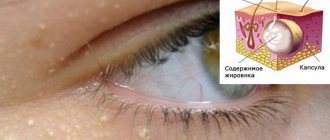
Boil or barley is an infectious and inflammatory disease that forms in the hair follicles of the eyelashes and eyebrows. Pathology manifests itself as a result of the inflammatory process and an increase in the amount of pathogenic microflora in this area.
The disease is accompanied by swelling, redness, and pain. A professional consultation with an ophthalmologist is recommended, who will prescribe the correct treatment after diagnostic procedures.
We recommend reading: Furuncle on the eye
Causes of a boil on the eye
The main reasons for the appearance of infectious and inflammatory conditions in the hair follicles are:
- the formation of microtraumas and small wounds into which infection penetrates;
- violation of hygiene rules, which leads to the gradual accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms;
- non-compliance with the rules for using contact lenses (dirty container, use of cleaning fluid several times in a row);
- infectious and inflammatory diseases in neighboring tissues or organs (bacterial conjunctivitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis);
- touching the eyes with dirty hands, especially after children play in the sandbox;
- contact with the eyes of a foreign object (specks, dust, fragments);
- systemic diseases;
- bacilli carriage (increased content of staphylococcal and streptococcal microflora);
- violation of the secretion of sebaceous glands;
- the formation of allergic reactions that are complicated by bacterial infection;
- frequent contact with chemicals and dust.
To completely eliminate the disease and eliminate the risk of its recurrence, the doctor needs to identify the root cause of the disease.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that the foci of inflammation are superficial (except for ulcers in the ear), it is not difficult to diagnose furunculosis. However, with long-term, treatment-resistant furunculosis, there may be a need for extensive diagnostics to establish the exact causes of the disease. In this case, immunodiagnostics, a detailed blood test are performed, and the boil is examined for bacterial seeding of the purulent contents. If the study does not produce results, it is necessary to do a full examination of the body, since furunculosis may be the result of some general disease (blood disease, diabetes, etc.).
Types of boils
Depending on the stage of development, boils are divided into several categories:
- the onset of the inflammatory process, which manifests itself as slight redness in the affected area;
- acute inflammatory process with the formation of a large amount of pus under the skin;
- full maturation, when the pus is located close to the surface of the skin;
- skin damage and pus coming out.
Based on the number of formations, the disease is divided into several groups:
- single formation, localized only at one point;
- the appearance of multiple boils along the hairline.
Depending on the location of the purulent discharge, boils are divided into several types:
- superficial, when purulent discharge is localized only in the hair follicle;
- deep, characterized by decay of the deep layers of the skin.
In the medical history, the doctor describes the type of boil and subsequent treatment.
Symptoms of stye
The appearance of stye begins with the appearance of itching, usually localized at a point on the edge of the eyelid. Then the skin in this place begins to turn red, swelling forms, and the eyelid swells. Painful sensations occur, which intensify if you touch or press on the sore spot. In some cases, stye prevents the eyelid from closing completely. The eye may become very watery. The parotid or submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged. The temperature may rise.
On the 2-3rd day, a white or yellowish head forms at the top of the barley. After some time, the barley “ripens” and breaks through. Pus flows out. After which the eye gradually returns to normal.
Early symptoms
When the inflammatory process in the area of the hair follicles has just begun to form, the disease is characterized by the following clinical symptoms:
- redness in the affected area;
- compaction on the skin;
- slight tissue swelling;
- sensation of a foreign body under the eyelids;
- itching, burning, pain in the affected area;
- redness of the eyes;
- increased production of tear fluid.
After passing the initial stage, compaction begins in the lesion. This means that pus has been released in large quantities and has accumulated under the skin.
Stages of development
It is worth noting! Barley does not usually form suddenly and goes through three stages of development:
- Initially, there is redness and mild swelling in the affected area. At this time, a person gets the impression that a foreign body has entered the eye, but no signs of debris or other parts are detected during visual inspection.
- At the next stage, itching begins in the affected area, and the patient may develop uncontrollable lacrimation. The redness of the mucous membrane intensifies, thick discharge begins to form in the corners of the eyes, which quickly dries out.
- After a few more days, you can clearly see the head of the boil: it differs in color compared to healthy skin and is most often yellow or yellowish-white.
Stages may have different durations. This is due to the varying degree of functioning of the immune system in each patient, as well as the causative agent of the disease and the severity of the lesion.
