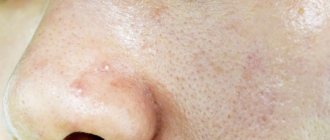
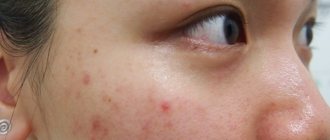
How papules and pustules appear
The mechanism of pimple formation is very simple. Due to the increased secretion of sebum - sebum - the sebaceous gland duct is blocked. A sebaceous plug is formed, that is, a comedon; they can be open or closed. But if such a comedon is affected by the bacteria P. Acnes, then inflammation occurs; over time, the purulent contents break into the skin, spread, which leads to the formation of other papules, and with more severe inflammation, purulent pustules appear.
There are many reasons for such activity of the sebaceous glands, the most common being hormonal changes during puberty. Nutrition, stress, hygiene habits, and lifestyle also play a role.
Causes of acne
You've probably heard the misconception more than once that acne is the result of poor hygiene. In reality, it is a complex skin condition involving hormonal, dietary and hereditary factors, and for all these reasons and more, acne requires a holistic approach. Treatment largely depends on the severity of the disease. If you have acne, never use alcohol or sulfates in hopes of freeing your skin from the unpleasant disease.
Acne can appear for the following reasons:
- Hormonal imbalance. With increased testosterone production in men and women, intense accumulation of sebum occurs in the glands. This turns out to be a favorable environment for the development of bacteria. Increased testosterone production in women may be associated with ovarian dysfunction. During adolescence (10-18 years), the formation of the endocrine system and puberty occurs. Often at this age, boys and girls experience active production of testosterone, which is what causes acne.
- Disorders of the autonomic nervous system. Frequent stress, lack of sleep, fatigue, increased physical activity, endocrine changes in the body (for example, after childbirth) lead to an imbalance in the work of the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system. In this case, again, the human sebaceous glands work more intensively.
- Decreased immunity. The skin's natural defenses can be disrupted by bad habits, stress, poor diet, and abuse of ultraviolet rays. As a result, bacteria and fungi multiply, causing acne.
- Hereditary predisposition. If parents have had acne, then there is a high chance that their children will also suffer from this problem. An increased level of testosterone, the level of sensitivity of the sebaceous glands to the effects of sex hormones, a tendency to form defective sebaceous glands, and much more can be inherited.
- Dietary disorder. Floury and sweet foods, as well as sugar, which is found in almost all foods, lead to the development of large amounts of insulin. As a result, the production of male sex hormone increases. And this, as we have already learned above, leads to increased production of sebum. The abundance of unhealthy fats in the body leads to the development of bacteria, which cause acne on the body and face.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, pathologies of the endocrine system. Acne is often a symptom of internal diseases. For example, diseases of the digestive system lead to the fact that food is not fully absorbed and stagnates. Acne is most often formed due to pathologies such as dysbiosis, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, acute and chronic gastritis, and stones in the bile ducts.
- Incorrect cosmetic care. This includes failure to comply with personal hygiene rules and the use of low-quality decorative cosmetics. On the contrary, if the skin is constantly subjected to cleansing, it loses its natural protection and the acid-base balance is disturbed. As for low-quality cosmetics: viscous products that contain oils and glycerin are considered especially dangerous. Such cosmetics clog pores and create a microfilm on the surface of the skin that impedes breathing.
Acne
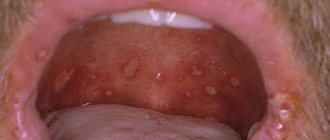
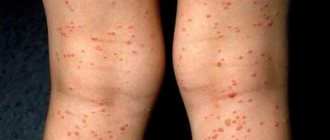
Acne is a disease in which papules, pustules, and comedones appear on the face and body (several follicles are affected at once). The inflammation is widespread, often the pimples are painful to touch, and as soon as one goes away, others appear. If a person has only comedones - white and blackheads, then we are talking about a non-inflammatory type of acne. And if there are papules and pustules, cysts, this is an inflammatory type. Pustules on the face should not be pressed, this will only worsen the situation; the contents may not break out, but subcutaneously.
It is worth saying that papules and pustules can appear not only as part of acne, for example, papular dermatosis with sterile papules is sometimes found, that is, P. Acnes is not detected in them, but acne is still the most common cause. Papular rashes also occur with psoriasis.
Differential diagnosis of papules for skin pathologies other than syphilis
Parapsoriasis or Broca's disease
Parapsoriasis is a rare, non-contagious skin disease that belongs to lymphoproliferative dermatoses.
It occurs predominantly in adult men of middle age.
Today there is no precise definition of this disorder.
Due to its variable clinical presentation and lack of specific histopathology findings.
However, the lesions usually appear as pink and scaly patches.
They vary in size from 1 to 5 cm.
The rashes are often chronic and resistant to medication.
There are two types of parapsoriasis: small-globular parapsoriasis (in English terminology SPP) and plaque parapsoriasis (LPP).
Of the two types, LPP is considered a premalignant dermatosis that can develop into T-cell lymphomas.
Whereas SPP is a chronic benign condition.
Again, because this disorder is difficult to diagnose, there are no specific epidemiological statistics.
In 10% of those who have plaque-type parapsoriasis, the disease progresses to a malignant form.
The cause of parapsoriasis is unknown; research on this topic is still underway.
It is conventionally accepted that parapsoriasis develops against the background of infectious processes and immune disorders.
Fine-grained psoriasis is usually asymptomatic.
