Scabies prevalence
Scabies has been known since ancient times.
In the Middle Ages, people with scabies were isolated outside the city. Scabies was considered the same contagious disease as pediculosis. In the 19th century there were already references to the pathogen. Scabies fully reflects the cultural, social, economic, and sanitary situation in a particular territory. The disease is widespread throughout the world. And accordingly, it has a higher percentage of infected people in countries with a low standard of living.
The reality is this: any person, regardless of material income, is susceptible to scabies.
In Russia, at the beginning of 1900, widespread infection with the disease was recorded in some cities and villages. Over the years, the number of people suffering from scabies has been declining. But during the Patriotic War, the number of infected people increased by hundreds of thousands. In the post-war period, the situation improved in the USSR and foreign countries, but outbreaks of morbidity were recorded from time to time.
Features of prevalence statistics among children
Scabies among children has its own characteristics. Young children tend to become infected within the family. But this rarely happens. Children in closed children's groups (preschool institutions, orphanages, camps, schools) are more often infected.
Children who suffer from scabies for a long time are also often identified and treated for allergies. Such patients are particularly dangerous to others. About 80% of all people with scabies are young people under 30 years of age. Moreover, every 5 patient is a child.
In the fall, there is a higher percentage of infected people being detected.
Scabies mite - getting to know the culprit
In order to fully understand the mechanism of infection and the clinical manifestations of the disease, it is necessary to know about the structure and abilities of the pathogen. In nature, there are a large number, namely, more than 20 species of scabies mites. They can parasitize both humans and animals.
But Sarcoptes scabie requires more careful study, since only this species parasitizes humans. This pathogen is not relevant for animals. The scabies mite in the environment dies after 2 days; it parasitizes in the stratum corneum of the skin.
Tick structure
Like most pathogens, the female tick is larger than the male. The latter (males) do not have a parasitic effect on humans; they have only one function - fertilization.
The male sells it on the surface of the skin, then dies after 2 days. To achieve fertilization, males have suckers in their structure, with which they can move across the skin to achieve their goal. The movement speed reaches 3 cm per minute.
Females move inside the skin, creating scabies burrows behind them, which are visible to the naked eye on the host’s skin. Such passages are necessary for tick breathing. And in order to produce them, the pathogen has special devices: multiple bristles and outgrowths throughout the body, spines and suction cups for movement and fixation in the thickness of the skin, and most importantly, ticks have a gnawing apparatus to make these same moves.
As the female moves deeper into the skin, she lays 50 eggs, which after 3 weeks turn into sexually mature individuals.
Life cycle of scabies mite
The life cycle of the scabies mite can be divided into 2 stages: cutaneous, which has a very short period, necessary only for fertilization, and intradermal, which is long. The last stage is also divided into 2 parts: reproductive and metamorphic.
The reproductive component consists of gnawing scabies ducts and laying eggs. The female can lay up to 2 eggs per day. At the location of the latter, the mite makes its way to the surface of the skin. After a while, larvae hatch from the eggs and immediately settle on the skin, at the base of the hair. It is in this place that metamorphosis (molting) occurs. The larvae develop into adults, and the process starts again.
In the life cycle of the pathogen, environmental temperature and humidity play an important role. Under favorable conditions (high humidity and low temperature), females retain their mobility for a long time. At high temperatures the tick dies.
Quite interesting is the fact that the pathogen is characterized by a certain daily rhythm of activity, which is important for a specialist during diagnosis. At night, the pathogen reproduces its own kind, and also gnaws through scabies ducts, thereby feeding. During the daytime, the female rests.
This circadian rhythm explains the clinical symptoms: painful itching appears in the evening and at night, and this fact also causes a higher degree of infection at night. A specialist can track the female’s night work by the length of the scabies burrows.
During the period of existence, the female is capable of laying a path up to 6 cm long.
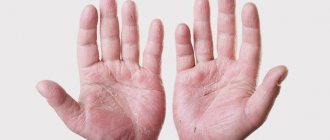
The favorite localization of the pathogen is the skin of the hands, feet, and wrists. In such places there is a greater thickness of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Mites also prefer skin with a lower temperature and lack of hair follicles.
How is the scabies mite transmitted?
It is important for everyone, without exception, to know how the scabies mite is transmitted in order to prevent infection.
The source of the disease is only a sick person. Animals can be the cause of the disease, but it has a different name - pseudosarcoptosis, and with this option the clinical picture and appropriate treatment measures will be different. There is usually no incubation period. If infection with larvae occurs, clinical symptoms appear as the pathogen transforms into sexually mature individuals (after about 2 weeks). Infection occurs through close contact and shared household items. This is observed more often in public places, as well as in the family.