Treatment
To receive treatment, you must consult with your doctor. Opening a boil on your own is unacceptable; it will lead to the formation of an additional infection that will spread to deeper tissues. The risk of severe tissue damage increases. Complex therapy is used aimed at eliminating the formation and preventing the possibility of its recurrence.
Medications
Since the boil is caused by the proliferation of a bacterial infection, the following drugs are used:
- antibacterial drops (Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Vigamox, Tobrex), the treatment method is safe for children of all ages, as it is used for local therapy;
- antibacterial ointments (Erythromycin, Tetracycline ointment, Levomekol);
- antiseptic solutions (Furacilin, Albucid).
Drugs that help accelerate the maturation of formation are also indicated:
- heparin ointment (attracts pus to the skin);
- Vishnevsky ointment (has an anti-inflammatory, antibacterial effect, helps improve the immune response) promotes rapid breakthrough of boils and further tissue healing.
Surgical procedures
This method is indicated when the boil remains in front of the patient for an excessively long time. It can only be performed by an ophthalmologist or surgeon. It is prohibited to remove the boil yourself, as this will lead to the spread of infection and tissue damage.
The doctor uses a scalpel, with which he makes an incision at the top of the boil, removes its contents, and applies an antibacterial drug. To accelerate tissue healing after surgical removal of a boil, the doctor may prescribe drugs that promote accelerated regeneration, for example, Solcoseryl. To reduce inflammatory reactions, use anti-inflammatory drops. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the surgeon’s instructions after removing the pus.
Diagnosis and treatment of lumps on the eyelid
Only an ophthalmologist can determine the true cause and type of seal on the eyelid during a consultation or diagnostic examination. Treatment of the tumor is selected individually in each case and can be carried out both with medication and surgery.
As you can see, there are many reasons for the appearance and types of neoplasms on the eyes, so only a specialist can determine their “nature”. The Eye Clinic of Dr. Belikova employs experienced doctors and uses modern equipment, which allows an accurate diagnosis to be made as quickly as possible, as well as the most effective manipulations.
Complications
If left untreated, the patient may experience the following complications after the formation of a boil:
- penetration of pus into the deep layers of the skin;
- an increase in the number of boils on the eyelids and eyebrows;
- spread of the infectious-inflammatory process to the conjunctiva, cornea, lacrimal sac;
- severe swelling of the eyelids, when the eyeball is practically invisible;
- chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases in the hair follicles of the eyelashes and other areas of the eyes.
To prevent complications, it is recommended to begin therapy immediately after swelling and slight redness appear on the eyelids.
Main signs of the disease
On the first day of illness, discomfort is felt in the eyelid area. Then more serious symptoms begin to appear, such as redness, itching, burning, and swelling. Sometimes stye on the eye causes headaches and fever. After 2 days, a tubercle with a yellow or white ending forms on the eyelid. In order to quickly cure barley, you do not need to touch the abscess and under no circumstances squeeze out the pus. The abscess will open approximately on the 4th day of illness, after which the discomfort in the eye should subside. Photo 2 was taken after opening the abscess. Since barley is not contagious, there is no need to isolate the patient from other family members. If internal inflammation occurs, then the pus will not come to the surface of the eyelid, but will pour into the conjunctival sac. True, there are cases when it is possible to cure barley of internal origin and get chronic inflammation of the meibomian gland. Chalazion will not cause pain, but will be noticeable visually.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of barley, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- daily hygiene procedures for the eyes and entire face;
- timely treatment of ophthalmological and systemic diseases;
- antibiotic therapy only as prescribed and no more than the course prescribed by the doctor (5-7 days);
- use of contact lenses according to all rules;
- frequent hand washing;
- timely antihistamine therapy for allergic diseases.
The use of preventive measures will not completely eliminate the possibility of barley formation. Their use will significantly reduce the risk of its manifestation. Boils are a fairly common occurrence in medicine. The prognosis for the patient's condition is favorable if treatment is started in a timely manner.
During the formation of pathology, it is strictly prohibited to independently extract the contents before the skin breaks through. At home, doctors recommend the use of antibacterial therapy, but not more than 7 days.
Acute infectious diseases
Abscess and phlegmon
These are infectious eye diseases in which a cavity filled with purulent contents forms on the eyelids. Provoking factors for the development of diseases are barley, boils, inflammation in the maxillary sinuses, ulcerative blepharitis, damage to the skin near the eyes, meibomitis.