There is no deterioration in general health, but rashes develop, ranging from pink to yellow-brown.
Round or oval spots (macula) ranging in size from 2 to 5 cm.
Maculae are mainly located on the abdomen, sides, back or lower extremities.
When examined under a microscope, there are very nonspecific data: mild spongiosis, parakeratosis, exocytosis of small lymphocytes.
There is also a variant of the disease called digital dermatosis.
In this case, the rashes look like elongated spots rather than round ones.
To make a definitive diagnosis, an epidermal biopsy is recommended.
It is advisable to perform several procedures on different areas of the skin.
Treatment begins with moderate-to-high potency corticosteroids for 8 to 12 weeks.
Wilson's ringworm
Lichen planus is an acquired, chronic, immune system-mediated disease.
Appears as polygonal, purple, itchy, papules or plaques on the skin and similar lesions on mucous membranes, such as the oral cavity.
Lichen planus is thought to be an immunologically mediated disorder.
This appears to be a response of CD8 cells to antigens in the basal cell layer and dermoepidermal junction.
Mainly in keratinocyte cells.
The reason for this phenomenon is still unknown.
There is only some speculation about the effects of certain viruses (eg, hepatitis C and hepatitis B) or drug factors.
Characteristic skin lesions of the lichen plan are polygonal, purple, itchy, flat papules.
They can stick together to form plaques.
Lesions may be close together or widely separated from each other.
They may have white spots or lines called Wickham's furrows, and they may also be hyperpigmented.
The lesions are usually distributed symmetrically on the upper/lower extremities, especially around the elbows and wrists.
However, they can be found anywhere on the body, including the glans penis and vulva.
Papules tend to disappear after some time, leaving signs of hyperpigmentation of the skin.
Psoriasis vulgaris (vulgar psoriasis)
Psoriasis vulgaris or scaly lichen is the most common form of psoriatic skin lesions.
Occurs in almost 80% of patients.
The disease is characterized by thickening of the epidermis, development of an inflammatory reaction on its surface, redness and silvery-white scales.
Skin lesions may be accompanied by itching, burning and pain on palpation.
Typical, inflammatory, erythematous, pruritic, and silvery-scaly patches of skin occur in psoriasis vulgaris on the extensor sides of the elbows and knees.
Also on the scalp, behind the ears.
However, other parts of the body may also be affected: the skin of the genitals, perineum, mammary glands, palms of the hands.
In turn, scaly lichen is divided into two subtypes:
- Type I: The disease usually occurs in patients under 40 years of age and is therefore called the early type. Other family members may also suffer from this form of psoriasis. Often, patients’ blood contains genetic markers of susceptibility to the disease.
- Type II. Called late type, it develops after 40 years. There is usually no family predisposition; DNA markers in the patient’s blood are significantly lower than in the first subtype. This type of psoriasis is milder and responds more effectively to treatment.
Miliary papular syphilide
Rapulosa milliaris nigra is a benign skin disease.
Often affects patients with secondary syphilis.
The symptom is accompanied by the appearance of soft, dermal papules on the skin.
The color is practically no different from the natural shade of the skin.
Often localized in the area of hair follicles, on the face, around the eyes, and back.
Papules are harmless, but may be accompanied by severe itching and irritation.
The disease is quite rare and tends to occur in patients with dark skin, more often in African Americans.
The pathology is quite difficult to respond to drug therapy and practically does not respond to medications.
There are several methods for removing and treating rapulosa milliaris: curettage, electrocoagulation, electrosurgery, cryotherapy and electrotherapy.
Each treatment carries a risk of scar tissue formation, decreased pigmentation, and keloid formation.
It is important to differentiate miliary syphilide from lichen scrofulous.
In this case, the rashes are grouped and are papules in the form of perifollicular nodules that affect children or adults with tuberculosis infection.
Yellowish-reddish-brown papules usually develop on the back, chest, and abdomen.
Not accompanied by the formation of scar tissue.
The pathology can be found under synonyms - Lichen Scrofulosorum, Tuberculosis Cutis Lichenoides.
How to treat papules and pustules
Now that we have found out what papules and pustules are, the question arises whether they need to be treated. In this case, everything depends on their number and frequency of occurrence. If they are isolated and rarely appear on the face and body, for example, due to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle, then there is no need to worry. You can simply choose suitable care cosmetics from a cosmetologist and cleanse your face efficiently. But if there are a lot of rashes, they can merge together and form spots; papules and pustules should be treated by a dermatologist.
Treatment of acne, papules and pustules is complex.
Lifestyle adjustments and adherence to doctor's recommendations are required. A non-hormonal ointment is used as a local remedy, which does not cause withdrawal effects in the future. Before treatment, the doctor will prescribe tests for hormones, the content of certain vitamins and a general blood test. This way you can choose an individual treatment plan. June 23, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
How many days will it take for the papules to resolve?
Within a few hours after the procedure, the papular tubercles noticeably increase (up to 30%), and then the drug begins to gradually be absorbed with their smoothing. It is impossible to say exactly how long papules last after biorevitalization, because everything depends on the characteristics of the body. The average period is 2-3 days, the maximum is 10 days. But with good skin condition and a high ability to regenerate, the tubercles become barely noticeable or disappear completely already on the 3rd day after the procedure. Those with sensitive skin should immediately prepare for a longer recovery period.
The cosmetologist can give an approximate time taking into account the following factors:
- skin density at the treatment site;
- thickness of the surface layer of the epidermis;
- degree of hydration of dermal cells;
- circulatory and lymph flow activity.