Sexual contact plays a significant role in scabies infection. Studies have shown that the disease is more common in people who have frequent promiscuous sex. It is interesting that scabies, along with sexually transmitted infections, has the same incidence dynamics.
The problem of infectious skin diseases is very relevant and is of great interest for practical healthcare. Its relevance is primarily due to the high incidence rate. Scabies is one of the most common contagious dermatoses that doctors of all medical specialties may encounter. The results of studies on the epidemiology of scabies have shown that the officially registered incidence rates of dermatosis do not correspond to its actual level. Thus, in 2003, 193 thousand cases of scabies were registered in Russia, in 2005-2006. - 70 thousand, in 2009 - 65.1 thousand, and in 2010 - 85.7 thousand cases of this dermatosis. At the same time, the population of Russia purchased anti-scabies drugs from the pharmacy chain ( Spregal
, medifox, benzyl benzoate ointment) is on average 4.5 times higher than the officially registered incidence rate.
And if we take into account sales data for benzyl benzoate emulsion, prepared ex tempore
, and sulfur ointment, then the true incidence of scabies turns out to be 8-10 times higher than the registered one [1-5].
Reasons for incomplete registration of scabies include [1, 3, 4]:
- the reluctance of doctors to carry out the entire range of treatment and preventive measures officially approved for this disease (at the same time, doctors often make diagnoses of “urticaria”, “insect bites”, “allergic dermatitis”, “pyoderma” and treat with provocative drugs);
— insufficient level of laboratory diagnosis of scabies and, as a consequence, diagnostic errors;
— treatment of scabies in commercial clinics or private practitioners;
— underestimation of patients when visiting doctors of the general medical network (general practitioners, pediatricians, gynecologists);
— self-medication if antiparasitic drugs are available in the pharmacy chain.
An increase in the incidence of scabies is usually observed during wars, natural disasters, and social upheavals, which is caused by population migration, economic recession, and deterioration of social and living conditions. The growth of prostitution and drug addiction, the increase in the number of homeless people and the criminal population, poor hygiene, and early onset of sexual activity are also the reasons for the increase in morbidity these days. The weakening of detection and prevention of scabies by healthcare institutions is another important reason for the increase in the number of sick and undertreated patients [1, 3, 6].
The causative agent of scabies is the scabies mite Sarcoptes scabiei
.
In medicine, the disease it causes in humans is called scabies ,
after the species name of the pathogen, and in animals, sarcoptic mange, after the generic name of the pathogen.
By analogy, a disease that occurs in humans as a result of an attack by scabies mites from animals is called pseudosarcoptosis. Scabies mites are permanent (obligate) parasites, spending most of their lives in the host’s skin and only during a short period of settlement leading an ectoparasitic lifestyle on the surface of the skin. The type of parasitism determines the clinical features, epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment tactics of this disease. Sarcoptes scabiei
parasitizes the superficial layers of the skin, but in a complicated course it can also affect deeper layers [6, 7].
The life cycle of the scabies mite is represented by two periods: short-term cutaneous and long-term intradermal. The intradermal part of the cycle is divided into two stages: reproductive and metamorphic. During the reproductive stage of the mite's life cycle, the following events occur: oval-shaped eggs are laid by the female in the scabies duct, where they then hatch into larvae. When they come into contact with the skin, they penetrate the hair follicles, forming follicular papules. The metamorphic stage is determined by the appearance of a larva, which penetrates the skin through a passage and, after molting, turns into a protonymph, then into a teleonymph, which in turn turns into an adult - a female or a male. Adults are found in papules and vesicles on the patient's skin. The development of the larva to a sexually mature female, capable of making passages, takes 2 weeks. Females and males of the new generation come to the surface of the skin, where mating occurs. Daughter females migrate to the hands, wrists and feet, penetrate the skin and immediately begin to make tunnels and lay eggs. Scabies can persist for up to 1.5 months and also serve as a source of infection [3, 5, 6].
Scabies infection occurs mainly through close bodily contact, usually while sharing bed. Infection often occurs through sexual contact, which is the reason for including scabies in the group of sexually transmitted diseases. An indirect route of infection through objects and clothing used by the patient is also possible.
In children's groups, the disease can be transmitted through soft toys, stationery, and sports equipment. Only females and larvae take part in invasion and infection. The latter, due to their large numbers, small size and high mobility, are the most aggressive. The incubation period in the case of infection by females is practically absent, since the invading female usually almost immediately begins to gnaw through the tunnel and lay eggs, and when infected with larvae, it corresponds to the time of tick metamorphosis - about 2 weeks [2, 3, 6, 7].
