolor.
Material and methods
termikon spray (terbinafine) was assessed on the basis of the Yekaterinburg Regional Clinical Clinical Hospital.
in 30 patients aged 8 to 43 years. The majority of patients were in the age groups from 20 to 30 years - 13 (43.24%) people and from 30 to 40 years - 8 (26.66%) people, over 40 years - 2 (6.66%), the rest 23, 3% were under 20 years of age. There were 56.66% men, 45.44% women.
The duration of the disease ranged from 1.5 months to 7 years, with an average of 3.45 years. In 46.66% of patients, this disease recurred.
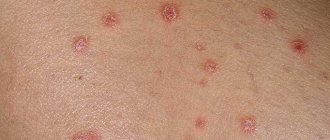
Most patients had limited forms of pityriasis versicolor, represented by single, multiple or merging light brown and/or flesh-colored spots with pronounced pityriasis-like peeling on the surface. In a number of cases, large lesions with scalloped edges formed (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Large hypo- and depigmented spots on the skin of the trunk and limbs with scalloped edges. In 3 patients, the process was widespread and occupied almost 40% of the skin (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Generalized mycotic skin lesions (almost 40% of the skin). An 8-year-old boy had an unusual localization of pityriasis versicolor - in the form of isolated rashes in the forehead.
Mild and moderate itching was noted by 60.00% of those examined.
Among the concomitant diseases, vegetative-vascular disorders accompanied by hyperhidrosis were noted in 8 (26.66%) patients, hypothyroidism - in 2 (6.66%), obesity of III-IV severity - in 5 (16.66%), discoid lupus erythematosus - in one (3.33%), HIV infection - in 2 (6.66%), diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (including chronic colitis, duodenal ulcer, chronic gastritis, chronic cholecystitis) - in 18 (60 %).
43.33% of patients had previously used external antimycotic drugs (clotrimazole, ecodax, etc.) independently or on the recommendation of a doctor. No patient received treatment with systemic antimycotics for pityriasis versicolor.
Before treatment, all patients underwent direct microscopy of skin flakes from lesions after KOH treatment, using the Balser test.
The effectiveness of therapy was assessed on the 7th and 14th days of treatment. The criteria for clinical cure were the absence of hyperpigmented spots and peeling; negative results of microscopic examination; negative iodine test. The presence of depigmented spots (secondary leucoderma) was not taken into account.
Results and discussion
After laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis, patients were prescribed the drug Termicon spray
, which was applied to the skin 2 times a day for 14 days.
As a result of treatment, on the 7th day, in 14 (46.6%) patients, the clinical manifestations of the disease regressed and were visualized only by iodine staining. Microscopic examination revealed negative laboratory tests in 16 (53.3%) patients.
After treatment (on the 14th day) in the group of patients, clinical and mycological recovery was noted in 29 (96.66%), the Balser test was negative in 90.14%.
When using Thermikon spray
None of the patients developed any adverse events or allergic reactions. All patients noted the ease of use and high effectiveness of the drug, especially its good absorption and lack of greasy shine on the skin.
We illustrate this study with the following clinical example.
Patient A., 25 years old, has been undergoing follow-up and treatment at the Regional Clinical Hospital for 4 years with a diagnosis of severe discoid lupus erythematosus. Throughout the entire period, he receives the drug diprospan 1.0 intramuscularly once every 14-20 days, and concomitant therapy. During treatment, the patient repeatedly developed various fungal diseases (oropharyngeal, urogenital candidiasis, rubromycosis of the feet).
Pityriasis versicolor developed for the first time in March 2008, the duration of the disease before the start of treatment (Fig. 3, a)
Figure 3. Pityriasis versicolor in a patient with DLE.
a — duration of the disease before the start of treatment, 1.5 months; b - on the 14th day of treatment with Thermikon spray. was 1.5 months. Microscopy revealed fungi of the genus Malassezia, the Balser test was positive. The patient was prescribed Thermikon spray (terbinafine)
2 times a day for a course of 14 days. After 7 days, weakly pigmented lesions and slight peeling remained on the skin; microscopic examination is negative, Balser's test is positive.
On the 14th day of treatment (Fig. 3, b) the rash completely regressed; microscopic examination, Balser test are negative. Upon further observation for 6 months, no relapse of the disease occurred in this patient.
Based on the data presented, we can conclude that Thermikon spray (terbinafine)
has a pronounced antifungal, anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effect, easy to use. It can be used in the treatment of pityriasis versicolor as monotherapy or in combination with systemic antimycotics.
Indications for use of Terbinafine
The main indication for prescribing Terbinafine ointment is damage to the skin by a fungal infection. First of all, these are mycoses of the skin of the foot. In addition to fungus on the legs, the remedy treats fungal infections of the groin area, which experts call tinea cruris. In addition, smooth areas of the body infected with fungus can also be treated with ointment.
