What is seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis?
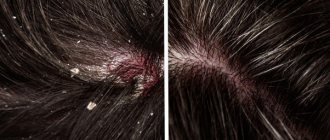
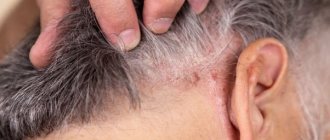
Seborrheic dermatitis (SD) is an inflammation of the skin that occurs in areas of the body where there are many sebaceous glands: the face (forehead, nose, chin, nasolabial triangle), scalp, area behind the ears, décolleté, shoulders and area between the shoulder blades. The pathology is manifested by the formation of dry or greasy scales on the scalp (dandruff), less often on the face and upper body, rash, redness of the skin and slight itching.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a consequence of seborrhea, a skin disease characterized by a malfunction of the sebaceous glands and a change in the composition of sebum (sebum), therefore both terms are considered synonymous. Seborrhea is a common pathology that affects adults and children. According to statistics, from one to three percent of the world's population have certain signs of seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis.
The disease often occurs in newborns (before the third month of life), adolescents and adults aged 30 to 60 years. Seborrhea is diagnosed more often in men than in women.
Why does seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis occur?
The exact causes of seborrhea are unknown. Hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands (increased sebum production) can be caused by a genetic factor, so seborrheic dermatitis is often a hereditary disease.
Endocrine pathologies also play a significant role in the development of seborrhea. The sebaceous glands are sensitive to sex hormones - androgens (testosterone and its derivatives). With increased levels of androgens (hyperandrogenism), sebum production increases. Seborrhea in women is caused mainly by an imbalance of androgens and female sex hormones (progesterone, estrogens). Hormonal imbalance is also the cause of seborrhea during pregnancy.
In men, seborrhea often develops with hereditary hyperandrogenism, a disorder of androgen metabolism, or a malignant testicular tumor (seminoma). Seborrhea in adolescents often occurs with the onset of puberty, when the level of androgens in the blood increases. With its end, sebum production usually returns to normal, and the manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis gradually disappear.
The cause of seborrhea in newborns is the relatively large size of the sebaceous glands and their hyperactivity. The disease usually goes away when the child reaches two years of age.
Overactivity of the sebaceous glands and excess sebum lead to increased proliferation of yeast-like fungi of the genus Malassezia. They are part of the normal microflora of the skin and are present in small quantities on its surface. But with seborrhea, the number of fungi of the genus Malassezia increases many times, as they feed on sebum (sebum).
During their life, fungi secrete enzymes - lipase and phospholipase. They break down triglycerides contained in sebum and convert them into free fatty acids, which disrupt the skin's protective barrier, causing inflammation, redness and peeling.
Factors that provoke the development of seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis also include:
- Parkinson's disease;
- epilepsy;
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- schizophrenia;
- affective insanity;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- obesity;
- long-term use of medications containing glucocorticosteroids, testosterone, progesterone;
- stress;
- HIV AIDS. At the initial stage of HIV, seborrhea is diagnosed in 24% of patients. In AIDS patients, the incidence is approximately 30% of all cases.
How to prevent seborrhea
To prevent seborrhea you need:
- strengthen your immunity;
- eat properly and balanced;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- take vitamins “A” and “B”;
- spend more time walking outdoors and being in the sun;
- reduce consumption of sweet, fatty and spicy foods;
- pay great attention to the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract;
- strengthen your immunity;
- choose the right shampoos and creams for your skin type.
Types of seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis
There are three forms of seborrheic dermatitis (seborrhea):
- dry;
- fat;
- mixed.
Dry seborrhea occurs when the function of the sebaceous glands is reduced, when they do not produce enough sebum. The pathology occurs mainly in children before the onset of puberty, since their sebaceous glands are not yet sufficiently developed. Dry seborrhea in adults is diagnosed less frequently and occurs at any age.
Oily seborrhea is characterized by increased sebum production and has two forms:
- liquid seborrhea - sebum is fluid and resembles vegetable oil;
- Thick seborrhea - sebum is thick, has a yellowish tint, and is released from the pores when pressed. Due to the increased thickness of sebum, the openings of the sebaceous glands become blocked and the pores become clogged, which leads to the formation of blackheads (comedones).