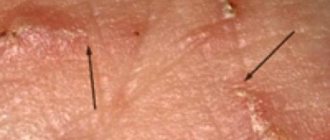
The pathognomonic sign of the disease is scabies. It usually appears as a slightly raised straight or curved whitish or dirty gray line ranging in length from 1 mm to several centimeters. At the anterior (blind) end of the passage, a vesicle is usually found - here there is a female mite, visible through the stratum corneum in the form of a black dot. Often, blackish dots are visible on the running tire, located at the same distance from each other (“ventilation shafts”). If a secondary infection occurs, the blisters turn into pustules. When the exudate dries, the passages take the form of crusts.
In some cases, in adults, in closed areas of the skin (usually in areas of pressure from clothing) and in infants, in any area of the skin, burrows may occur in the form of a whitish line or linear peeling of the epidermis on the surface of dense bluish-purple papules [7].
The distribution of female mites, and therefore scabies burrows, over the skin is determined by several factors: the structure of the skin, the hygrothermal regime and the rate of regeneration of the epidermis. The predominant localization of scabies is observed in areas of the skin where the epidermis is thin and dry: the lateral surfaces of the fingers, the flexor surfaces of the wrist joints, the external genitalia in men, and the mammary glands in women. Brushes are the most favorite localization of scabies and are a kind of “mirror of scabies”. Clinical manifestations of scabies in the form of small papules arranged in pairs in the form of colons, vesicles, point and linear excoriations can be observed on the hands, flexor surfaces of the upper and lower extremities, trunk, abdomen, lower back, and male genital organs. In children, manifestations of scabies can be localized on any part of the skin [6, 7].
Clinical manifestations of scabies are caused by the activity of the mite, as well as the body’s reaction to the influence of the pathogen and its waste products. Itching is a characteristic but subjective symptom of scabies. It, as a rule, intensifies in the evening, which is due to the daily rhythm of tick activity with its intensification at night. The intensity of itching is individual for each patient and depends on many factors: the level of sensitization of the body to the mite and its waste products, the number of mites, neuropsychic status, concomitant diseases, and medications used [1, 2, 4, 6].
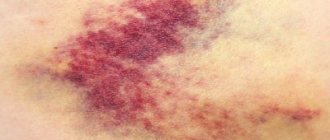
Thus, the main clinical symptoms of scabies are scabies, polymorphic rashes outside the burrows, the characteristic localization of both on the patient’s skin and itching, which intensifies at night. For scabies, the symptoms of Ardi (pustules and purulent crusts on the elbows and in their circumference), Gorchakov (blood crusts on the elbows and in their circumference), Michaelis (blood crusts and impetiginous rashes in the intergluteal fold with transition to the sacrum), Sezari (detection of scabies burrows in the form of a slight elevation upon palpation) [6, 7].
There are several clinical types of scabies: typical (most common), scabies without burrows, Norwegian scabies (against the background of immunosuppressive conditions), scabies of the “clean” or scabies “incognito” (minimal clinical manifestations of typical scabies). Scabies can be complicated by secondary pyoderma and/or examatization, which often causes difficulties in diagnosis. Sometimes in patients with scabies, post-scabiosis lymphoplasia of the skin occurs in the form of nodules of reactive hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue, localized on the genitals, thighs, abdomen, and axillary fossae [6, 7].
Diagnosis criteria for scabies can be divided into four groups [2, 6, 8]:
- clinical criteria (presence of scabies, polymorphic rashes, typical localization, night itching, symptoms characteristic of scabies - Ardi, Gorchakova, Michaelis, Sezari);
— epidemiological criteria (the presence of itchy dermatosis in one or more family members, among members of an invasive contact group, the sequential appearance of patients in the outbreak, the possibility of infection through household items);
— laboratory criteria (detection of scabies pathogens by methods of removing the mite with a needle, thin sections or scraping of pathological material;
- therapeutic diagnostic criteria (disappearance of itching after the 1st treatment with scabicides and resolution of rashes by the end of the week).
To improve the visual diagnosis of scabies, the method of oil in vitro compression was proposed, which allows you to quickly detect scabies. It is based on visualization of superficial cutaneous granulomas due to bleeding of the capillary bed under pressure with a glass slide. Parasitic elements (female, eggs, larvae) are foreign inclusions in the epidermis. The brightening effect is enhanced by preliminary application of mineral oil to the scabies tract before vitropression. The use of mineral oil when scraping the passage, in addition, prevents the scattering of the epidermal scales on which eggs, egg membranes and feces are fixed. Dermatoscopy is a new modern diagnostic method designed for more detailed visualization of scabies rashes. This non-invasive study allows you to detect the contents of passages, papules, and vesicles. The main purpose of dermatoscopy is laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis during the initial examination of the patient. To increase diagnostic efficiency, the patient’s skin can be pre-stained with aniline dyes, lubricated with 40% lactic acid or mineral oil. The assessment of the diagnostic significance of the dermatoscopy method is high. When using it, 27% more scabies are detected than during an objective examination without optical instruments. Dermoscopy is especially significant in diagnosing scabies against the background of other dermatoses, when the clinical manifestations of both diseases overlap each other [2, 8].