Diaper rash, in the absence of timely and adequate skin care, can become a breeding ground for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Fungi of the genus Candida especially love this humid environment. This is a yeast type that quickly spreads in folds, on the crooks of the arms and fingers, as well as on hairy areas of the body (head, armpits, groin). Treatment with Terbinafine ointment makes it possible to get rid of this pathogen.
Signs of lichen versicolor are also a reason to prescribe Terbinafine. Mycosis is a common skin disease that affects not only adults, but also children. The first signs of the spread of a fungal infection are the following markers:
- Redness on the skin, usually with clearly defined boundaries of the source of infection. The borders may be uneven and irregular in shape.
- The edges of the lesion often have a whitish tint, especially for lesions of fungi of the genus Candida.
- The inflamed area is itchy.
- The surface of the skin of the affected area peels off.
- At the site of inflammation, vesicles with serous contents appear. Violation of the surface of the bubbles leads to the separation of liquid and the formation of crusts.
Fungal infections are transmitted by contact and airborne droplets. In addition, failure to comply with hygiene standards provokes the spread of mycoses. Therefore, when visiting baths, saunas, public showers and other public places with high humidity, it is necessary to avoid contact of bare feet with the floor.
Mycosis can also appear as a result of wearing low-quality shoes made from non-breathable materials. It is also not recommended to wear synthetic socks in closed shoes.
Interaction with other drugs
Combination with foreign drugs provokes:
- influence on the clearance of drugs - Cyclosporine, oral contraceptives, Tolbutamide;
- increased concentration of histamine blockers in the blood;
- slowing down the excretion of Rifampicin;
- changes in the menstrual cycle - when combined with oral contraceptives.
Drug-induced liver damage occurs when taken with hepatotoxic drugs or ethanol.
Instructions
The ointment is used strictly externally. Recommended for use by adults and children over 12 years of age. Before applying the product, it is necessary to remove all contaminants from the surface of the skin and dry it. A small amount of cream is rubbed into the lesion, covering a small area beyond the edges of the inflammation. Repeat the procedure in the morning and evening.
The course of treatment depends on the degree of damage and the type of fungal infection:
- smooth skin, including areas on the back, abdomen and lower legs, require 1 week of treatment;
- foot fungus goes away within 8-9 days of using Terbinafine ointment;
- treatment of candidiasis can last up to 2 weeks;
- It also takes 10 to 14 days to get rid of tinea versicolor.
If the use of the ointment does not give the desired effect over time, or during treatment there is a clear progression of the disease, accompanied by growth of the affected area, it is necessary to contact a specialist to prescribe systemic antifungal agents or to change the treatment regimen with local agents.
Contraindications to treatment
Terbinafine tablets are not used:
- for acute or chronic liver pathologies;
- renal failure;
- allergies to lactose, lactase deficiency;
- intolerance to the component composition;
- body weight less than 20 kg or under 3 years of age;
- breastfeeding.
Particular care is needed when carrying out therapeutic measures for people:
- with chronic renal failure, neoplasms;
- alcohol addiction;
- problems with the functionality of the hematopoietic system;
- diseases of the endocrine department;
- psoriasis, narrowing of the lumens in the blood vessels of the legs, etc.
Therapy is carried out with monitoring of the functioning of the kidneys and liver. Terbinafine is discontinued if:
- discomfort in the abdomen, jaundice;
- weakness, nausea;
- changes in the color of urine to dark, and stool to a light shade.
Local forms of the medication are not used for allergies or hypersensitivity to components.
The list of relative contraindications to the use of Terbinafine is presented:
- insufficient performance of the liver and kidneys;
- alcohol addiction;
- diseases of the endocrine department;
- tumor-like processes.
The drug is not recommended for patients under 12 years of age.
Terbinafine cream - instructions
Unlike ointment, cream does not penetrate so deeply into the skin. Part of the applied layer is often rubbed off on clothing and surfaces with which the affected area of the body comes into contact. Therefore, the use of cream can be increased up to 3 times a day.
The advantage of the cream is its effectiveness even on moderately wet surfaces, which is especially important for fungal skin infections. If it is not possible to dry the surface due to the constant release of liquid, it is better to buy a cream, since the ointment in this case will be ineffective.
Overdose symptoms
Accidental use of large quantities of Terbinafine tablets may cause:
- dermatological rash, cephalalgia;
- frequent urination;
- attacks of vomiting with dizziness;
- discomfort from the gastrointestinal tract.
Therapy includes gastric lavage with activated charcoal. In difficult cases, symptomatic treatment is prescribed.
There is no information in the annotation about cases of ointment overdose. These adverse reactions occur when an external agent is accidentally taken orally.