With mixed seborrhea, both forms of the disease are present, but, as a rule, in different parts of the body. With oily seborrhea on the face, dry seborrhea of the scalp may be observed.
According to the form of seborrhea, it can be acute (occurring for the first time) and chronic. Chronic seborrhea is characterized by frequent periods of exacerbation. They can be triggered by stress, poor nutrition, weakened immunity and other unfavorable factors.
Types of seborrhea depending on the location of the skin lesion:
| Types of seborrhea depending on location | Manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis |
| On the head | Dandruff (flaking) on the scalp, redness of the skin |
| Possible plaque formation | |
| Expansion of the affected area to the skin of the forehead, in some cases the appearance of serous-purulent crusts, after removal of which a weeping surface is revealed | |
| Itching may often occur | |
| On the face | Rashes in the forehead, nasolabial folds, wings of the nose, eyebrows |
| Redness and swelling (hyperemia) with unclear boundaries, round spots, against which peeling and yellowish crusts appear | |
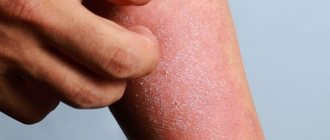
| On the body and limbs | The appearance of inflammation and swelling, yellowish-pink spots |
| Formation of plaques with peeling on the surface, pink in color, covered with yellow crusts |
What are the symptoms of seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis?
Symptoms of seborrhea depend on the form of the disease and its severity. Signs of oily seborrhea on the body and face:
- enlarged pores, thick skin;
- skin lesions: areas of redness with peeling or plaques consisting of small papules (nodules) of a yellowish-pink color, covered with whitish or yellowish greasy scales. The rash appears predominantly in the area of the bridge of the nose and nasolabial triangle;
- constant oily shine on the skin;
- presence of blackheads (comedones);
- periodic inflammation of the sebaceous glands (acne).
If symptoms of oily seborrhea appear on the face or body, you should make an appointment with a dermatologist to prevent the development of the disease. With oily seborrhea on the head, the hair quickly becomes dirty, sticks together in strands and takes on an unkempt appearance due to increased sebum secretion. Multiple flakes of skin in the hair (dandruff) also appear, which can be quite large.
In infants, seborrheic dermatitis usually appears in the second or third week of life. Most often, the scalp is affected - yellowish crusts (gneiss) are formed from sebum-soaked and sticky skin flakes. Less commonly, crusts appear in the forehead, cheeks, and behind-the-ear folds. A small, scaly rash may appear behind the ears, in the armpits and groin.
Dry seborrhea of the scalp is characterized by reduced sebum secretion, dry skin, moderate itching and the formation of many scales that almost completely cover the skin under the hair. Sometimes the scales can form crusts of a yellowish or grayish tint. Hair with dry seborrhea is thinned and prone to brittleness. With dry seborrhea, pinkish or reddish spots may appear on the body - seboreids.
With seborrhea, hair loss is possible - seborrheic baldness (alopecia). This happens when the disease reaches an advanced stage. Seborrheic alopecia is caused by two factors: damage to the hair follicles as a result of picking off crusts or scratching the scalp with nails and inflammation of the skin due to excessive proliferation of yeast-like fungi of the genus Malassezia. Fungal infections of the skin negatively affect the growth of new hair due to seborrhea.
Hair loss due to seborrheic dermatitis is temporary - if treatment is started in time and the inflammation of the scalp and itching are eliminated, the hair will grow back over time. Therefore, when the first symptoms of seborrhea appear, you must immediately make an appointment with a trichologist.
Treatment
If you do not show vigilance in a timely manner and allow the development of oily dandruff, it will take a long time to get rid of it in the future. Treatment and hair restoration after seborrheic dermatitis is especially effective if you take an integrated approach.
Of course, the prescription of procedures and medications is a medical diocese; one’s own knowledge from the field of medicine, especially in advanced cases, is inappropriate. But you can always use suitable means for prevention, especially when it comes to folk methods of combating oily seborrhea.