Successful treatment of scabies requires an integrated approach to this problem as a highly contagious infectious process. This algorithm is aimed not only at treating the patient, but also at identifying and treating all persons who are in close contact with the patient in order to prevent the spread of infection. In the Russian Federation, domestic (sulfur ointment, benzyl benzoate, medifox) and imported ( Spregal
) drugs. Regardless of the drug chosen by the doctor, there are general principles for the treatment of scabies, the observance of which is mandatory [3, 4, 6].
— Treatment of patients identified in the same outbreak should be carried out simultaneously to avoid reinvasion.
— Rubbing of anti-scabies in children under 3 years of age is carried out over the entire skin, in others - with the exception of the face and scalp.
- Rubbing in any drug is done with your hands, not with a napkin, which is due to the predominance of scabies on the hands.
— Treatment must be carried out in the evening, which is associated with the nocturnal activity of the pathogen.
— Each patient must be explained in detail the method of using a particular drug.
— Treatment of complications is carried out simultaneously with the treatment of scabies. Treatment of complicated scabies is best done with benzyl benzoate ointment or Spregal
.
— All healthy individuals in family outbreaks and invasive-contact organized groups, as well as during sexual contacts outside the outbreak, must undergo a one-time preventive treatment to eliminate the possibility of a “ping-pong” infection.
Spregal should be used to treat pregnant women
.
— It is recommended to wash the patient before and after the course of treatment. If necessary, the drug can be washed off every morning. Its exposure on the skin should be at least 12 hours.
— Change of underwear and bed linen is carried out at the end of the course of therapy.
— Long-term persistent scabious lymphoplasia, as a result of the body’s immunoallergic reaction, does not require additional specific therapy.
Sulfuric ointment
used for the treatment of uncomplicated scabies.
For the treatment of adults, 20% ointment is used, for children - 10%. The ointment is rubbed over the entire skin every night for 5-7 days. On the 6th or 8th day, the patient washes and changes his underwear and bed linen. This is the cheapest treatment option, but doctors rarely use sulfur ointment due to the frequent development of allergic contact dermatitis, a long course of therapy (5-7 days), the impossibility of use in the presence of complications, and poor tolerance in the heat. In addition, it has an unpleasant odor and stains laundry. At the same time, all doctors give preference to it in the absence of effect from treatment with other drugs. Benzyl benzoate
is used in Russia in the form of a water-soap suspension and ointment, and abroad - soap-alcohol solutions (Ascabiol and Benzoseptol), oil suspensions (Novoscabiol), aqueous solutions with the addition of DDT and anesthesin (Nbin). The death of the pathogen after a single treatment with benzyl benzoate at all active stages of development (females, males, larvae, nymphs, as well as eggs with embryos) has been experimentally proven. The formed larvae in the egg shells are resistant to the action of the drug. Taking into account the maximum residence time of formed larvae in the egg (58 hours), an etiologically based treatment regimen for scabies with benzyl benzoate has been proposed: a water-soap suspension or benzyl benzoate ointment (concentration 10% for children and 20% for adults) is rubbed with hands once a day at night. 1st and 4th days of the course of therapy; for the treatment of complications associated with scabies, days 2 and 3 are used; Underwear and bed linen are changed on the 5th day.
Medifox is a 5% concentrate of the synthetic pyrethroid permethrin in alcohol and castor oil. Rubbing in Medifox, like benzyl benzoate, is carried out once a day at night on the 1st and 4th days of the course of treatment [1, 5, 6, 8, 9].
Spregal
- one of the modern effective drugs for the treatment of scabies in the form of an aerosol.
Its active ingredient is esdepalletrin, a neurotoxic poison that disrupts the cation exchange of tick nerve cell membranes. The second component, piperonyl butoxide, enhances the effect of esdepaletrin. To maintain the effect of the drug overnight, Spregal
is applied in the evening (after 18-19 hours) to the entire surface of the skin, except for the face and scalp, from a distance of 20-30 cm from the surface of the skin.
First, the aerosol is applied to the torso, and then to the limbs (at the same time, the treated areas begin to become shiny). The drug is sprayed especially carefully and rubbed into the favorite locations of scabies (between the fingers, wrists, armpits, perineum, all folds, elbows) and into other affected areas and left on the skin for 12 hours. Then you need to wash thoroughly with soap and dry . As a rule, a single use of the drug Spregal
for uncomplicated scabies is sufficient.