Clinical manifestations:
- skin redness;
- swelling of the eyelid;
- area tension and pain.
When the cavity is opened (spontaneously or surgically) and the pus is removed, the inflammatory process quickly stops. Drug therapy consists of taking bactericidal and bacteriostatic agents in the form of eye drops or intramuscular injections.
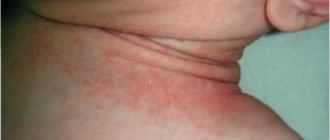
Erysipelas of the eyelids
The cause of the development of the disease is often a hemolytic streptococcal infection, and in some cases, infection with other microorganisms. Inflammation, as a rule, begins in a number of areas of the face, after which it affects the eyelids.
Symptoms:
- intense pain syndrome;
- increased body temperature;
- chemosis of the conjunctiva.
If treatment is started in a timely manner, the outcome is favorable in most cases. For drug therapy, antibacterial drugs (penicillins) for intramuscular injections, vitamin complexes, and Streptonitol ointment are prescribed.
Furuncle
This disease of the eyelids is a purulent necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle and adjacent tissues. The cause of development is staphylococcal infection. The inflammatory process affects the eyebrow area, in rare cases it is localized in the corner of the eyelid.
Clinical manifestations are the formation of a dense edematous node, accompanied by pain. After a few days, a necrotic core forms in its central part, after which it is opened and purulent contents are released. Then the wound heals and a scar forms.
Drug therapy is carried out with antibacterial drugs for internal use or intramuscular injections. The edges of the eyelids and the skin near the affected area are treated with camphor alcohol or hydrogen peroxide. If purulent inflammation spreads, surgical opening is recommended.
Chronic infections
Tuberculous lupus is a chronic infectious disease of the eyelids. The disease affects the skin of the face in most cases, but can also spread to the eyelids.
Symptoms:
- the formation of translucent pinkish-yellow small tubercles;
- eversion of eyelids;
- inability to close eyelids;
- trichiasis (abnormal direction of eyelashes towards the eyeball).
General anti-tuberculosis treatment is prescribed. Desensitizing drugs are used. If no complications occur, therapy lasts up to six months.
Herpetic diseases
The course of herpetic dermatitis of the eyelids in most cases does not differ from ordinary herpes or herpes zoster.
The pathology is characterized by an acute onset of development. The following symptoms occur:
- redness and swelling of the eyelid;
- the appearance of transparent bubbles, which then burst;
- the formation of crusts at the site of burst blisters.
After 7-14 days, the crusts disappear, leaving no traces. A relapse of the disease is possible.
Therapy: the blisters are treated with brilliant green. When crusts form, oxolinic ointment or Zovirax cream is applied to them. To prevent secondary infection, local antibacterial agents are used.
Allergic diseases of the eyelids
Allergy dermatitis occurs due to a reaction to medications or cosmetic products. Its development takes about 6 hours from the moment the allergen begins to act. Symptoms that accompany this condition:
- redness and swelling of the eyelid;
- vesicular or bullous rashes that can cause maceration of the skin.
Therapeutic measures involve eliminating the effect of the substance that triggered the development of the allergy. Use local corticosteroids (not containing antibacterial components). Desensitizing drugs are prescribed for internal use.
Eczema
Inflammation of the eyelids, accompanied by itching and rashes. Usually takes a chronic form.
Symptoms include swelling of the eyelid skin and the appearance of small blisters. When they burst, serous exudate comes out, after drying, yellow crusts form. A long course of the disease can lead to thickening of the eyelid, as well as its eversion. Eyelashes may fall out.
Acute forms are treated with lotions of cool lead water and boric acid solution. When the inflammation subsides, topical corticosteroid drugs are used.
Meibomian gland diseases
Meibomian are the sebaceous glands located in the cartilage of the eyelids. When coccal flora gets into them, they become inflamed, the edges of the eyelids thicken, the skin turns red, and yellow crusts appear on the eyelashes. This disease is called meibomitis. When the secretion of the meibomian gland penetrates into the conjunctival cavity, chronic conjunctivitis develops.
For therapy, the eyelids are treated with alcohol or brilliant green. Dexamethasone or antibacterial instillations are performed. Apply local antibacterial agents to the skin. Sometimes the affected cavity is opened surgically.