Drug treatment
The composition of medicinal preparations includes components that regulate the functioning of the sebaceous glands and have an antifungal effect. They stop inflammation, relieve skin from itching, and eliminate oily dandruff on hair. Special medicated shampoos are suitable for therapeutic purposes:
- Nizoral 2% - available in volumes of 60 milliliters (price - from 700 rubles) and 120 milliliters (costs approximately 850 rubles). A small bottle is enough for 1.5–2 months of treatment and prevention of oily seborrhea of the head. The hair product reduces inflammation, relieves itching and dandruff, and fights fungus;
- Sebozol is a shampoo in bags of 5 milliliters (a set of 5 pieces costs about 150 rubles) and in bottles of 100, 200 milliliters (350–470 rubles). Recommended for hair restoration after seborrhea, treatment and prevention of dandruff. Has an antifungal effect;
- Sulsena - there is shampoo paste (40 and 75 milliliters, cost 80-120 rubles), peeling shampoo (150 milliliters will cost 300 rubles) and regular shampoo for hair covered with dandruff (volume - 150 milliliters, price - about 250 rubles ). The drugs normalize the functioning of the sebaceous glands, reduce the tendency of cells to exfoliate, and suppress pathogenic microflora.
Attention! You can also find Sulsen shampoos with nettle or Sulsen Forte on sale. They have a different manufacturer, and the price starts from 200 rubles.
A line of drugs against seborrhea is offered by the Ducray brand. Products from the Squanorm series are intended specifically for the treatment of dandruff (separately for dry and oily). Ducray Squanorm improves the activity of the sebaceous glands and permanently eliminates white flakes.
For oily scalp seborrhea, the following are recommended:
- shampoo marked Grasses (Sèches products are suitable for dry dandruff) - there are bottles of 125 milliliters (from 700 rubles) and 200 milliliters (from 840 rubles). Contains palm extract;
- Ducray Squanorm Lotion is a universal lotion with zinc sulfate, citric acid and other ingredients that accelerates skin regeneration, disinfects and softens it, and eliminates itching. The product does not need to be washed off from the hair. Suitable for daily use. Price - about 900 rubles for 200 milliliters;
- Ducray Squanorm set for oily scalp - the same products, but in combination: shampoo (200 milliliters) and a mini bottle of lotion (30 milliliters) will cost from 800 rubles.
There are other medicinal shampoos for seborrhea: Fitoval, Perhotal. Many of them contain ketoconazole, an effective antifungal component, and are used not constantly, but according to a certain scheme, in courses. According to the principle of action, special preparations differ from cosmetic products for hair (Head & Shoulders, Clear Vita), which are more suitable for preventing the problem and are suitable for long-term use.
In addition to shampoos, you can treat oily seborrhea of the head with ointments :
- salicylic acid - to destroy the fungus that causes peeling of the skin. Costs from 20 rubles;
- zinc - for healing, drying, achieving an antiseptic effect. Price - from 15 rubles. To avoid drying out your hair and skin, you need to combine this ointment with essential or vegetable oils;
- sulfur - in advanced cases. The cost is approximately 35 rubles.
To eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of seborrhea, boric and salicylic acid and other drugs are used.
If the source of problems with hair and skin is problems with internal organs or nervous tension, the appropriate medications will help: Pancreatin (to improve digestion, costs from 20 rubles), Novopassit (to provide a sedative effect, the price depends on the form of release), Roaccutane (for severe forms acne, cost from 2 thousand rubles) and many others. But only a doctor should prescribe any medications!
Traditional methods
Home recipes are not a panacea when it comes to pathology that manifests itself in the form of oily seborrhea of the scalp. However, they are effective in eliminating dandruff and giving hair a well-groomed appearance. Such methods are best used as an addition to the main therapy, as well as for the prevention of the disease. Masks, rinses, lotions prepared according to folk recipes regulate the functioning of the sebaceous glands, relieve inflammation, and soothe sensitive skin.
Popular ingredients in the fight against white flakes and increased oiliness of hair are: lemon, calendula, onion peels, fresh berries and fruits.
Lemon
Prepare a citrus decoction from it:
- cut the peel removed from 4 fruits into pieces;
- fill it with a liter of water and place it on the stove;
- Bringing to a boil, boil the zest for 25 minutes over low heat;
- filter;
- use as a mouthwash once a week. During the procedure, also massage your scalp.
You can prepare a simple mask for oily hair:
- squeeze out fresh citrus juice;
- dilute with water in a 1:1 ratio;
- rub into scalp;
- after 10–15 minutes, rinse it out of your hair using shampoo;
- use 1-2 times a week for a month.