However, for scabies complicated by microbial eczema, secondary pyoderma, in the presence of scabious lymphoplasia and deep scabies on the palms and soles, it is advisable to repeat the treatment after 3 days. When rashes are localized on the face, they are treated with a cotton swab moistened with the drug. When treating children, the mouth and nose are covered with a napkin. The convenient form in the form of an aerosol makes it easy to apply it to the surface to be treated, and a special excipient facilitates rapid penetration of the drug through the surface layer of the epidermis without causing unpleasant sensations on the skin. An important advantage of the drug is the absence of an unpleasant odor. One bottle of aerosol is enough for a whole family (2 adults and 2-3 children). Spregal
can be used from the neonatal period.
However, it must be borne in mind that even if the treatment is effective, itching and other symptoms may persist for another 8-10 days. If symptoms persist after this period, you can reapply the drug. When using the drug Spregal
, you should avoid getting it into the eyes and mucous membranes, and in case of accidental contact, you should rinse them thoroughly with warm water. Contraindications for use are bronchial asthma, obstructive bronchitis, lactation and individual intolerance [3, 6, 8-10].
Efficacy and safety of the drug Spregal
in the treatment of scabies has been proven in a number of clinical studies.
So, at the National Medical University. A.A. Bogomolets, 29 patients (16 men, 9 women and 4 children) from 3 to 74 years old with typical manifestations of scabies (presence of paired elements and scabies tracts in the favorite localization of the pathogen) were examined and treated. Among them, 8 patients had pyoderma and eczematization, 2 children had rashes on the skin of the palms and soles and scabies in the arch of the feet, 6 patients noted the ineffectiveness of previous anti-itch therapy. All patients were prescribed Spregal
.
It was applied by spraying onto the entire surface of the skin (except for the face and scalp), then putting on clean clothes and changing bed linen. Things were disinfected using the insectoacaricidal agent A-PAR in the form of an aerosol. In 17 (25.6%) patients, clinical recovery was noted after a single use of the drug. In 12 (41.3%) patients, unexpressed postscabiosis elements remained, accompanied by swelling and itching, but on days 8-10 all pathological symptoms regressed. The effectiveness of the therapy was also confirmed using laboratory control: microscopic examination did not reveal any elements of scabies mites. Spregal
tolerated in all patients; no side effects were noted. During a 3-month follow-up, no relapses of the disease were detected [11].
In another study, 29 patients (11 men, 12 women and 6 children) with scabies disease duration from 3 days to 5 months were observed. All patients and contact persons had typical manifestations of the disease with the presence of paired elements and scabies tracts in the places of favorite localization (hands, forearms, abdomen, thighs, buttocks, genitals). In 3 children, scabies were detected in the area of the palms, arches of the feet, and rashes on the skin of the cheeks. All patients were prescribed Spregal
in the form of an aerosol once, followed by a change of linen and washing after 12 hours. The observation period for patients ranged from 1 to 4 weeks. As a result of treatment, all patients showed clinical recovery. Complete regression of the rash usually occurred on the 5-8th day after a single use of the drug. There were also no side effects; the aerosol was well tolerated [12].
Efficacy and safety of Spregal
was assessed by Yu.N.
Perlamutrov and K.B. Olkhovskaya in 34 patients aged from 7 to 49 years with disease duration from 2 weeks to 1 year. The ineffectiveness of previous treatment was noted by 55.8% of them. All patients were prescribed Spregal
in the form of an aerosol according to the following method: first the patient was treated, then the rest of the family members, including those who had no signs of the disease. The interdigital areas, armpit and perineal areas, and elbow bends were treated especially carefully. 12 hours after treatment, patients washed thoroughly with soap without a washcloth and dried themselves. Treatment of bed and underwear, clothes, furniture, carpets and other items was carried out using A-PAR aerosol. The effectiveness of therapy was assessed on the 14th and 45th days. On the 14th day, only one patient showed reliable signs of a parasitic disease, and therefore a second course of therapy was carried out according to the treatment regimen for complicated scabies. After 45 days, all patients showed complete recovery [13].
On the basis of the Department of Dermatovenereology of the State Institute for Advanced Medical Studies of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation and the 25th Central Military Clinical Hospital of the Strategic Missile Forces T.V. Sokolova and A.P. Malyarchuk conducted a study, the purpose of which was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of anti-scabies drugs, as well as to identify the preferences of dermatovenerologists when prescribing therapy. The results of the study showed that the priority scabicides in the treatment of scabies are often benzyl benzoate ointment and Spregal
.
Efficacy when prescribed Spregal
was observed in 95.6% of patients, and postscabiosis itching - in 3.5% of cases (for comparison, when treated with Medifox, postscabiosis itching was observed in 11.5% of patients, and in treatment with benzoyl benzoate - in 10.7%) . Resistance to the drug and drug complications were not observed, while when using benzoyl benzoate and Medifox, resistance was observed in 7.2 and 7.8% of cases, respectively [9].