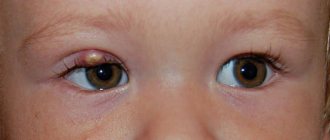
Chalazion
A disease characterized by the formation of a dense formation in the cartilage of the eyelid. The cause of this phenomenon is chronic meibomitis. Several chalazions can form simultaneously.
At the first stages, the chalazion is a small nodule, which over time increases to 5-6 mm. The skin above it rises, the eyelid is slightly deformed. If you press on the node, you will notice a dense formation, but no pain is felt. The conjunctiva in the affected area rises, thickens, and turns red. Subsequently, it may become thinner and break through, after which the contents of the nodule come out.
During therapy, drops of hydrocortisone emulsion, antibacterial solutions, and local preparations are used. Dry heat recommended. If such measures do not help, surgical treatment is resorted to. Small nodules sometimes resolve on their own.
What is an eyelid abscess?
Purulent inflammation can sometimes occur in the eyelid , in which the affected area begins to redden, swell and swell , and the patient feels pain and general weakness in the body.
This symptom is characteristic of most infectious diseases.
Technically, such inflammations are concentrated in certain foci, which in ophthalmology are called abscesses.
Reference! The danger of such a disease is that it can quickly spread to other organs of the head, and it is difficult to predict how long after the diagnosis of the disease this can happen.
The worst case scenario is the spread of purulent processes to the brain, which is located in close proximity to the organs of vision.
to begin treatment of an eyelid abscess immediately after diagnosis , while the use of folk remedies and methods in this case is unacceptable, and all procedures should be carried out only in a hospital setting .
Fungal diseases
Candidiasis
Lesions on the skin of the eyelids occur due to exposure to yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. The disease is accompanied by swelling of the eyelids, redness, and the appearance of small pustules. Therapy is carried out by treating the affected areas with nystatin ointment and taking nystatin internally.
Trichophytosis (ringworm)
The cause of the disease is fungi of the genus Trichophyton. Clinical manifestations are hyperemia and swelling of the eyelids, the formation of pustules and yellow crusts. A coating of spores appears on the eyelashes. In some areas of the eyelids, eyelashes fall out or break off.
It is possible to develop concomitant diseases – conjunctivitis or keratoconjunctivitis.
During therapy, the affected area is treated with a solution of alcohol and iodine. Griseofulvin is recommended for internal use.
Actinomycosis
The disease is caused by actinomycetes (radiant fungi). A dense knot forms in the outer or inner corner of the eyelid, but there is no pain. Over time, it softens and forms an intradermal infiltrate, after opening which a fistula with purulent discharge remains (it does not heal for a long time). Antibacterial therapy and actinolysate are prescribed. An x-ray is taken, the abscess is opened and scraped out.
Causes
Most often the condition is caused by reproducing staphylococci. But other opportunistic microflora may appear, which are activated under the influence of negative environmental factors:
- severe skin contamination;
- use of low-quality cosmetics;
- lack of hygiene procedures that must be performed daily, especially when it comes to removing makeup;
- decreased functionality of the immune system;
- increased secretion of secretions from the sweat and sebaceous glands, which leads to blockage of the canal;
- microscopic injuries in the gland area due to frequent scratching, dermatological diseases, mechanical damage;
- frequent occurrence of bacterial infections in the eyes (bacterial conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis).
A boil does not always form when exposed to a negative factor. This is due to the fact that most people have a normally functioning immune system. A decrease in activity is possible under the influence of the following factors:
- congenital or acquired immunodeficiency;
- long-term therapy with glucocorticosteroids, antibiotics, chemotherapeutic agents;
- malignant neoplasms in the body;
- frequent viral and infectious diseases of the whole body.
Under the influence of a negative factor, a boil does not form immediately. First, a small compaction appears, only then pus accumulates. In the early stages, the condition is quite difficult to identify and can be confused with other diseases. That is why it is worth contacting a professional doctor to accurately identify the root cause and carry out therapy.
Features of treating a boil in a child
In the treatment of children, all methods are preserved. The only difference is the use of drugs that must be age appropriate. For children, you can use the same drugs for systemic antibiotic therapy, but only in a reduced dosage, in accordance with the instructions for use.
For local effects on the eyes, Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Erythromycin, Metronidazole are used.
It is also recommended that children treat affected areas with antiseptic agents. This can be salicylic acid, hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine. They effectively eliminate multiplied staphylococcus.