Another recipe for a mask for oily seborrhea of the head:
- take natural lemon juice, mayonnaise, honey, aloe juice and castor oil in equal parts;
- mix and add 1-2 cloves of garlic;
- rub into the roots of your hair, warm your head;
- after 30–45 minutes, rinse with shampoo.
Attention! In addition to getting rid of oily dandruff, such a mask can improve hair growth.
Calendula
Buy a pack of dried flowers at the pharmacy and prepare a decoction:
- pour a tablespoon of the mixture into 2 cups of boiling water;
- leave to infuse;
- Rub the lukewarm liquid into the skin;
- cover your hair with plastic, then with a towel;
- After 40 minutes, remove the insulation, but do not rinse off the product. Use this recipe against oily seborrhea on the scalp to eliminate white flakes and strengthen your hair.
An effective remedy for oily dandruff is tincture of marigold (another name for calendula) in alcohol. You can also buy it at the pharmacy. A mask with this component improves the activity of the sebaceous glands and suppresses the proliferation of fungal infections. The drug is used in two ways:
- rub in pure form into the skin half an hour before washing your hair, be sure to insulate your hair;
- combine with burdock or castor oil, measuring 10 teaspoons of tincture and 1 teaspoon of oily base. Distribute over the head 2 hours before going to the shower.
Burdock
For oily seborrhea of the head, prepare a decoction of the roots of a medicinal plant to rub into the skin and rinse the hair:
- pour 2 tablespoons of crushed raw materials with a glass of boiling water;
- simmer over low heat for 15 minutes;
- cool and use as intended.
You can rub this decoction into the roots every other day.
Onion
A well-known remedy against hair loss, as well as oily dandruff. You can mix the plant juice and vodka in equal parts, and then rub the mixture into the skin half an hour before hygiene procedures. To prepare the rinse, steam 50 grams of husks with a liter of boiling water.
After cooling, filter. Apply after every hair wash. After regular use of the decoction, blondes will notice that their curls have acquired a golden hue.
Also, to get rid of oily seborrhea of the scalp, prepare a mask:
- combine the juice of one onion with a couple of tablespoons of dry mustard;
- diluted with hot water to obtain the consistency of thick sour cream;
- add chicken yolk, 1 tablespoon each of honey and aloe extract, 1 ampoule of vitamins B1 and B6;
- Apply to hair roots, warm and leave for an hour.
Fresh vegetables, fruits, berries
If you have dandruff and oily hair, apply the juice/gruel of cucumber, pumpkin or zucchini to your hair. Strawberries, currants, and apple peels are also suitable. Keep the mask on your head for 30 minutes, repeat twice a week.
Effective remedies for oily dandruff - nettle, chamomile, propolis extract, walnut leaves, soda, sea salt and other ingredients. Prepare herbal infusions, soda rinses, or rub salt grains into dry scalp to give your hair a well-groomed look.
Alternative Methods
- Vitamin therapy . If the body lacks nutrients, the doctor may prescribe treatment with vitamins. For oily seborrhea of the head, components of group B are needed, as well as A, E, D. They are found in certain foods (carrots, citrus fruits, fish, vegetable oils, eggs and others). However, it is not always possible to obtain from food the necessary amount of vitamins that would satisfy the body’s daily needs. Therefore, in advanced cases, it is necessary to compensate for the deficiency with medicinal methods. But an excess of nutrients (hypervitaminosis) is also bad. To prevent this, consult your doctor before going to the pharmacy.
- Mesotherapy . A method for those who are not afraid of injections. Thanks to them, hair and skin will become healthier and get rid of oiliness. The composition of the injections includes vitamins, microelements, amino acids, which directly affect the source of the problem. This is also the main drawback of the procedure: if the cause of oily seborrhea of the head lies in a hormonal disorder, nervous strain or pathology of internal organs, mesotherapy will not be effective.
- MIL therapy . It involves exposing the affected areas to magnetic and laser beams. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, improves tissue microcirculation, which has a positive effect on the condition of the skin and hair.
- Ozone therapy . Has bactericidal and drying properties. Normalizes metabolic processes, improves hair structure and root nutrition.
- Physiotherapy . In addition to meso-, MIL- and ozone therapy, it includes other procedures that can cure oily seborrhea of the head. This is darsonvalization (improving blood flow using a special device), cryomassage (exposure to cold), ultraviolet irradiation and others.