Thus, Spregal
has proven itself as a highly effective and safe scabicide for the treatment of scabies.
The effectiveness of its therapeutic action, if well tolerated, according to studies, is more than 90%. Spregal
has high compliance, is easy to use, and economical to use.
To treat scabies, a single use of the drug is sufficient for most patients. Resistance does not develop to it, it is well tolerated and practically does not cause drug complications. This medicine can be used in the treatment of scabies in newborns, children and pregnant women. Positive experience with the use of Spregal
in clinical practice allows us to recommend it as a first-line drug in the treatment of scabies.
Manifestation of scabies in children
Scabies in children has typical and atypical forms of manifestation.
Typical shape
The typical uncomplicated form is most often recorded among patients with scabies. Clinical signs of scabies in children are quite easy to identify. The leading manifestation of the disease is itching. As mentioned earlier, it manifests itself to a greater extent at night, since the pathogen begins its activity at this time.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the body's response to the infectious process. On the skin you can observe papules, nodules, scabies, scratches, purulent elements, and crusts.
The fact of the simultaneous appearance of clinical manifestations in contact persons greatly facilitates the diagnostic search for the doctor.
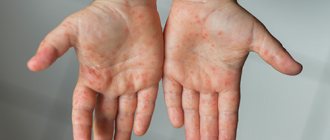
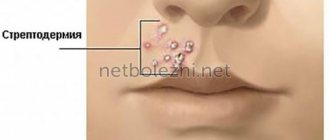
A specialist can observe various rashes on the skin of the fingers (more precisely, between them), feet, buttocks, anterior abdominal wall, mammary glands, and genitals. However, scabies in the area between the fingers of the hands are more common.
Such elements look like white-gray stripes with a total length of 4 - 7 mm, and the size increases every day. At the end of the course, a papulo-vesucule can be visualized. It is often possible to see a mite through the stratum corneum of the skin; this symptom is called “Bazin’s itch . Bloody crusts are observed between the fingers.
Typical symptoms for scabies are: Hardy, Gorchakov, Cesar, "triangle" . About each in order. Ardi's symptom is the appearance of hemorrhagic or purulent (with the addition of secondary microflora) crusts on the extensor surface of the elbow joint. Gorchakov's symptom is small bloody crusts on the elbow joint itself.
All scabies on palpation have a slight elevation, as evidenced by a positive Sezari sign. The “triangle” symptom is the observation of the transition of hemorrhagic crusts from the intergluteal fold to the sacrum (Michaelis rhombus).
On the feet, identification of typical elements is possible when they are initially infected (in a bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool) or during a prolonged illness.
In older children and adolescents, scabies on the face, palms, and head are practically not found.
However, in infants such localization is not uncommon. When a child is infected from a mother suffering from mammary gland scabies, elements of the disease will be observed in the facial area, namely the cheeks and nasolabial triangle. Also, infants may experience scabies in the occipital area of the scalp.
A peculiarity of the course of the disease in infants is that the elements become infected more often, thereby becoming more severe, and scabies is often complicated by allergic dermatitis.
Atypical forms
The following forms that will be offered for study are atypical.
"Scabies without moves"
A form of the disease that is much less common. This atypical form is observed in contact persons located in the outbreak. With this type of disease, scabies burrows are not detected, because the process is started by the larvae, which are not able to produce what a mature individual can do.
Scabies of the “clean” or “incognito”
It is also a rarer phenomenon than the typical form of the disease. This form does not differ in etiology and pathogenesis. It occurs in people who often take water procedures and change their underwear in a timely manner.
Under such conditions, the parasite is mechanically removed from the host’s skin, so clinical manifestations are minimal and may not bother the person. However, without treatment you cannot get rid of the disease. The positive aspects include the fact that this form is extremely rarely complicated.
Nodular form of scabies
It is distinguished by the preserved elements after treatment at the site of former rashes. Clinical symptoms remain and can cause the patient significant discomfort up to 6 months after treatment.
Norwegian uniform
Particular attention should be paid to the Norwegian (crusted) form of scabies.
This type of disease occurs in people with an immunosuppressive state, Down syndrome, and can also include patients who have been using glucocorticosteroid drugs for a long time. The Norwegian form of scabies is very contagious!
Such scabies is characterized by the absence of itching, the presence of a large number of crusts, under which there is a huge number of scabies mites, which can be localized in any part of the body. Such patients emit an unpleasant odor.
This type of scabies can affect hair and nails. The disease is severe, and an increase in temperature is often observed. The Norwegian form is so contagious that outbreaks of the disease are possible in certain social circles of the patient.
All forms of scabies have a risk of secondary infection. When combing, the patient creates an entrance gate for the attachment of microbial flora. More often, scabies is complicated by staphyloderma.
Despite the fact that all atypical and typical forms are caused by Sarcoptes scabie, it is necessary to remember and differentiate the disease from pseudoscabies (pseudosarcoptosis). This disease is caused by ticks that parasitize animals. The pathogen does not produce scabies, since it does not multiply in the thickness of human skin. The mite can only penetrate the epidermis, causing severe itching. The disease is not transmitted to another person.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
Types of scabies in humans and animals: what are they, symptoms and treatment
What do mosquitoes eat, besides blood, females and males, in the swamp and in nature?
Scabies during pregnancy: symptoms, how to treat, the best ointments
Sulfur ointment for scabies: how to use and treat scabies in children and adults
Parasites in children's bodies: signs, medications, treatments, how to identify them
Signs of worms in children aged 2 years: how to determine the presence of parasites in a baby
What is the essence of diagnosing scabies in children?
Parents who notice unusual elements on the child's skin, as well as if there is itching, should immediately contact their pediatrician. After the examination, the latter will refer you to a dermatologist for consultation. He, in turn, must carefully collect anamnesis and complaints. Information about contact with patients is important, and it is also necessary to find out the situation in the family and in the institution that the child visits.
Initially, the doctor should pay attention to the external manifestations of the disease. Clinically suspicious elements will be: scabies, rashes, scratching. Favorite localization will also suggest the disease: interdigital spaces, hands, wrists, lower abdomen, flexor part of the elbow joint.
Additional research methods do not always provide an accurate answer. Therefore, the diagnosis can be established without laboratory diagnostics. But you shouldn’t neglect it. For better visualization, scabies are stained with iodine solution or brilliant green . After the dye is absorbed, clearly colored, sinuous lines remain on the skin.
The mechanical method of removing a mite involves the doctor inserting a sterile needle into the scabies tract. There, the tick attaches to the needle and it is removed from the affected area of the skin. The resulting pathogen is placed on a glass slide and examined under a microscope.
also used for microscopic examination . A special solution is dripped onto the suspicious area of skin. After a few minutes, scraping is performed with a scalpel. The contents are placed on a glass slide and microscopy is performed.
Through a microscope you can see the female mite, eggs, and larvae. If only waste products are found, then scraping must be carried out on other areas of the skin.
Reasons for development
Scabies is caused by a mite that finds thin places on the skin, it penetrates under the skin, releasing a special substance and thereby loosening it.
The ways in which babies become infected can be different:
- close contact with the patient (using only toys);
- contact with carriers of parasites - homeless or pets;
- failure to comply with traditional hygiene rules.
The risk of infection increases if there are small wounds on the body, and if the child has reduced immunity.
The incubation period of scabies, that is, the time that passes from the moment the mite gets under the skin until the disease manifests itself, varies from approximately one to six weeks. It depends on the state of the child’s immune system. However, it only takes the parasite half an hour to get under the skin once it is already on the body.
Differential diagnosis
Scabies is differentiated from insect bites, allergic reactions, and dermatological diseases (psoriasis). Allergic diseases pose a great difficulty, since a similar reaction is observed with scabies.
When you find a person with scabies, it is important to pay attention to the favorite location of the scabies mite (hands, wrists, area near the navel, intergluteal fold).
Allergic reactions are rarely observed in the interdigital spaces. If you have an allergy, it will not be possible to detect scabies. Also, allergic conditions do not have a daily rhythm in the occurrence of clinical manifestations. Itching occurs throughout the day and is of low intensity.
History also helps to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Treatment of scabies: types and principles
Scabies treatment must be carried out strictly according to certain rules. The goal of treatment should be aimed at the complete destruction of the parasite, as well as its waste products and inactive forms. It is also important to prevent the development of complications and infection of healthy individuals.
Types of therapy
It is customary to distinguish several types of therapy:
- specific;
- trial;
- preventive treatment.
The nature of the treatment is determined by the doctor at the appointment, based on the situation. A specific type of therapy is prescribed to patients with scabies whose diagnosis is beyond doubt. Preventive treatment is aimed at contact persons in the outbreak.
As a rule, these are people who have been in close contact with the sick person for a long time (family members, a group in a kindergarten group, in a school class). It is also necessary to pay attention to the presence of sexual intercourse during illness and prescribe preventive treatment to the partner.
There are cases when clinical symptoms of scabies are present and at the same time the pathogen cannot be identified in the laboratory. Then the doctor prescribes a trial treatment. This type of therapy occurs under the careful supervision of a specialist; if there is a positive effect, the diagnosis is confirmed.