Attention! Any alternative method used against oily dandruff requires courses of treatment.
Treatment of seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis
Treatment of seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis begins with differential diagnosis, the purpose of which is to distinguish diabetes from other skin diseases: psoriasis, rosacea, atopic or contact dermatitis and others. Since seborrhea in adults is a chronic disease, it cannot be cured once and for all, but the period of remission can be significantly extended. Pediatric seborrheic dermatitis is completely curable.
To treat seborrhea, they use mainly external agents (ointments, creams) designed to relieve inflammation, itching of the skin, regulate sebum secretion, and also have an antifungal effect. These are drugs containing zinc pyrithione, fungicides, antibiotics, glucocorticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors and other active ingredients.
If external therapy is ineffective, a course of systemic antifungal drugs is prescribed. In the most severe cases, medications that suppress sebum production are prescribed for the treatment of oily seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis. An important stage in the treatment of the disease is diet correction.
The diet for seborrheic dermatitis involves limiting sweet, spicy, fried and fatty foods (especially those containing animal fats), as well as smoked foods. It is necessary to consume more foods that support a healthy immune system and have anti-inflammatory properties. These are green vegetables and herbs, tomatoes, berries (cherries, blueberries, strawberries), avocados, citrus fruits, potatoes, olive oil and almonds.
Your doctor may also prescribe certain vitamins and minerals (sulfur, calcium, and others). The list of vitamins for seborrhea includes:
- vitamin A;
- B vitamins (B1, B2, B6);
- vitamin C (ascorbic acid);
- vitamin D;
- vitamin E.
Drug treatment of seborrhea can be supplemented with folk remedies, but before this you need to consult a doctor. As additional care for seborrhea, the doctor may also recommend the use of medicinal cosmetics: shampoos, lotions, balms containing antifungal substances, zinc, tar, salicylic acid, vitamins.
Fighting oily seborrhea
If the doctor has determined oily seborrhea, then in terms of nutrition you will need:
- exclude smoked meats and pickles, as well as cakes, sweets, cookies and other sweets;
- do not eat canned and pickled foods, as they provoke itching and deterioration of the skin;
- eat fresh vegetables and fruits;
- eat enough fiber, fish dishes, cereals, meat;
- refuse flour products;
- limit consumption of foods containing animal fat.
Popular questions
1. Is it possible to dye your hair if you have dry seborrhea?
Dyeing your hair for dry seborrhea is not recommended, especially during an exacerbation. As a result of the disease, the hair is already weakened and prone to loss, and after dyeing with permanent dye, this process may worsen. Aggressive substances in hair dye can increase dryness and flaking of the scalp. It is better to first contact a trichologist and undergo treatment for dry seborrhea.
2. What to do if seborrhea does not go away?
Seborrhea is a chronic disease that cannot be completely cured. But proper therapy and compliance with doctor’s recommendations can prolong periods of remission. If exacerbations of seborrhea occur frequently, you need to consult a doctor (dermatologist or trichologist) to correct the treatment regimen.
3. Is seborrhea contagious?
The contagiousness of seborrhea is a myth. The disease develops under the influence of internal factors (immunological, neurological diseases, stress and others).
0
0
1
Article rating:
4.57 out of 5 based on 7 ratings
Author: Rozhkova Natalya Viktorovna
Dermatovenerologist, trichologist. Highest category. Work experience over 25 years.
Preparations and regimens for use for dandruff and seborrhea
Scheme 1: Oily scalp and dandruff.
1. Option a. Anti-dandruff cream shampoo No. 19 b. Dermocapillary mask No. 58 (28) once a week after shampoo for 10 minutes. V. Balm 12 herbs No. 46 (70) 3 times a week. within 2-3 months.
2 options. Shampoo No. 17 (for oily hair) b. Dermocapillary mask No. 58 (28) once a week after shampoo for 10 minutes. V. Herbie lotion No. 3 (25) 3 times a week. within 2-3 months.
3 Option a. Shampoo No. 142 (Dixidox). b. Anti-dandruff gel No. 100B 2 times a week. before shampoo for 20 minutes. V. Dermacapillary mask No. 58 (28) once a week after shampoo for 10 minutes