Principles of treatment
The principles of treating scabies must be strict and must be followed regardless of the type of therapy:
- treatment should begin at the same time for both patients and contacts;
- due to the fact that the maximum activity of the pathogen is recorded at night, therefore treatment begins after 19 hours ;
- before starting treatment, it is necessary to take a shower with a hard washcloth , for a more effective effect of the medications;
- for infants and children under 3 years of age, medications are applied to the entire skin , while at an older age, application to the face and scalp is avoided;
- Medicines should be applied with bare hands and rubbed especially carefully into the areas of the hands and palms. If a child is unable to perform this procedure due to his age, then parents are given recommendations based on their infection;
- Hands should not be washed after treating the skin.;
- bed and underwear are changed on the first day of starting therapy and after completion of the course of treatment;
- the drug, evenly applied to the skin, should remain on the body throughout the night ;
- Treatment of complications of scabies is carried out simultaneously with therapy of the underlying disease ;
- When registering a disease in pregnant women, it is necessary to assess the risks and benefits for the fetus and mother . If a nursing woman is infected, it is recommended to stop lactation for the period of treatment;
- After completing the course of treatment , bedding, underwear, and clothes must be boiled , shoes must be treated, and the room must be wet cleaned. It is recommended to iron the patient’s clothes and underwear on both sides. It is important not to forget about toys. If things cannot be boiled, then they must be isolated from the treated clean things for more than 3 days, during this period of time the parasite will die;
- if there is itching after a full course of therapy, antihistamines , since this clinical symptom is allergic in nature and does not require continued specific treatment;
- control of the treatment is assessed no earlier than after 2 weeks ;
- Treatment in most cases is carried out on an outpatient basis .
Indications for hospitalization
This may include the following indications:
- in the absence of an individual providing direct care to the patient during the illness;
- children living in orphanages and boarding schools. In a word, in places where isolation of the patient is impossible. In such cases, the child is hospitalized in order to prevent further spread of the disease;
- severe course of the disease with complications;
- children whose disease occurs with high fever and swollen lymph nodes.
Characteristics of basic drugs
In modern medicine, there are several regimens and drugs for treating the disease.
Sulfur-containing drugs
Sulfur-containing preparations: sulfur ointment, sulfur vaseline, Sulfodecortem, Miliana paste and others. This series of drugs has more historical significance.
Sulfur-containing drugs have side effects, have an unpleasant odor, and damage linen that comes into contact with the body when the drugs are applied. The drugs are used rarely, in special cases.
Benzyl benzoate preparations
Benzyl benzoate preparations (Askabiol, Benzoseptol, Novoskabiol). An aqueous solution of benzyl benzoate is quite effective when freshly prepared. If the solution has been stored for some time, its effectiveness drops sharply.
Rub the prepared solution in a certain sequence. First, the hands and palms are thoroughly treated, then the upper limbs, then the stomach, chest, back, face and scalp (children under 3 years old), genitals, buttocks, lower limbs, feet. Usually 2 treatments are enough for a course.
Crotamiton (Yurax)
It comes in the form of ointment, cream, lotion. This drug can be used for infants, pregnant women, and nursing mothers. But at the same time, Crotamiton does not have absolute effectiveness.
Permethrin preparations
Permethrin preparations - Medifox, Nittifor. The preparations are rubbed into the skin at night for 3 days. These drugs can “kill” adult sexually mature individuals, as well as eggs.
Pyrethrin preparations
Pyrethrin preparations - Spregal. The convenient aerosol form allows you to quickly and evenly apply the drug to the entire skin. Children need to cover their mouth, nose and eyes with a napkin during treatment.
A single use of the drug can be quite effective. But clinical symptoms can persist for up to 2 weeks. In such cases, re-treatment of the patient's skin is possible.
The drug is widely used in both pediatric and adult practice. However, it has contraindications. Since the drug is in aerosol form, it cannot be used in children with bronchial asthma or obstructive bronchitis, due to the risk of developing bronchospasm.
Nature of the disease
Scabies is a contagious disease caused by a parasite, the scabies mite. Among its obvious characteristics are night itching, the formation of scabies on the skin (in the form of a straight or winding line measuring from 1 mm to several centimeters, white or dirty gray in color, at the front end of which you can see the female mite visible through the skin in the form blackhead), as well as a rash in the form of small nodules and blisters. The tick is not visible to the naked eye, since it reaches a size of only 0.25 x 0.35 mm. The scabies mite parasitizes humans and can be found on pillows, clothing, door handles, and bedding for a short time.
1 Parasite is an organism that uses other organisms as a source of food and/or habitat.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis in most cases is favorable. The Norwegian form is characterized by a more serious prognosis. And also the presence of complications worsens the course of the disease.
Preventive measures are primarily aimed at early identification of patients with scabies. Timely identification and isolation of patients is the main principle of disease prevention.
Health care workers should undergo regular medical examinations, which can also be sources of infection. Parents need to take responsibility for learning the rules of personal hygiene for children.